7.1 to 7.3
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Equilibrium
A state in a reversible reaction where the rates of the forward and reverse processes are equal, resulting in no net observable change.
Dynamic Equilibrium
A condition in a reversible reaction where reactants and products are continually interconverting at equal rates but their concentrations remain constant. Reactants are continually turning into products, and products are continually turning back into reactants(same rate).
At equilibrium, forward and reverse processes occur at equal rates, resulting in no net observable change. The concentrations and/or partial pressures of all species remain constant, yet they will rarely be equal.
Think like you are trying to go up an escalator as it is moving down(you stay in the same place).
Rate of forward reaction= rate of reverse reaction. Concentrations of reactants and products no longer change.
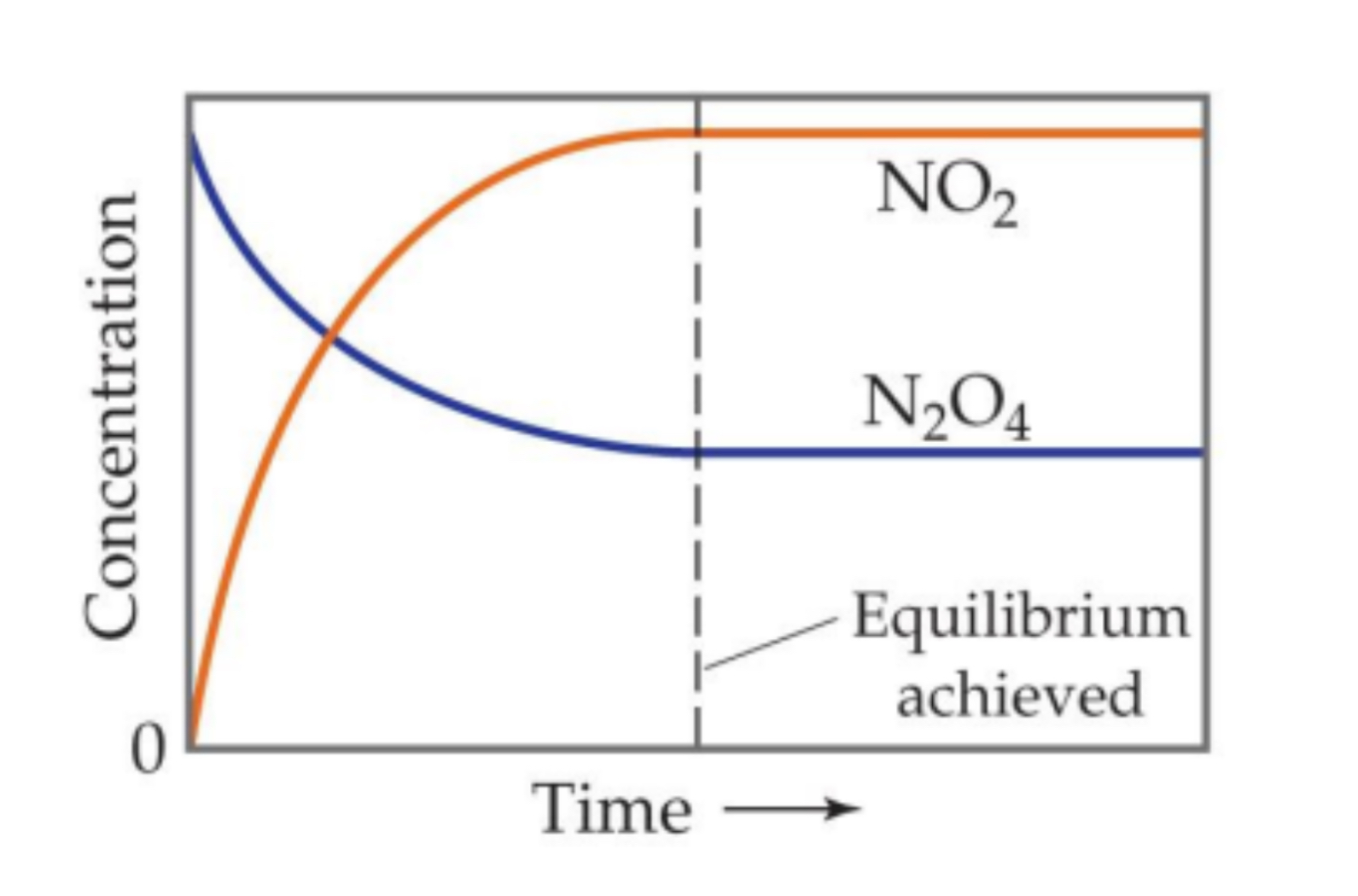
Dynamic Equilibrium(Concentration v Time Graph)
Reactants keep decreasing while products increase and then once equilibrium is established the two concentrations stay the same.(rate of forward reaction slows down and rate of reverse reaction speeds up). Once Equlibrium is established, the concentrations of the reactants and products remain the same.
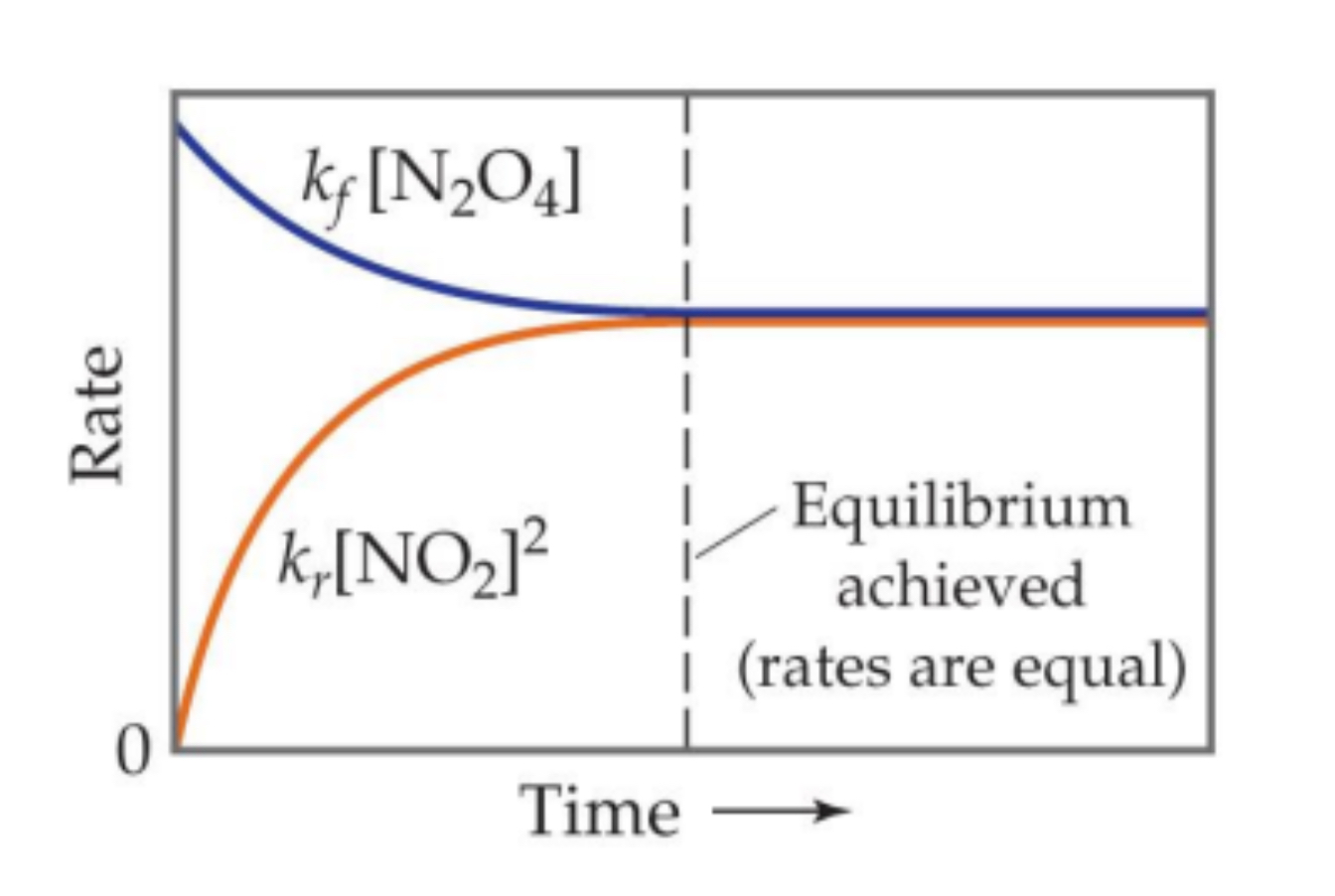
Dynamic Equilibrium(rate v Time Graph)
When equilibrium is achieved the rates(of forming products and forming reactants is equal).
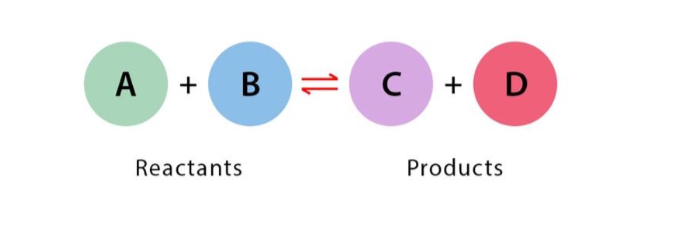
Reversible Reaction
A reaction that can occur in both forward and reverse directions, often represented with a two-way arrow. Sometimes proceeds in each direction simultaneously.
All reactants are NOT consumed
Evaporation & Condensation of Water: H2O ←→H2O (g)
Dissolving & Precipitating a Salt: NaCl (s) ← →NaCl (aq)
Absorption & Desorption of a Gas: CO2 (g)← →CO2 (aq)
Reversible Redox reactions(transfer of electrons)
Discharging and recharging a lead-acid battery
Pb + PbO2 + 2 H2SO4← →2 PbSO4 + 2 H2O + electrical energy
Reversible Acid-Base Reactions(Transfer of protons)
Acetic Acid and Water in Vinegar
CH3COOH (aq) + H2O (← →) CH3COO- (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
Characteristic of reversible reactions(Proceeding to the right) Proceeding to the left
When the rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse
reaction, there is a net conversion of reactants into products
The reversible reaction is proceeding to the right
Characteristics of reverse reactions: Proceeding to the left
When the rate of the reverse reaction is greater than the rate of the forward
reaction, there is a net conversion of products into reactants
The reversible reaction is proceeding to the left
Completion Reaction
A reaction in which all reactants are consumed to form products, represented with a one-way arrow. Usually involve the production of water, gas, or a precipitate.
ex: CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g)
Reaction Quotient (Qc)
A measure of the relative concentrations of products and reactants at any point in time.
aA+bB—>cC+dD is expressed as Qc=(C^c)(D^d)/(A^a)(B^b)
No units. Describes the relative concentrations of products and reactants at any point in time, not just at equilibrium like the equilibrium constant.
Equilibrium Expression
A mathematical expression that relates the concentrations of the products and reactants at equilibrium.
Solids and liquids are left out of the equilibrium expression(concentrations-ratio of mass to volume-are constant).
When writing an equilibrium expression, include gases and aqueous species, do not include solids and liquids.
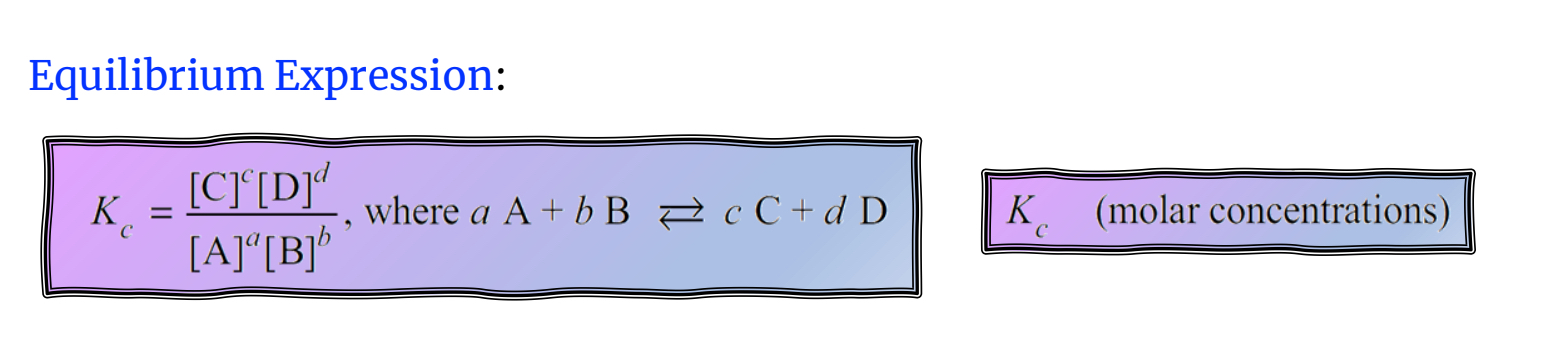
Equilibrium Constant (Kc) or (Keq)
A constant value that describes the ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants at equilibrium for a given reaction. Based on stoichiometry of the reaction only. No units.
Value obtained when molar equilibrium concentrations are substituted into the equilibrium expression; depends on reaction and temperature.
Solids and liquids are left out of the equilibrium expression(concentrations-ratio of mass to volume-are constant as long as some solid or liquid is there). Only include gases and aqueous species.
Kp
The equilibrium constant for gas-phase reactions measured in partial pressures.
Same equation as equilibrium expression but use P sub c(for each one) instead of the capital of that letter.
Partial pressure
The partial pressure of a gas is the pressure exerted by that specific gas; the partial pressure of all the gases add up to the total pressure in that system.
QP
Describes the relative partial pressures of products and reactants at any point in time, not just at equilibrium like the equilibrium constants.
Dimerization
A chemical reaction where two molecules combine to form a larger molecule, known as a dimer.
What does it mean when Qp=Kp or Qc=Kc?
The system is at equilibrium.
Closed System
A condition where neither reactants nor products can enter or leave, allowing for equilibrium to be established.
No Net Change
A situation at equilibrium where concentrations of reactants and products no longer change.
Forward Reaction
The reaction progress where reactants are converted into products.
Reverse Reaction
The process in a reversible reaction where products are converted back into reactants.
Equilibrium can only be maintained if:
1.A Closed system is present(reactants and products are not able to escape the system, and new species that could influence the equilibrium cannot enter the system.)
2.Volume Remains Constant(if the volume changed, the partial pressures of gases would change.)
3.Temperature Remains Constant(Temperature affects reaction rates(k))
CVT
Closed system
volume(constant)
Temperature(constant)