Chemical Kinetics in Pharmacy- Miroshnyk
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Definition of Reactions and Kinetics
Reactions: defined in their broadest sense to mean transformation or any event. Includes degradation of parent drug into product, as well as transport from one part of the body to another.
Kinetics: the effect of time on different processes. (how fast or slow does a process occur?)
What is the pharmaceutical significance of kinetics?
It is critical in many processes like:
dissolution of solid dosage forms
drug degradation
drug absorption
CrCl
asses drug elimination rate
Definition of Reaction Rate (dA/dt):
the change in amount (conc) of a reactant or product with unit time
What are the different types of reaction orders? (n)
zero
pseudo-zero
1st order
2nd order
If a reaction goes from A→ B and A is reactants, B is products.
What is the only difference in the rate of the reactant versus product?
SIGN!!!!!!!!!
for the reactant- rate is negative
for the product- rate is positive
The reaction rate (-dA/dt) is proportional to the ________________ at any given time.
concentration
WHAT SHOULD WE LOOK AT FOR AN EASY WAY TO DETERMINE THE REACTION ORDER?
UNITS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
In zero order reactions, the rate is equal to the _____________________.
rate constant
In zero order reactions the rate is ___________________ of the concentration of the reactants. (dependent/independent)
independent
In first order reactions the rate is __________________ of the concentration of the reactants.(dependent/independent)
dependent
Is a rate constant always positive or negative?
ALWAYS positive!!!!!!
How does the graph of a zero order reaction look on regular graph paper?
straight line
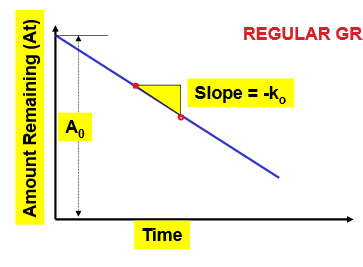
What is the slope and how is the slope of a zero order reaction found?
slope= -k0
slope is found by rise/run = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
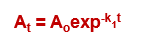
How does the graph of a first order reaction look on regular graph paper? Using this equation:
exponential curve
What steps would I take to solve a problem like this?
The degradation process of a vitamin is a zero-order reaction. If the initial drug product strength is 200 mg and k0 = 0.015 mg/day, how long will it take for the initial conc to decrease by 15%?
Determine which equation to use—> says 0 order, so we use that integrated equation.
Figure out, what variable we are solving for… we want “how long” so we’re solving for t
Before plugging everything into the equation we must find the conc after a 15% decrease. 200 × 0.85 = 170 mg
Plug numbers into equation. At=170 mg , A0= 200mg, k= 0.015mg/day t=?
Answer: 2000 days
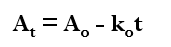
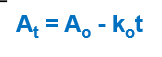
What order and type of equation is this?
zero order
integrated equation

What order and type of equation is this?
first order
reaction rate equation
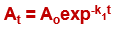
What order and type of equation is this?
first order
integrated rate equation

What order and type of equation is this?
first order
integrated rate equation
ln version

What order and type of equation is this?
first order
integrated rate equation
log version
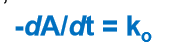
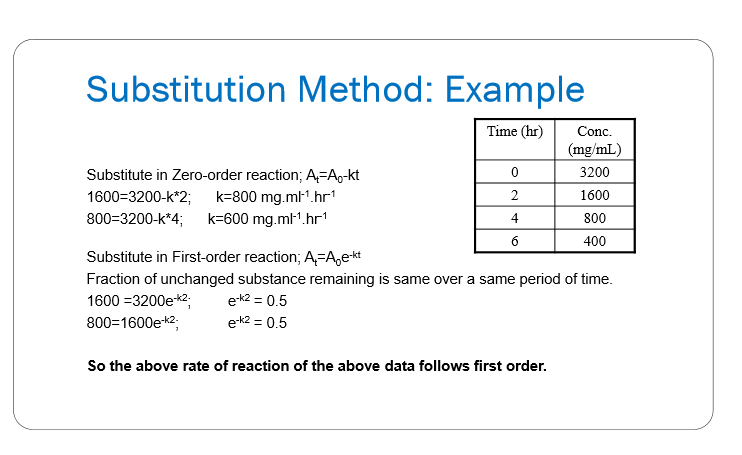
What order and type of equation is this?
zero order
reaction rate equation
How do I determine the slope of a first order reaction?
graph on SEMI LOG PAPER
slope = rise/run = (log y2- log y1)/(x2-x1)
How do we use the substitution method to determine the reaction order?
will be given various times and their according concentrations (like a table)
need to substitute the times/concentrations into the INTEGRATED rate equations of zero order and first order
if you see that 2 of the rate constants are the same= it follows that order rxn
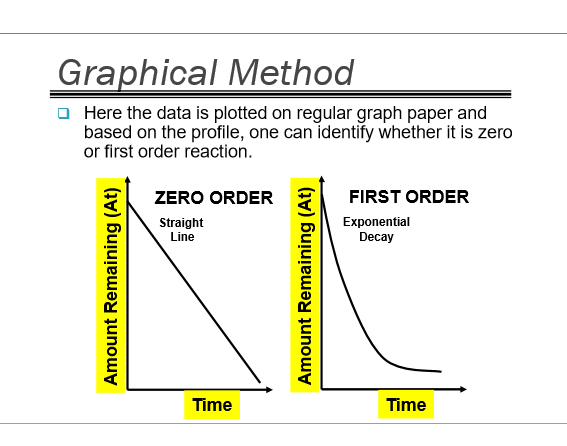
How do we use the graphical method to determine the reaction order?
plots the times and concs on REGULAR GRAPH PAPER!!!
if straight line= zero
if exponential curve= first
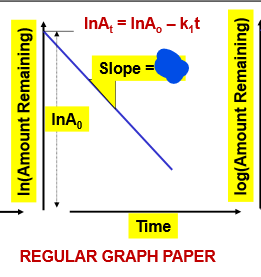
What is the slope of this graph? (We don’t have to memorize equations, just be able to RECOGNIZE!!!!!!)
slope= -k1
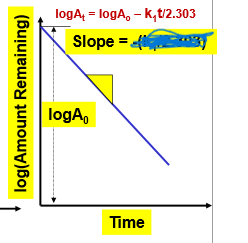
What is the slope of this graph? (We don’t have to memorize equations, just be able to RECOGNIZE!!!!!!)
slope= -k1/2.303
In this equation, what is k1?
At (mg/ml) = 11 exp-0.0045t
k1= 0.0045 (remember: constants are POSITIVE)
In this equation, what is the initial concentration?
At (mg/ml) = 17 exp-0.0032t
17 mg/ml
Assuming zero order, estimate the reaction rate constant and write the integrated reaction rate based on the following data:
Time | Drug Concentration |
|---|---|
0 | 281 |
2 | 274 |
6 | 260 |
find the slope, since in zero order the slope is the rate constant
use the rate constant and initial conc to write the integrated rate equation
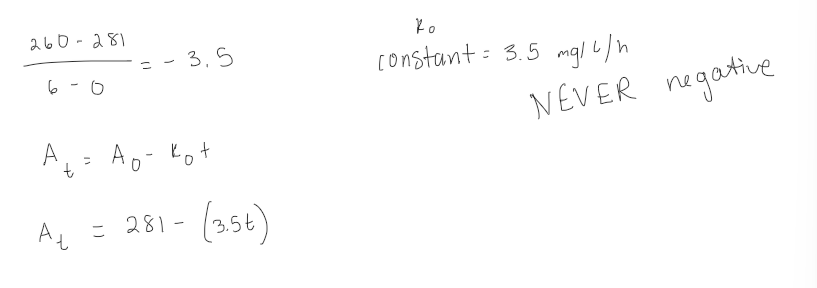
What is an example of a drug degradation process that follows pseudo order ?
a. emulsions
b. solutions
c. suspensions
d. aerosols
c. SUSPENSIONS
Pseudo order uses the same equations as ________ order.
zero ( I think of them as the same thing k0= kapp )
A suspension formulation was compounded and the final conc is 15 mg/ml. If the apparent rate constant is 1.4 mg/ml-month, what will be the suspensions conc after 2 weeks of storage?
suspension indicates its pseudo zero order
use integration rate equation to solve for At (conc)
BE CAREFUL, the rate constant unit is in months, so must convert weeks to months
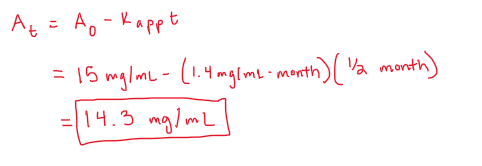
Definition of half-life (t1/2) :
time t required for 50% of the initial reactant amount to be consumed
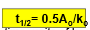
Is this half-life equation used for zero or first order reactions?
zero

Is this half-life equation used for zero or first order reactions?
first
The half life of zero-order processes depends on what?
initial concentration
reaction rate
The half life of first-order processes depends on what?
ONLY reaction rate
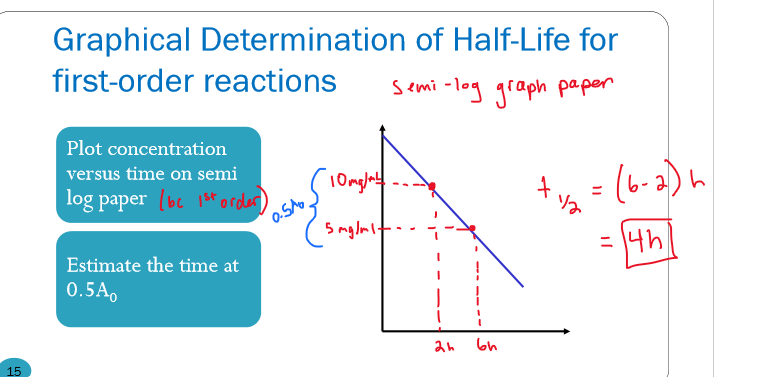
How would I determine the half-life of a first-order reaction graphically?
plot conc v time on SEMI LOG PAPER
estimate the time when ½ the initial conc is gone
A suspension formulation was compounded with a final conc of 12 mg/ml. If the apparent rate constant is 1.7 mg/ml-month, what is the product’s t1/2?
suspension and apparant rate constant indicate rxn is pseudo order
we will use ZERO ORDER half life equation
plug in numbers and solve
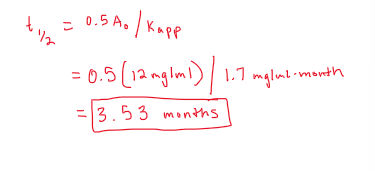
What is the half-life (t1/2) of tetracycline at pH 1.5 if the degradation reaction is described by the following equation:
At (mg/ml) = 12 exp-0.0045t
from the equation we can see the reaction is first order
look at the equation and we can figure out the rate constant
k1= 0.0045
use half life equation for FIRST ORDER to solve
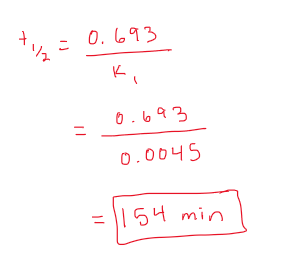
How would we use half-life to determine reaction order?
in zero order- t1/2 increase w/ increasing intial conc
in first order- t1/2 is independent of conc