chemical changes (incomplete+pqs)
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
i actually give up on finishing these let's be real here
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
the more reactive a metal is:
the more vigorous its reactions are
the more easily it loses electrons to form positive ions
when metals react with other substances, what ions do the metal atoms form?
positive
why are hydrogen and carbon sometimes included in the reactivity series?
to compare the reactivity of metals with
what is the general equation for the reaction of a metal with water?
metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
order potassium, sodium, lithium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, iron and copper in terms of their reactivity, using their reactions with water and dilute acids to help you
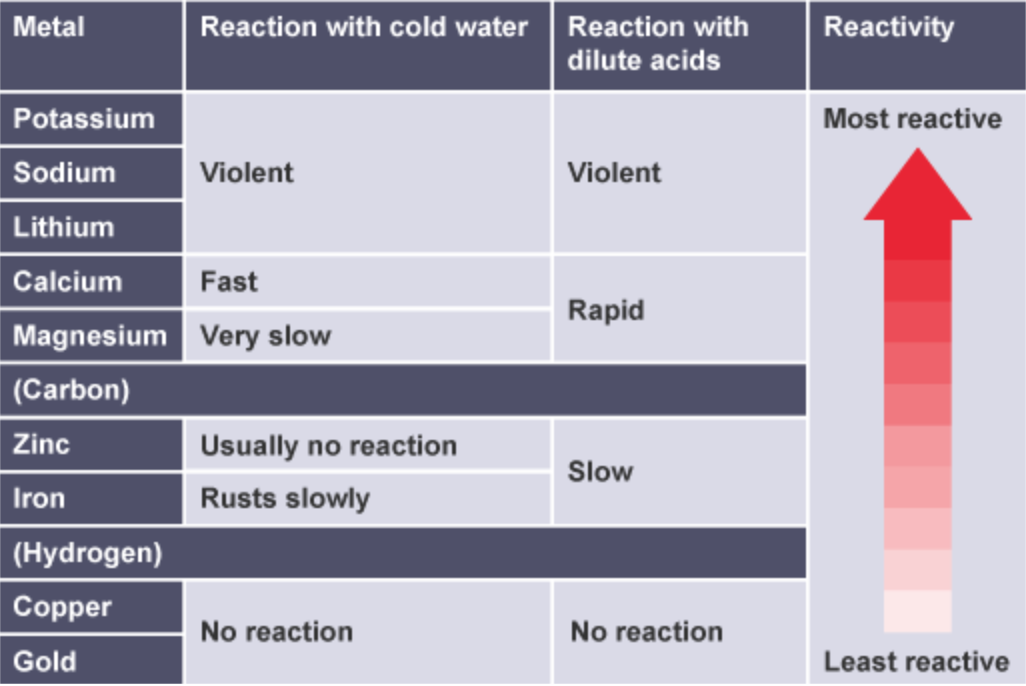
explain how the reactivity of metals with water or dilute acids is related to the tendency of the metal to form its positive ion
more reactive metals lose electrons more easily than less reactive metals
when a more reactive metal reacts with a compound containing a less reactive metal, the more reactive metal atoms form positive ions more easily
what is the general equation for the reaction of a metal and dilute acid?
metal + dilute acid → salt + hydrogen (M.A.S.H.)
will a metal below hydrogen in the reactivity series react with a dilute acid?
no :(
how can metals be found in the earth? which metals are found in different ways and what are the names given to these metals?
most metals are found in the ground as compounds and require extraction - these are called ores
unreactive metals, e.g. gold, are found in the earth as the metal itself (and therefore do not require extraction) - these are called native state metals
name two methods of extracting metals:
electrolysis
reduction w/ carbon
what is an oxidation reaction?
metal + oxygen → metal oxide
loss of electrons (OIL RIG) and gain of oxygen
metal oxides are usually the ores that metals have to be extracted from (e.g. magnesium oxide)
what is a reduction reaction?
gain of electrons (OIL RIG) and loss of oxygen
usually used w/ carbon to extract metal ores (e.g. copper oxide + carbon → copper + carbon dioxide)
electrolysis and chemical cells both involve chemical reactions and electricity.
explain the difference between the processes in electrolysis and in a chemical cell (2)
electrolysis uses electricity to produce a chemical reaction
but cells use a chemical reaction to produce electricity
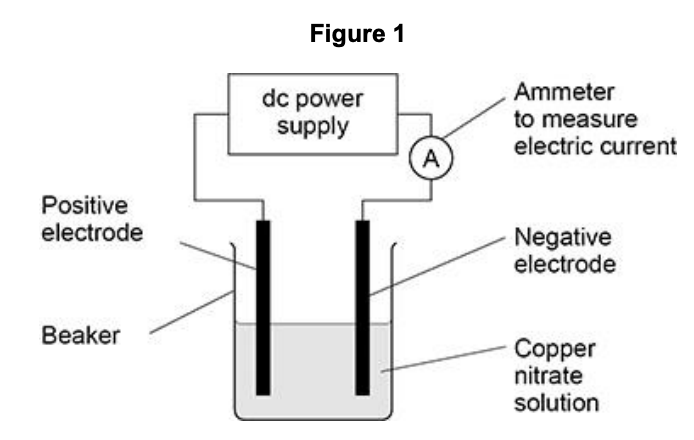
some students investigated the electrolysis of copper nitrate solution using inert electrodes.
some of the copper produced did not stick to the negative electrode but fell to the bottom of the beaker.
suggest how the students could find the total mass of copper produced (4)
filter the mixture
wash and dry copper/residue
weigh the copper collected
add to the increase in mass of the electrode