Electrons & Electron Configuration Profile Picture
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
How to find the # of electrons?
same as # of protons
What is electron configuration?
Show how the electrons are arranged/organized in an atom or around the nucleus.
What is a shell in electron configuration?
It the ring of each orbit. The floor in the house.
What is the subshells?
Are subdivision of electrons shells. The room on each floor. Subshells(rooms) such as: s, p, d, and f.
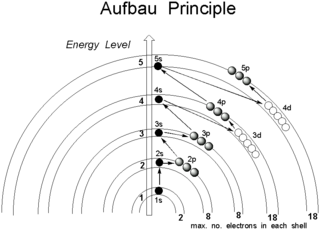
What is orbitals?
Area where electron handout (or be found). Each orbitals can hold 2 electons max.
How much orbital in S? How much electron max?
1 orbital and can hold 2 electrons max
How much orbital in P? How much electron total?
3 orbital and can hold 6 electrons max
How much orbital in D? How much electron max?
5 orbital and can hold 10 electrons max
How much orbital in F? How much electron max?
7 orbital and can hold 14 electrons max
What is Valence electrons?
An electron that is found in the outermost shell (energy level) of an atom and that determines the atom's chemical properties (maximum at any time is 8.) Have the MOST ENERGY
Why does atom want their outermost shell to be FULL?
Because it make the atom stable = happy
What wil happen if the outermost shell is not full?
The atom will want to interact with another atom outmost shell to achieve stable. Interaction involves either by sharing, donating, or accepting electrons between the valence shells of the reacting atoms.
What is the Octet Rule?
Where each element seeks to have 8 electrons in their outermost energy shell.
Describe the Metallic character trend on the periodic table.
Metallic character = Metal characteristic (easily losing electrons) Increase as you go down a group and toward the left side of the periodic table. Increase as you go from right to left across a period(row)
Increase as you go down a group and toward the left side of the periodic table. Decrease as you go from left to right across a period(row)
Describe the Atomic Radius trend on the periodic table.
Measurement of the size of an atom, specifically the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Increase as you go down a group and toward the left side of the periodic table. Increase as you go from right to left across a period(row)
Describe the Electronegativity trend on the periodic table.
Measurement of how strongly an atom attracts electrons. Fluorine has the highest electronegativity. Increase as you move from left to right across a period(row) and Increase as you move up a group.
Describe the Ionization energy trend on the periodic table.
How much energy is required/needed to remove an electron from an atom. Helium have the highest ionization energy. Increases as you move from left to right across a period (row). It increase as you move up the group.