Methods of Localization, how to study the brain
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 3 Sept. 19
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Methods of localization
Accident
Manipulation
Measurement
Neuropsychology
Branch of psychological science that examines how brain injury affects the mind
Vascular injury (e.g. strokes)
anoxia (loss of oxygen)
disease
penetrating wounds (e.g. gun shots)
surgery
Brain damage
In an injury to a specific brain regions reliably causes a specific dysfunction → this region is necessary for correct functioning
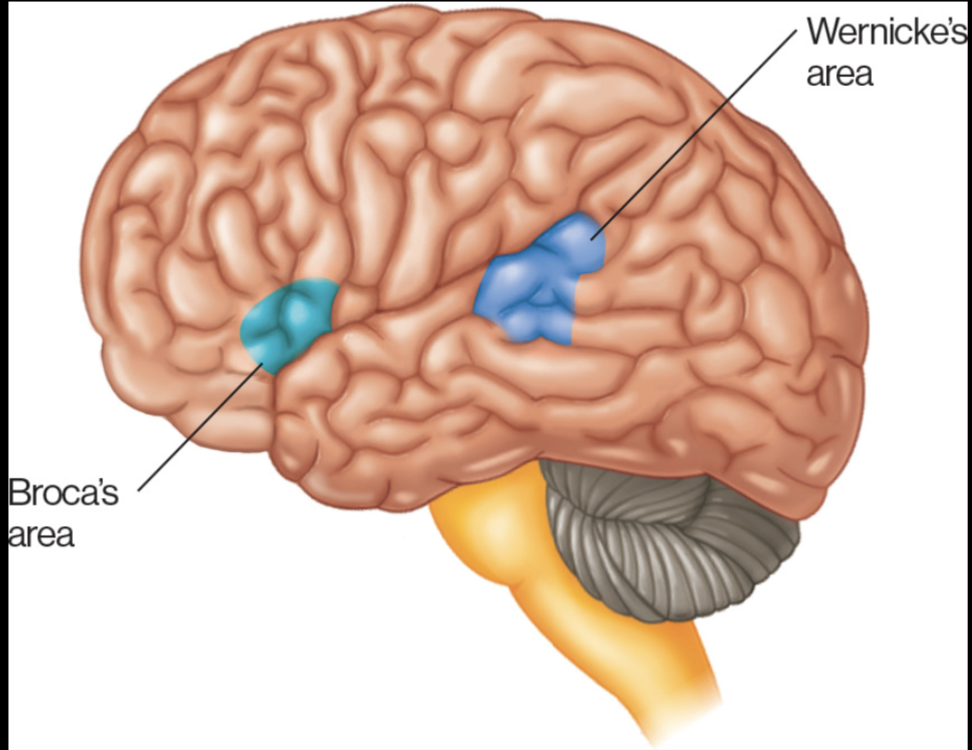
Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area
Wernicke’s Area
TEMPORAL
speech comprehension
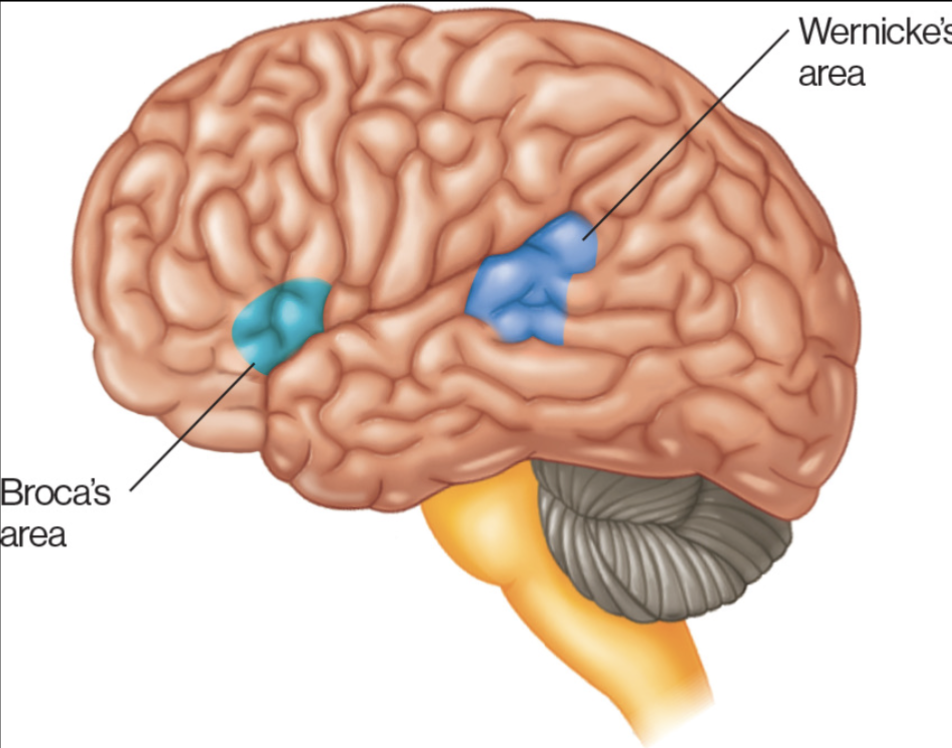
Broca’s area
FRONTAL LOBE
Speech production
think hearing blah, blah, blah, saying words
Aphasia
Inability to comprehend or produce speech, or both
Agnosia
Inability to recognize objects, shapes, sounds, smells, and people
Amnesia
Inability to remember
Five seconds of summer….I wish that I could wake up with amnesia and forget about the stupid little things
Brain mapping system
Ex vivo; after death (post-mortem)
Ex vitro; slices, culturs (VITRO Latin for "in glass")
In vivo; with all the living, invasive and non-invasive
Vivo; living
What type of activity is neural activity and how do we measure it?
ELECTROCHEMICAL
Ways to measure
Electrical activity
Chemical activity
Methods for recording brain’s electrical/magnetic output
The electroencephalogram (EEG)
Even-related potentials (ERPs)
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
Single-cell recordings
What two methods measure brain activity?
electroencephalogram (EEG)
Magnetoencephalograph (MEG)
they record electrical and magnetic activity in the brain
they DO NOT visual brain activity
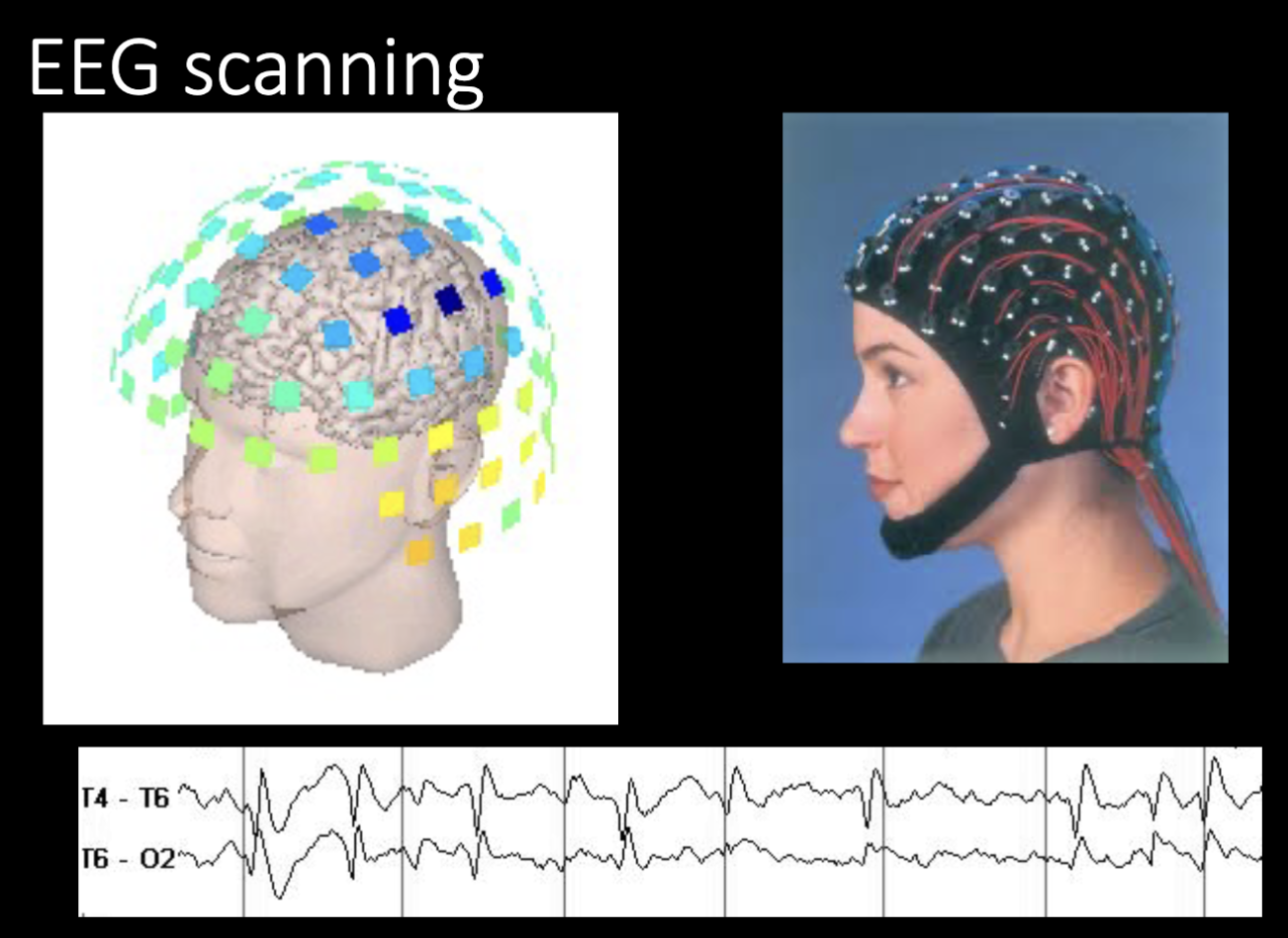
EEG Method
Electrodes placed on the scalp
Activities of cortex zones are recorded
Temporal resolution is very good
Spatial resolution is not so good
Reflects the sum of all postsynaptic potentials occurring in multiple neurons
used in sleep studies
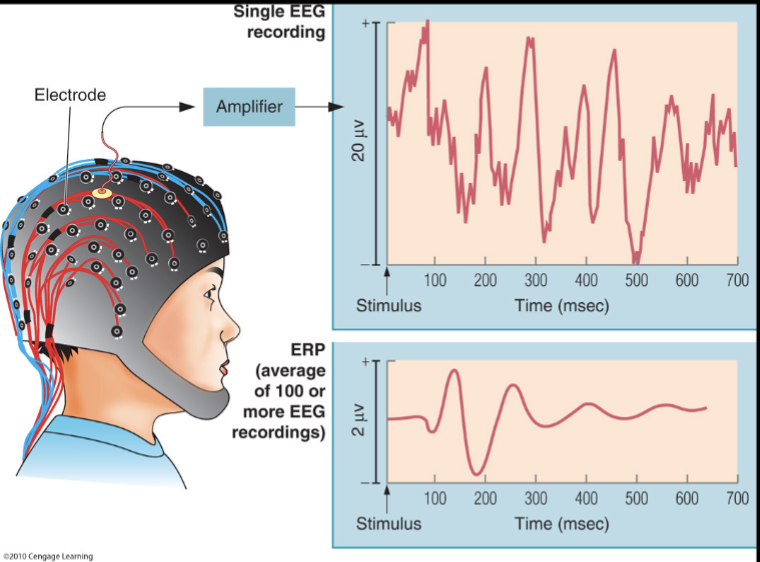
Event related potentials (ERPs)
Used in cognitive studies
Event-related potentials
Analysis allows researchers to map the brain’s EEG response to environmental stimuli
In this examples, a characteristic waveform emerges
when responses to the presentation of a tone are average over 100 trials
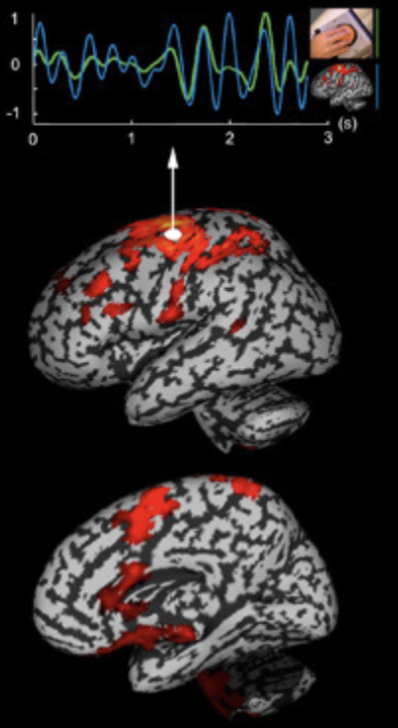
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
Electrical activity in the brain generates measurable magnetic fields
Electromagnetic fields generated by the brain
Cannot take activity from all over the brain
Difference from EEG; conductivity of the tissues inside the skull has little effect on the magnetic fields outside of the skull
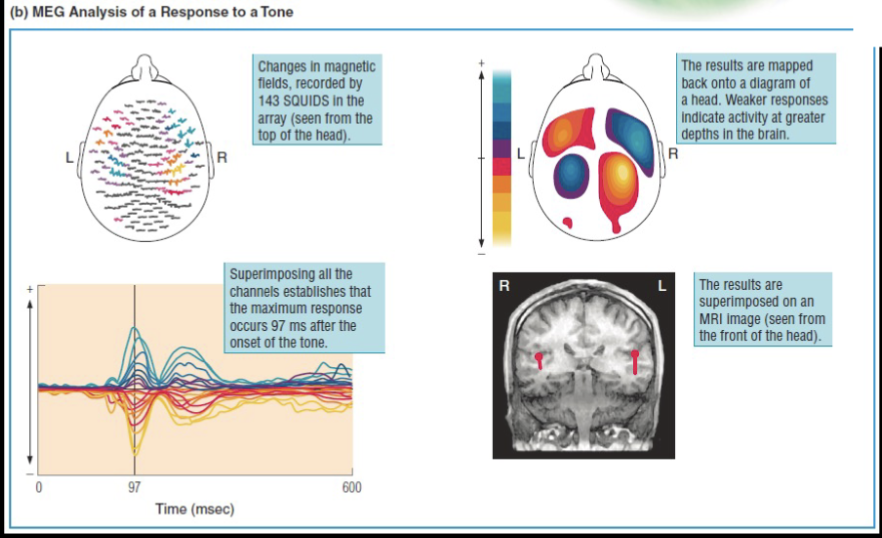
Difference between EEG and MEG?
The conductivity of the tissues inside the skull has little effect on the magnetic filed outside of the skull
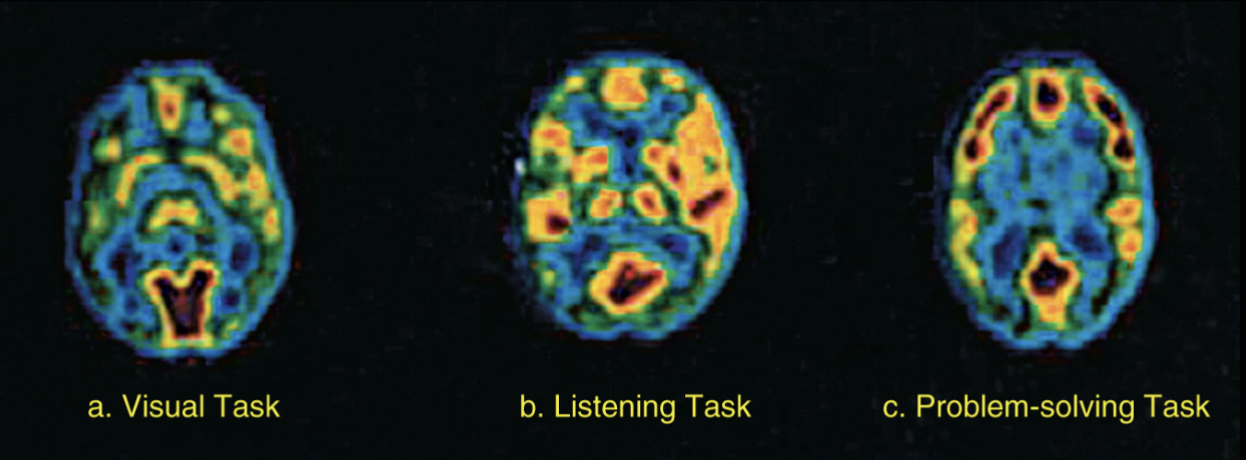
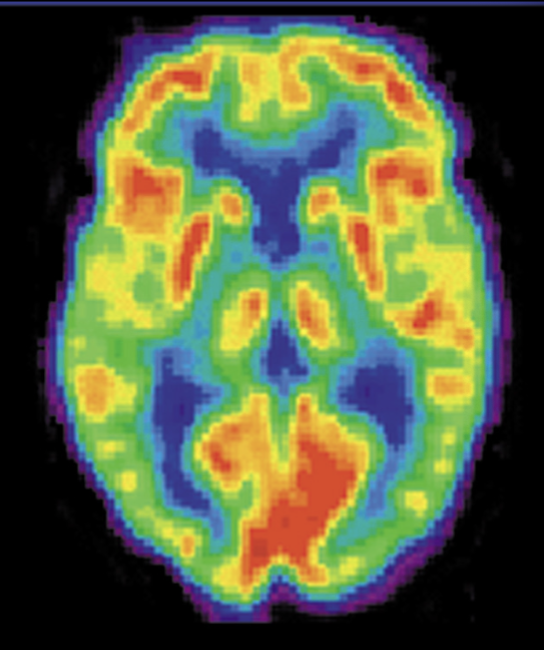
Positron emission tomography (PET)
High resolution of the brain is obtained
Radioactive chemicals (marker) injected into the blood
Relationship between the density signal of that marker and the blood flow in that area
Color of the image indicates the level of activity
RED most active, followed by yellow, green, blue for least active
Involves taking dose of radiation
Functional magnetic resonance imagine (fMRI)
Magnetic detectors amount of hemoglobin and oxygen in different areas of the brain
Highly active areas of the brain appear to use more oxygen
Indicate where blood flows in brain for specific cognitive processing, based on magnetism
Used to develop brain regions maps
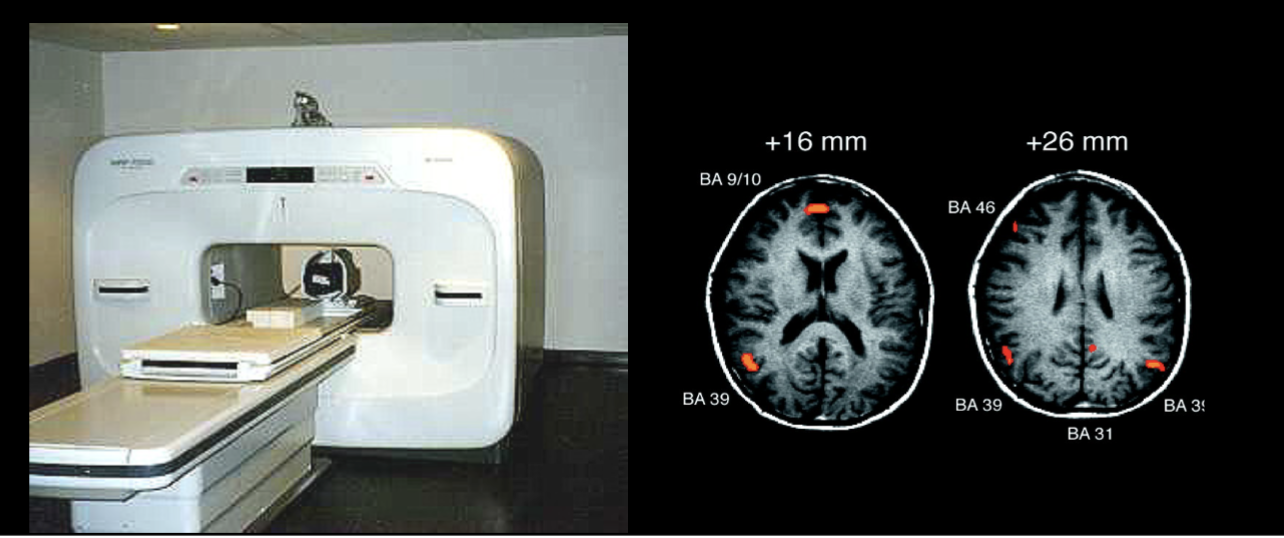
fMRI pros and cons
Provides images of the structure and activity of the brain
High detail and safe
Time-consuming, expensive, patient must be lying still on the table
Studying the relative activity of brain tissues in real-time
The brain and the self
If you lose part of the brain, you lose part of your unique experience
Brain activity and mind are inseparable
on is the other