AP Euro Unit 1 Study Guide + Overview
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:31 AM on 9/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
Spanish and Portuguese conquest in the New World
- Conquered Incas and Aztecs
- Superior military-wise against natives
- Came on horseback
*Horses were not known to natives
- Diseases spread (smallpox, influenza, etc.)
- Superior military-wise against natives
- Came on horseback
*Horses were not known to natives
- Diseases spread (smallpox, influenza, etc.)
2
New cards
Conquistadors - Specific Names
- Bartolome de las Casas
- Balboa
- Balboa
3
New cards
Conquistadors
- Traveled to conquer in the 1500s
- Enslaved (and killed mainly due to diseases) natives
- New cattle pushed natives into European settlements, causing natives to have diseases
- Enslaved (and killed mainly due to diseases) natives
- New cattle pushed natives into European settlements, causing natives to have diseases
4
New cards
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, disease, and technology from the Old World to the New World during the Age of Exploration
5
New cards
Thoughts on Diseases
- Europeans believed that God was killing natives in the Americas so that they could conquer more land
- Natives thought God was abandoning them after seeing their population decline
- The real reason was because indigenous people did not have immunity to European diseases
- Natives thought God was abandoning them after seeing their population decline
- The real reason was because indigenous people did not have immunity to European diseases
6
New cards
Bartolome de las Casas
The first to protest against the actions of Europeans towards indigenous people in the Americas and slavery
7
New cards
Vasco de Balboa
Spanish; First European to see the Pacific Ocean (1510)
8
New cards
Hernando Cortes
Spanish; Conquered the Mexica (aka Aztec) empire by 1521 w/ to technology and smallpox
9
New cards
Vasco da Gama
Portuguese; First to reach India in search of silk and spices for the crown
10
New cards
Christopher Columbus
Italian that sailed for Spain; The first to discover the New World (1492); Originally was looking for China; The Columbian Exchange was named after him
11
New cards
Joint-Stock Companies
- Allowed people to pool investments & lowered financial risks
* Kings joined joint-stock companies and would force things to go his way by taking members' charter/authority
- Funded entrepreneurial activities in Europe and expeditions to the New World
- Disrupted normal political & economic structures in the Renaissance world
* Kings joined joint-stock companies and would force things to go his way by taking members' charter/authority
- Funded entrepreneurial activities in Europe and expeditions to the New World
- Disrupted normal political & economic structures in the Renaissance world
12
New cards
Commercial Economic Growth
- 1450-1600 Trends
- Putting value on coins changed the economy
- Items were gained by trading prior to money
- Prices increased after gold and silver were used to make coins
- Putting value on coins changed the economy
- Items were gained by trading prior to money
- Prices increased after gold and silver were used to make coins
13
New cards
Guild System
- Early "union" where one has to work for a long period of time to be a licensed worker in a field of work
- Guilds were undermined by entrepreneurial attitude of the Renaissance era since people wanted their work done quickly
- Guilds were undermined by entrepreneurial attitude of the Renaissance era since people wanted their work done quickly
14
New cards
Entrepreneurs
People who risked money to make/do something new
15
New cards
Price Revolution
- Prices increased (inflation); benefitted middle class and made the lives of poor people harder
16
New cards
Marriage Patterns in the Renaissance
- Marriage patterns were important for tracking population growth
- Money was hard to earn individually, so people would marry to legally share money
* Marriage %s increased, birth rates decreased
- Money was hard to earn individually, so people would marry to legally share money
* Marriage %s increased, birth rates decreased
17
New cards
Humanism
- Embracing individuality, others, being human, etc.
18
New cards
Renaissance Art
- Art that celebrated individuality, classical Greek and Roman cultures, often patronized by rich families (e.g. the Medici Family)
19
New cards
Renaissance Architecture
- Emulated Greek and Roman architecture (e.g. arches, pillars, etc.)
20
New cards
Effects of the Printing Press
- Allowed more people to become literate
- Literacy rates increased and more books were produced
- Literacy rates increased and more books were produced
21
New cards
Political Changes in the Renaissance - New Monarchies
- Centralized forms of government under a monarchy
- Happened by getting rid of powerful nobles and clergy members
- Northern Renaissance was different from the Italian Renaissance
* Division of Italy into the 5 city states instead of nobles and the clergy losing power
* Northern had more monarchs
- Happened by getting rid of powerful nobles and clergy members
- Northern Renaissance was different from the Italian Renaissance
* Division of Italy into the 5 city states instead of nobles and the clergy losing power
* Northern had more monarchs
22
New cards
Unit 1.1
- Renaissance revolutionized Europe
- Renaissance was when people discovered forms of literature from ancient Greece and Rome that changed and birthed new values (socially, politically, and religiously) in Europe
- Renaissance was when people discovered forms of literature from ancient Greece and Rome that changed and birthed new values (socially, politically, and religiously) in Europe
23
New cards
Renaissance
Rebirth of arts and classical antiquity, ranged from the 14th-17th century
24
New cards
Unit 1.2
- The Church provided people w/ their own interpretations, people realized this and began to come up with their own ideas
- During the Italian Renaissance, new values of secularism and individualism challenged the teachings of the Catholic Church, institutional powers of universities, artistic and political behaviors.
- During the Italian Renaissance, new values of secularism and individualism challenged the teachings of the Catholic Church, institutional powers of universities, artistic and political behaviors.
25
New cards
Unit 1.3
- Northern Renaissance and its scholars were a catalyst for the Protestant Reformation, they began reading the original Latin text of the Church and recognized discrepancies between those readings and the Catholic teachings.
- - The biggest societal change during the Northern Renaissance:
*The invention of the printing press (Johannes Gutenberg)
*The printing press with moveable type was created in Germany during the 15th century
- - The biggest societal change during the Northern Renaissance:
*The invention of the printing press (Johannes Gutenberg)
*The printing press with moveable type was created in Germany during the 15th century
26
New cards
___ invented the printing press
Johannes Gutenberg
27
New cards
Unit 1.4
- Printing press can be seen as the cause for the protestant reformation and propelled the Scientific Revolution (16th-17th c.)
- Prior to the printing press, handwritten scientific accounts were hard to come by, expensive, and usually inaccurate
- Prior to the printing press, handwritten scientific accounts were hard to come by, expensive, and usually inaccurate
28
New cards
Unit 1.5
- Hundred Years War -> Great Schism, nobility and clergy members no longer had the ability to block the power of growing monarchies
- New Monarchies began making standing armies (15th c). Cavalry was dismantled and instead it was replaced by artillery and infantry
- New Monarchies began making standing armies (15th c). Cavalry was dismantled and instead it was replaced by artillery and infantry
29
New cards
Unit 1.6
- Portugal mainly began exploring to find spices. They were also in search of slaves, gold, and wanted to launch missionary efforts in order "save" the Muslims
- Portugal focused on finding a route east to India
- Spain focused on finding a route traveling west across the Atlantic
- Spain had Christopher Columbus travel to (what he thought was) Japan and China. He had not realized he had landed in the Americas until his third trip
- Portugal focused on finding a route east to India
- Spain focused on finding a route traveling west across the Atlantic
- Spain had Christopher Columbus travel to (what he thought was) Japan and China. He had not realized he had landed in the Americas until his third trip
30
New cards
Unit 1.7
- The French had three motives behind their explorations: fish, fur, and faith. The French colony of Haiti established profitable sugar plantations w/ the use of African slaves.
- Many European countries began to establish colonies after Spain and Portugal did, this caused rivalries between the countries
- Many European countries began to establish colonies after Spain and Portugal did, this caused rivalries between the countries
31
New cards
Unit 1.8
- Mercantilism came around due to the Columbian Exchange.
- European expansions prompted the Columbian Exchange and food, new diseases, and new cultural practices changed the lives of indigenous civilization
- European expansions prompted the Columbian Exchange and food, new diseases, and new cultural practices changed the lives of indigenous civilization
32
New cards
Mercantilism
An economic system that creates a favorable balance of trade to gain wealth (through colonialism) & promotes government regulations of the economy to enhance state power.
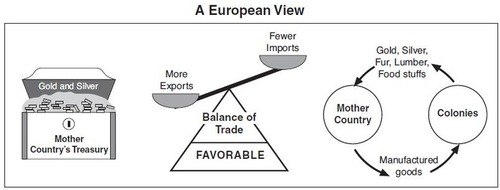
33
New cards
Unit 1.9
- Slaves were kept in extremely close quarters, given little food, and were subject to diseases on the ships. If they survived, their lives on the plantations were harsh as well
- Slaves converted to Christianity, preaching they should accept their slavery and their place under their masters.
- Slaves converted to Christianity, preaching they should accept their slavery and their place under their masters.
34
New cards
Unit 1.10
- Increase in food led to an increase in the population, this led to the migration from rural areas to urban centers
- The Commercial Revolution was a sweeping reform of Europe’s economic system centered around trade and developing ideas of capitalism.
- The Commercial Revolution was a sweeping reform of Europe’s economic system centered around trade and developing ideas of capitalism.
35
New cards
Unit 1.11
- The Columbian Exchange had the longest lasting effects on the world.
- Development of a commercial economy made colonies overseas even more attractive for economic reasons.
- The Renaissance and the Age of Discovery were generally the age of rediscovery of ancient Greece and Rome works. They led to new values in society and religion
- Development of a commercial economy made colonies overseas even more attractive for economic reasons.
- The Renaissance and the Age of Discovery were generally the age of rediscovery of ancient Greece and Rome works. They led to new values in society and religion
36
New cards
Capitalism
The process of selling slaves, using them to farm cash crops, cash crops being sent to Europe to be turned into finished goods and then those goods being sold back to the colonies essentially created capitalism
37
New cards
Causes of New Monarchies
- Reducing the power of nobility
- Reducing the power of the clergy
- Creating bureaucracies to govern
- Finding new sources of income (outside of nobles)
- Reducing the power of the clergy
- Creating bureaucracies to govern
- Finding new sources of income (outside of nobles)
38
New cards
Secular System/Secularism
A movement towards the separation of religion and government
39
New cards
Lorenzo Valla
_____ investigated a scandal involving the forged will of Constantine. The catholic church forged the document.
40
New cards
Marsilio Ficino
The philosopher, ___, revived plato's works.
41
New cards
Pico Della Mirandola
Wrote "Oration on the Dignity of Man" which was about the self-worth of humankind and its achievements. He was also a philosopher.
42
New cards
Machiavelli
Wrote the book, "The Prince," on how a prince should behave (to be loved not feared)
43
New cards
Castiglione Greco-Roman
Wrote a book on how a nobleman should behave
44
New cards
Francesco Guicciardini
____ was a nobleman and a friend of Machiavelli. He was an official in the church and wanted a leader that represented the people.
45
New cards
Michelangelo
Made the statue "David" out of marble, a humanistic, grekoromen sculpture and painted the top of the Sistine Chapel
46
New cards
Donatello
___ made another David (a statue originally built by Michelangelo) out of bronze.
47
New cards
Raphael
___ made the school of Athens painting. He was a Greek philosopher.
48
New cards
Brunelleschi
___ made the dome on the Florence cathedral.
49
New cards
Popes and Noblemen
___ and ___ commissioned works of art from people (e.g Brunelleschi and Donatello) to increase their prestige.
50
New cards
Bartholomew Diaz
Portuguese; Rounded Cape of Good Hope (Tip of S. Africa) (1487)
51
New cards
Amerigo Vespucci
Florentine; Realized the Americas was a new continent
52
New cards
Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese; First circumnavigation of the globe (1519-1522)
53
New cards
Francisco Pizarro
Conquered the Incas; Inca leader (Atahualpa) planned to trap Spaniards but was captured and held for ransom then executed. Cuzco fell in 1533.
54
New cards
Three G's
God, Glory, Gold
55
New cards
Prince Henry the Navigator
A Portuguese prince that sponsored many explorations, especially along the west coast of Africa
56
New cards
When was the fall of Constantinople?
1453