Forces
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Force
a push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object
all forces are either non-contact or contact
Non-Contact force
objects are physically seperated
e.g electrostatic: charges cause a force of attraction/repulsion
gravitational attraction: mass creates a force of attraction
Contact force
the objects are physically touching
e.g Normal contact force: felt in opposite direction to contact
Friction: surfaces and their roughness cause friction when moved in contact
Scalar
Magnitude (size) but no direction
Generally cannot be negative
Vector
Magnitude (size) and direction.
Can be represented by arrows (length / size = magnitude)
Displacement
a vector quantity that means the distance travelled in a straight line from the start to the finish AND the direction of that straight line
Typical speed of a person walking
1.5 metres per second
Typical speed of a person running
3 metres per second
Typical speed of a person cycling
6 metres per second
Typical speed of sound waves in the air
330 metres per second
Typical speed of a car
25 metres per second
Typical speed of a train
55 metres per second
Typical speed of a plane
250 metres per second
Velocity
Vector quantity that is speed in a given direction
When an object moves in a circle
it may travel at constant speed BUT the velocity will
be constantly changing because velocity is a vector quantity that depends on speed and direction
Distance-Time Graph: Curved upwards line means
the object is accelerating and a tangent must be drawn to find speed
DTG vs VTG gradient.
DTG - Speed
VTG - Acceleration
Stopping Distance
Thinking Distance + Breaking Distance
Gravity
All matter has a gravitational field, and attracts all other matter
The larger the mass, the stronger the field, the greater the attraction
Weight
The force exerted on a mass by the gravitational field, in Newtons
considered to act as object’s centre of mass
What is weight measured by?
Measured by a force meter (also known as calibrated spring-balance)
Weighing scale measures the force you exert, and then divides by 10 to give mass
Gravitational field strength (n/kg)
for each kg of mass, experiences n of force
gravitational field strength (g) on earth
9.8
If the same person was on two different planets..
-mass = same
-g will be different
-so weight different
Why does acceleration in free falling occur?
gravity
acceleration = g
resultant force
single force representing the sum of all the forces acting on an object
more than one force on a straight line, find resultant by adding (act in same direction) or subtracting (act in opposite direction)
terminal velocity
max. velocity
Work done (motion)
when energy is transferred from the object doing the work to another form
Work Done = Force × Distance
where ditstance = distance moved along the line of action of the force
To stretch, bend or compress an object..
more than one force has to be applied
If a single force is applied to an object…
it will just move in that direction
-if pulled on opposite sides of object = stretch
-if fixed at one point then stretched, force still being applied by fixed point
deformation
changing shape
elastic deformation
object returns to original shape when load removed
e.g elastic band
plastic deformation
object does not return to original mistake when load removed
e.g spring when pulled too far
hooke’s law
The extension of an elastic object, such as a spring, is directly proportional to the force applied, provided that the limit of proportionality is not exceeded.
When a force stretches/compresses a spring
spring does work
Elastic potential energy is stored in the spring
if it doesn’t inelastically deform, work done in spring = elastic potential energy stored
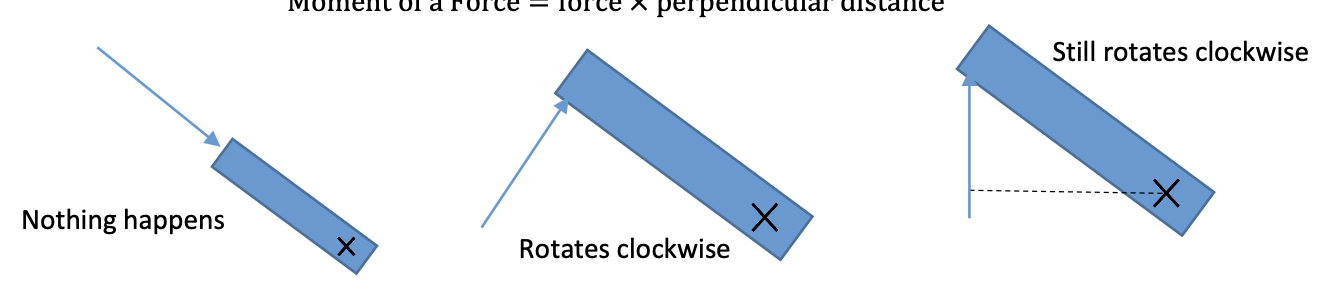
pivot point
a point which it can rotate about, but cannot move away from
Moment of a Force
force × perpendicular distance
Example of moment
Bike Riding – pressing your foot down on the pedal, causes a moment about the pivot, turning the pedal arms.
Equilibrium (motion)
sum of anticlockwise moments = sum of clockwise moments
Pivots
-if force applied along line passing through pivot, object held still
-if distance between pivot and line of action of force, object rotates about pivot in direction of force applied
-if force applied isn’t perpendicular, we have to consider perpendicular distance from pivot to line of force
Gears can change…
speed, force or direction
by rotation
Pressure produces a net force at..
right angles to any surface
When does an object float?
if it’s weight is less than the weight of the water it displaces
e.g 1000kg boat will sink until it has displaced 1000kg of water (if it doesn’t submerge, it will float)
What does pressure in a liquid vary with?
depth and density. this leads to an upwards force on a partially submerged object
The buoyancy force
the upwards force that counteracts the weight of the floating object
equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object
Why does a ping pong ball float on water?
-its density is less than the water
-so, for volume displaced, weight of equivalent amount of water is GREATER than weight of ball
-resultant force is buoyancy, so it floats
increasing depth
increases pressure (greater weight of water above you)
upthrust
partially / totally submerged object
experiences greater pressure on bottom surface than top surface
this creates a resultant force upwards
known as upthrust
what is earth’s atmosphere?
A thin layer (relative to size of the earth) of air around the Earth.
atmosphere gets less dense with increasing altitude
Why does earth’s atmosphere get less dense with increasing altitude?
-because it is the total weight of the air above a unit area at a certain altitude
-weight of air IS force that causes pressure
-so, higher elevation = fewer air molecules above unit area than the same at lower heights, so smaller weight, less pressure
idealised assumptions for a simple model of the atmosphere
Isothermal, so it is all at the same temperature
Transparent to solar radiation
Opaque to terrestrial radiation