day 13 Autonomic Nervous System
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
autonomic nervous system
is concerned with maintaining homeostasis within the body by increasing or decreasing the activity of various organs in response to changing physiological conditions
- Regulates homeostasis
Sympathetic
prepares body for physical activity (arousal, competition, stress, danger, anger or fear)
“Fight or Flight” or Thoracolumbar
what happens to your body with sympathetic
- Increased heart rate
- Increased blood pressure
- Increased respiratory rate
- Increased blood sugar glucose
- Mental awareness increases
- Pain signals decrease
- Pupils dilate, increasing visual acuity
- Decreased digestion and urinary
lateral horns are only found in which sections
T1-L2
motor neurons only come out of which sections
T1-L2
are motor neurons found in the sympathetic nervous system
no
it doesn’t come out of anywhere else in the spinal cord besides T1-L2
Parasympathetic
calming of body
”Rest and Digest” or Craniosacral
what happens to your body with parasympathetic
- Lower heart rate
- Lower blood pressure
- Lower respiratory rate
- Increased digestion, nutrient absorption, storage of nutrients
- Increasing gland secretion
- Increase urination and defecation
- Pupils are constricted
where do motor neurons come out of for parasympathetic
either cranial nerves or the sacral region
motor neurons that come out of the cranial area/nerves are
parasympathetic
motor neurons that come out of the cervical are
neither sympathetic or parasympathetic
motor neurons that come out of the thoracic and T1-L2 of the lumbar are
sympathetic
motor neurons that come out of sections L3-I4-I5 are
neither sympathetic or parasympathetic
motor neurons that come out of the sacral region are
parasympathetic
ganglion
area where two neurons synapse
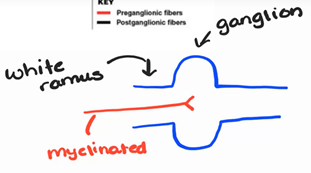
preganglionic neuron
cell bodies in the lateral gray horns of spinal segments T1-T12 and L1, L2; axons are myelinated
enters into the ganglion through a white ramus (myelinated)
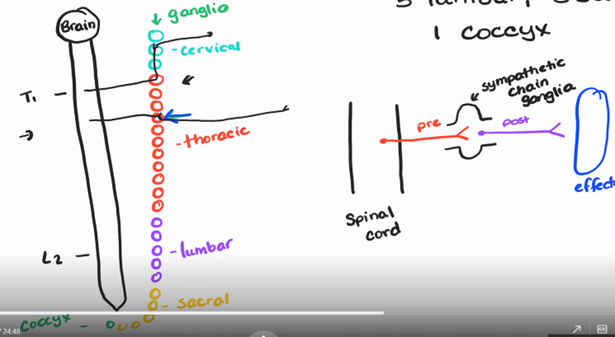
autonomic ganglia
sympathetic chain ganglia (paired (meaning both sides) – 3 cervical, 11 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccyx)
preganglionic nerve fibers enter the chain ganglia via white rami (ramus)
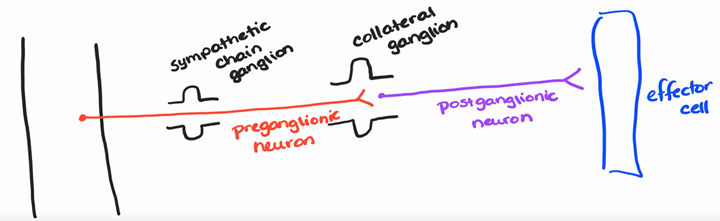
collateral ganglia - celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric
- They are not paired
- They are found anterior to the spinal cord
- they go to organs and tissues that are in the abdominal cavity
- they come out of the spinal cord between T1-L2, coming out of the lateral column
- travels through without stopping through a sympathetic chain ganglia
- synapses inside of a collateral ganglia
adrenal medullae
- travels through a sympathetic chain ganglia and through collateral ganglia and synapses directly on the adrenal medulla with multiple different neurons
- releases both epinephrine and norepinephrine (neurotransmitters)
postganglionic neurons
Axons unmyelinated; fibers long
Leaving the ganglion through a gray ramus (unmyelinated) and going to the effector
pathways of ANS nerve fibers
Chain ganglia
Collateral ganglia (celiac, superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric)
Adrenal medullae
§ A single sympathetic preganglionic fiber has many axon collaterals and may synapse with 20 or more postganglionic fibers; then postganglionic fibers may innervate several visceral effectors (Widespread response)
what does this mean?
- This allows one neuron to have a widespread effect on multiple effector cells
- One message goes to multiple post ganglions neurons which goes to multiple effector cells
- Widespread effect
- This also activates the adrenal medullae since this is releasing epinephrine or norepinephrine into the bloodstream
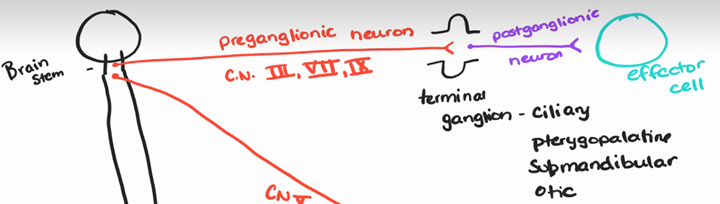
preganglionic neuron
cell bodies in the nuclei of the four cranial nerves that initiate in the brain stem (III, VII, IX, X) and segments S2-S4
cranial nerve III
oculomotor – pupil diameter - For parasympathetic, it will decrease the size of pupils
cranial nerve VII
facial – controls submandibular salivary glands
cranial nerve IX
glossopharyngeal – controls parotid salivary gland
cranial nerve X
vagus – controls cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive
S2-S4
goes to reproductive, bladder, and colon
types of ganglionic neurons
terminal ganglia
intramural ganglia
terminal ganglia
§ they go near target organs but they’re not on it (ciliary (III), pterygopalatine (III), submandibular (VII), and otic (IX))
intramural ganglia
embedded in the wall of the target organ (they go to the target organ)
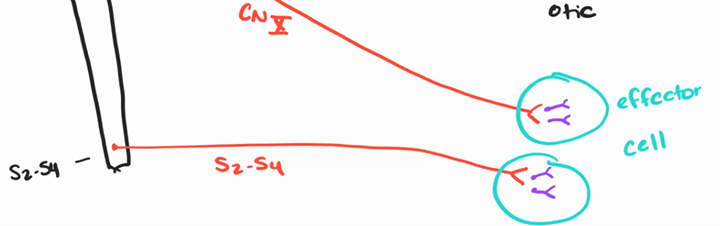
postganglionic neurons
Postganglionic fibers are short passing between the terminal and intramural ganglia and the target organ; - synapses with only 4 to 5 postsynaptic neurons from one effector (Localized response)
- Example being: it can increase your digestive system without having to lower your heart rate at the same time
neurotransmitters
what sends signals from the neuron to whatever the next cell (chemical signal)
all preganglionic sympathetic neurons release
ACh (cholinergic)
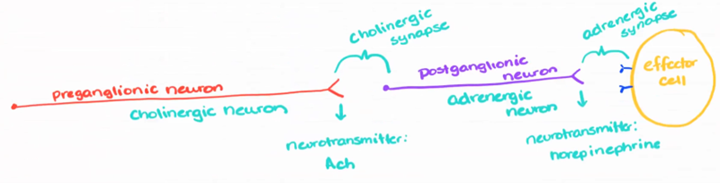
postganglionic neurons have what receptors for ACh
nicotinic receptors for ACh
varicosities
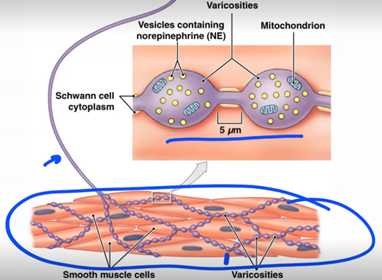
adrenergic neurons can release what
norepinephrine (NE): released by sympathetic postganglionic
adrenergic receptors can bind ____
either NE released by adrenergic neurons or epinephrine released by adrenal gland
a1 - excitatory
open up sodium channels (muscle = contraction)
smooth muscle and blood vessels
a2 - inhibitory
inhibiting the parasympathetic response
if we want to ramp up sympathetic, we’d need to turn down the parasympathetic
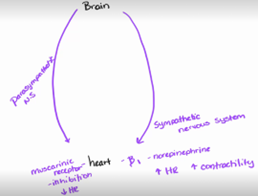
b1 - excitatory
- Heart and liver
- Liver – increase metabolic activity (increased blood sugar
- Heart – increase heart rate and contractility
b2 - inhibitory
- Inhibits airway smooth muscle – causes bronchodilation (bronchi of the airway gets bigger, meaning airway gets bigger)
b3 - excitatory
- Adipose tissue – cause lipolysis (breakdown of lipids for an energy source)
norepinephrine activity ends when
it is taken up by the presynaptic cell and broken down by MAO or diffuses out of the cleft and is broken down catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
norepinephrine
released by adrenergic neurons and the adrenal medulla, only a1 and a2
epinephrine
released by adrenal glands, only b1, b2, b3
which is used for emergencies: epinephrine or norepinephrine
epinephrine
cholinergic neurons release
acetylcholine (ACh)
where does ACh diffuse
across the synaptic cleft and binds with specific cholinergic receptors
nicotinic receptors are excitatory or inhibitory
excitatory
muscarinic receptors are excitatory or inhibitory
both excitatory or inhibitory
ex. heart rate can decrease but digestion can increase
dual innervation
when the viscera receives nerve fibers from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
they both innervate the heart and based on who had the most binding will determine if the heart rate is decreasing or increasing
vasomotor control
only sympathetic
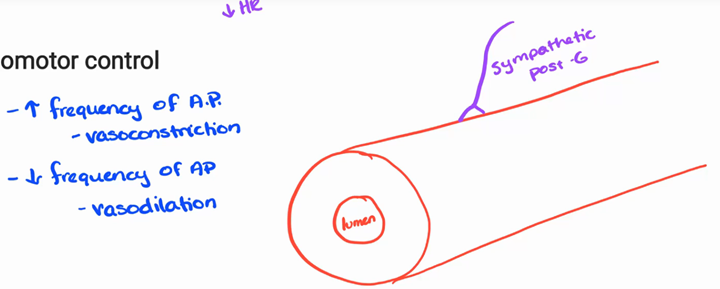
autonomic tone
balance in the activities of sympathetic and parasympathetic
always releasing neurotransmitters but just different amounts
- meaning if you need to activate your sympathetic system, you can do so quickly because you already have sympathetic neurotransmitters being released and get a faster response
ANS receives input from what
CNS, but it doesn’t work in a vaccum
cerebral cortex
emotions and thoughts
hypothalamas
control center for the autonomic nervous system and regulates thirst and hunger and thermoregulation
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
contains your cardiac, vasomotor, respiratory center, salivation, swallowing, sweating
spinal cord
gives you reflexes for urination and defecation
visceral reflexes
unconscious, automatic responses to stimuli
reflex arc
receptor —> sensory neuron —> interneurons (1 or more) —> 2 visceral motor neurons
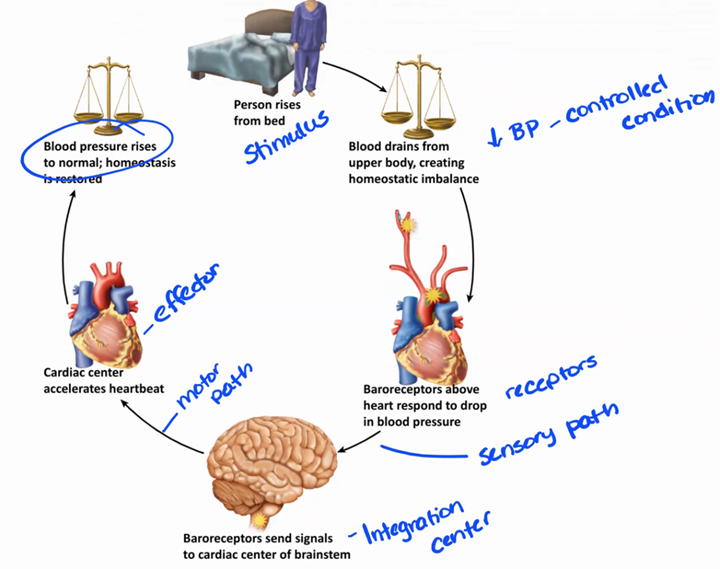
all visceral reflexes are (polysynaptic or monosynpatic)
polysynaptic