BIOL LAB Unit 1: Body Regions & Mitosis & Histology & Integumentary
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
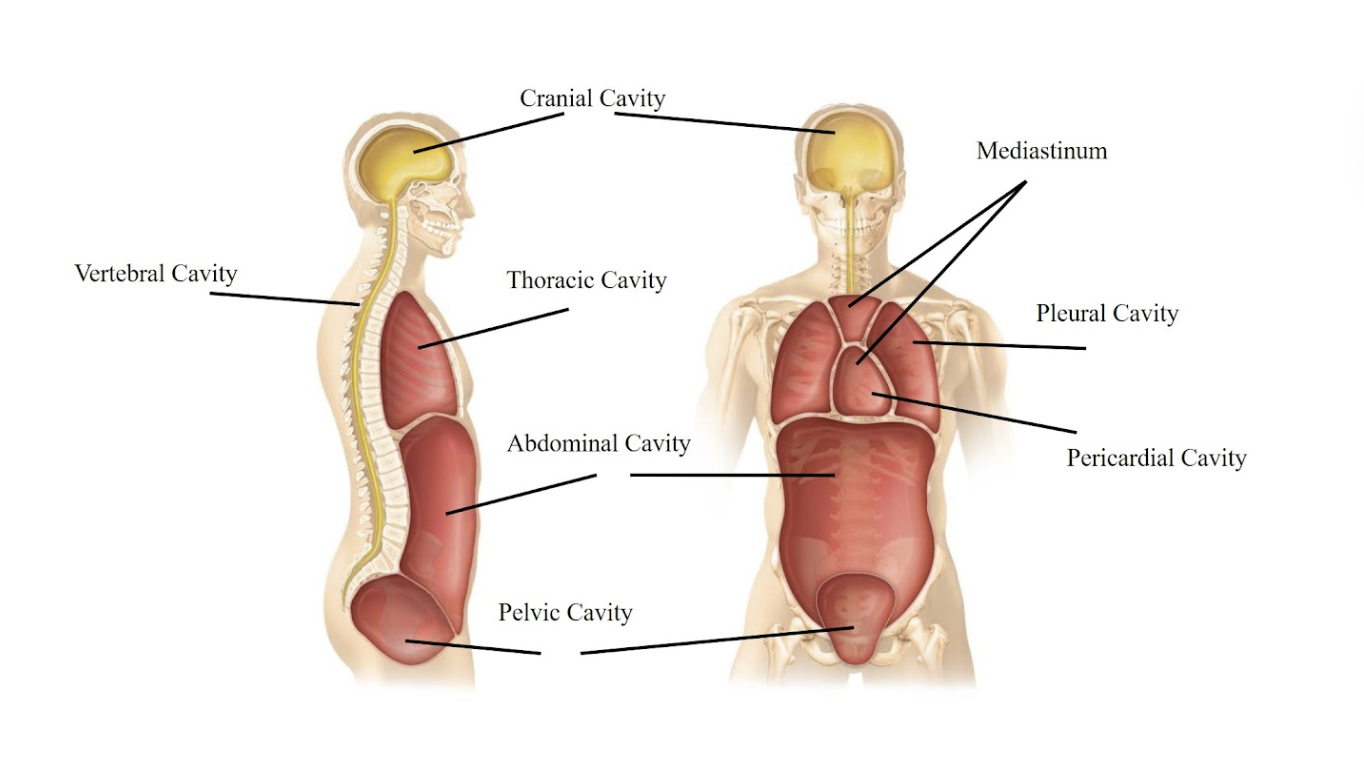
Cranial cavity
The space inside your skull, where your brain is located.
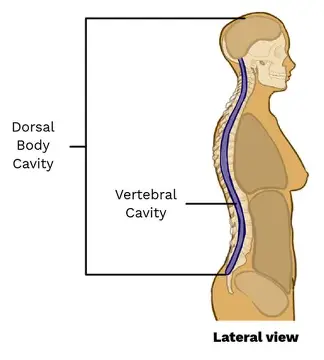
Vertebral cavity
The cavity that runs down your back and protects your spinal cord.
Thoracic cavity
The chest area that contains your heart and lungs.
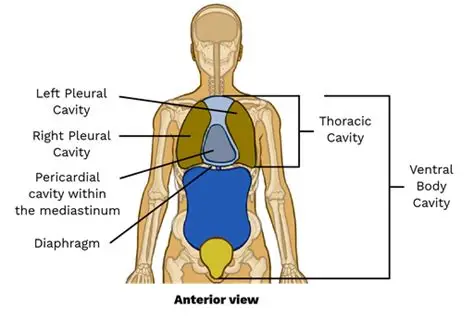
Mediastinum
The central area in your chest, between the lungs, containing the heart and large blood vessels.
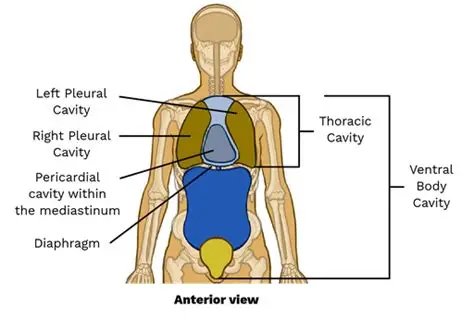
Pericardial cavity
The space directly surrounding your heart.
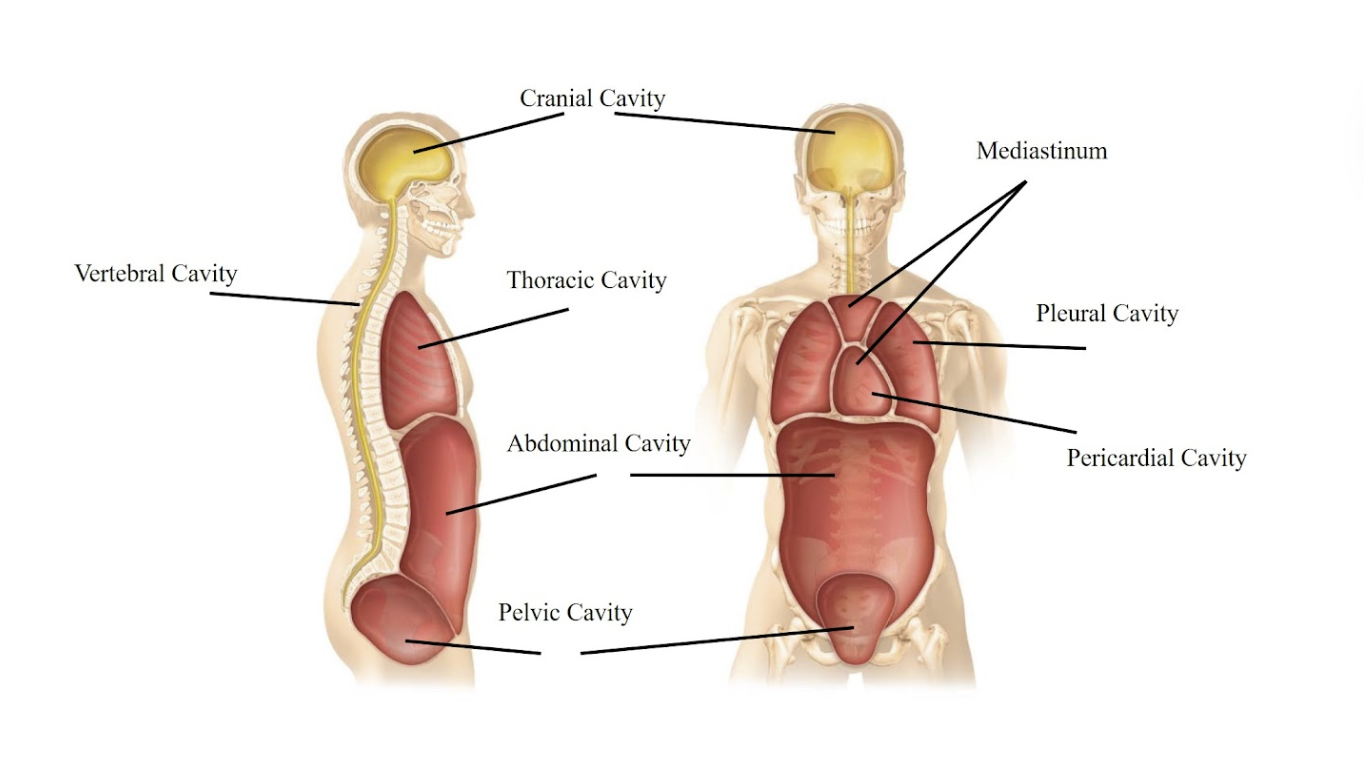
Pleural cavity
The spaces around your lungs, one for each lung.
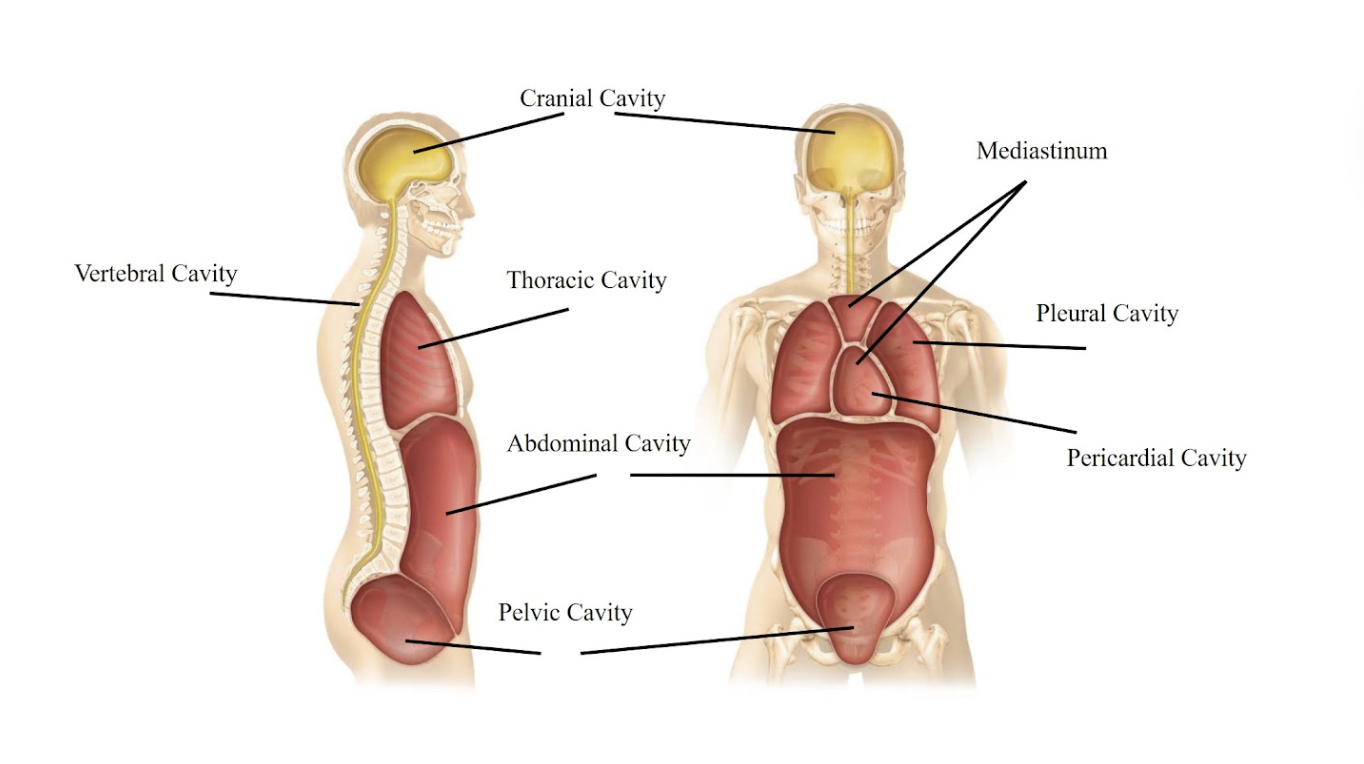
Abdominal cavity
The main part of your belly, holding your digestive organs like the stomach and intestines.
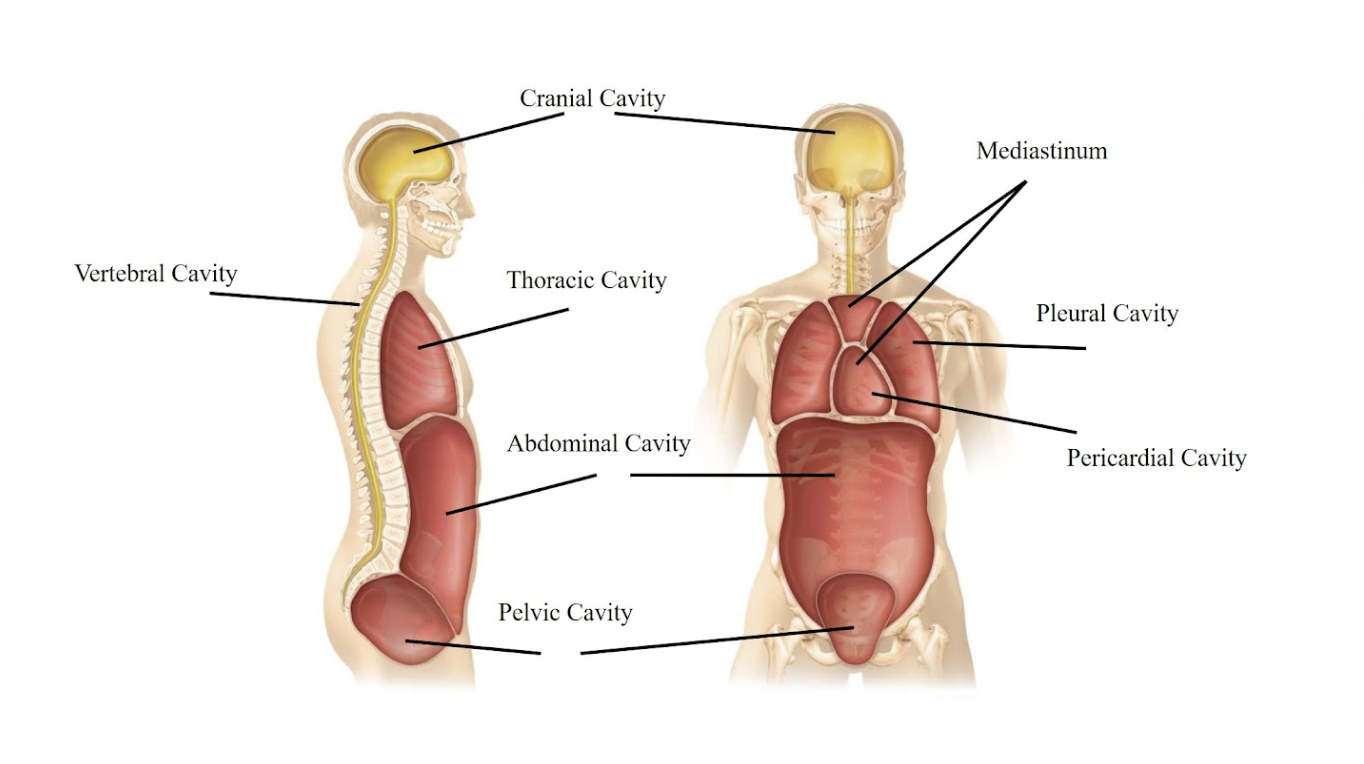
Pelvic cavity
The lower part of your belly, holding your bladder and reproductive organs.
Right upper quadrant (RUQ)
The top right part of your belly, where your liver and gallbladder are found.
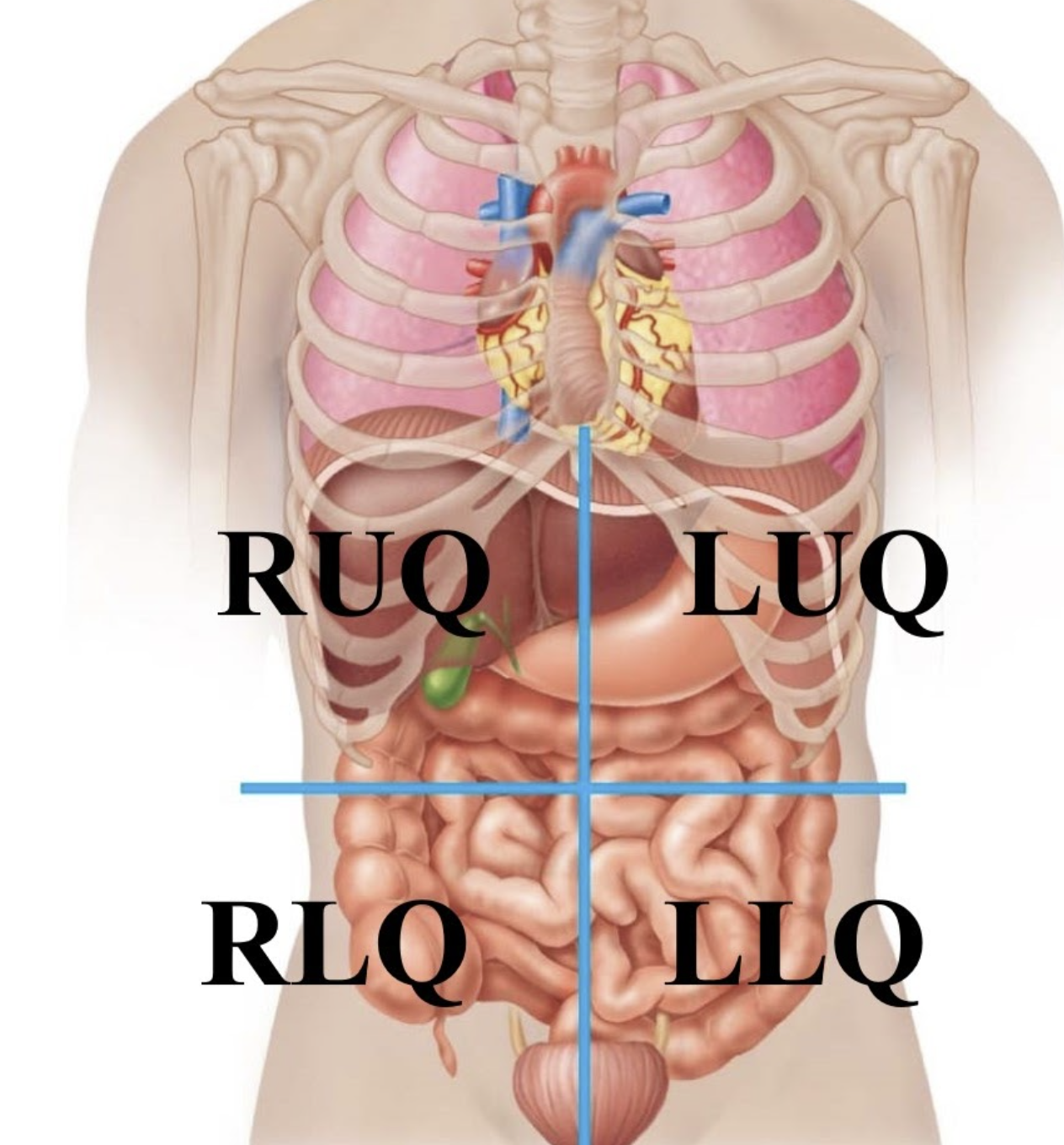
Left upper quadrant (LUQ)
The top left part of your belly, containing your spleen and a part of your stomach.
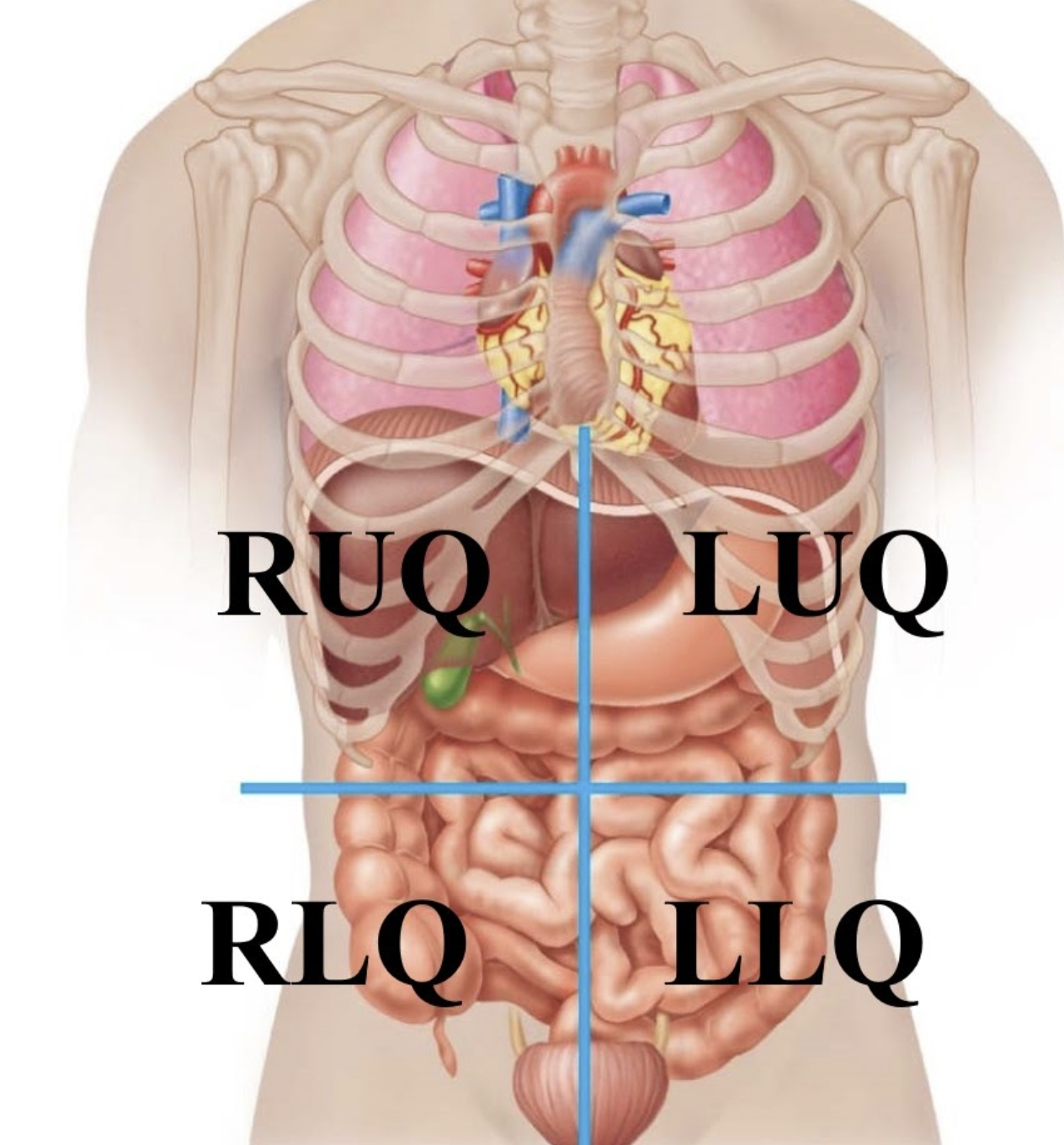
Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
The bottom right part of your belly, where your intestines and appendix are.
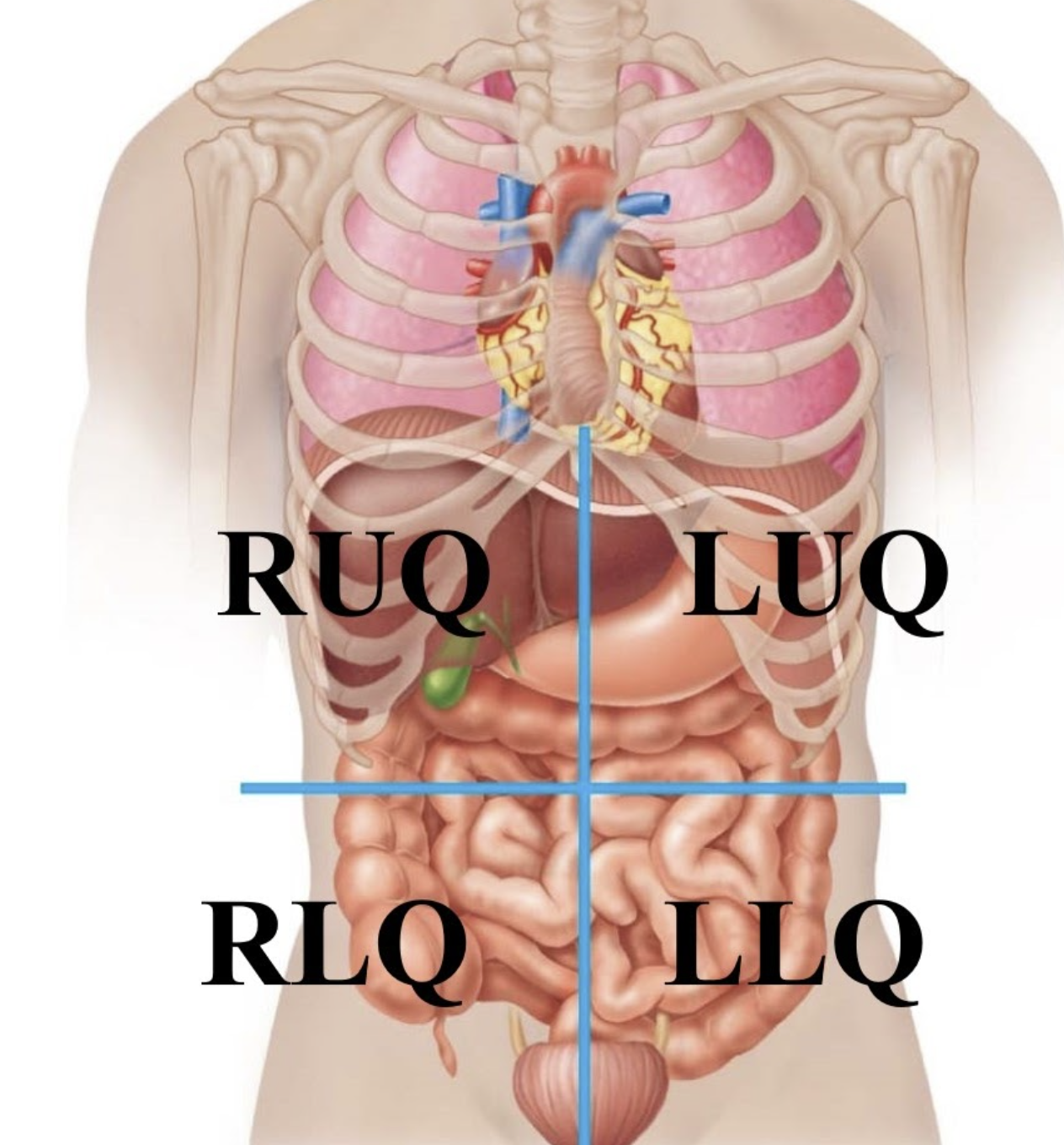
Left lower quadrant (LLQ)
The bottom left part of your belly, primarily containing parts of your intestines.
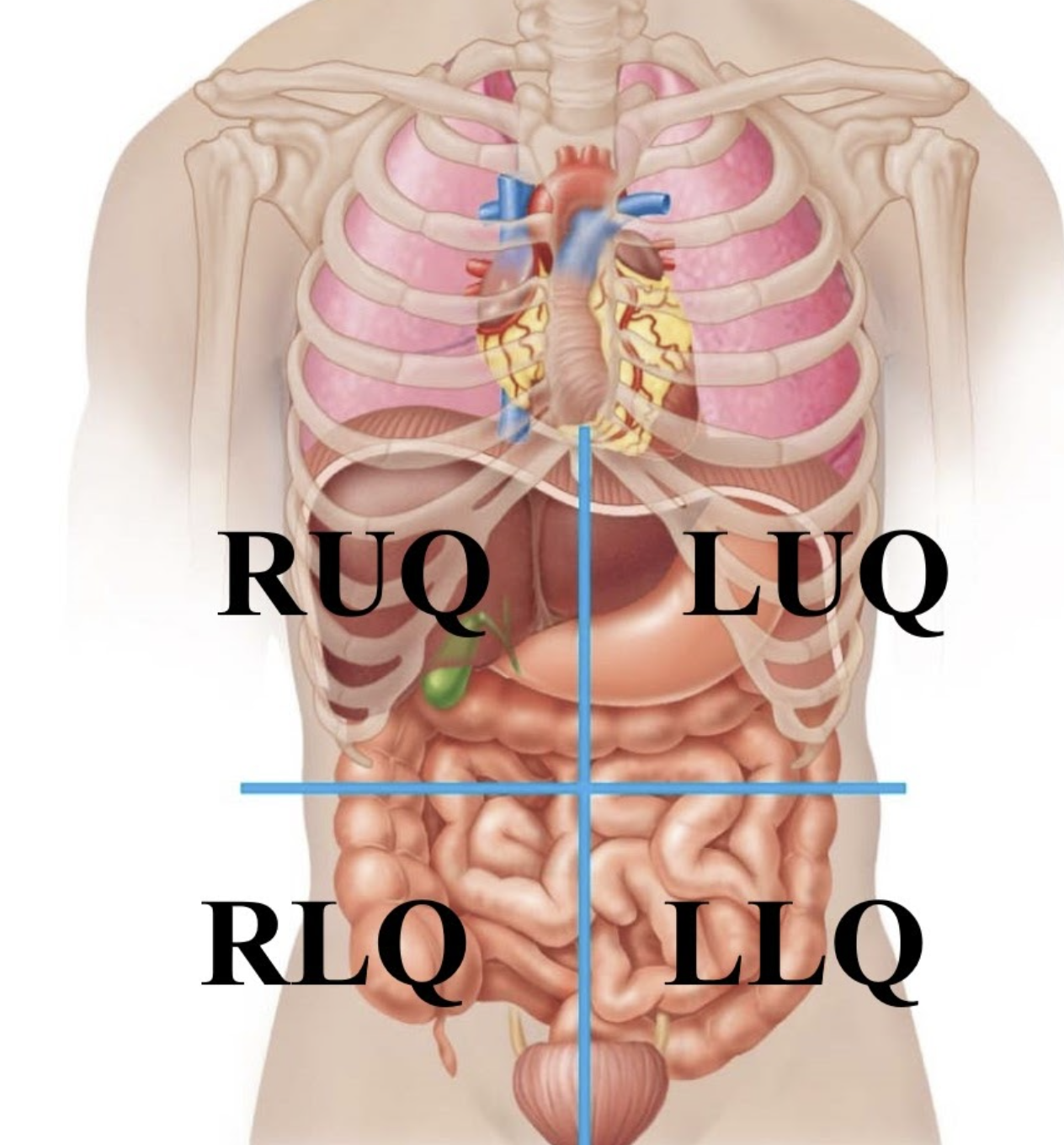
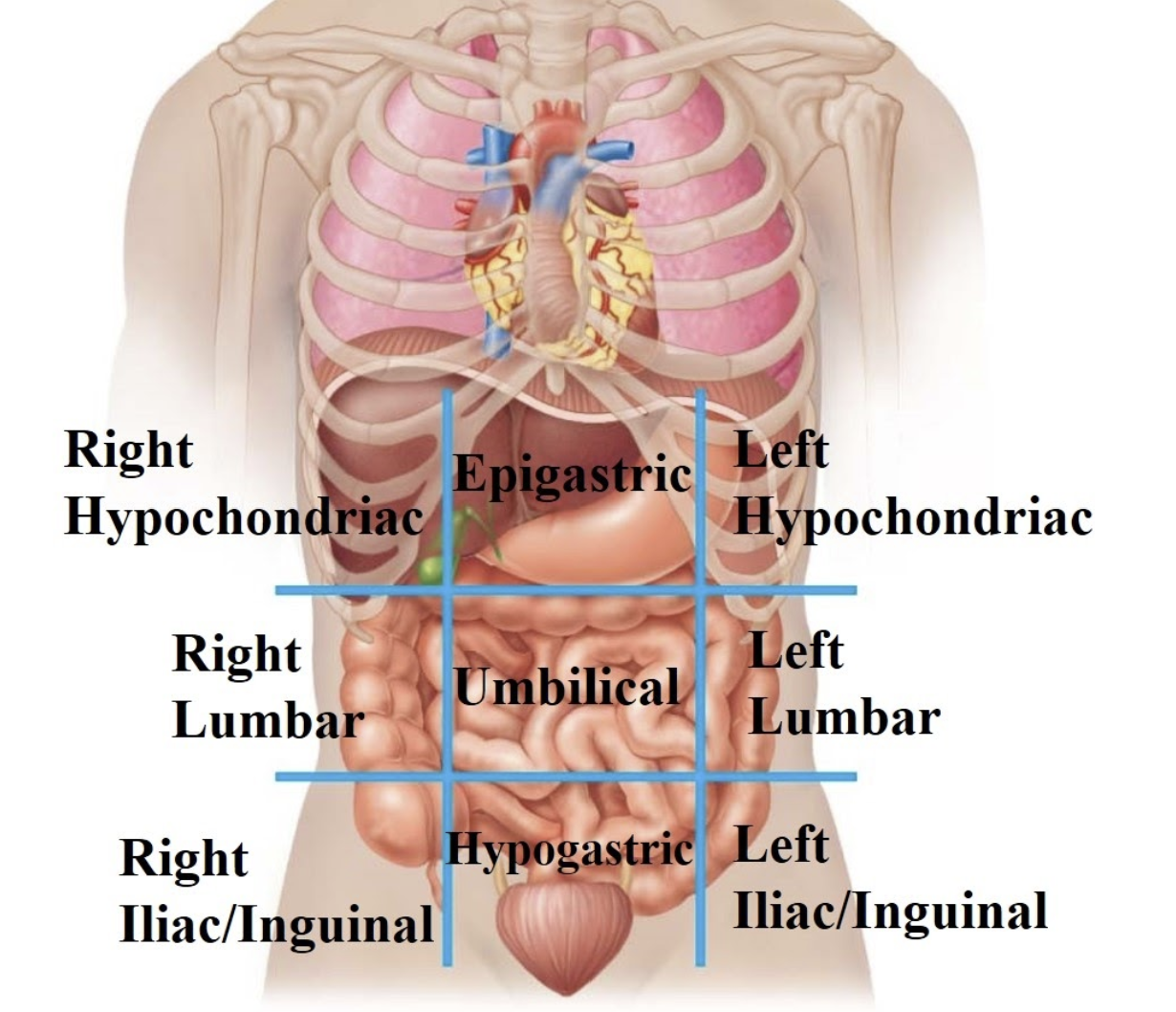
Right hypochondriac region
Contains the liver and gall bladder.
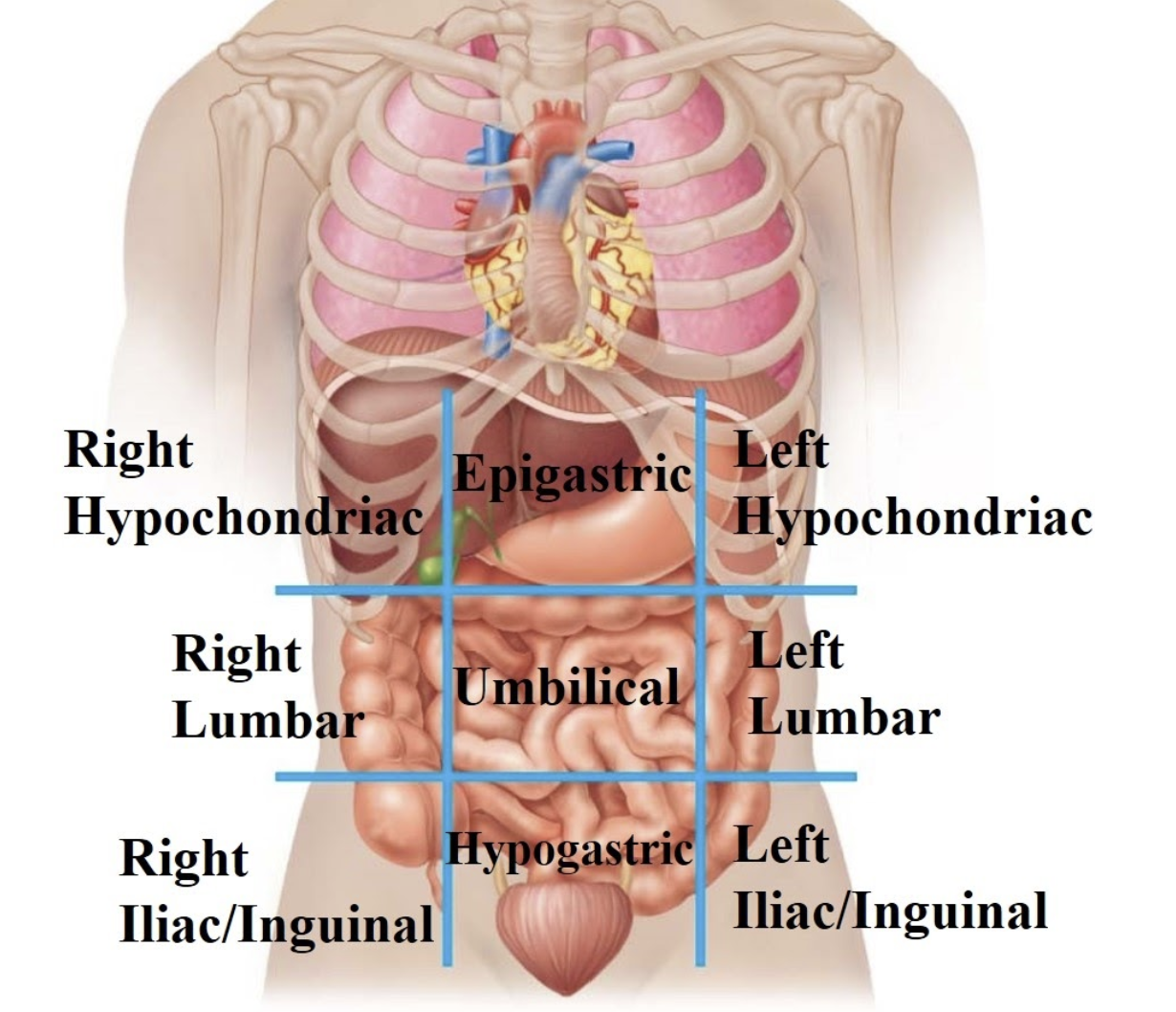
Epigastric region
Contains the stomach and pancreas.
Left hypochondriac region
Contains the spleen.
Right lumbar region
Contains the ascending colon.
Umbilical region
Contains the small intestines.
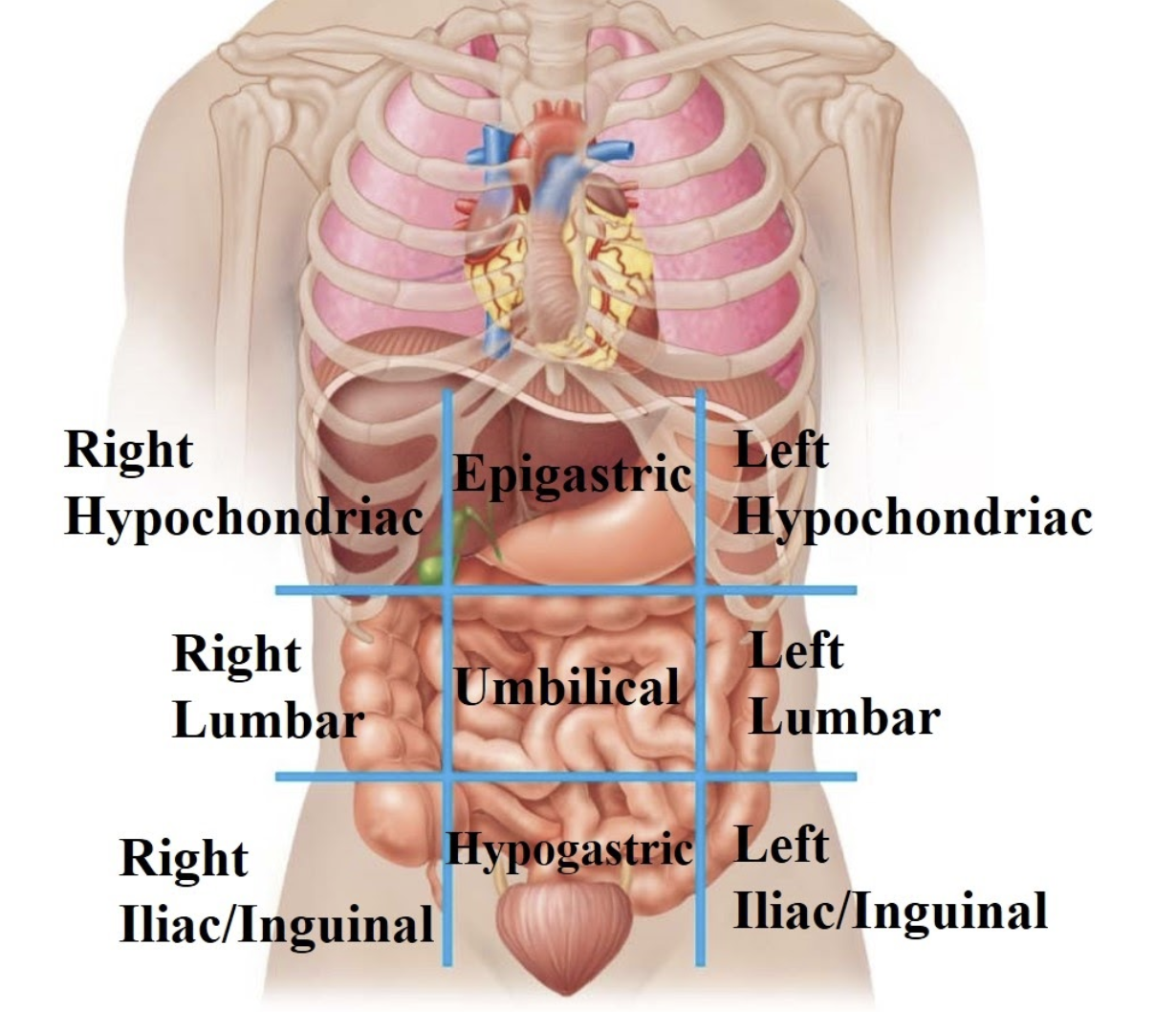
Left lumbar region
Contains the descending colon.
Right Iliac (inguinal) region
Contains the appendix.
Hypogastric region
Contains the urinary bladder and reproductive organs.
Left iliac (inguinal) region
Contains the sigmoid colon.
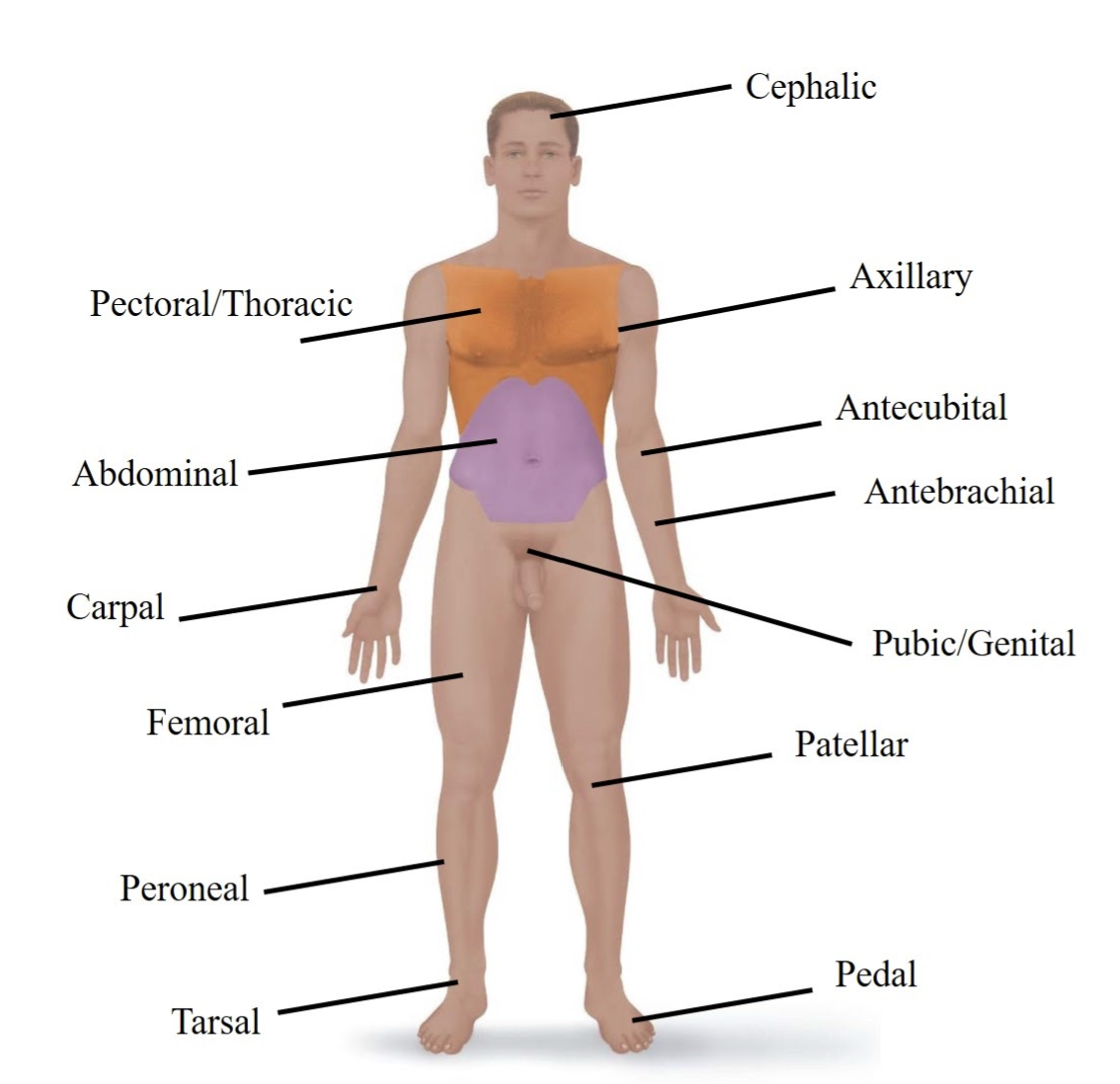
Cephalic
Refers to your head.
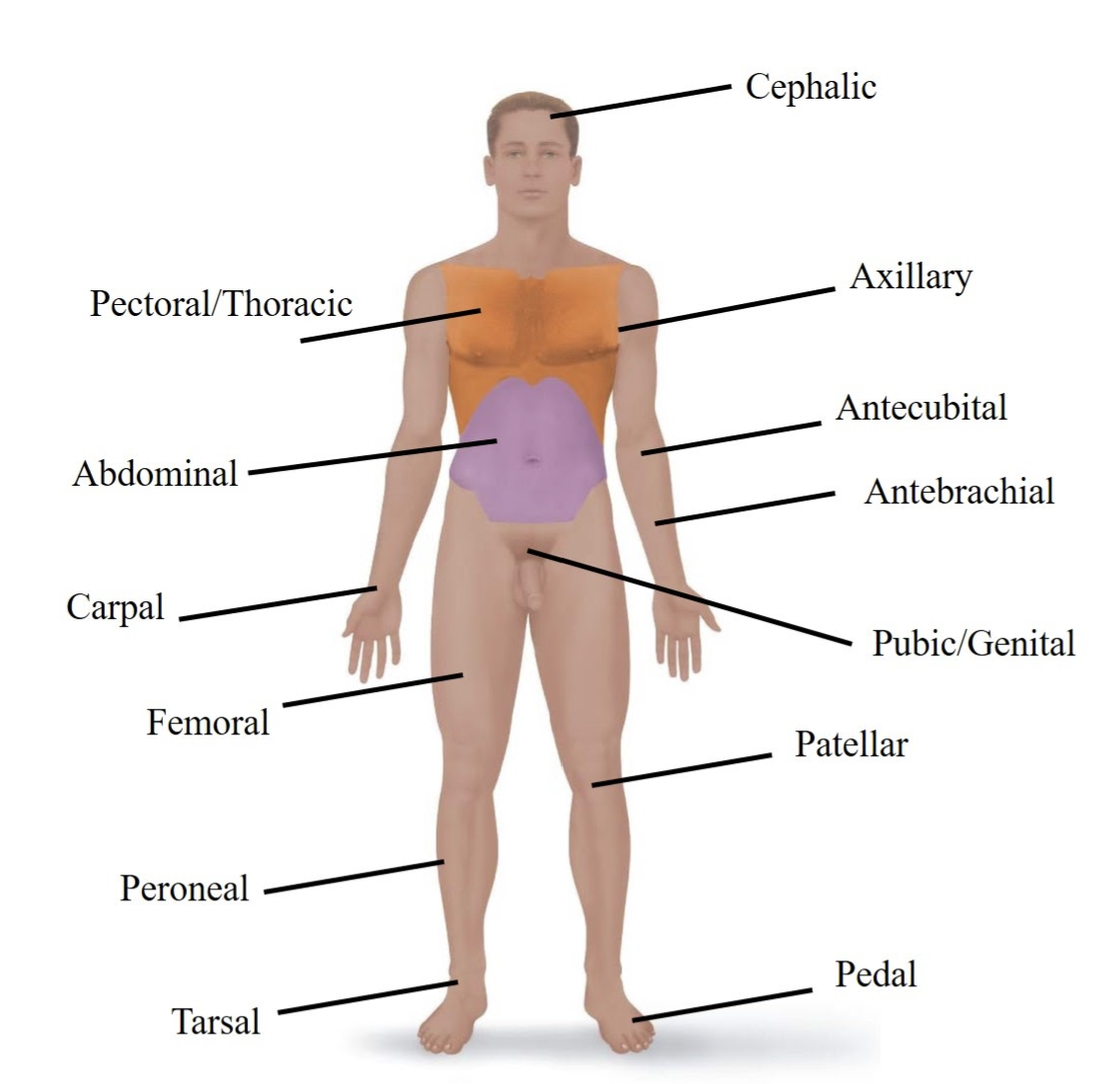
Pectoral/Thoracic
Refers to your chest area.
Axillary
Refers to your armpit.
Abdominal
Refers to your belly.
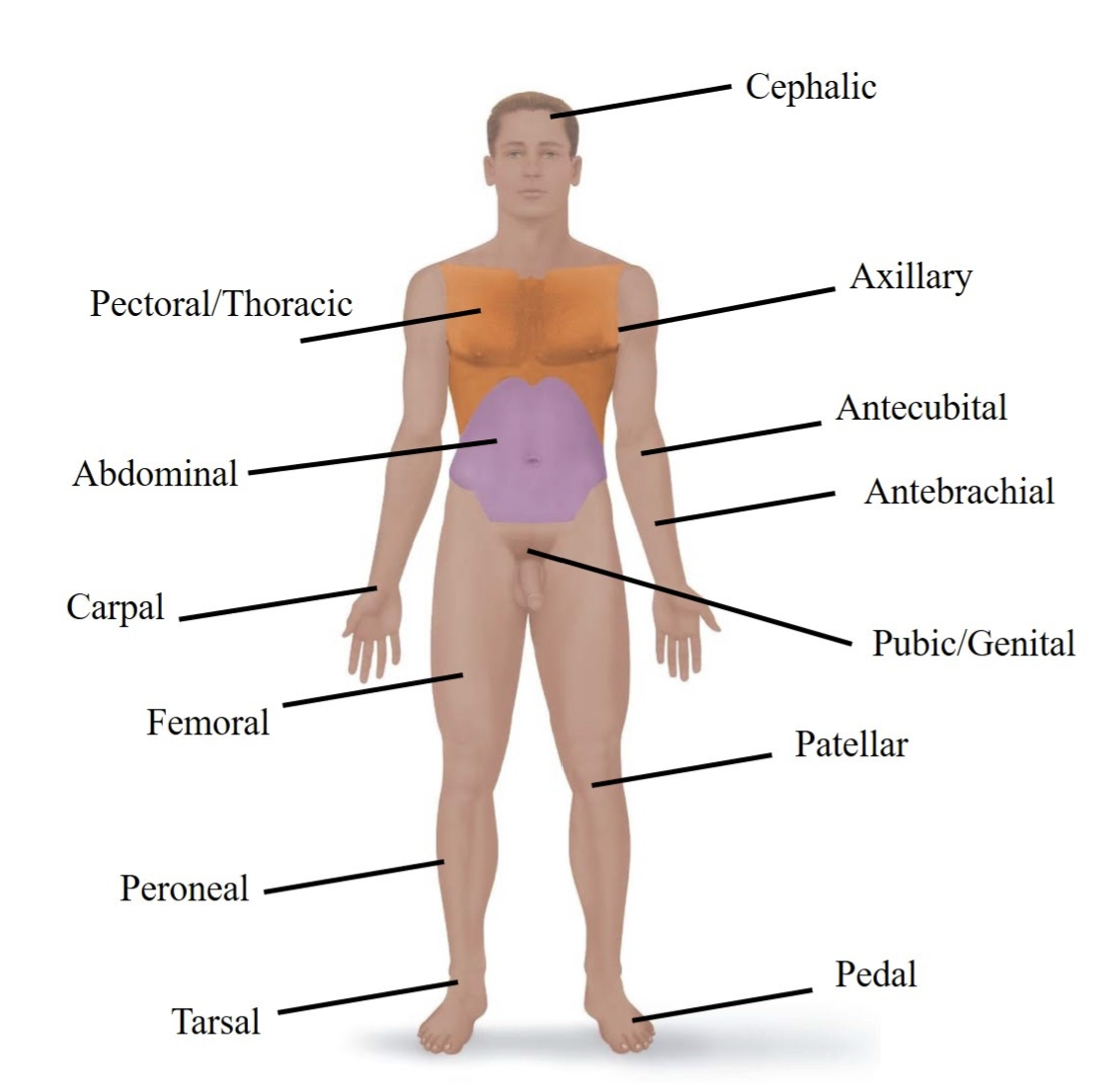
Antecubital
Refers to the front of your elbow.
Antebrachial
Refers to your forearm.
Carpal
Refers to your wrist.
Pubic/Genital
Refers to your groin or private areas.
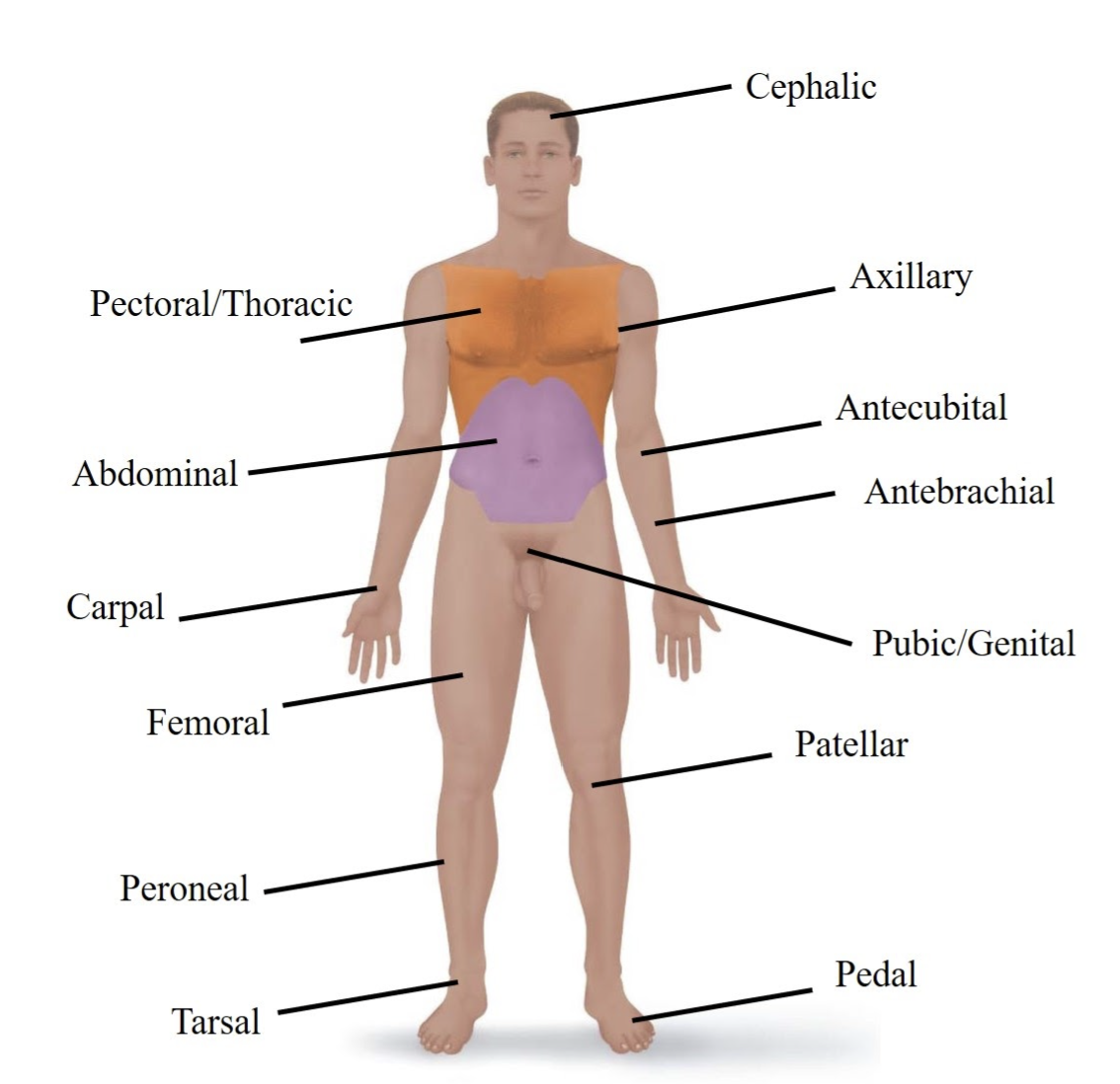
Femoral
Refers to your thigh (upper leg).
Patellar
Refers to your kneecap.
Tarsal
Refers to your ankle.
Pedal
Refers to your foot.
Cervical
Refers to your neck.
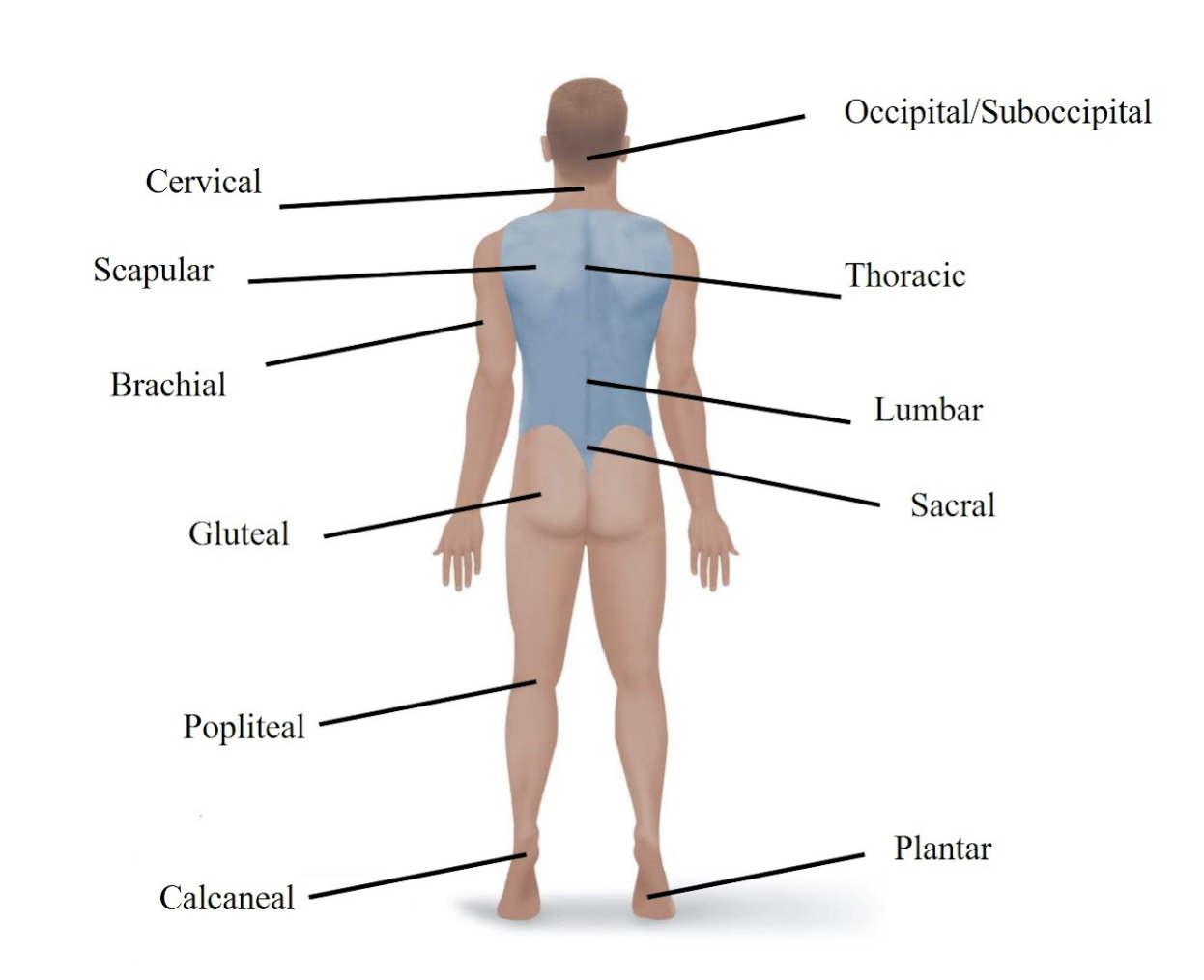
Occipital/Suboccipital
Refers to the back of your head.
Scapular
Refers to your shoulder blade area.
Lumbar
Refers to your lower back.
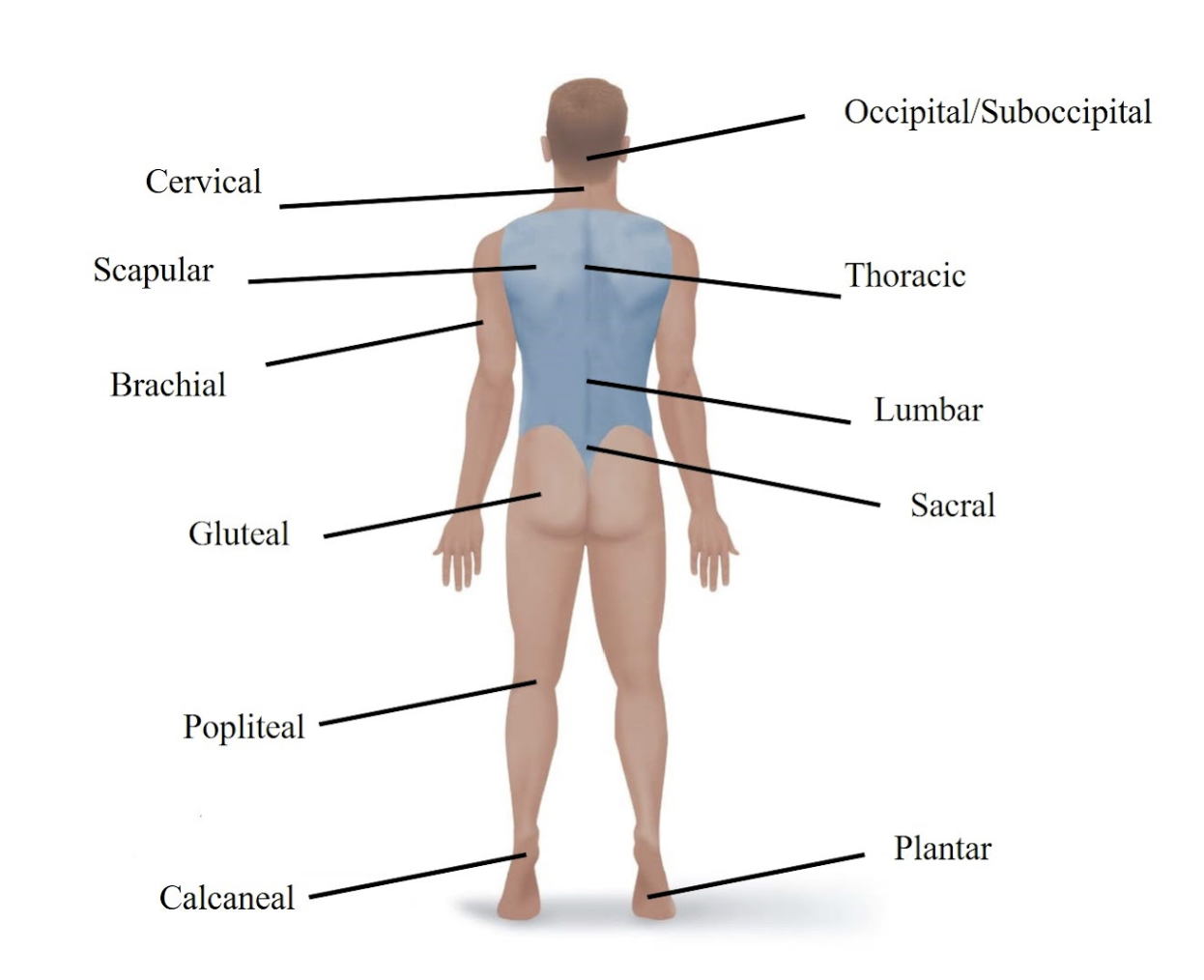
Gluteal
Refers to your buttock.
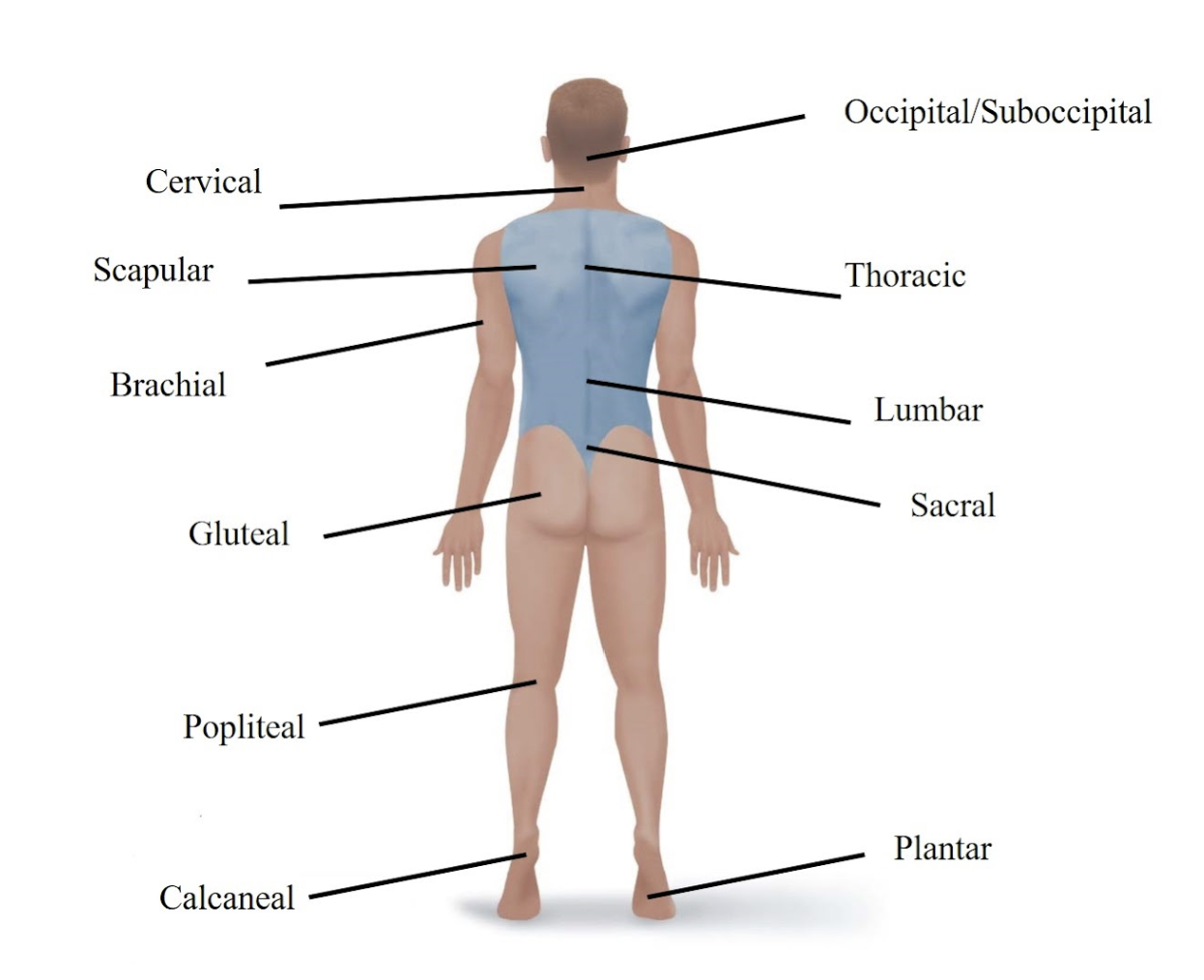
Sacral
Refers to the area just above your tailbone in your lower back.
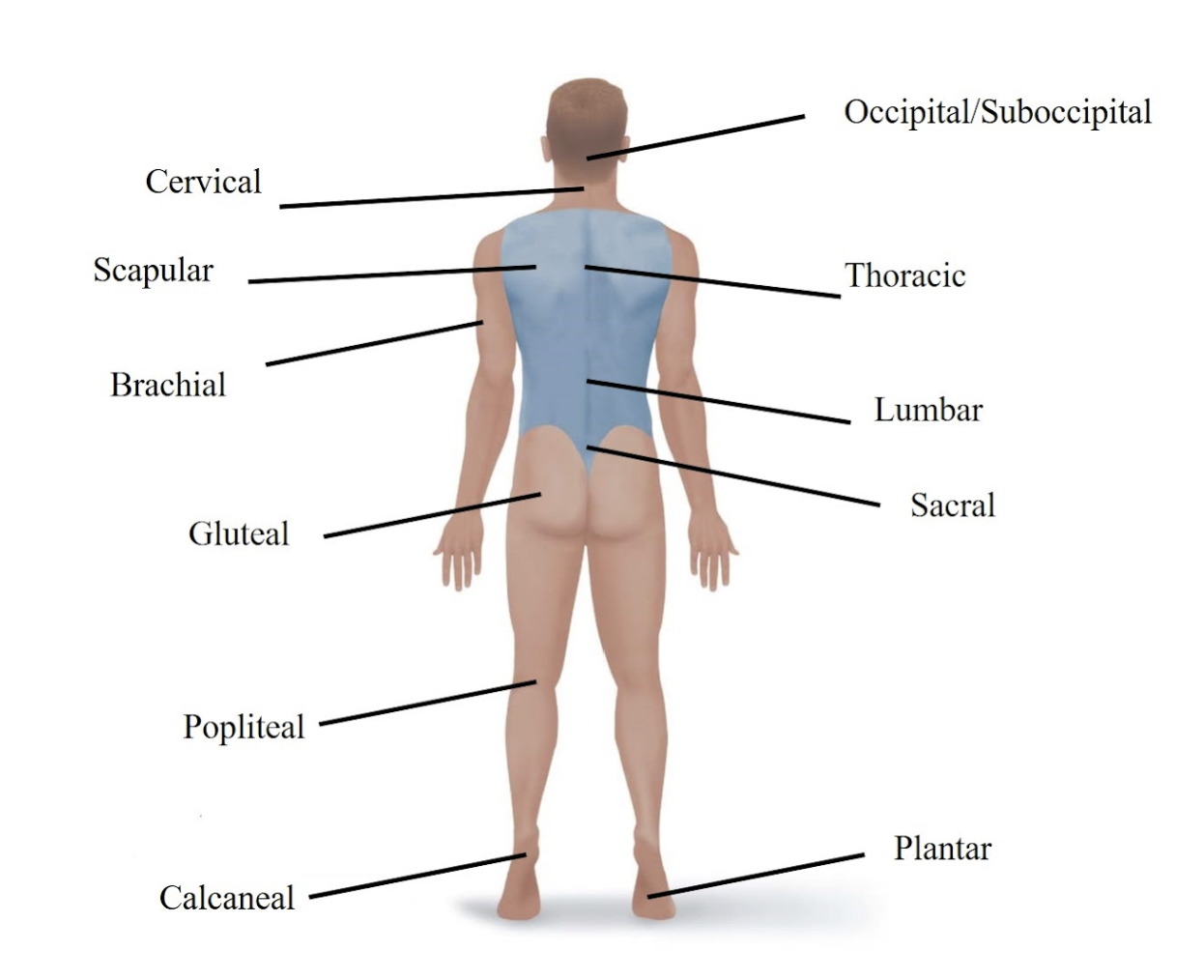
Popliteal
Refers to the back of your knee.
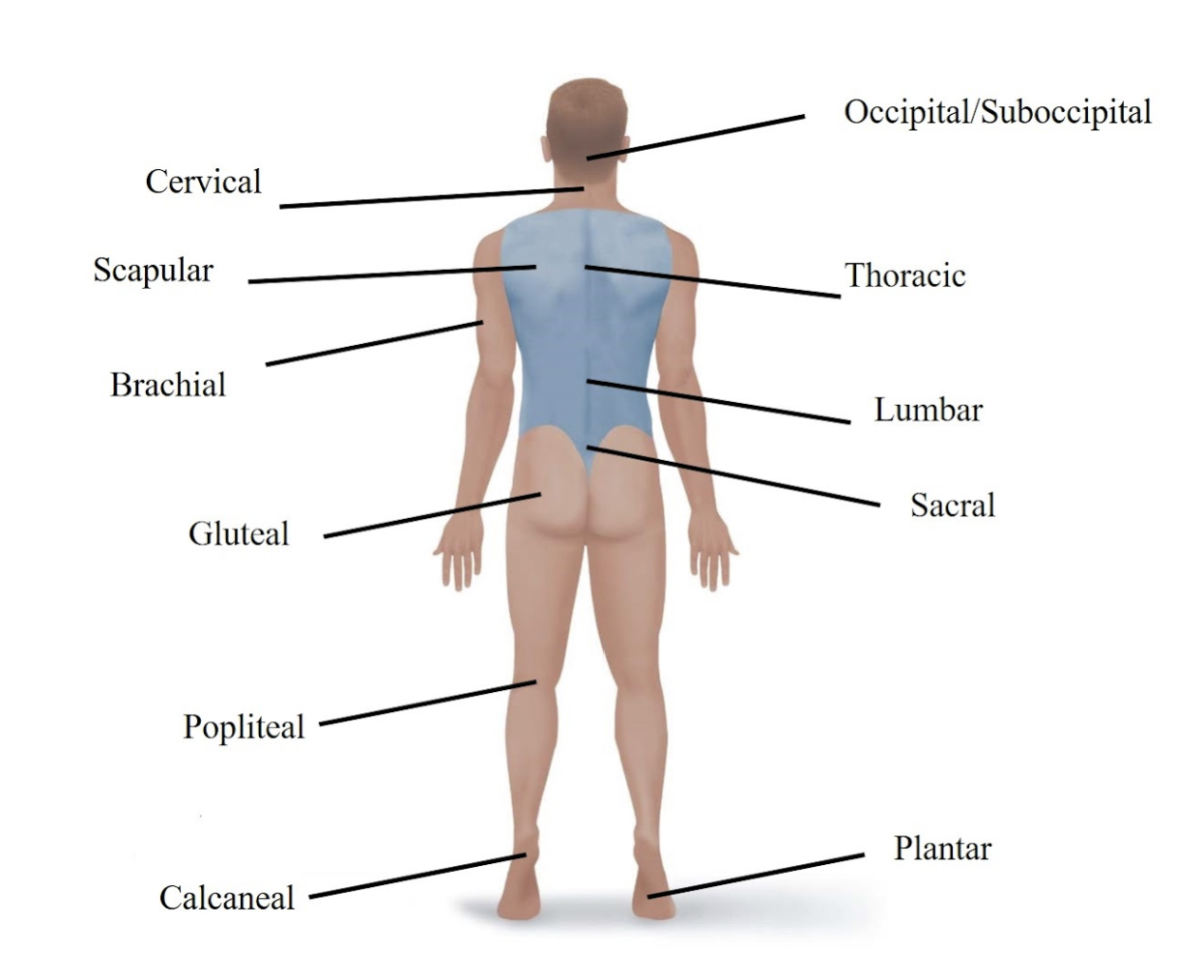
Calcaneal
Refers to your heel.
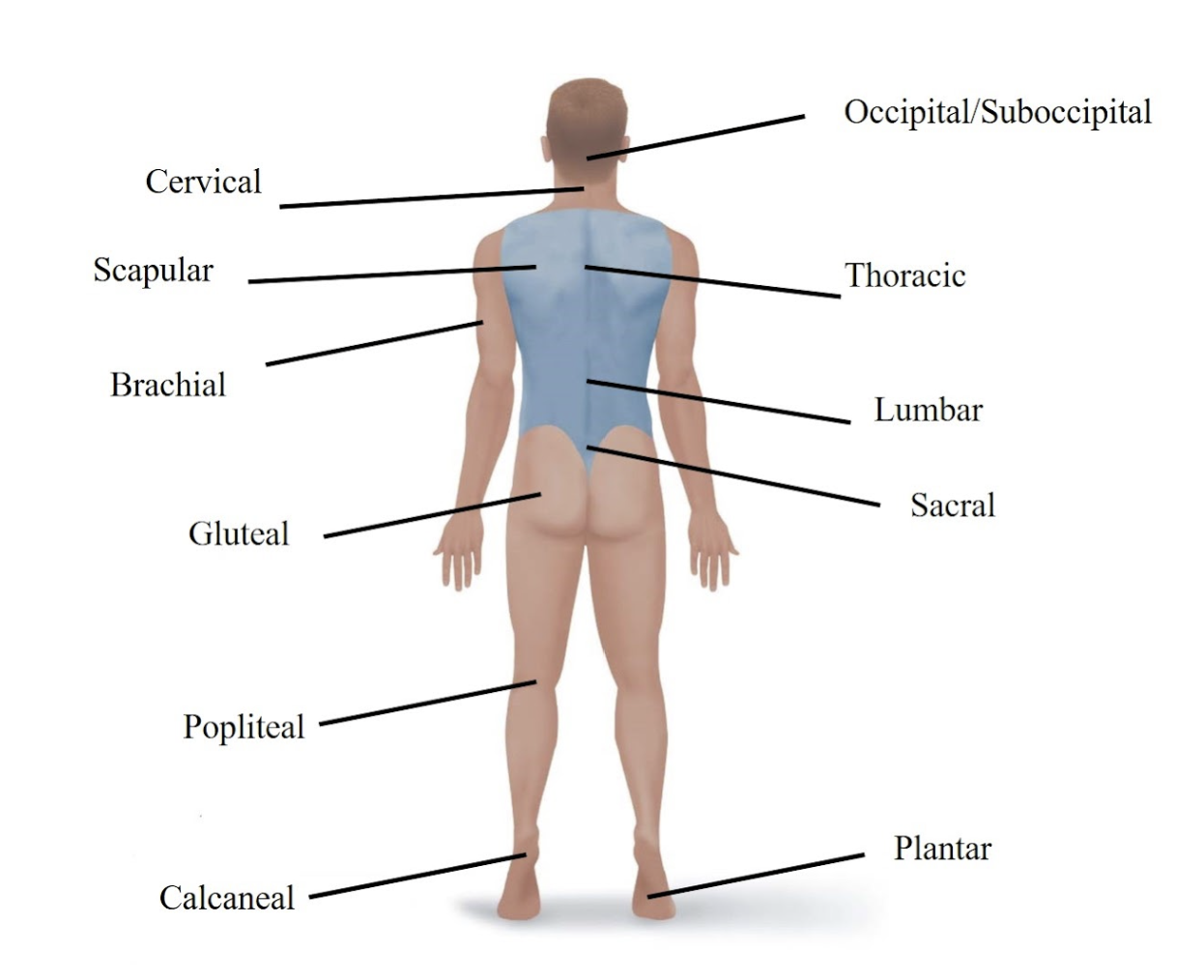
Plantar
Refers to the sole (bottom) of your foot.
Nucleus
Stores DNA; site of DNA transcription.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Site of protein synthesis.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Site of calcium synthesis.
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis.
Golgi apparatus
Packages and modifies proteins.
Mitochondria
Site of ATP synthesis.
Lysosome
Breaks down cell debris and foreign pathogens.
Peroxisome
Breaks down fat, alcohol, and hydrogen peroxide.
Centrioles
Assist in mitotic spindle formation.
Mitosis
The division of a cell which results in genetically identical daughter cells.
Prophase
The phase where DNA condenses into chromosome form and the mitotic spindle forms.
Metaphase
The phase where chromosomes line up on the equator of the cell.
Anaphase
The phase where the duplicated chromosomes are pulled apart by the mitotic spindle.
Telophase
The phase where the separated chromosomes uncondense into DNA form and the mitotic spindle disappears.
Cytokinesis
The process that begins with the formation of the cleavage furrow.
thoracic
relates to the thorax (chest) area of the body and can refer to the thoracic spine
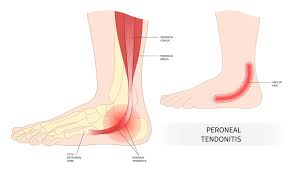
peroneal
refers to the fibula bone or structures associated with it, particularly the peroneal muscles and tendons on the outer side of the lower leg and ankle
Epithelial Tissue
Widespread tissue type: Part of skin, body cavity/organ linings, & glands.
Simple & Stratified/ Squamous, Cuboid, Columnar
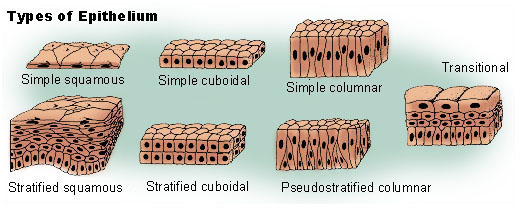
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Found in blood vessel linings & lung alveoli. Maximizes diffusion because the membrane is thin.
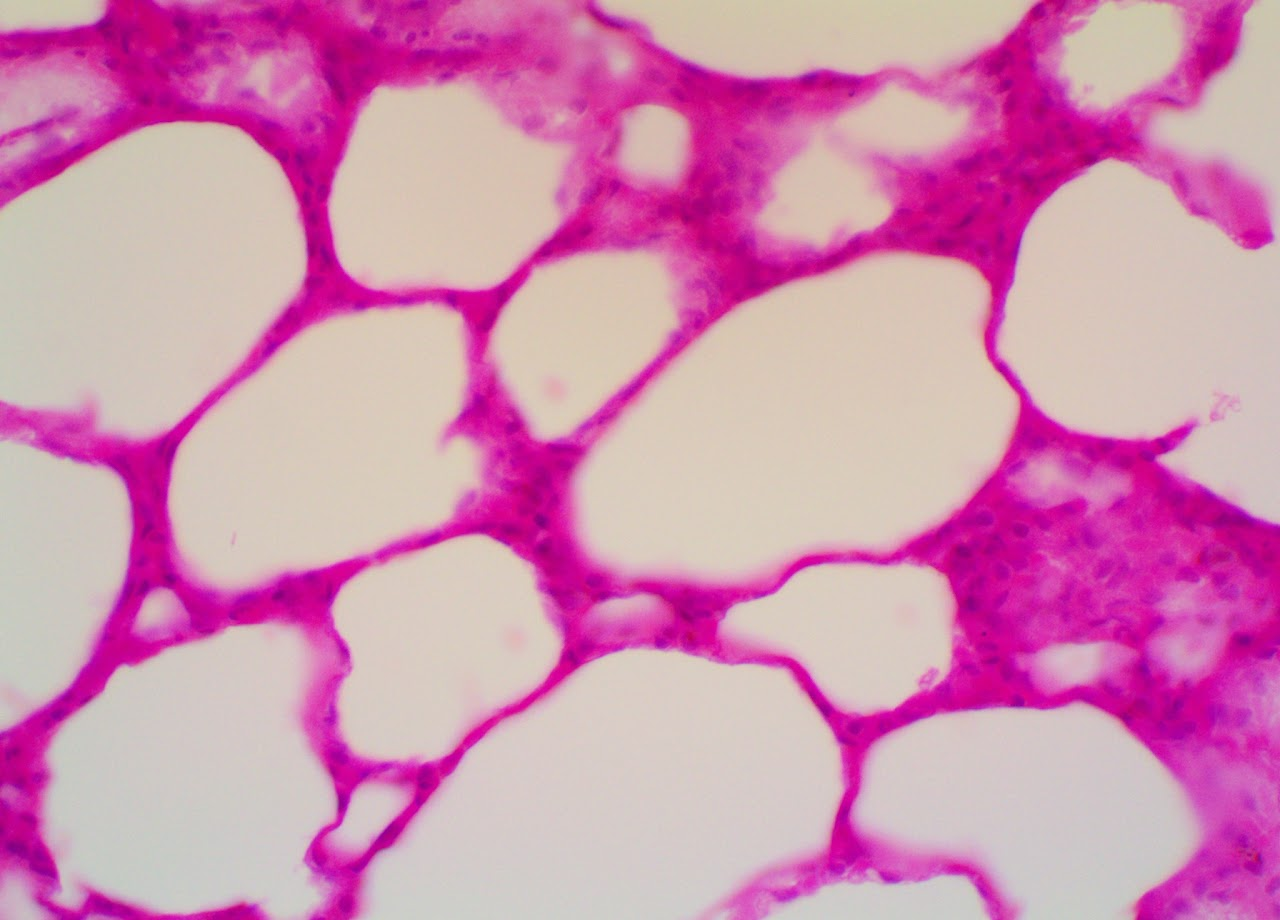
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Found in glandular structures & kidney tubule system. Provides slightly thicker barrier than squamous, allowing selective permeability for secretion and re-absorption
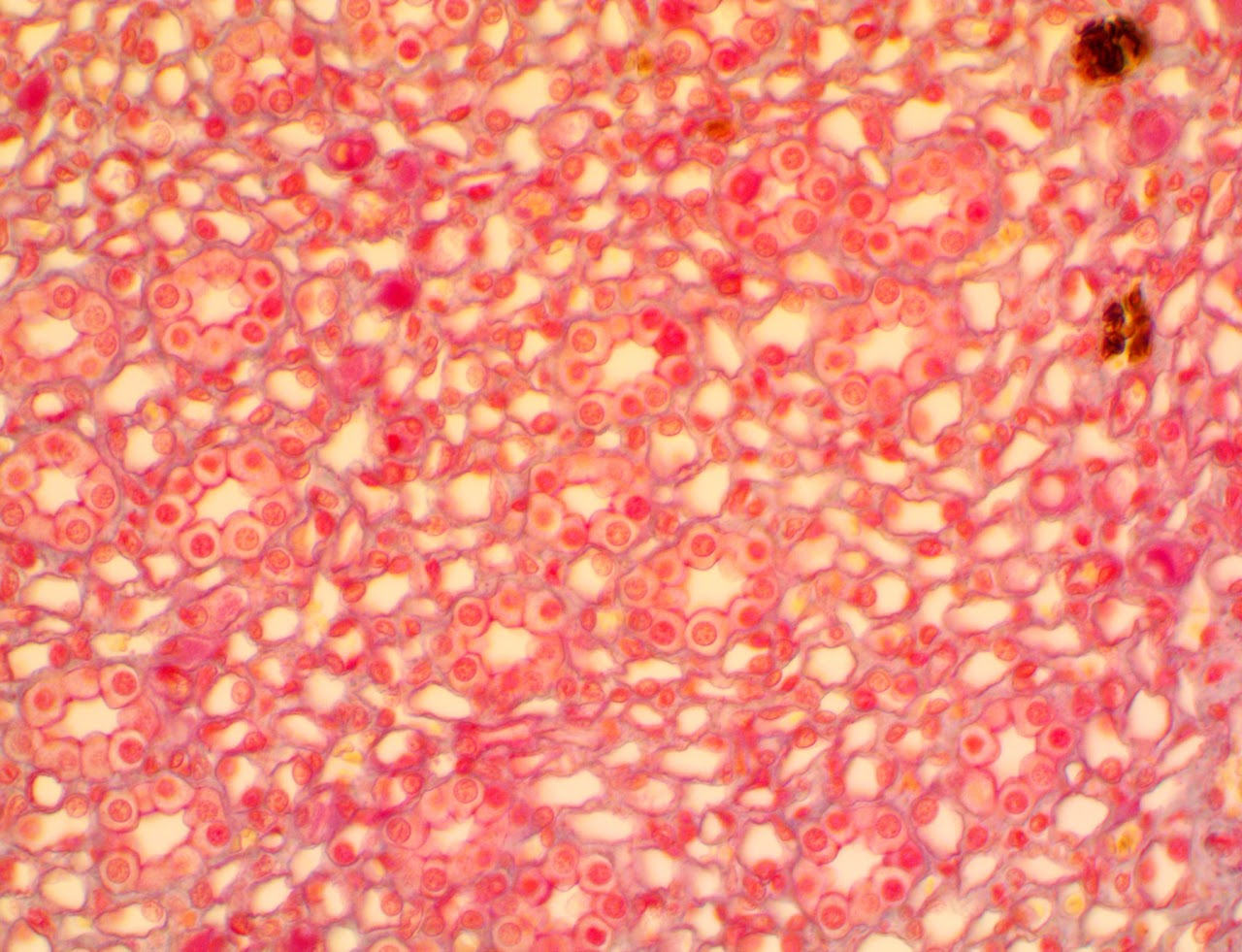
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Found in the lining of the small intestines. High absorption of nutrients while remaining selective against digestive enzymes and acids.
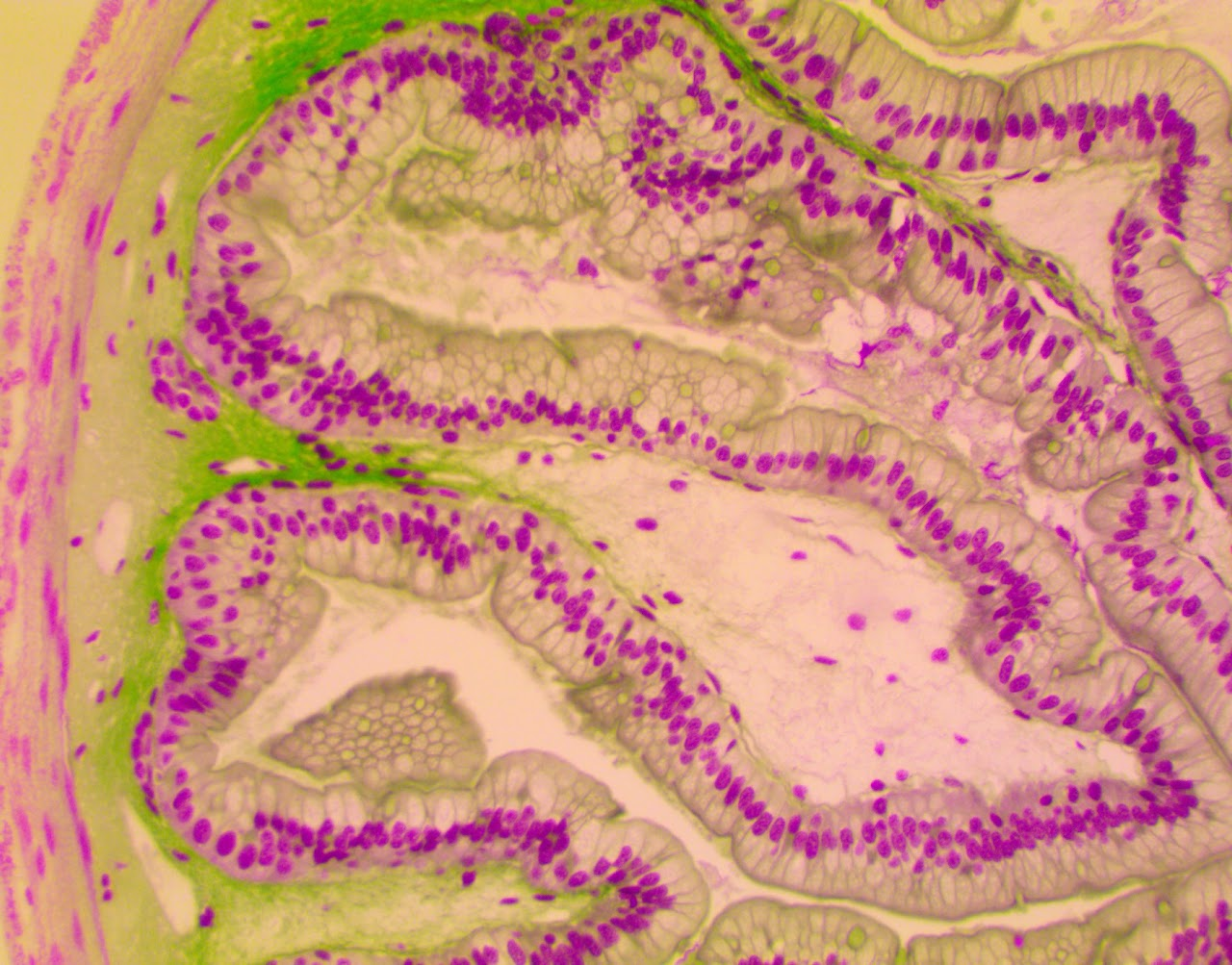
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Found in respiratory airways
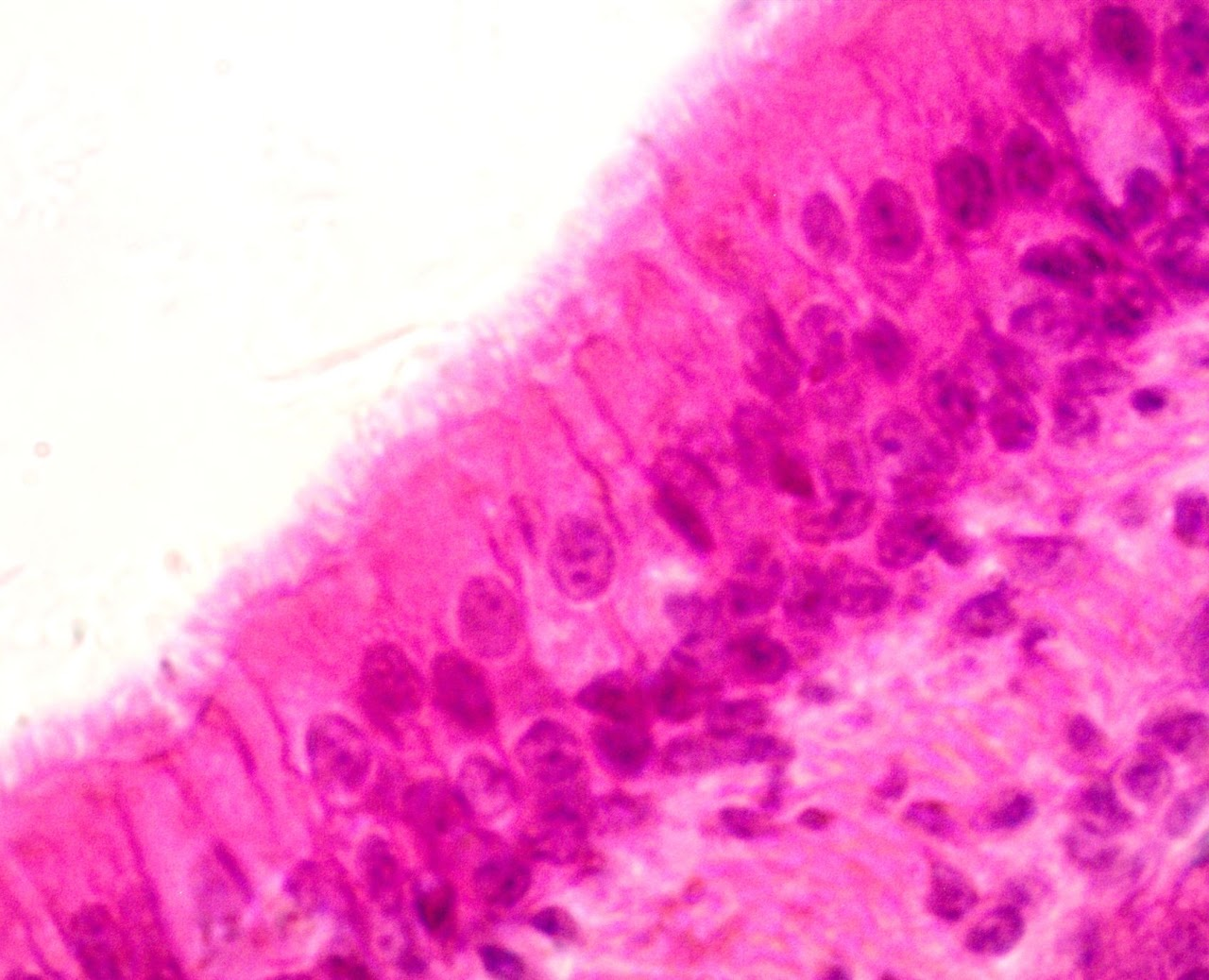
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Found in the epidermis of skin
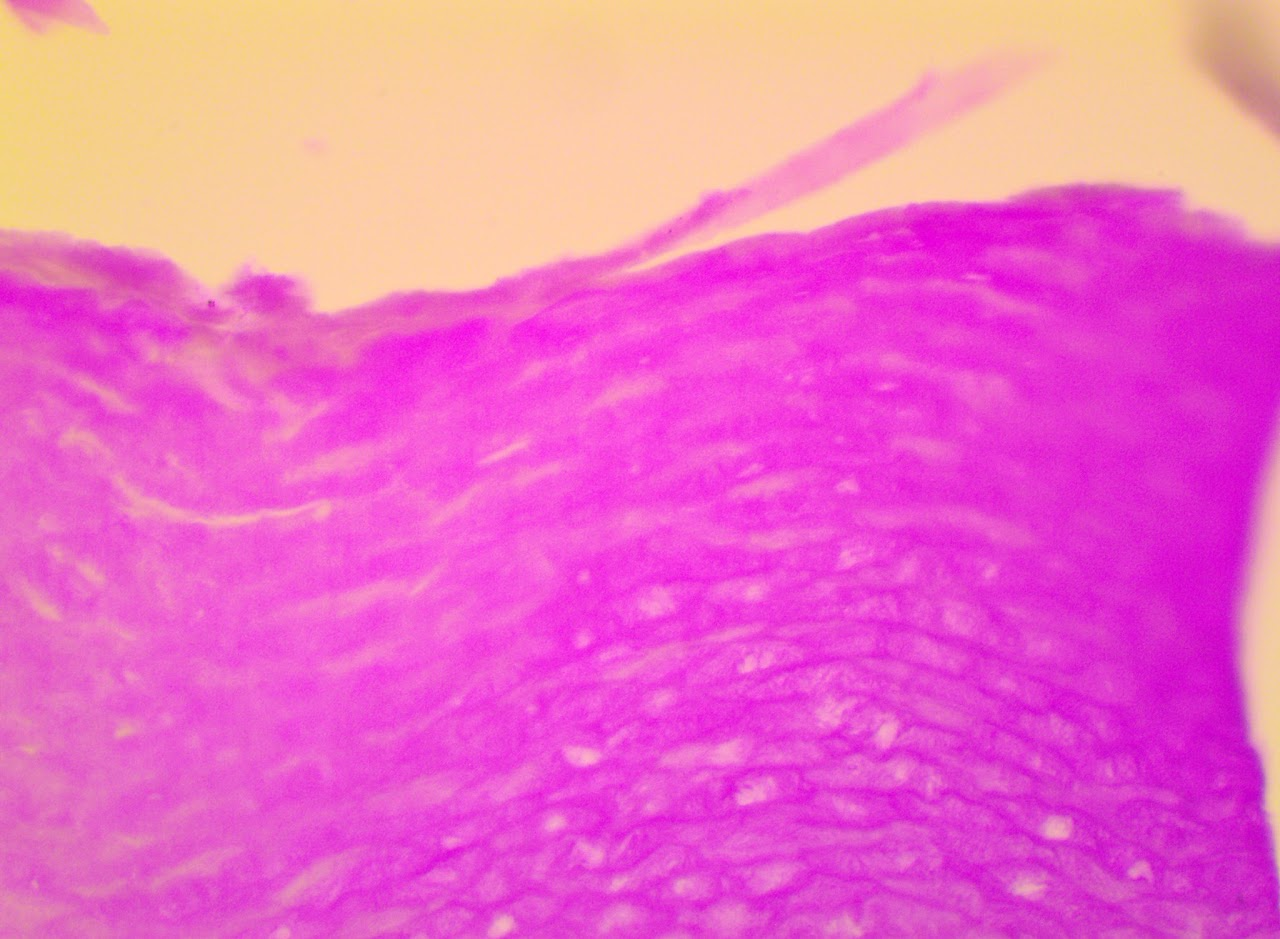
Transitional Epithelium
Lines Urinary organs such as Urinary Bladder
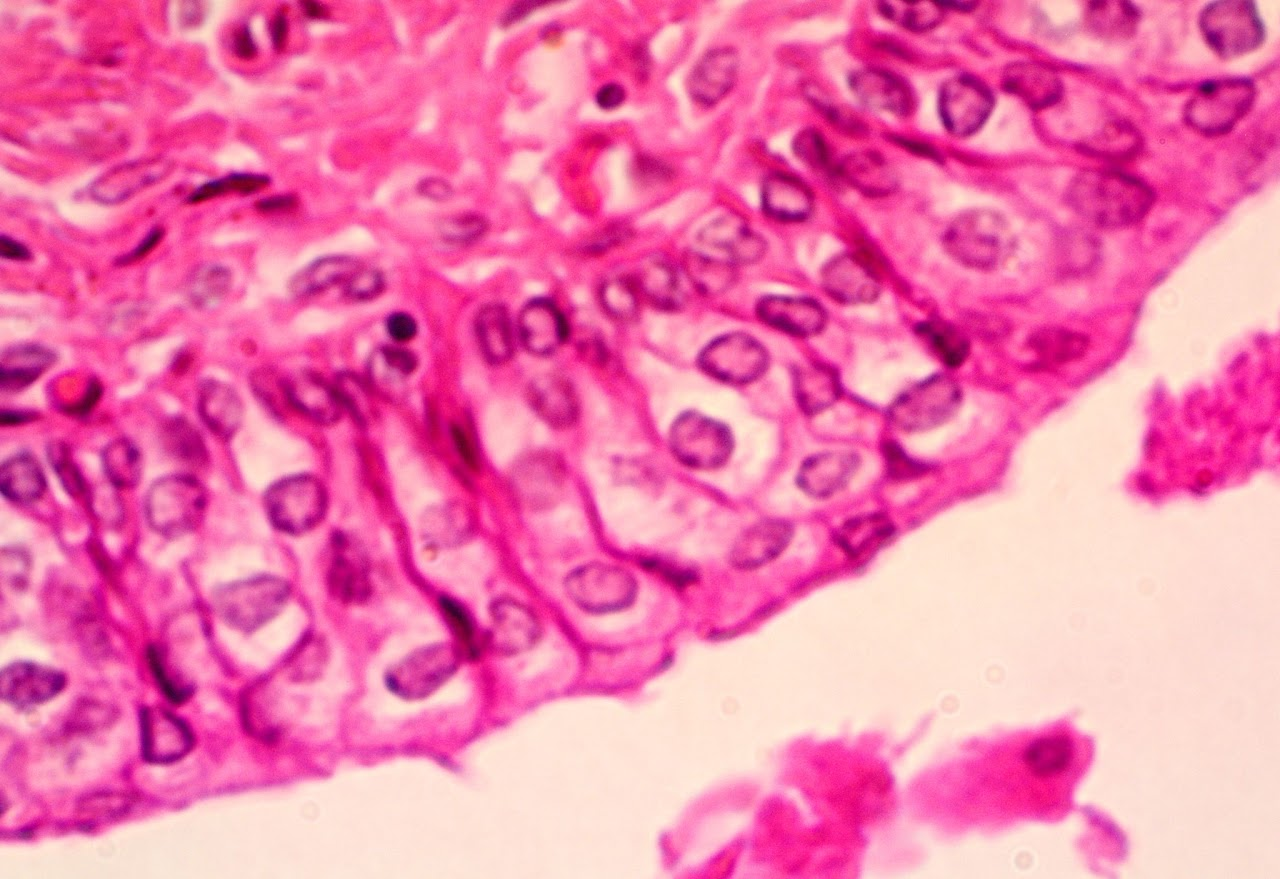
Connective Tissue:
Connective Tissue is diverse is includes four main types: Fibrous, Cartilage, Bone, & Blood
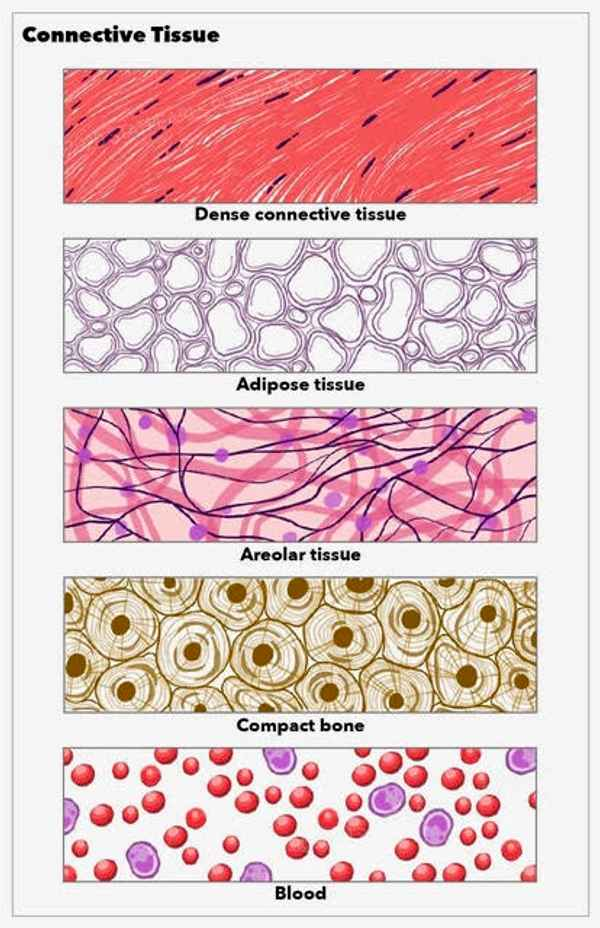
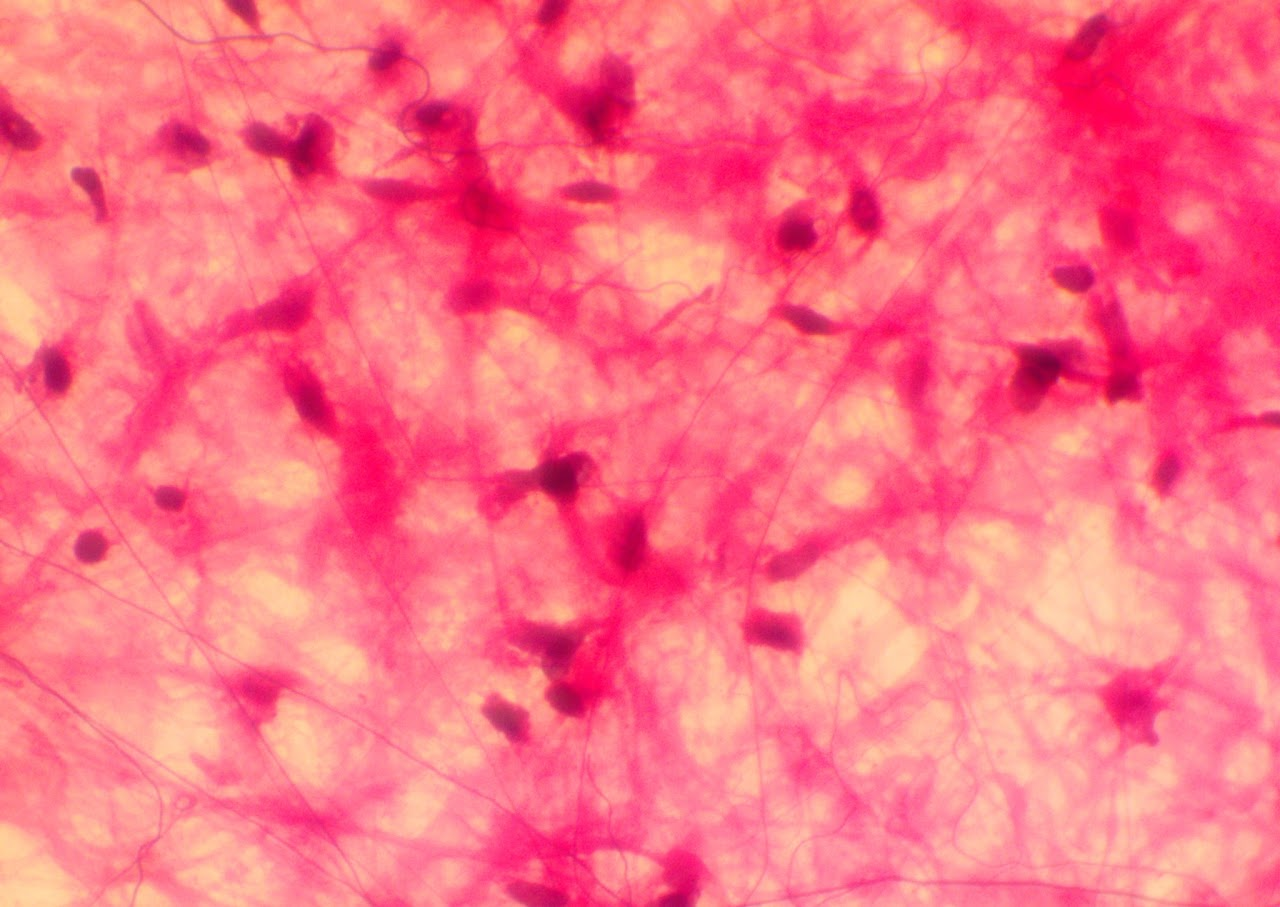
Loose Fibrous Connective Tissue
Areolar Loose Fibrous Connective Tissue, Adipose Loose Fibrous Connective Tissue, Reticular Loose Fibrous Connective Tissue
Areolar Loose Fibrous Connective Tissue
Found in the papillary layer of the dermis
Adipose Loose Fibrous Connective Tissue
Found in all fat tissue, such as subcutaneous tissue
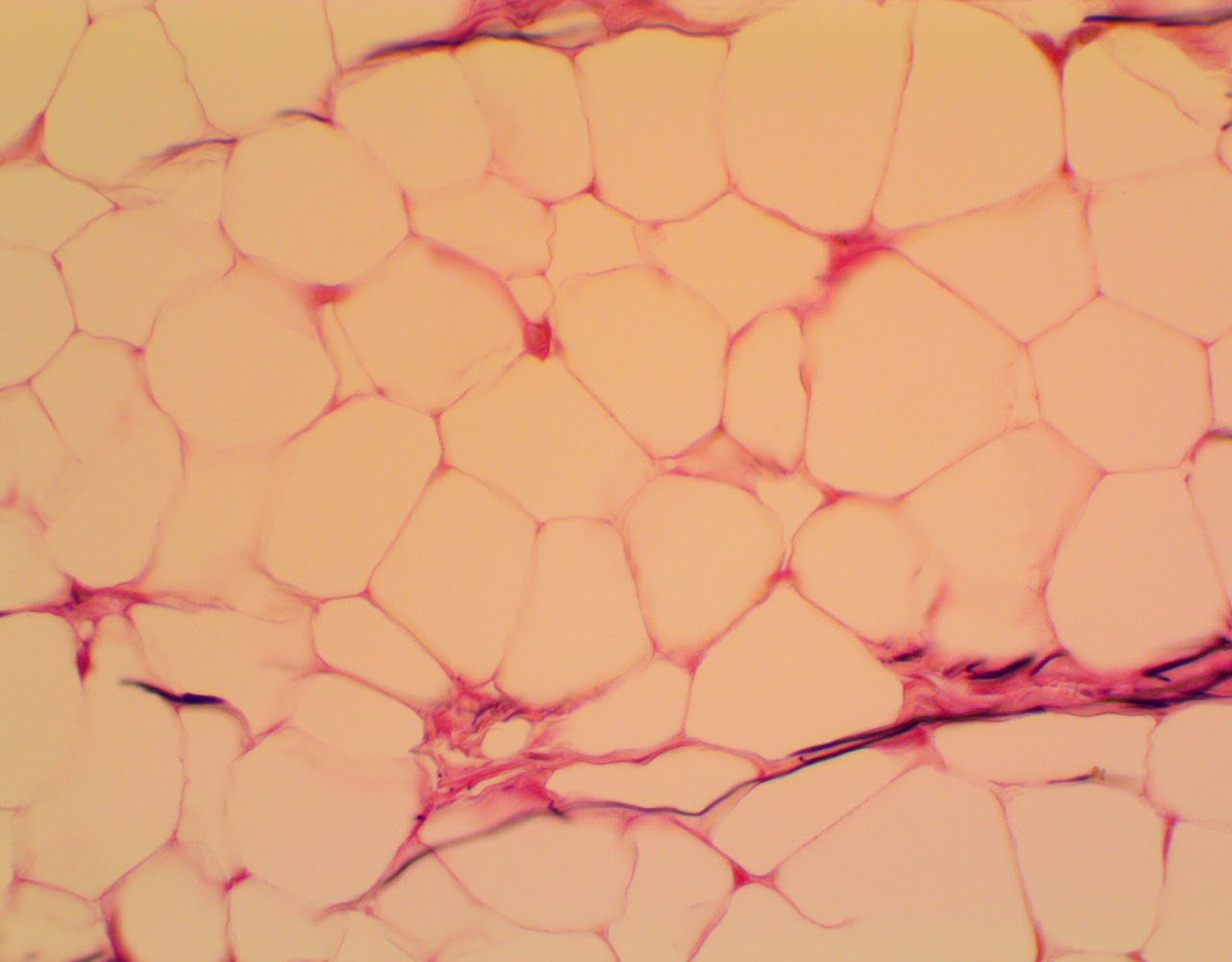
Reticular Loose Fibrous Connective Tissue
Found in lymphatic tissue, such as the spleen
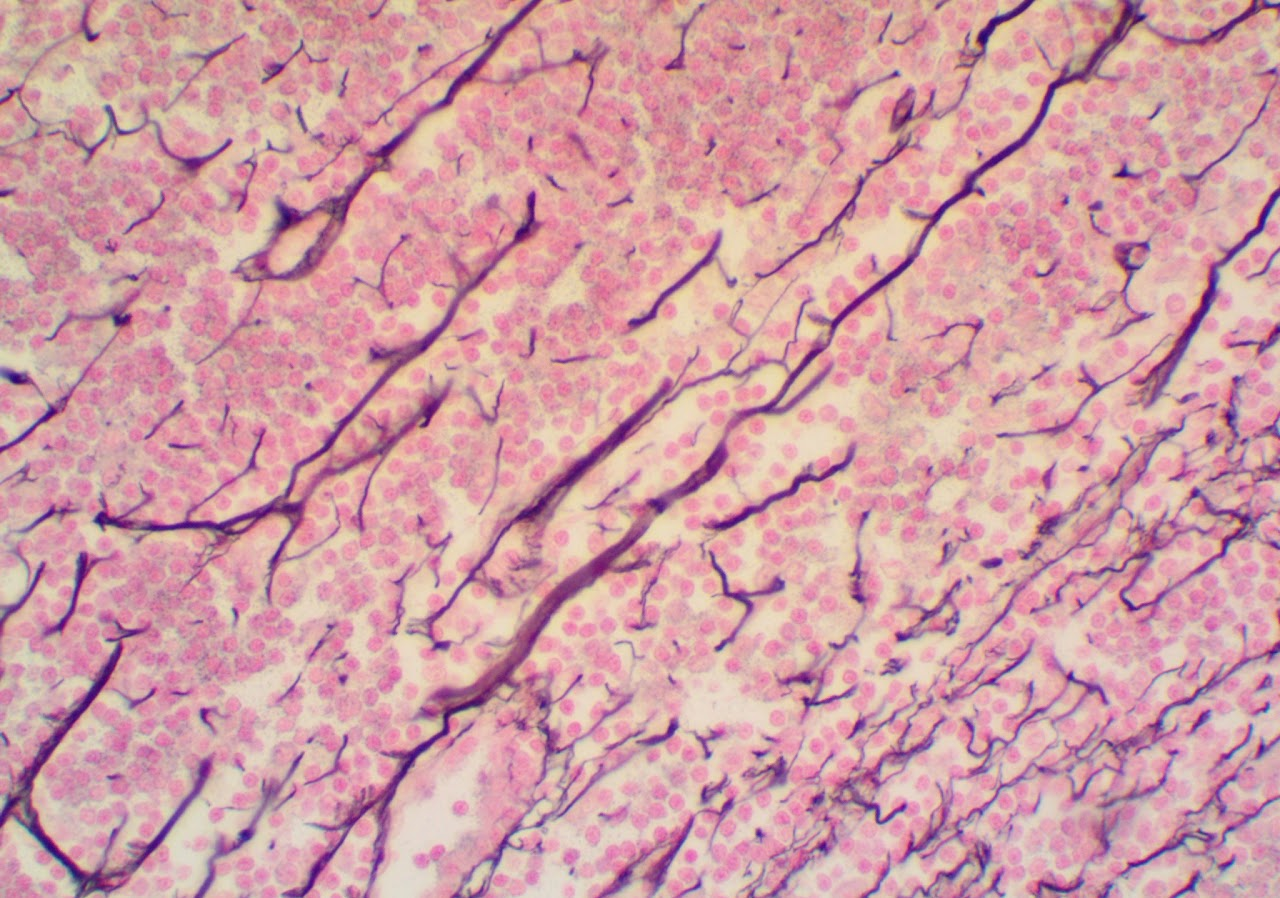
Dense Fibrous Connective Tissue
Dense Irregular Fibrous Connective Tissue, Dense Regular Fibrous Connective Tissue, Dense Elastic Fibrous Connective Tissue
Dense Irregular Fibrous Connective Tissue
Found in the reticular layer of the dermis
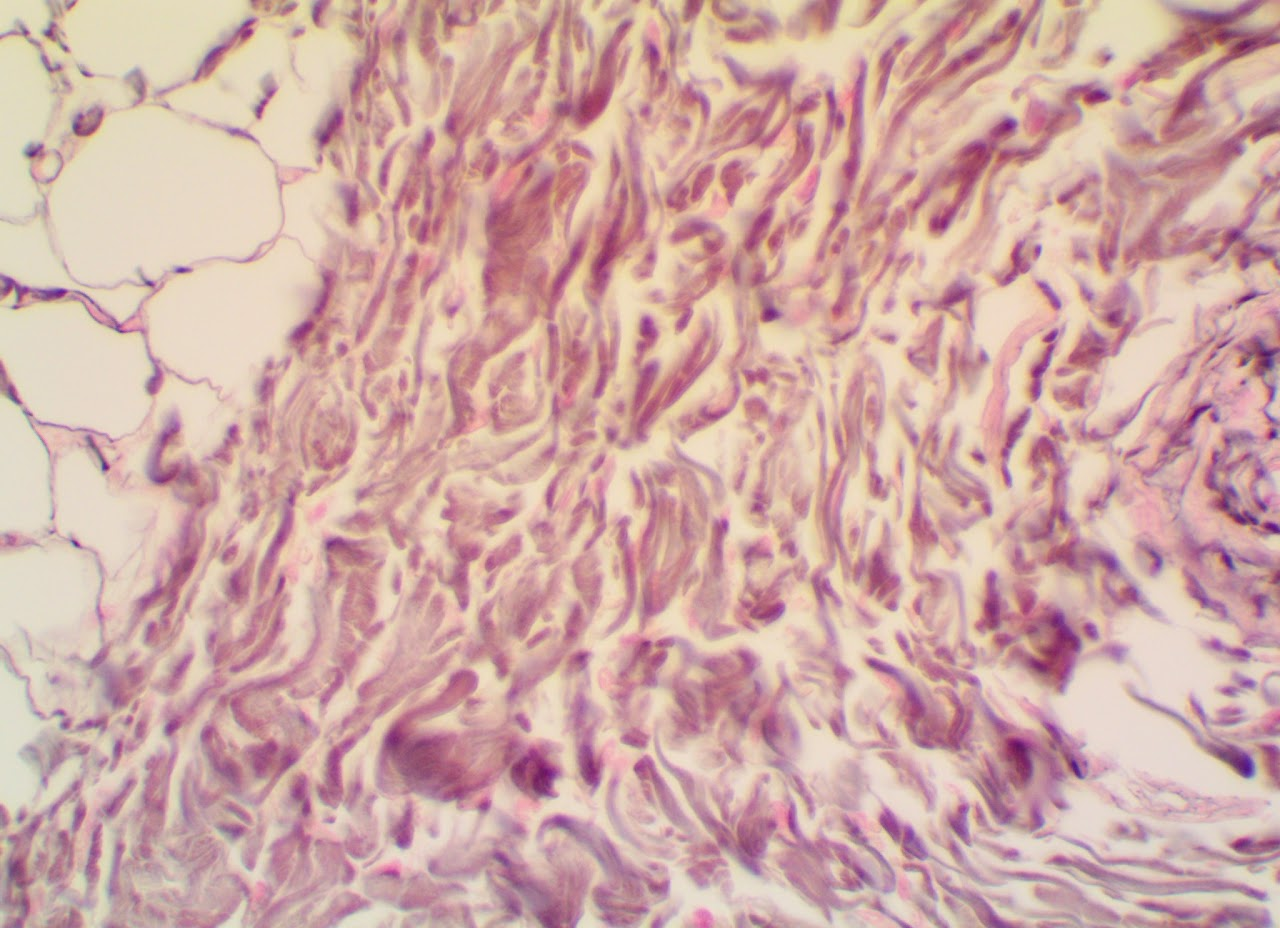
Dense Regular Fibrous Connective Tissue
Found in tendons & ligaments
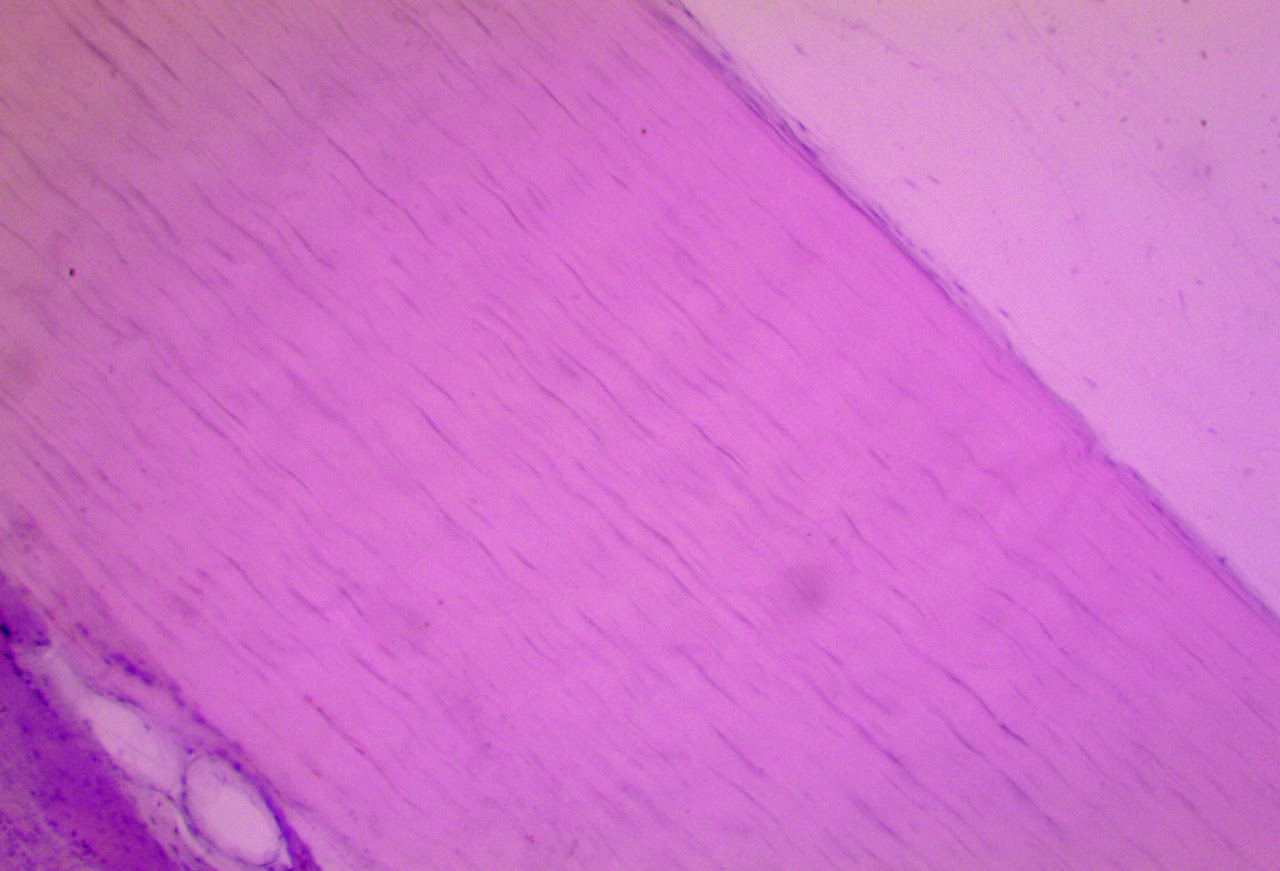
Dense Elastic Fibrous Connective Tissue
Found in large arteries, such as the Aorta

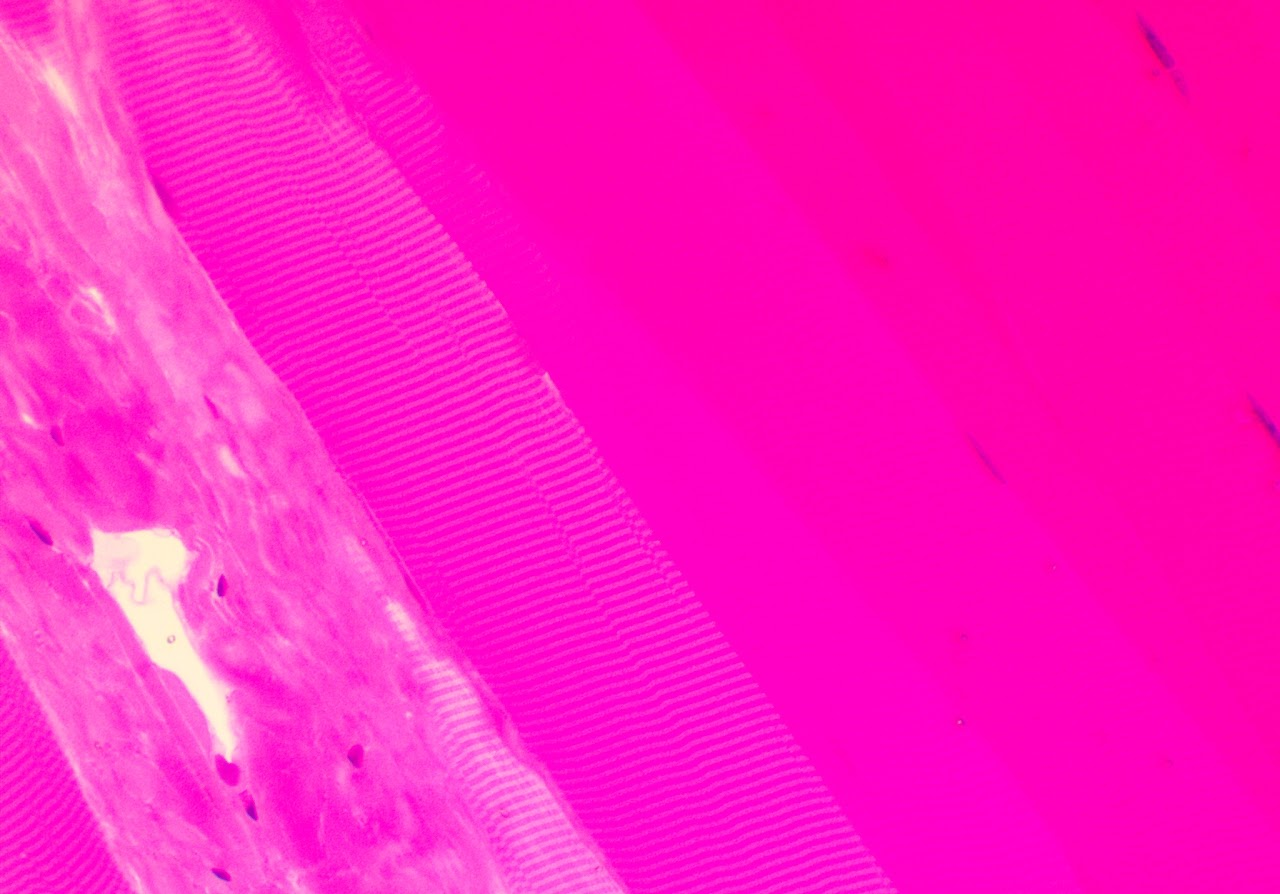
Cartilage
Fibrocartilage Connective Tissue, Hyaline Cartilage Connective Tissue, Elastic Cartilage Connective Tissue
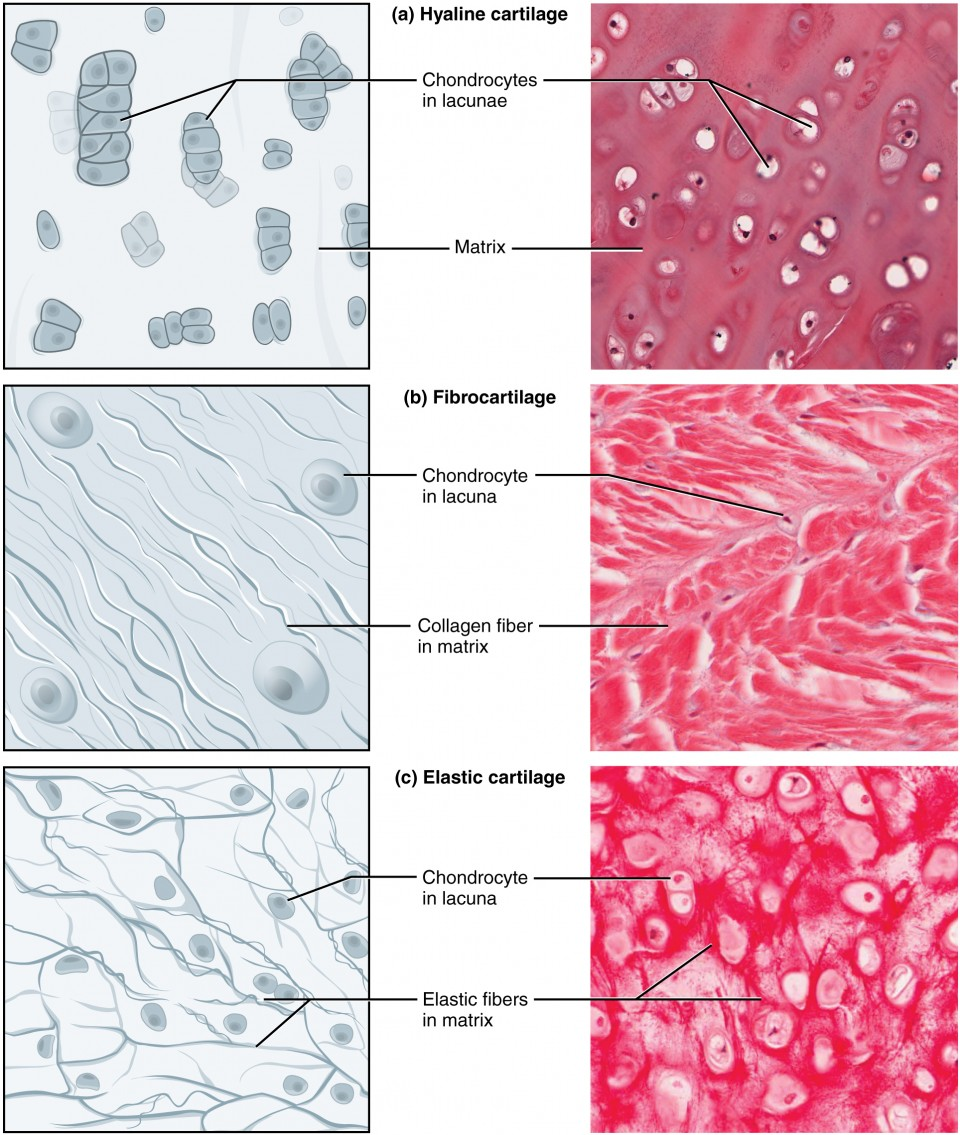
Fibrocartilage Connective Tissue
Found in the menisci of the knee, intervertebral discs of the spine, and the pubic symphysis

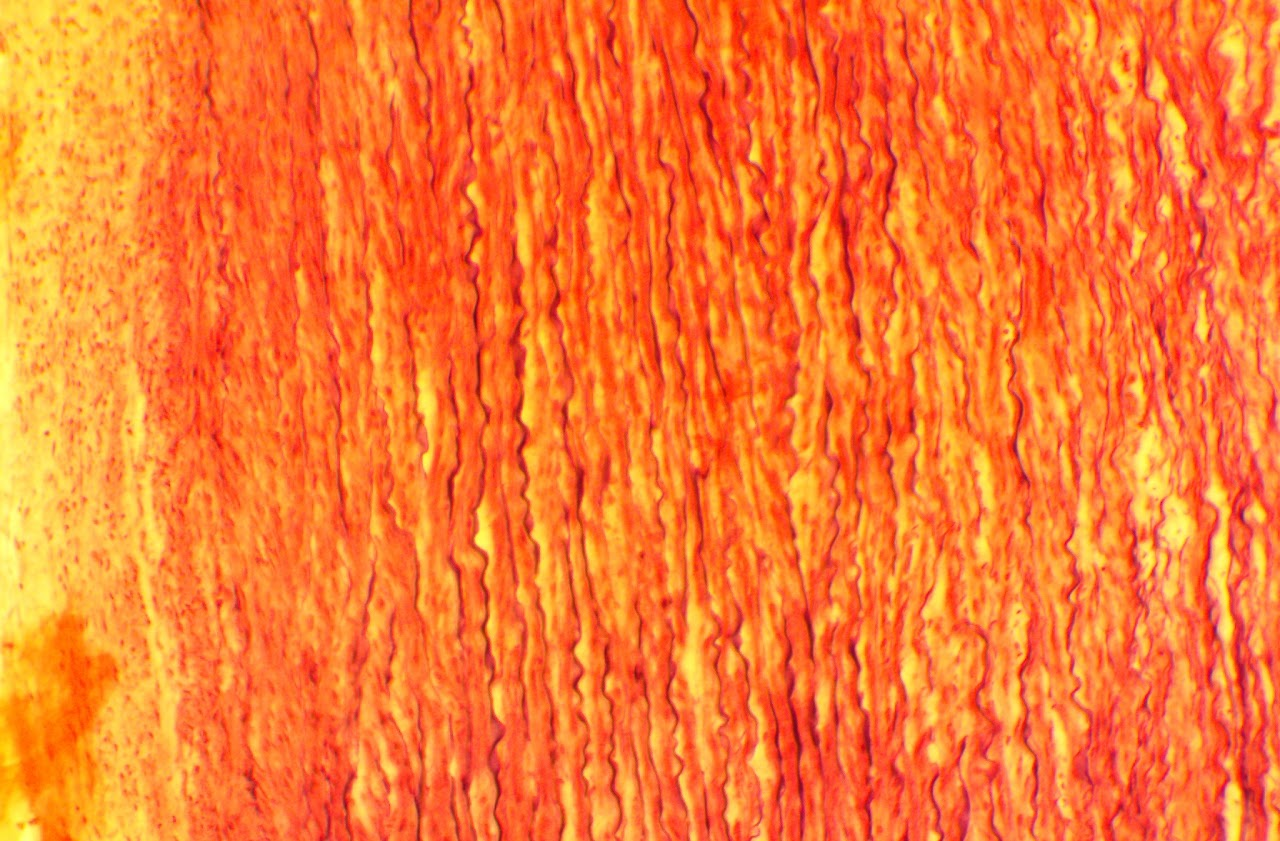
Hyaline Cartilage Connective Tissue
Most abundant cartilage
Located in areas such as the ends of long bones
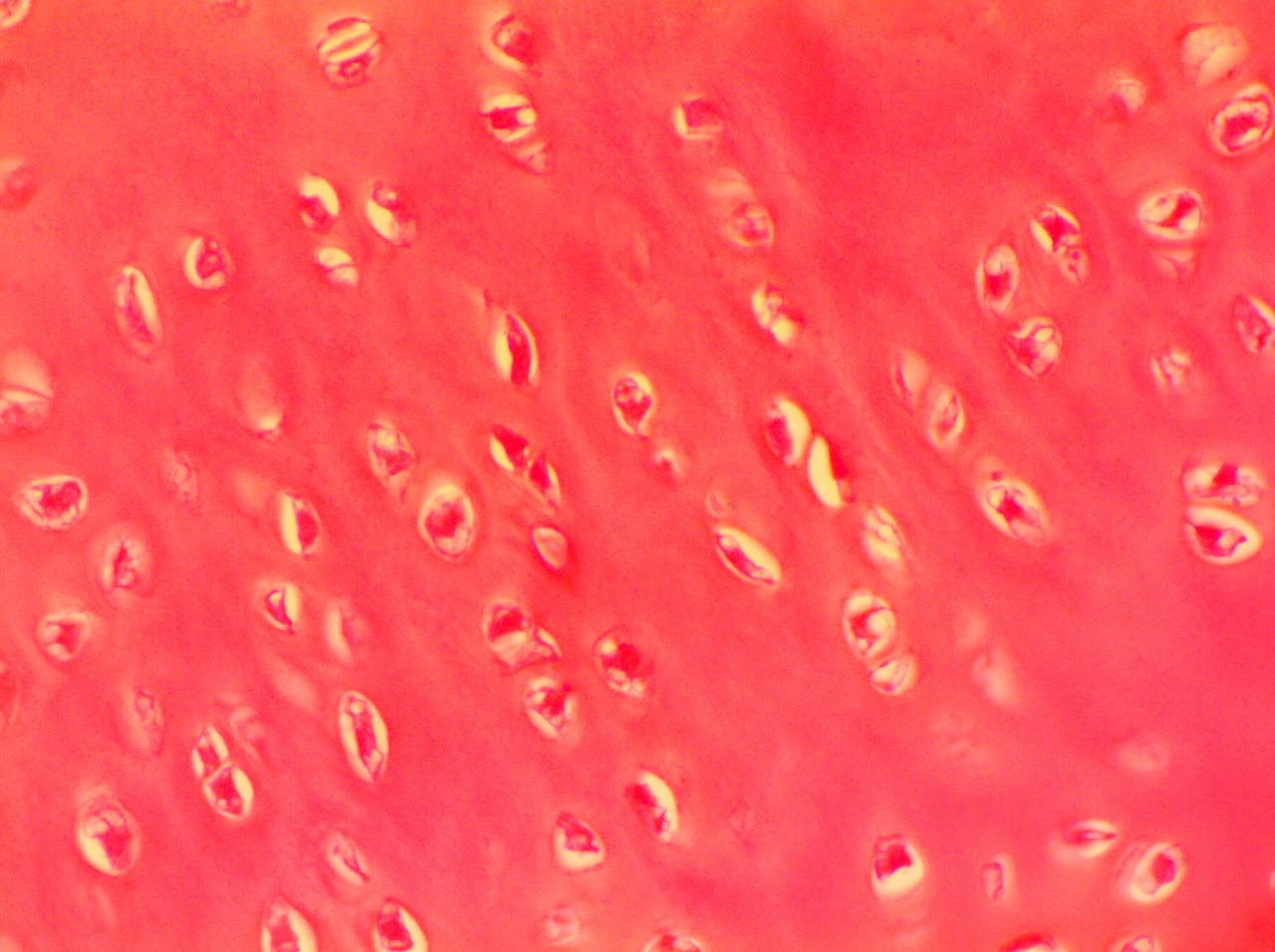
Elastic Cartilage Connective Tissue
Found in the external ear, epiglottis, and part of the larynx
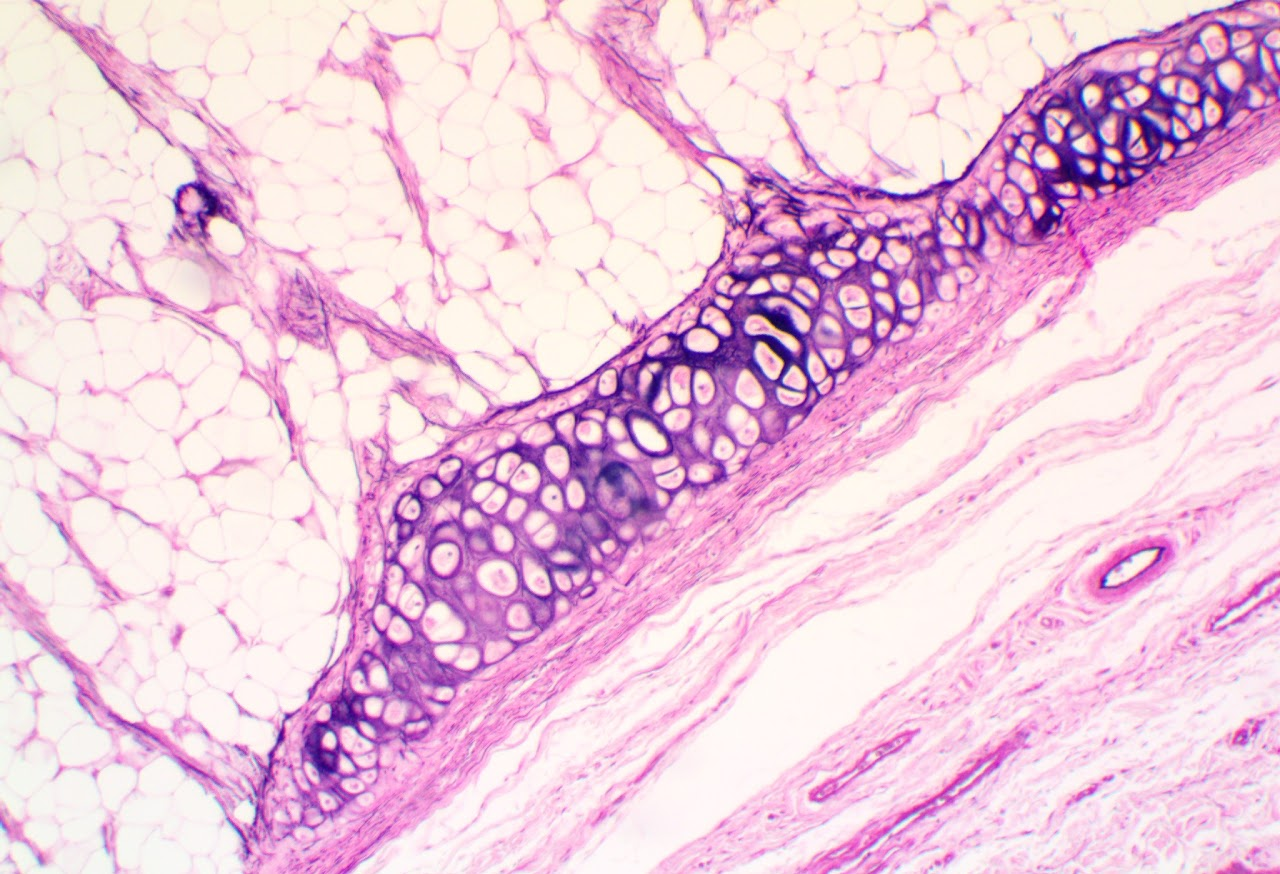
Bone Connective Tissue (Compact)
Found in all bones of the axial and appendicular skeleton
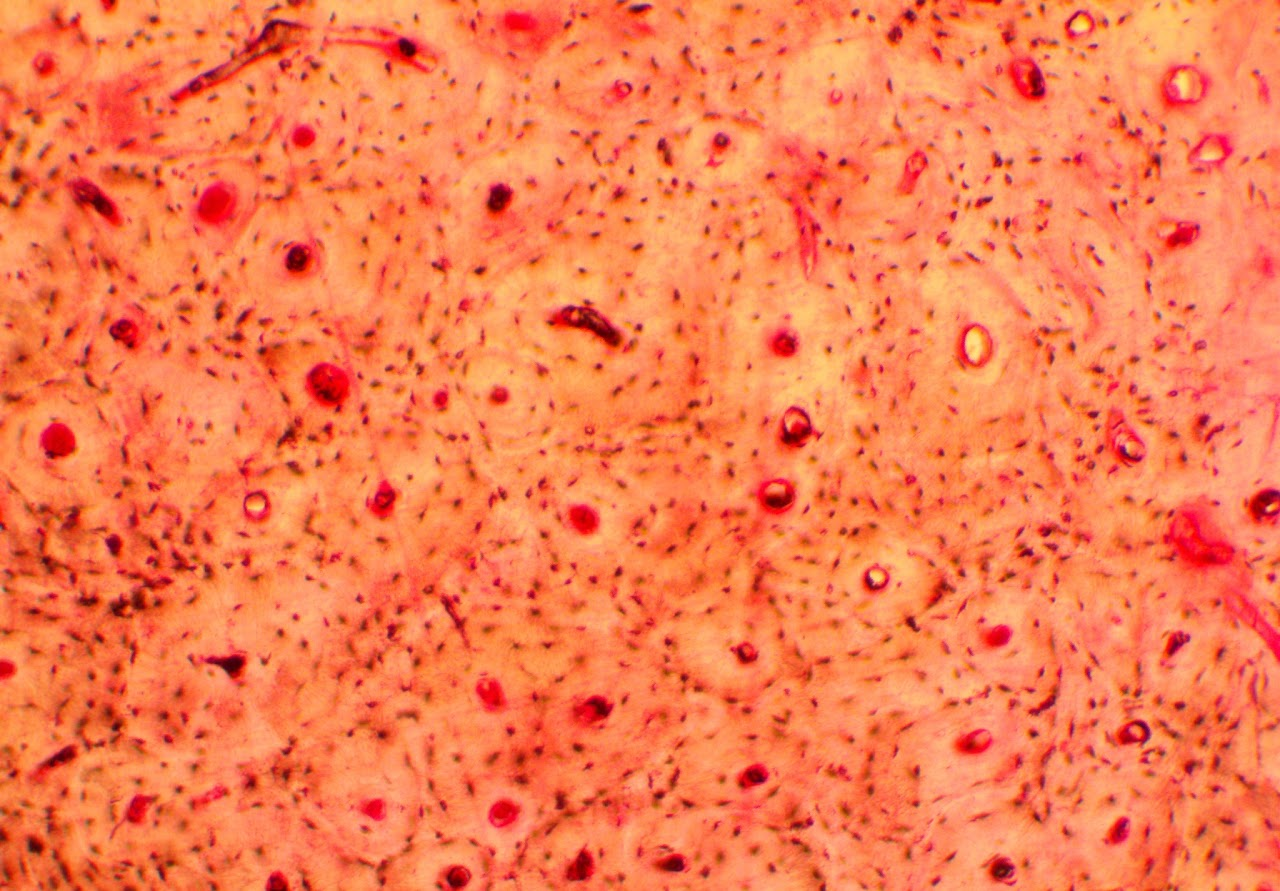
Blood Connective Tissue
The Human Body has approximately 5 liters of blood at a given time
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle, Smooth Muscle, Cardiac muscle
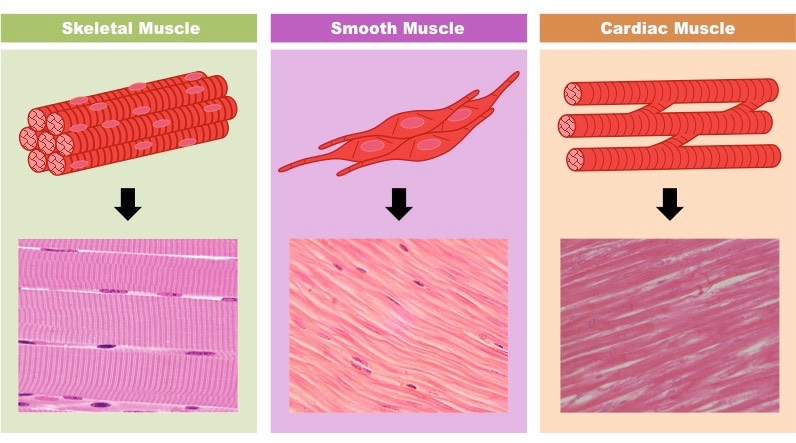
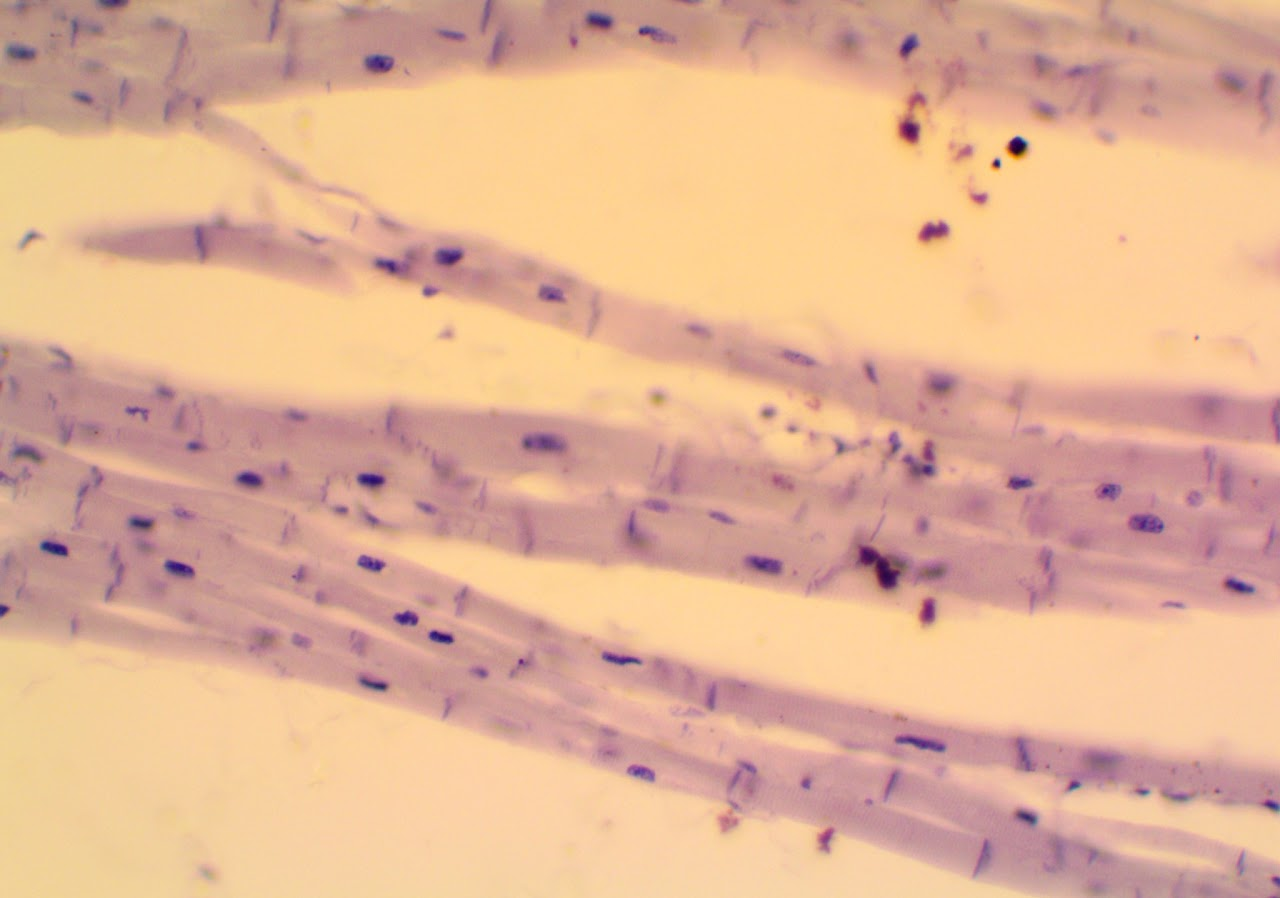
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle is voluntary and found in all the muscles that help move the skeleton

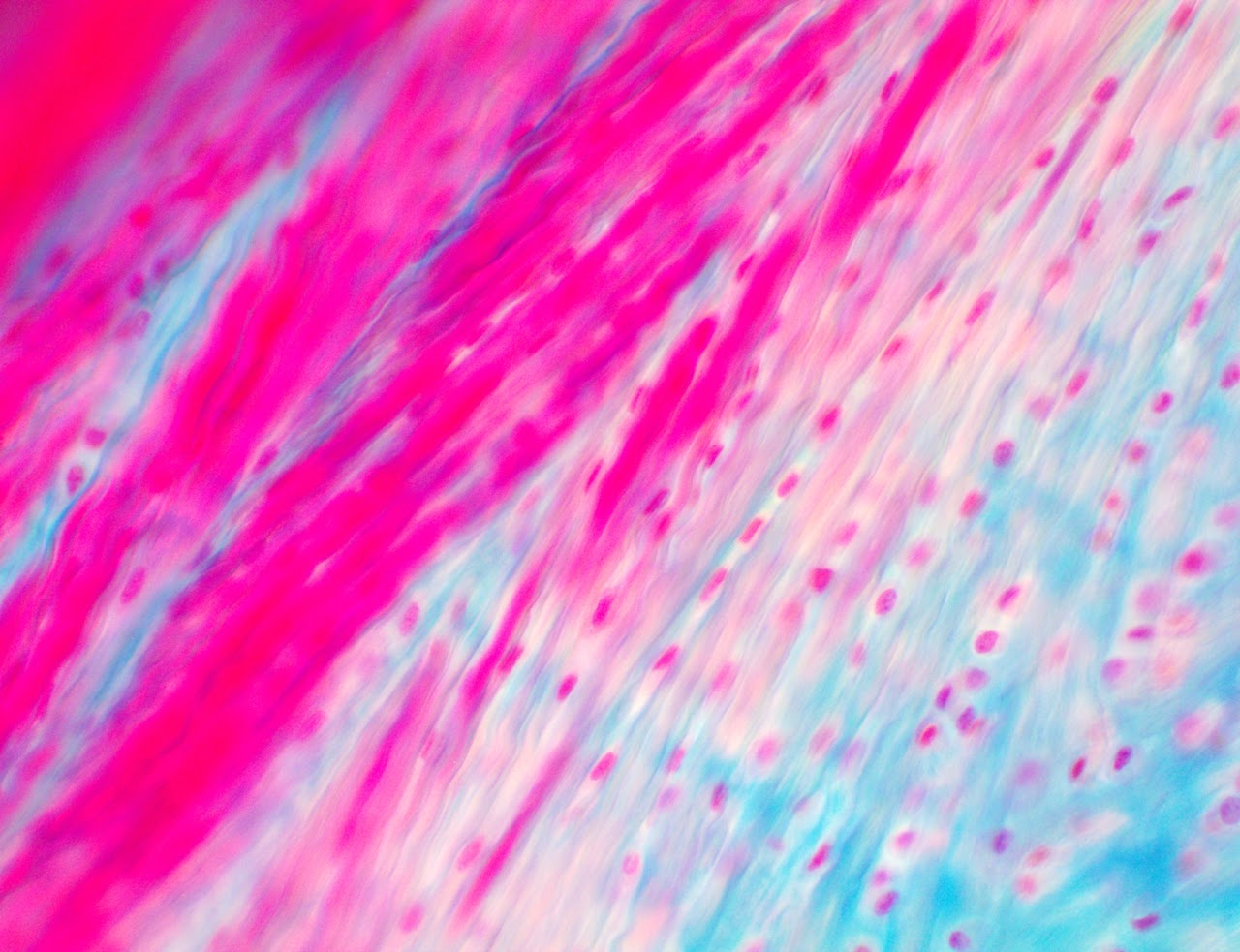
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscles in involuntary and located in areas such as blood vessels, linings of the GI tract, & urinary bladder
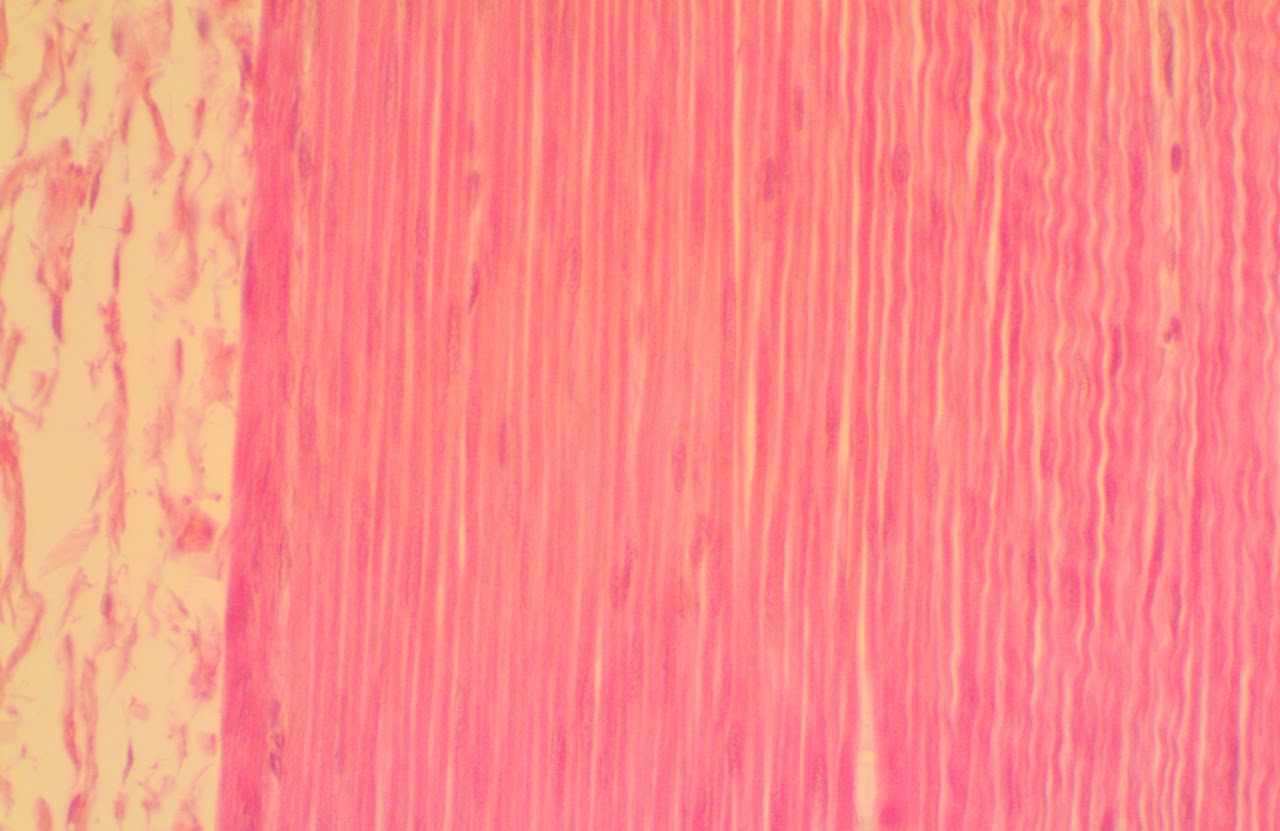
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle is involuntary and found in the heart
Nerve Tissue
Nerve tissue contains neurons and neuroglia and can be found in the brain, spinal cord, and all nerves of the body
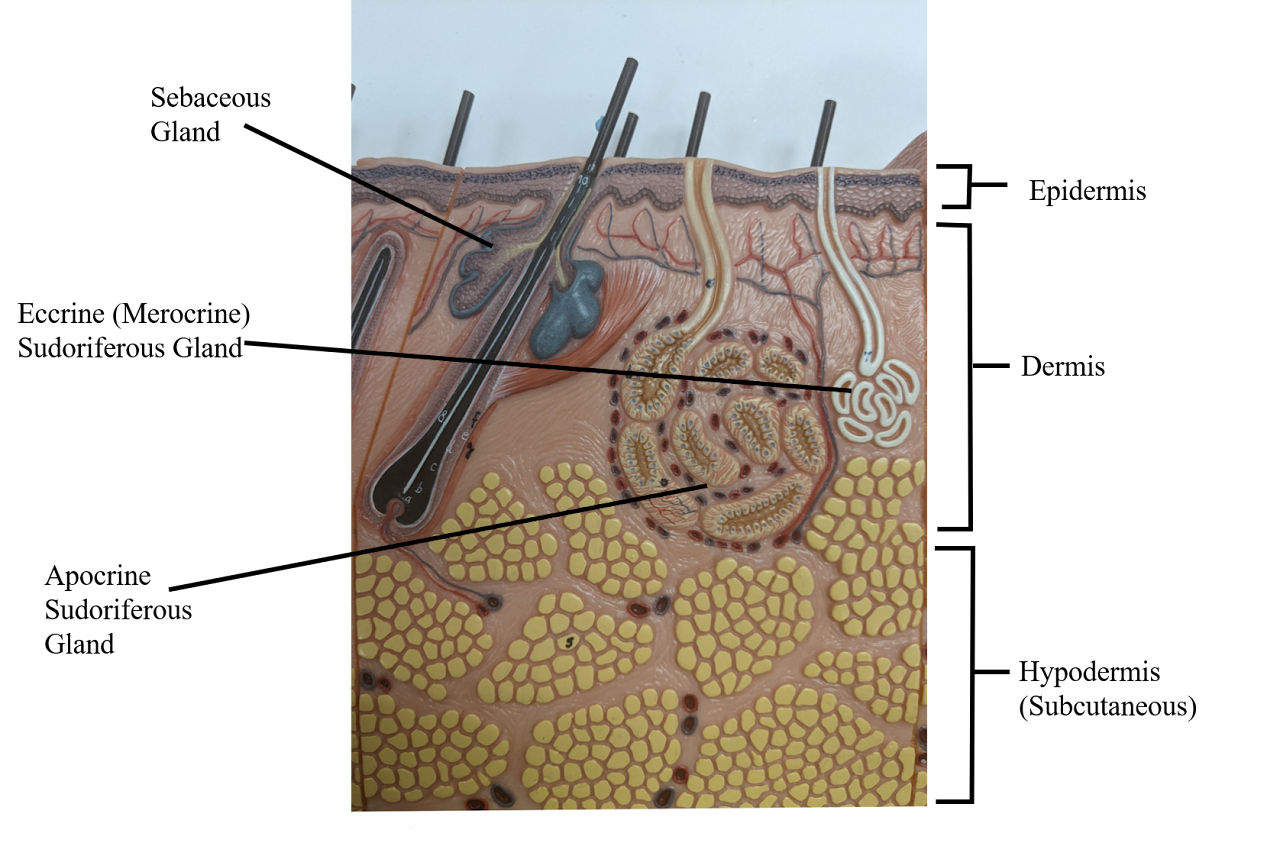
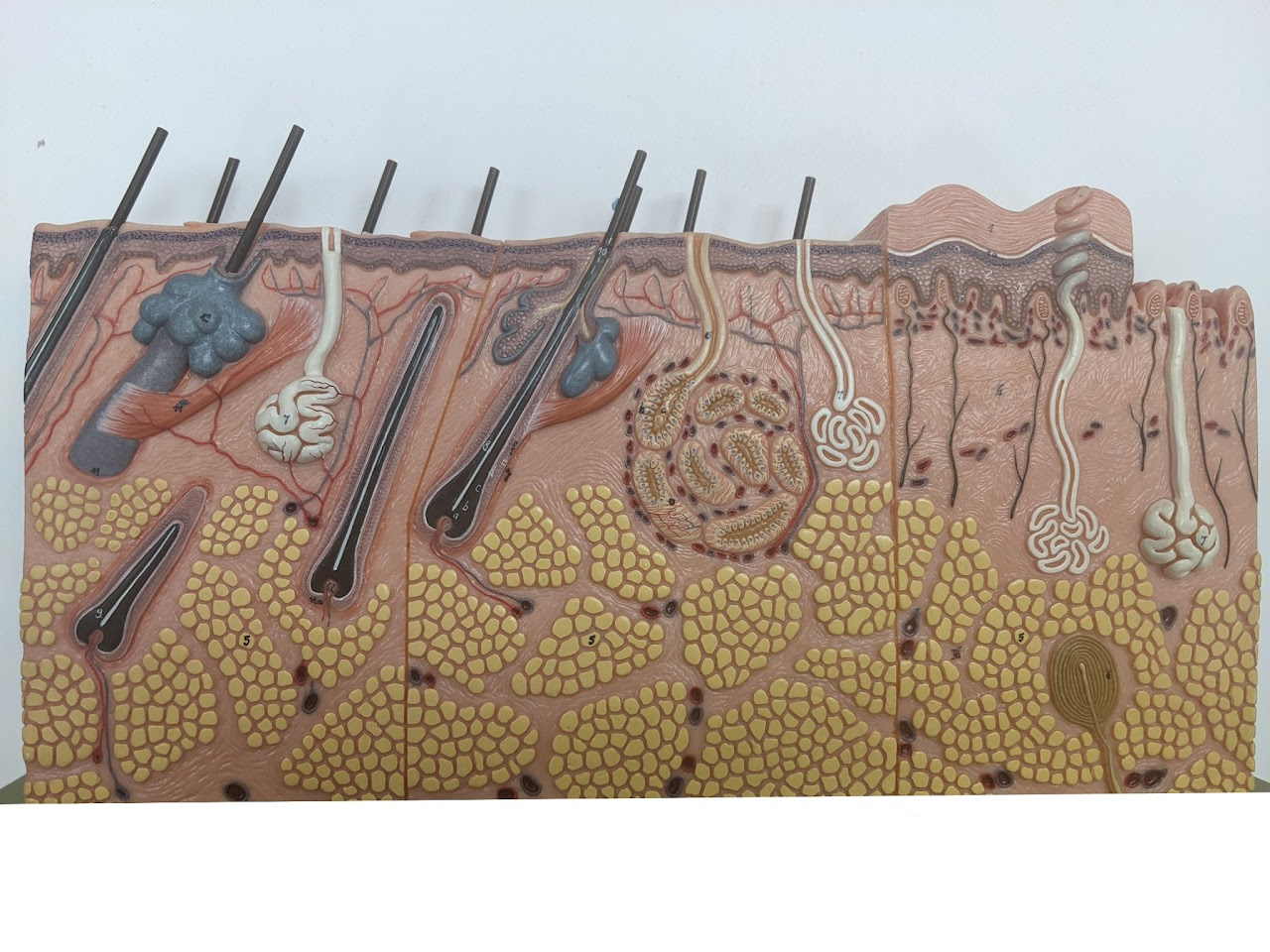
Integumentary
The Integumentary System includes the skin, hair, nails, and various glandular structures contained within
Stratum Basale
Mitotically active layer, deepest layer
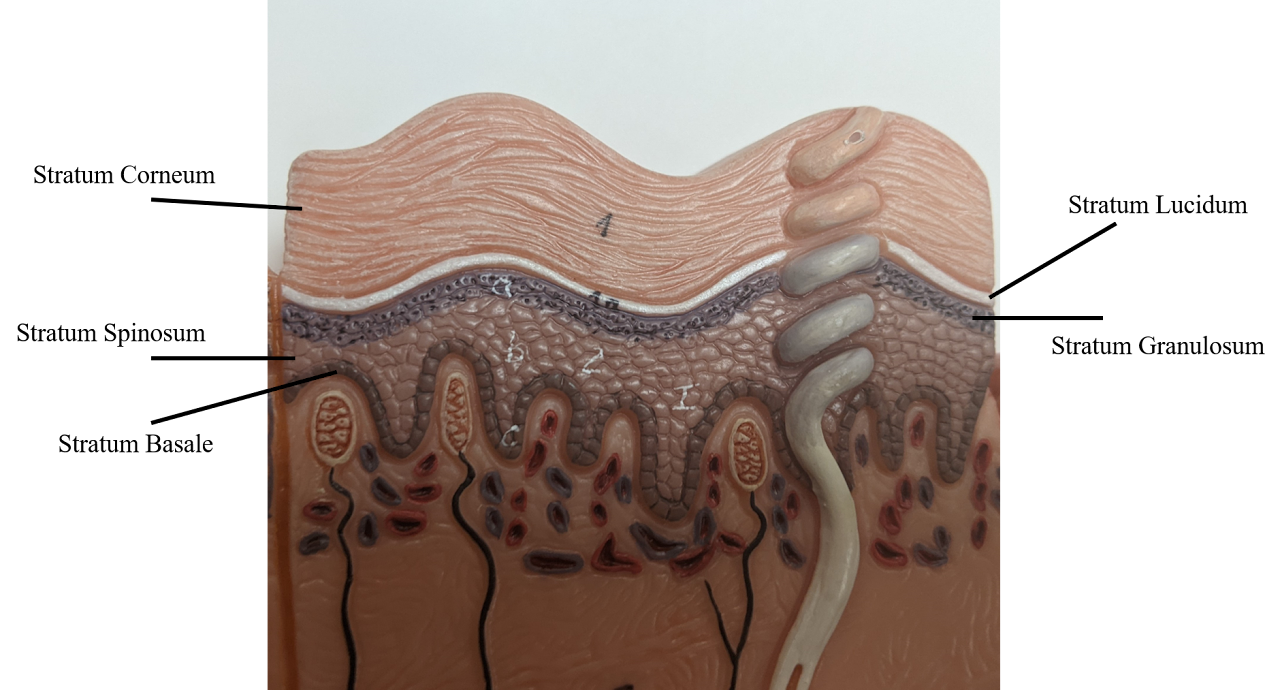
Stratum Spinosum
Contains Dendritic (Langerhans) cells for Immunity (2nd deepest)
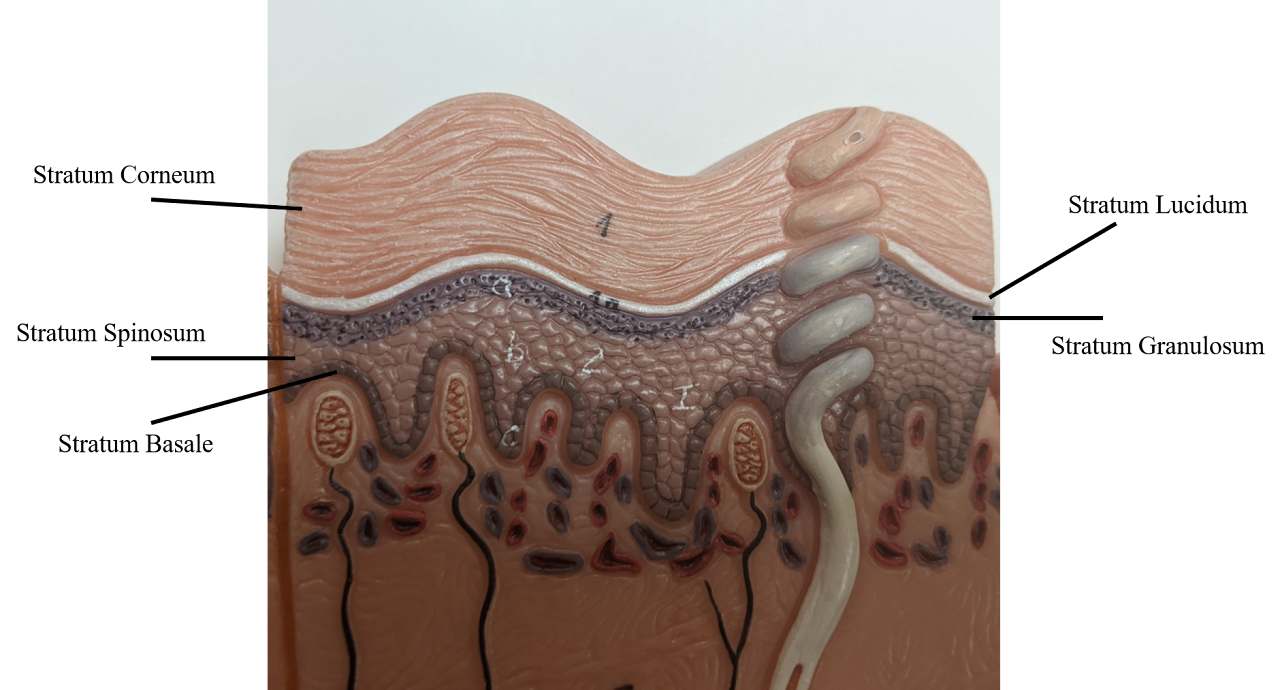
Stratum Granulosum
After this layer, there’s no sufficient nutrients. all the layers after are dead
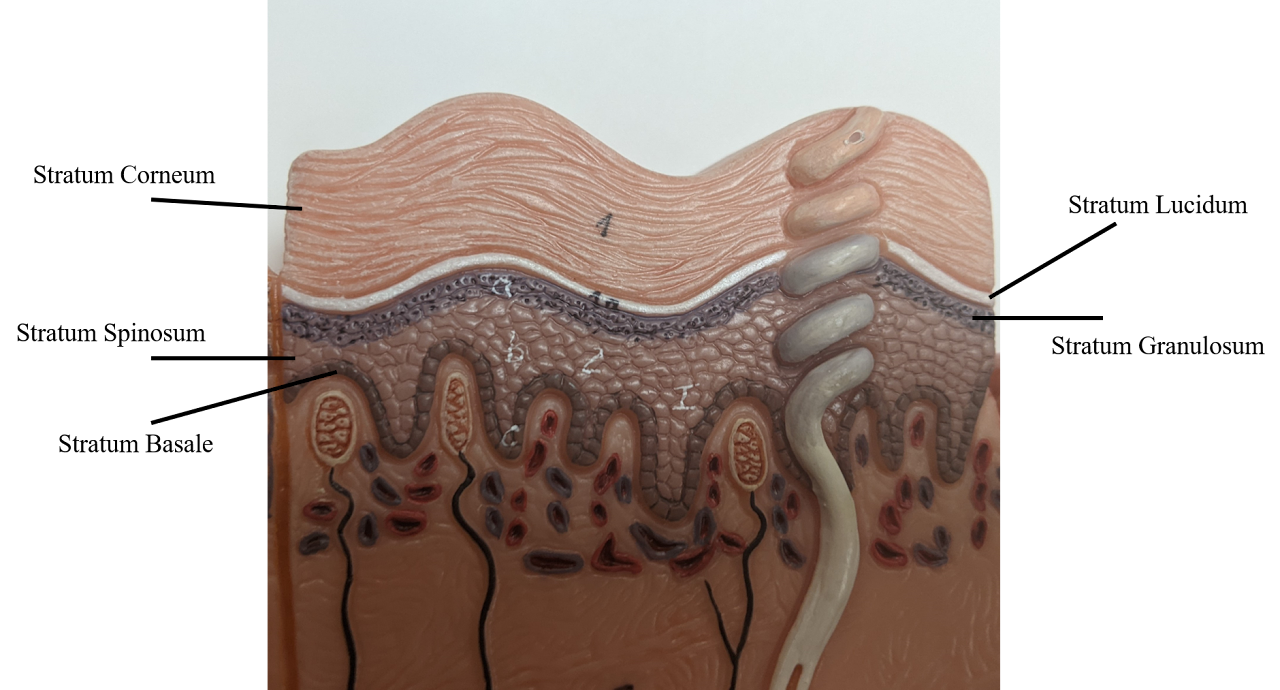
Stratum lucidum
Only in palms of hands & soles of feet
Stratum Corneum
very thick layer of dead cells
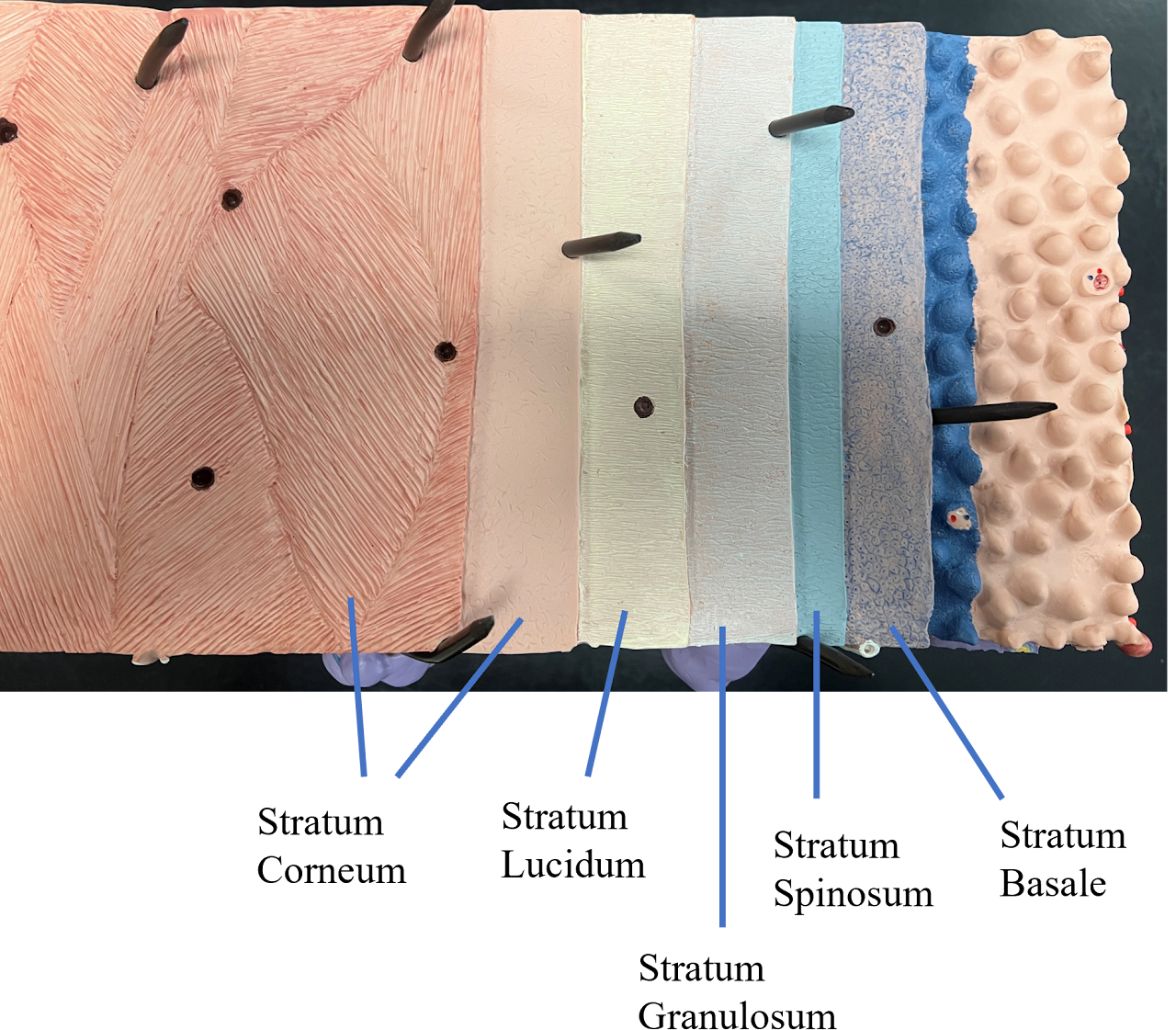
Basale, spinosum, granulosum, lucidum, corneum
BSGLC
Sebaceous gland
creates oil (holocrine), moisten the skin + can cause acne
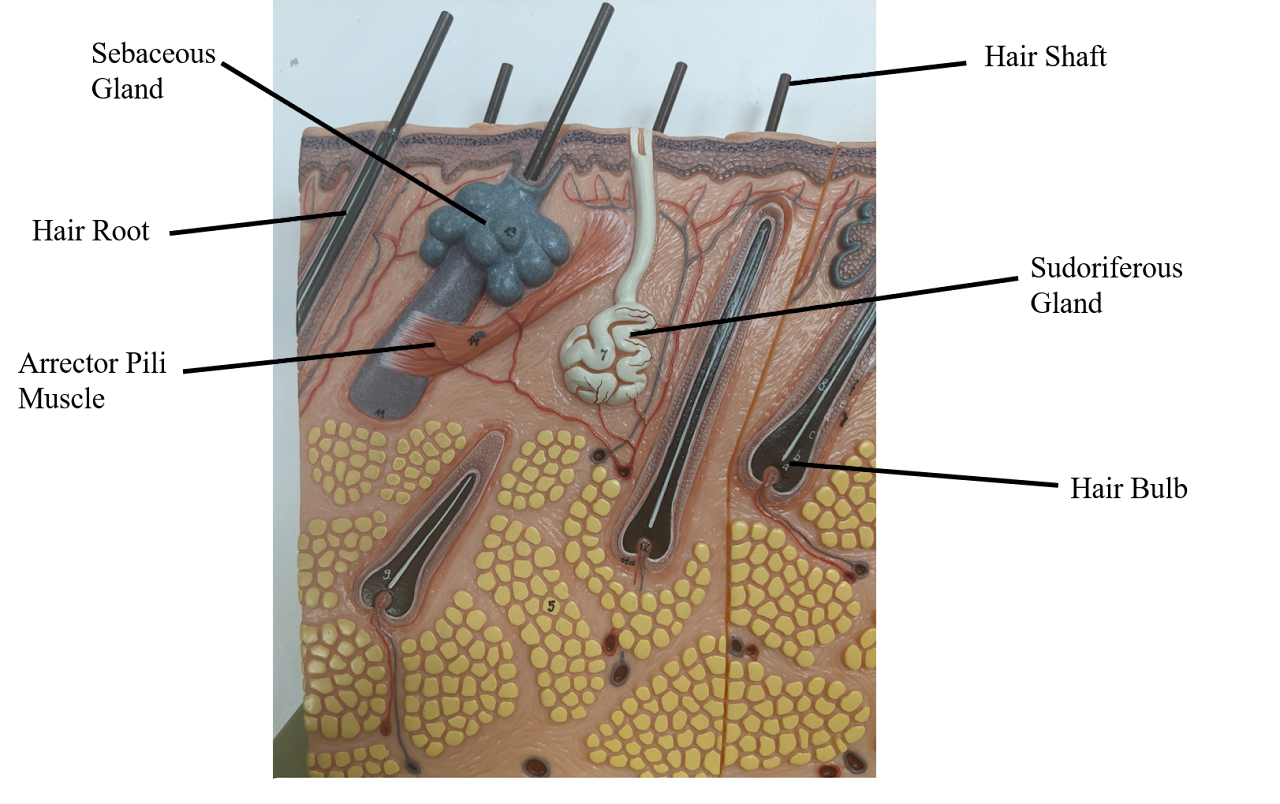
Sudoriferous gland
Sweat (eccrine) - release water
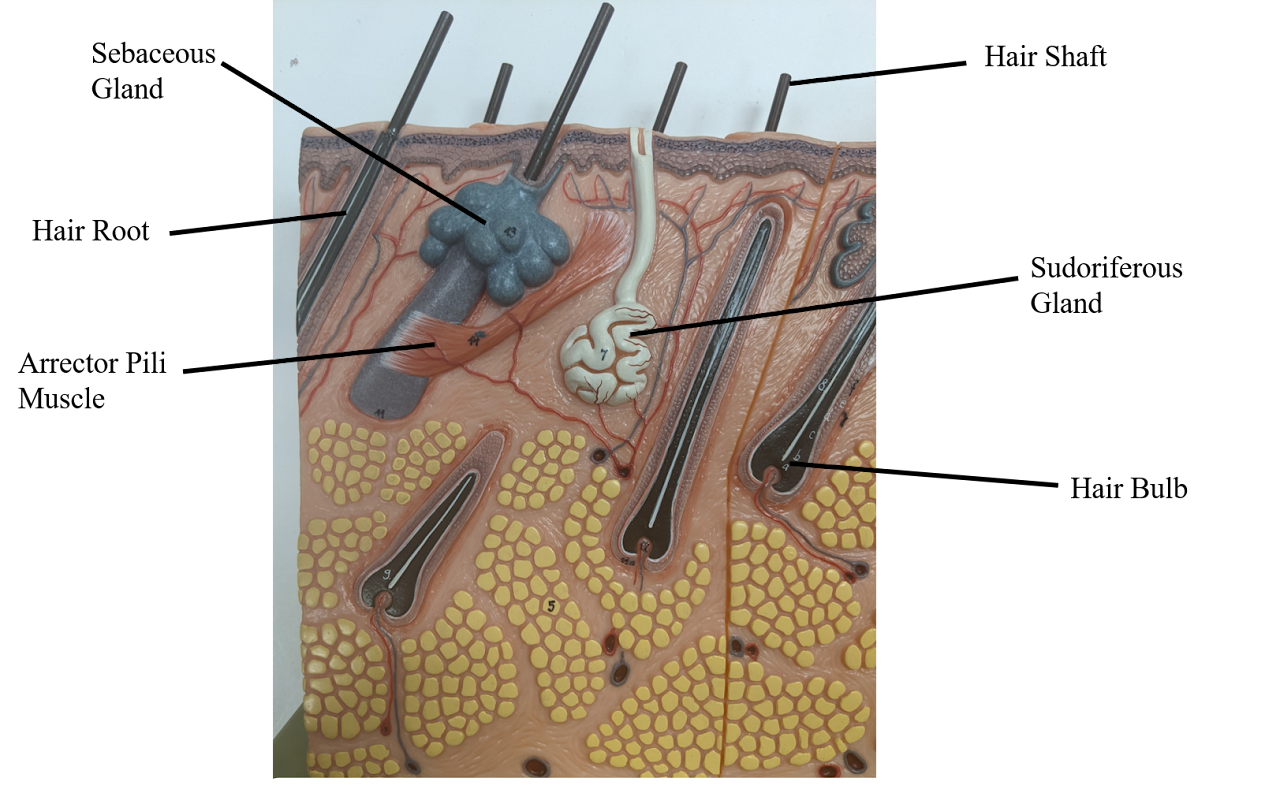
Arrector Pili Muscle
“goosebumps”
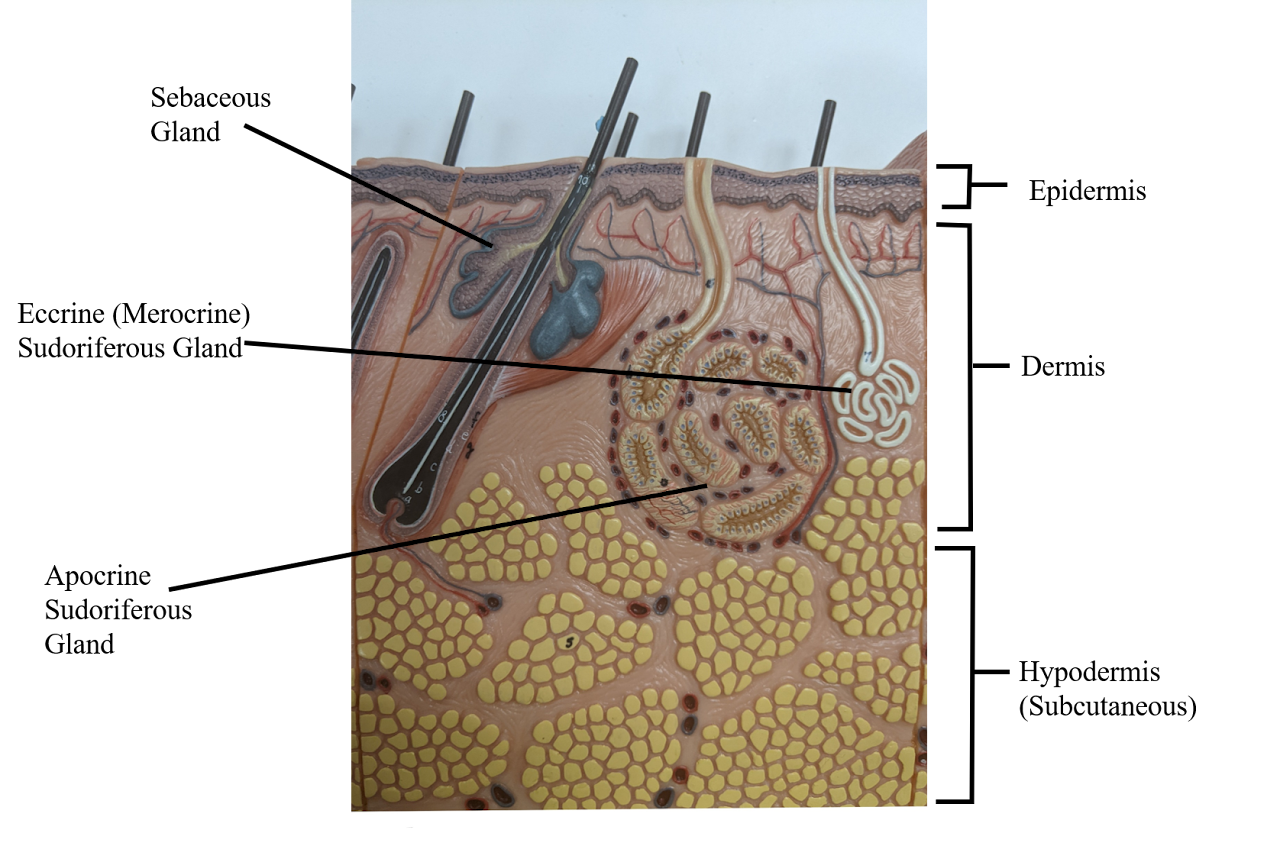
Hypodermis
deepest layer of skin
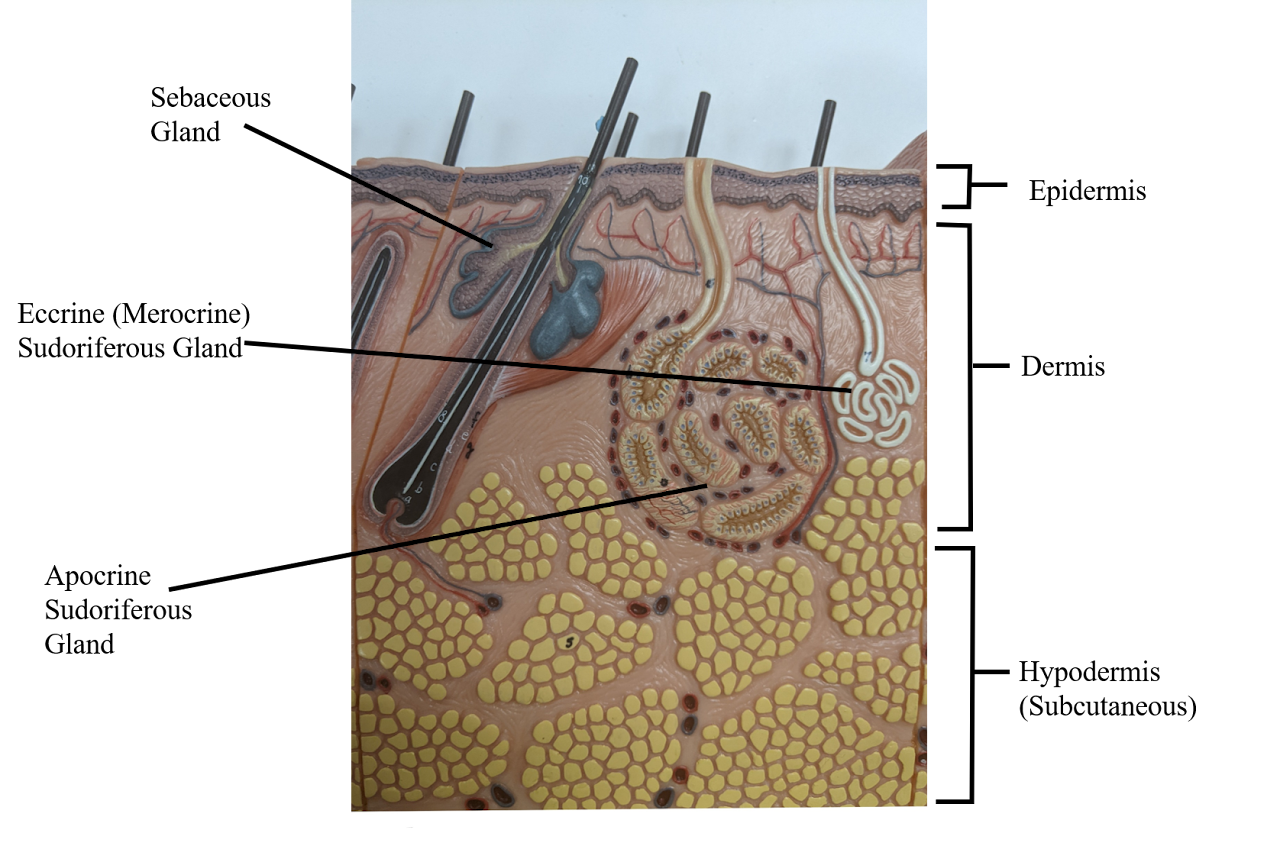
Dermis
middle layer of skin
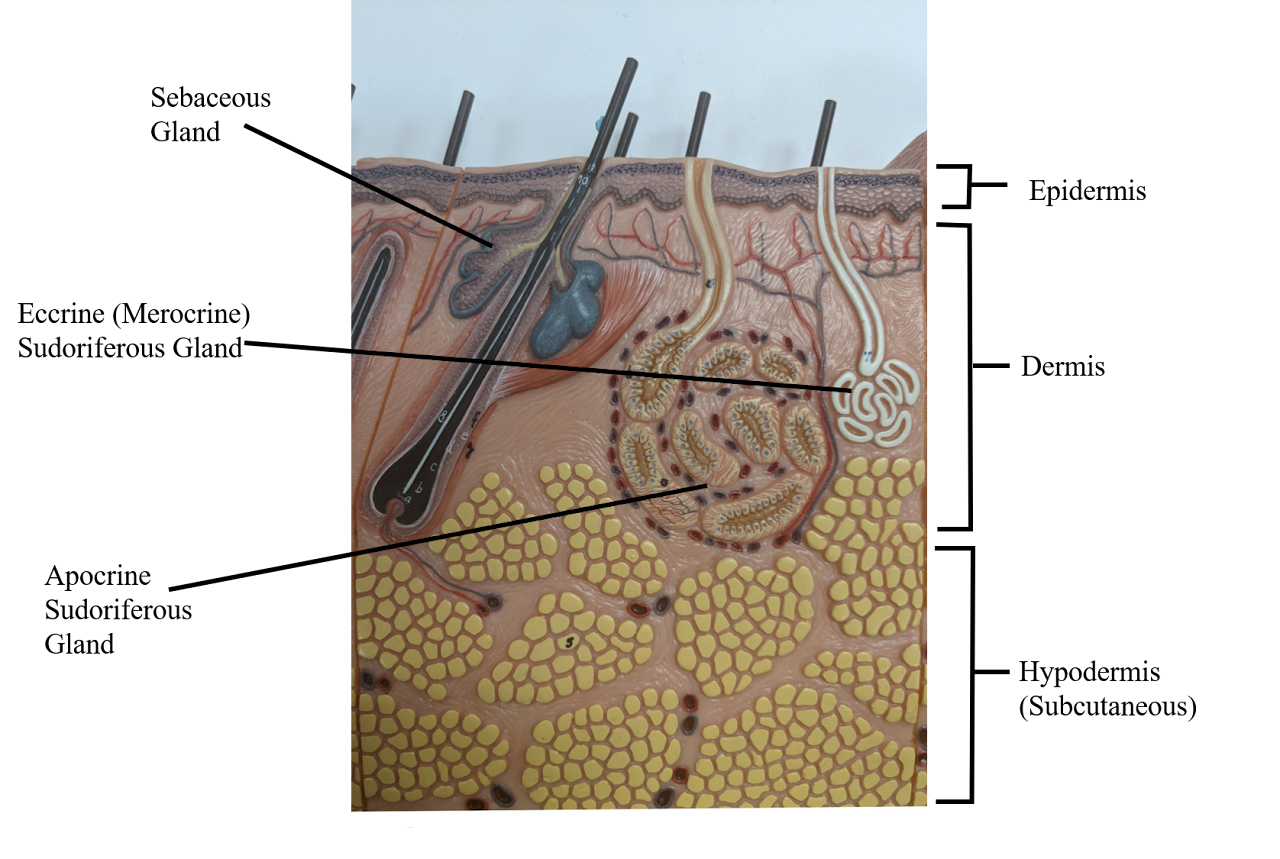
Epidermis
the outerlayer of skin
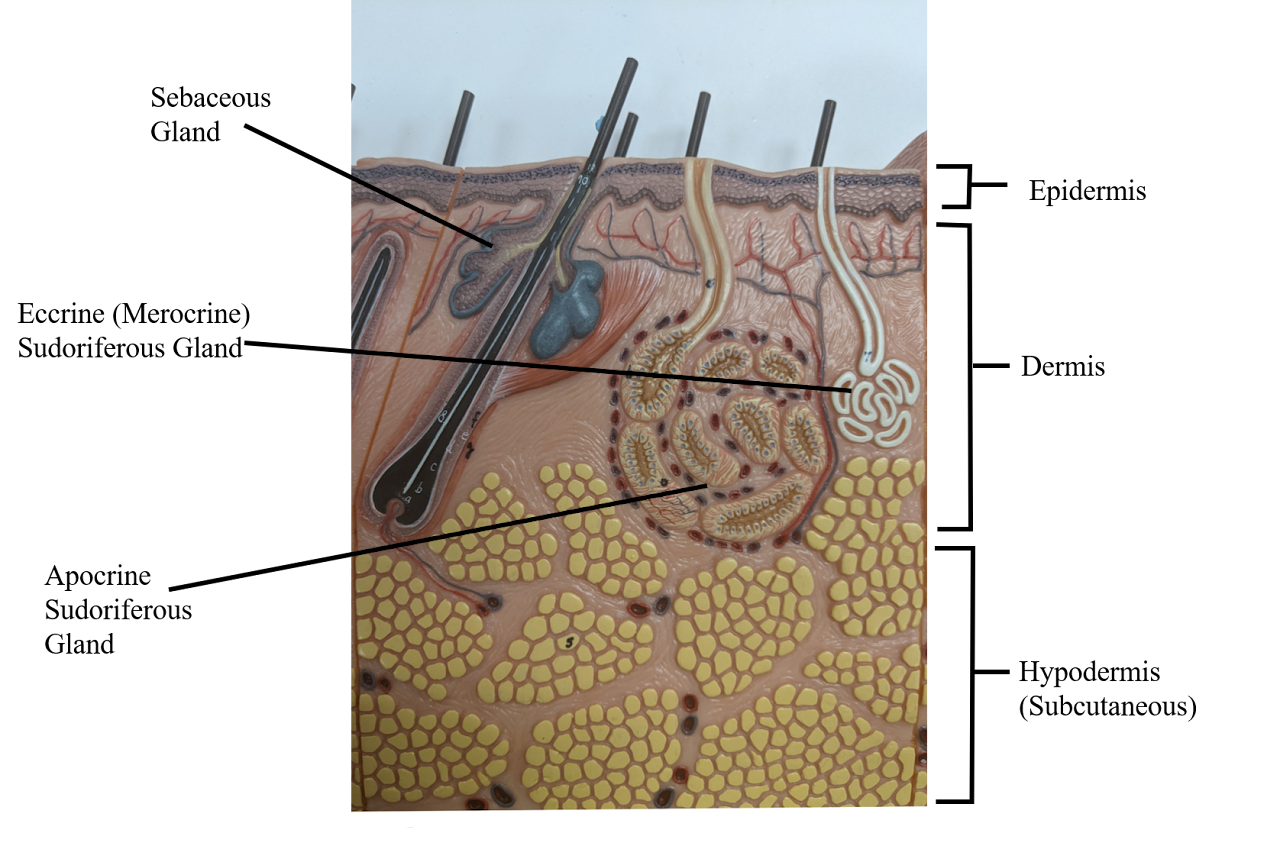
Apocrine sudoriferous gland
Malodorous sweat glands (armpit, anogenital),
only in armpit, becomes functional after puberty, smell of bo