conjunctiva III - lumps and bumps
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what are the 3 categories of conjunctival abnormalities
degenerations
pigmented lesions
non-pigmented lesions
state the different degenerations (4)
sub-conjunctival haemorrhage
pinguecula
concretions
pterygium
what is a Sub-conjunctival haemorrhage (3)
•Blood under conjunctiva- between sclera and conjunctiva
•Asymptomatic - VA normal, no pain, no discharge - occasionally a dull ache or mild discomfort - usually an incidental finding
•Usually unilateral
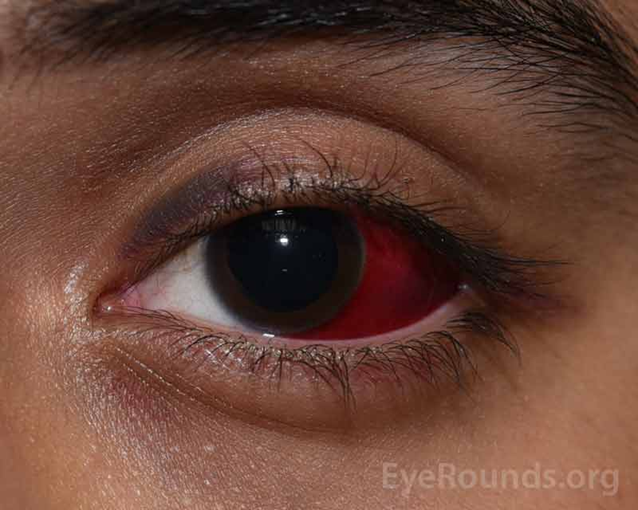
aeitology of sub-conjunctival haemorrhage (3)
•Idiopathic
•Valsalva manoeuvre - coughing, straining, vomiting
•Trauma (surgery)
pre-disposing factors of a sub-conjunctival haemorrhage (3)
•Older age (60-80 years)
•Systemic hypertension, diabetes, vascular disorders
•px who are on anticoagulants (warfarin, aspirin)
signs of sub-conjunctival haemorrhage (3)
•Blood in sub-conjunctival space
•Visible clear space between the cornea and conjunctiva - around the limbus
-Trauma ? intracranial hemorrhage if posterior border cannot be seen (rare) - bleeds into sub-conjunctival space
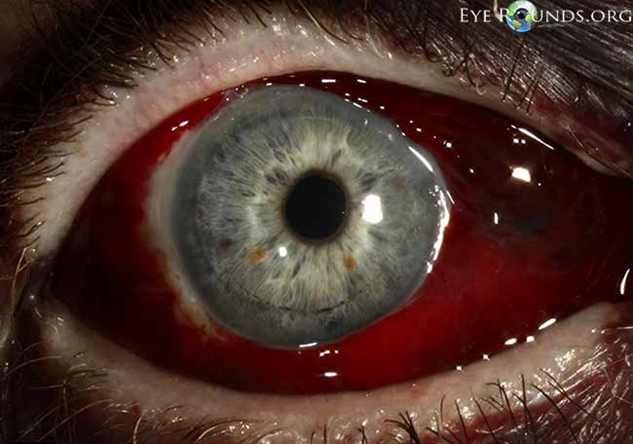
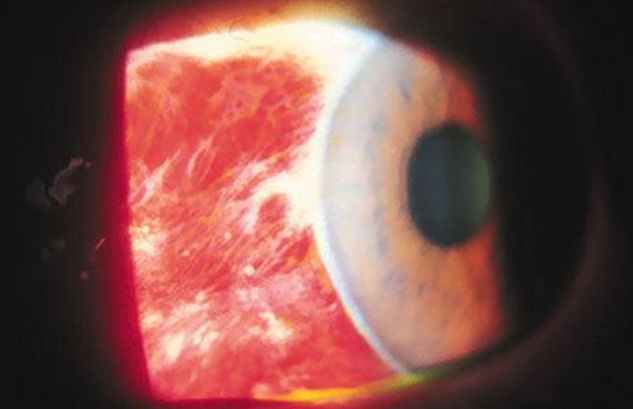
management of a sub-conjunctival haemorrhage (2)
•Reassure patient - Usually resolves 1-3 weeks
•Refer to GP if recurrent (BP check) or history of bleeding/blood clotting abnormalities
explain what pinguecula is (5)
•Yellow-white deposits - slightly raised on conjunctiva at 3/9 oclock
•Exposed peri-limbal bulbar conjunctiva, nasal and/or temporal - usually bilateral
Degeneration of collagen fibres of the conjunctival stroma - Degenerative condition (benign)
•Common, especially in elderly - Seen in most eyes > 70 years
•May be associated with chronic UV exposure
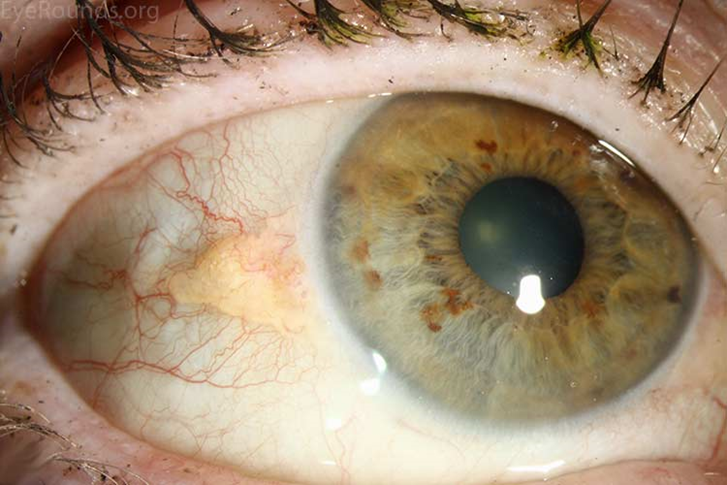
treatment/management of pinguecula
•No treatment needed although if unsightly/very protuding may be removed through surgery
explain what concretions are (4) (conjunctival lithiasis)
•Small soft or hard yellowish-white deposits in tarsal conjunctiva - Usually < 1mm diam, up to 3mm - Usually low profile
•Epithelial inclusion cysts (keratin/calcification)
•Common in older people (>50 yrs)
•Usually asymptomatic - can cause foreign body sensation
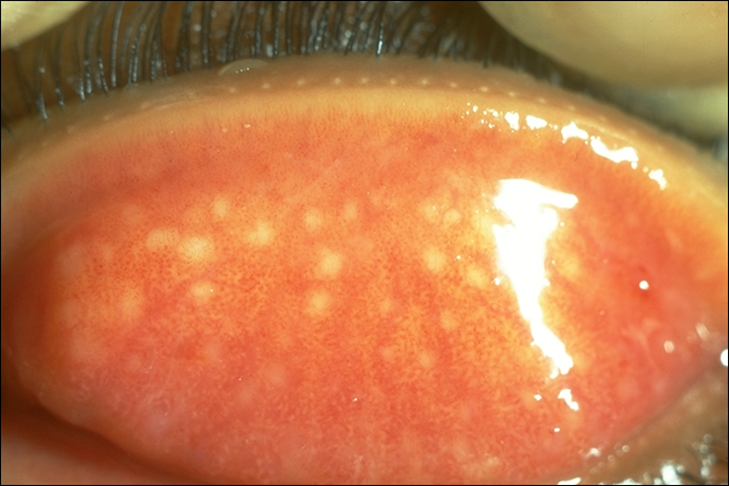
treatment/management of concretions
•Treatment rarely required
•Can be teased out with hypodermic needle after anaesthetising the surface
describe what a pterygium is (3)
•Fibrovascular growth from bulbar conjunctiva across to involve the cornea - often a triangular shape
•?Tissue response to irritants
•Attributed to chronic UV exposure, dust and wind
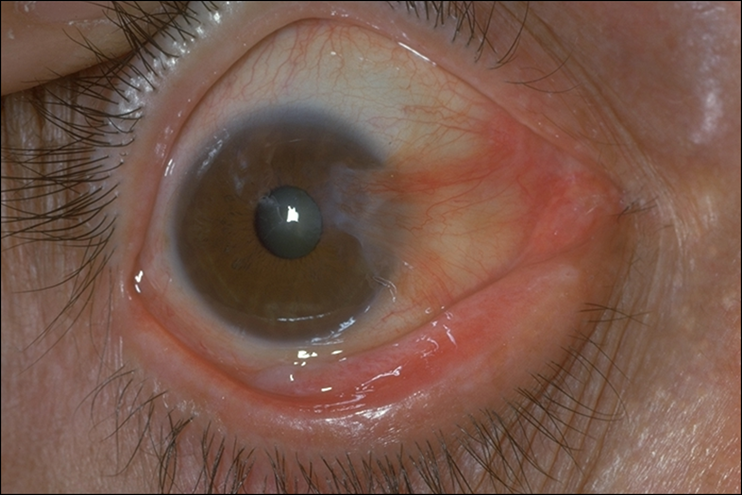
risk factors of pterygium (3)
•Sunlight - living near equator, working out of doors, occupational exposure to UV
•Arid climate - dry climate - little rainfall - dust and wind
•Older age
symptoms of pterygium
mild irritation, may be periodic acute exacerbations
signs of pterygium (3)
•Usually bilateral (asymmetrical)
•Starts with thickening/distortion of bulbar conjunctiva, small grey opacities near the limbus, conjunctiva overgrows the opacities
•Stocker’s line - epithelial iron deposit ahead of advancing pterygium
optometric management of pterygium (4)
•Monitor development
•Photographic evidence
•Lifestyle advice - the conditions that might deterioate (UV/wind)
Refraction (astigmatism)
secondary care options for pterygium (2)
•May need surgical excision if: cosmesis important or visual axis threatened
•Tends to recur following surgery
summarize the 3 categories of pigmented lesions (2:3:1)

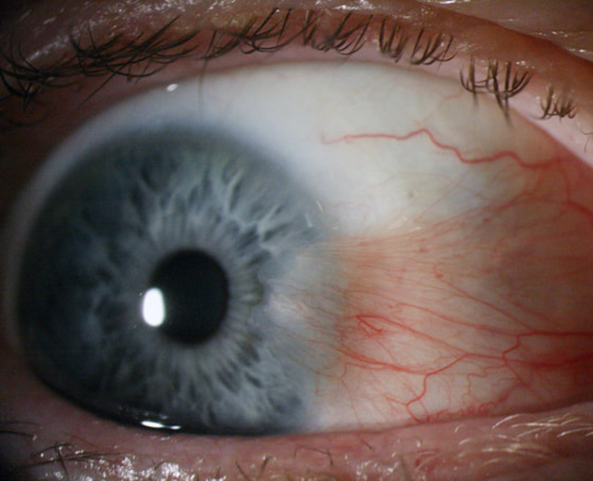
describe conjunctival epithelial melanosis and its features (6)
•also called Racial/ethnic melanosis - associated with dark skin
•Flat, Patchy and Brown pigmentation
•Bilateral - Asymmetrical
•Intra-epithelial - moves freely over sclera - between conjunctiva and sclera
•Develops in early years
•Unlikely to progress to melanoma
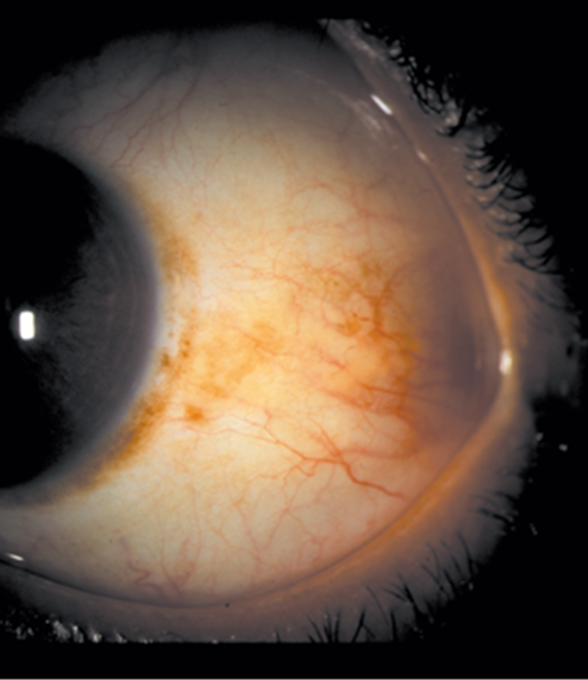
explain what Secondary acquired melanosis is (3)
•Adrenochrome deposits - pigment spots on the conjunctiva - can be due to:
•Oxidation of epinephrine drops
•Addison's disease
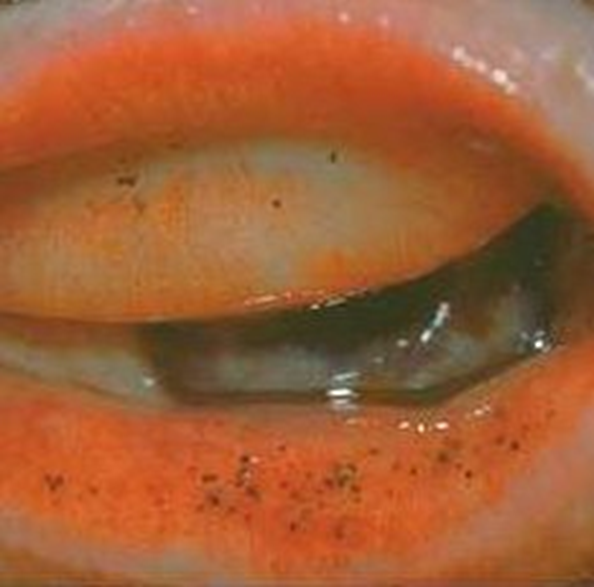
describe the features of (pre-malignant) naevus (5)
•Common (52% of ocular pigmented lesions)
•Congenital or acquired
•May change at puberty or during pregnancy
•Asymptomatic
-Malignant transformation rare - does occasionally happen so monitor
describe the signs of naevus (4)
•Solitary, well demarcated, flat or slightly elevated
•Brown/black (30% amelanotic no colour/pigment)
•Often cystic spaces - reassuring sign that it is a naevus
•Intraepithelial - moves freely over sclera
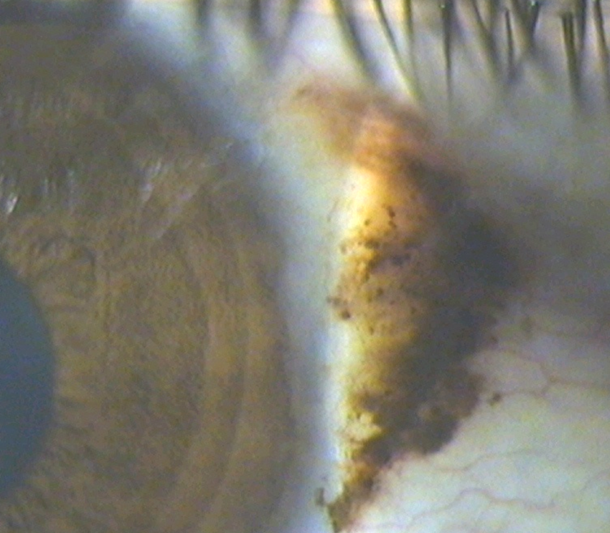
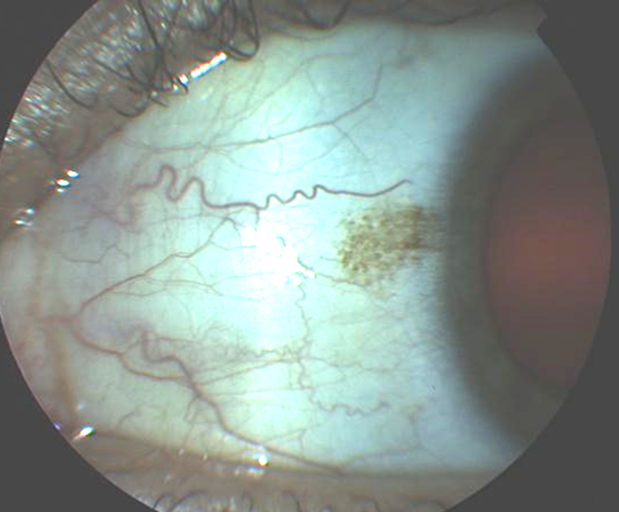
what is the management for naevus (3)
•Advise px to report any changes (increase in size, elevation, colour)
•Review after 6/12, then annually
•Photograph if possible
(unlikely to be malignant)
what is primary acquired melanosis (PAM) (4)
or also known as conjunctival melanocytic intraepithelial neoplasia (C-MIN)
•New conjunctival pigmentation
•Potential for malignancy (20%) - refer (biopsy)
•Elevation is suspicious for malignancy
describe the clinical features of PAM (6)
•Middle-aged to elderly white patients
•Unilateral
•Flat, intraepithelial, single or multiple
•Light to dark brown, indistinct areas
•No cystic spaces (naevus), no nodules (melanoma)
•Can change - enlarge, shrink, darken or lighten - refer promptly for investigation
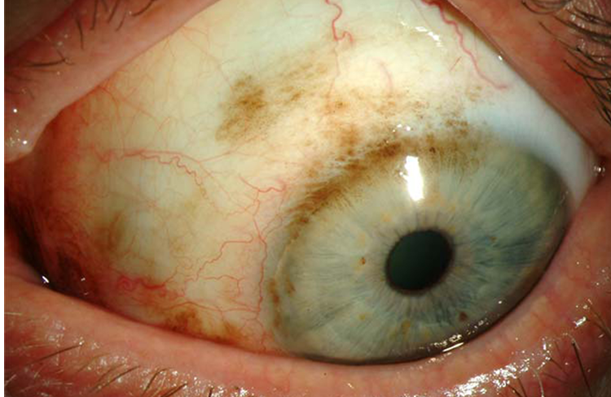
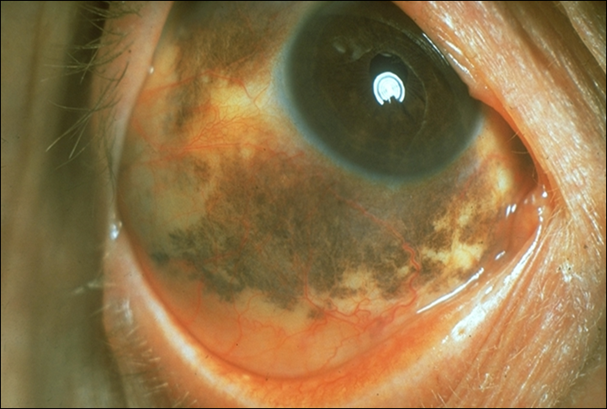
describe what melanoma is (4)
•Rare (3-5% of ocular malignancies)
•May arise from nowhere OR , from a naevus or PAM
•Mainly affects white adults
•Metastasise (lymph)
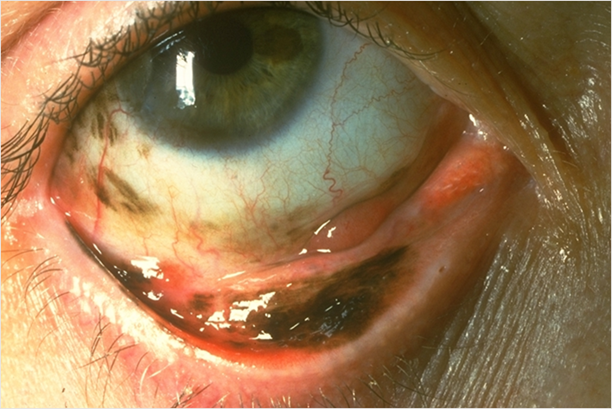
what are the signs of a melanoma (5)
•Diffuse, nodular or mixed
•Unifocal or multifocal
•Melanotic or amelanotic - pigmented/non-pigmented
•+/- Dilated feeder vessel
•Fixed to underlying sclera
optometric management of melanoma
urgent referral !!!
summarize the 3 categories of non-pigmented lesions (2:1:2)

explain what papilloma is (its 2 types) (4:4)
viral (HPV):
often pedunculated (attached by a stalk)
multiple and bilateral
in children & young adults
May spontaneously resolve
Non viral:
single, sessile (flatter/no stalk) lesion
in older patients
Appears similar to squamous cell carcinoma
treatment: Excision and cryotherapy (freezing)
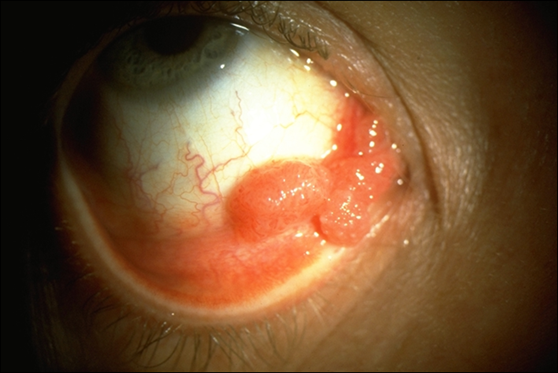
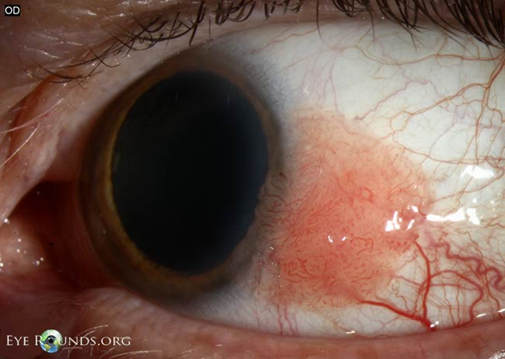
explain what Epibulbar choristoma is and its management (4)
•Dermoid - soft yellow limbal mass and Lipodermoid - soft white mass
normal tissue growing on the surface of the eye where it doesn’t belong.
monitor if vision isn’t affected
surgical excision: cosmesis, significant astigmatism, affects eyelid closure/ocular movement
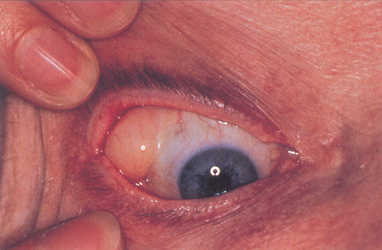
explain what intraepithelial dysplasia is (4)
•Raised, reddish lesion - crosses the limbus
•Seen more in older age group (>50)
•Slow growing
•May transform to squamous cell carcinoma - refer for second opinion
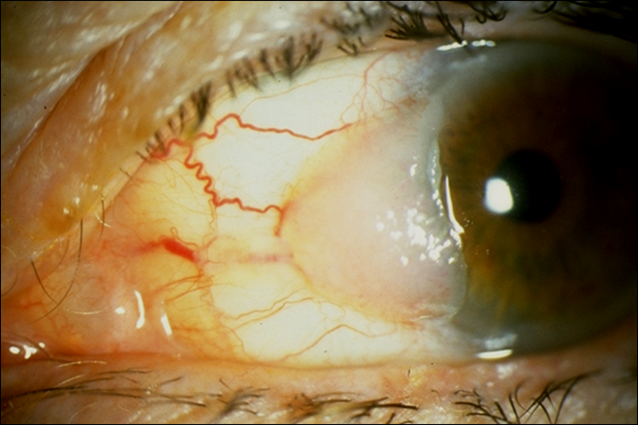
describe squamous cell carcinoma (3)
•Similar in appearance to intra-epithelial dysplasia
•Requires excision Good prognosis (may re-occur)
•Local invasion
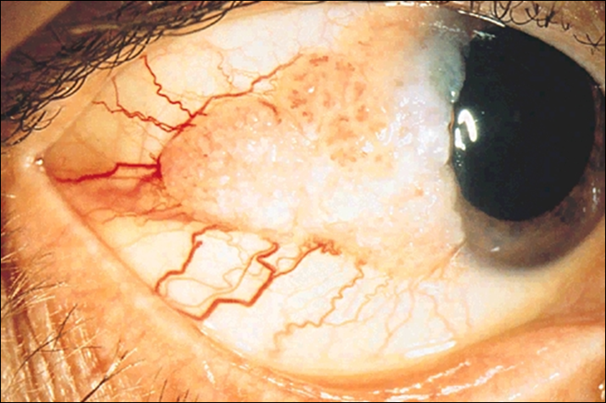
describe lymphoma (4)
•Salmon pink subconjunctival mass
•Most often located in the fornices
•Usually older pts 60-70 years
•Very rare - life threatening - refer urgently
what i need to know
Must knows
•Subconjunctival Haem
•Pinguecula
•Concretions
•Key features of malignant lesions
Should know
•Pterygium
•Pigmented lesions
Good to know
•Papilloma
•Squamous cell carcinoma
•Lymphoma