Specialised cells- Yr 9
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What is a specialised cells?
A cell that has a special shape and features (structure) that helps it do it’s job
How is an egg cell specialised?
Function
Adaptations
Carries mothers DNA
Layer of jelly
How is an RBC specialised?
Function
Adaptations
Carries oxygen around the body
Flexible, bi concave shape to increase surface area, no nucleus to maximise space for oxygen
How is an sperm cell specialised?
Function
Adaptations
To fertilise egg cell
Tail, midpiece with mitochondria for energy, produced in large quantities to increase chance of fertilisation
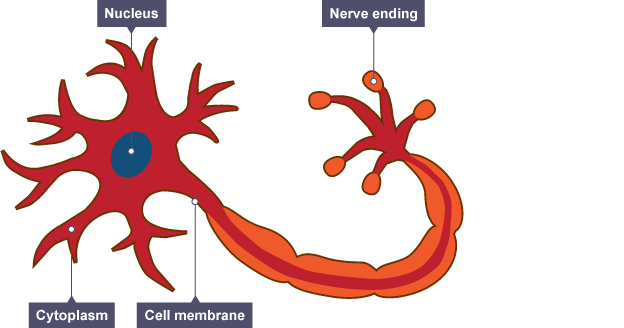
How is an nerve cell specialised?
Function
Adaptations
They are thin, passing messages quickly
Nerve cells have branched connections at each end. These join to other nerve cells, allowing them to pass messages around the body.
They have a fatty (myelin) sheath that surrounds them. The fatty sheath increases the speed at which the message can travel.
How is an muscle cell specialised?
Function
Adaptations
Muscles cells are found in bundles which make up our muscles. These cells are able to contract (get shorter) and relax (return to original length).
Cardiac (heart) muscle cells contract and relax to pump blood around our bodies for our entire lives.
Smooth muscle cells make up thin sheets of muscle, such as the stomach lining.
How is an cilia cell specialised?
Function
Adaptations
These hairs move mucus containing dust and other particles upwards and out of the airways.
How is a root hair cell specialised?
Function
Adaptations
Holds plant in place as they grow, and absorb water and minerals from the soil
Large surface area to absorb as much water and minerals as possible
How is a palisade cell specialised?
Function
Adaptations
When the Sun shines, photosynthesis in plant cells makes sugar for growth, reproduction and other life processes.
They are towards the tops of leaves for maximum light and they have lots of chloroplasts
What does a xylem cell do?
Transport water from the roots to other parts of the plant.
What does a phloem cell do?
Transport sugary water from the leaves to the rest of the plant.