Basic Laws of Inheritance
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Chromosomes
is made up of DNA tightly coiled around the protein called histones that supports its structure.
Chromosomes 1
It is easily visualized during cell division, when seen they take on distinctive lenghts and shapes.
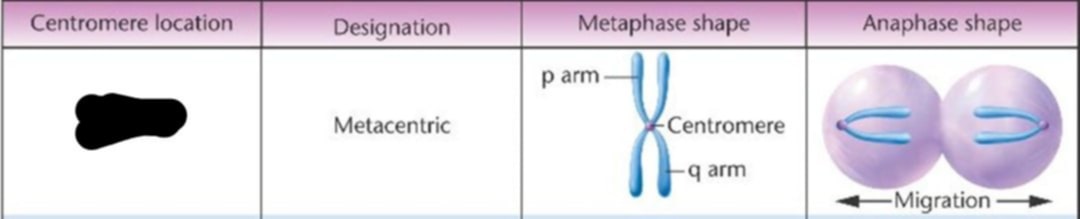
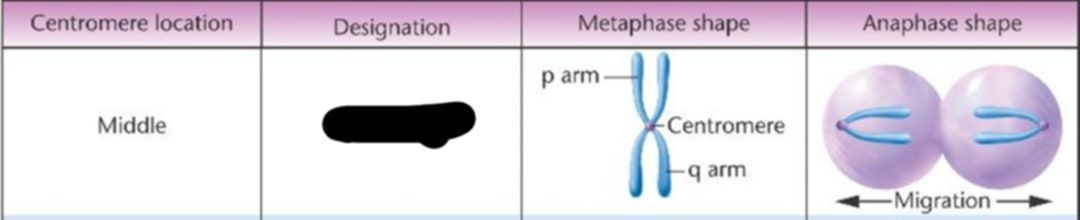
Centromere
Each chromosomes has a constriction point
Centromere1
It devides the chromosomes into two section or "arms".
p arm
The short arm of chromosomes is called
q arm
the long arm of the chromosomes is labeled as the
location
The _____ of the centromere on each chromosomes gives its characteristic shape and can be used to help describe the location of specific gene.
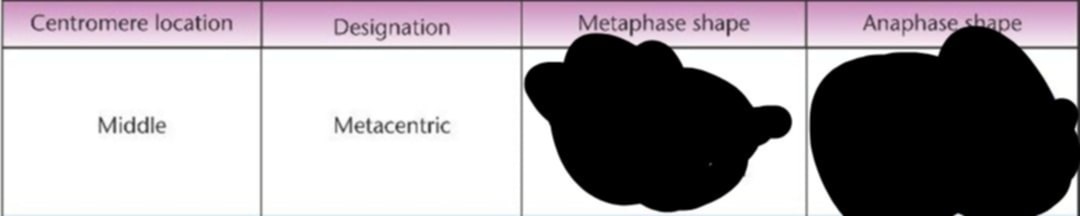
Middle
Where is the centromere location?
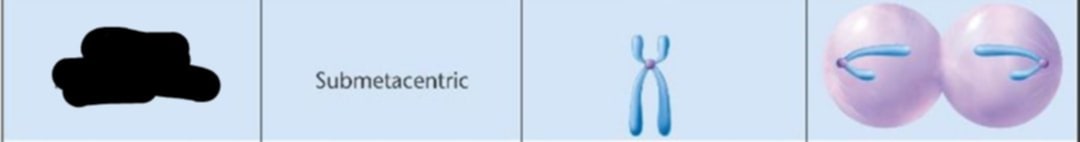
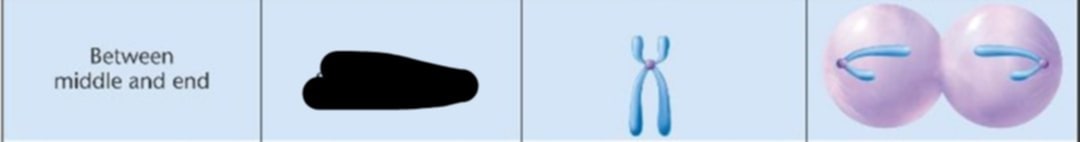
Between middle and end
Where is the centromere location?
Close to end
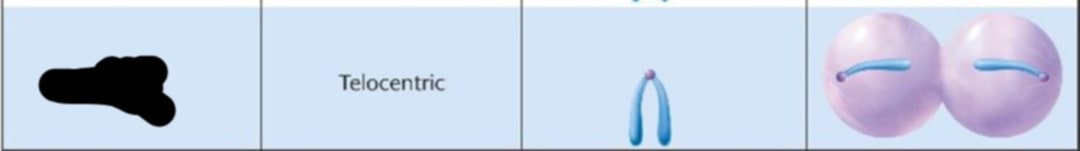
Where is the centromere location?

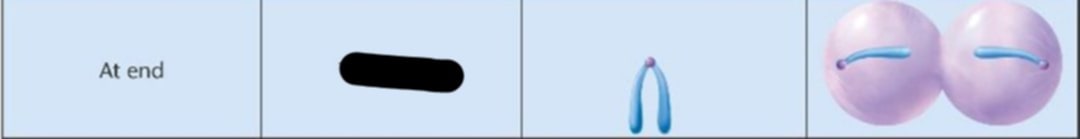
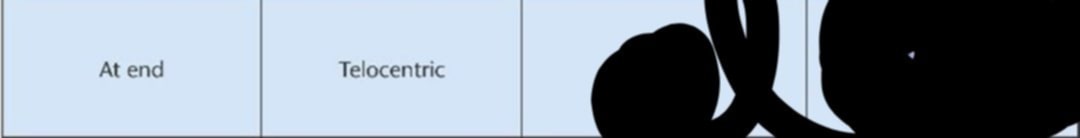
At end
Where is the centromere location?
Metacentric
Where is the designation?
Submetacentric
Where is the designation?
Acrocentric
Where is the designation?

Telocentric
Where is the designation?
Done - 1
What is the Metaphase and Anaphase shape of The centromere at the middle with metacentric designation (Draw the figure to familiarize)
Done - 2
What is the Metaphase and Anaphase shape of The centromere between middle and end with submetacentric designation (Draw the figure to familiarize)

Done - 3
What is the Metaphase and Anaphase shape of The centromere close to end with Acrocentric designation (Draw the figure to familiarize)

Done - 4
What is the Metaphase and Anaphase shape of The centromere at the end with telocentric designation (Draw the figure to familiarize)
Homologous chromosome pair
it consist of one paternal and one maternal chromosome.
Homologous chromosome
one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and centromere location.
Karyotype
a human complete set of chromosomes
1,2,3
What chromosome numbers are in A?
4 5
What chromosome numbers are in B?
6 7 8 9 10 11 12
What chromosome numbers are in c?
13 14 15
What chromosome numbers are in D?
16 17 18
What chromosome numbers are in E?
19 20
What chromosome numbers are in F?
21 22
What chromosome numbers are in G?
Sister Chromatids
two parallel structure that composed the chromosomes
Genome
collectively, the total set of genes contained in a haploid set of chromosomes
Locus
a specific site along the lengths of homologous pair that contain identical genes.
Alleles
one of the two or more versions of DNA sequence at a given genomic locations.
Mendel’s Experiment
Described the unit of inheritance and how they pass from generation to generation.
24,034
Mendel conducted experiments from 1857 to 1863 on trait in __,___plants.
24,034
How many plants did Mendel experimented on?
1857 to 1863
When was the duration of Mendel’s Experiments.
No Knowledge
Mendel had __ ________ of DNA, cells, or chromosomes.
Diploid
His laws of inheritance explain trait transmission in any what species?
P1
Parental generation
F1
First Filial generation
F2
Second filial generation
True-breeding
Offspring have the same traits as parents
Dominant
The observed trait
recessive
The masked trait
Monohybrid Cross
follows one trait.
Hybrids
Self-crossed plants
UNIT FACTORS IN PAIRS
Genetic characters are controlled by unit factors that exist in pairs in individual organism.
DOMINANCE/RECESSIVENESS
When two unlike unit factors responsible for a single character are present in a single individual, one unit factor is dominant to the other, which is said to be recessive.
Segregates Randomly
During the formation of gametes, the paired unit factors _________-____ so that each gamete receives one or the other with equal likelihood.
Law of Independent Assortment
This law states that the alleles for different traits are sorted into gametes independently of one another. For example, the inheritance of a gene for pea color is not dependent on the inheritance of a gene for pea shape. This leads to new combinations of traits in the offspring that were not present in the parents, as seen in Mendel's dihybrid crosses.
Law of Segregation
This is Mendel's idea that the two alleles for a trait separate, or "segregate," during the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells). As a result, each gamete receives only one allele from the pair. This separation is random, meaning each allele has an equal chance of being passed on. This postulate accounts for the reappearance of the recessive trait in the F2 generation.
Dominance/Recessiveness
When two different alleles for a single trait are present in a pair, one allele will be dominant and its trait will be expressed, while the other will be recessive and its trait will be masked. This explains why a cross between a true-breeding tall plant and a true-breeding short plant resulted in all tall offspring in the F1 generation.
Unit Factors in Pairs
This postulate states that genetic characters are controlled by "unit factors" that exist in pairs within individual organisms. We now know these unit factors as genes and the different versions as alleles. A diploid organism inherits one factor (allele) from each parent, creating a pair.
Unit factors in Pairs
Dominance/Recessiveness
Segregation
Independent assortment
What are the 4 postulates of Mendel
Hide one expression
Experiments confirmed that hybrids ____ ____ ______ of a trait, which reappears when hybrids are self-crossed.
Elementen
Mendel speculated that each _________ was packaged in a separate gamete
Law of segregation
is Mendel's idea that elementen separate in the gametes.
Mendel's First Law- Segregation
Reflects the action of chromosomes and the genes they carry during meiosis.
Homozygous
carry same alleles (TT or tt)
Heterozygous
carry different alleles (Tt)
Genotype
organism's alleleles
Phenotype
outward expression of an allele combination
Wild Type
most common phenotype (recessive or dominant)
Mutant phenotype
variant of a genes expression that arises when the gene undergoes mutation.
Mendel were able to observed the events of meiosis.
Two copies
_____ ______ of a gene separate with the homologs that carry them when a gamete is produced.
At fertilization
gamete's combine at random
Mendels law of segregation Done
Illustrate Mendels law of Segregation
Reginald C. Punnett.
Who devised a simple visualization on how genes in gametes join if they are on different chromosomes.
Punnett square
The genotypes and phenotypes of all potential offsprings are ascertained by reading the entries.
Test Cross
Mendel devised a rather simple method to infer alleles present in parental gametes based on the observation of offspring phenotypes.
A test cross
Mendel distinguished the "uppercase letter T, uppercase T" from "uppercase T, lowercase t" tall plants with?
Rare
Single-gene disorder are?
influenced by other genes and environmental factors.
Phenotypes associated with single genes are
Families
In ________ the probability can be deduced by knowing how the affected person is related to a family member.
Cystic fibrosis
Some single-gene diseases have modes of inheritance, such as _______ ______
Mode of inheritance
are the patterns in which single-gene traits and disorders occur in families.
autosomal dominant
Huntington's disease is ______ ________, which affects both sexes and appears in every generation.
autosomal recessive
Cystic fibrosis is ______ ______ which affects both sexes and can skip generations through carrier.
Illustration DOne
Illustrate the Single gene inheritance of autosomal dominant and recessive.
True
People differ in the amount of melanin and number of melanosomes. (True or false)
surface of the back of the iris
The _____ ___ ____ ___ ___ __ ___ contributes to the intensity of eye color.
OCA2
confers eye color by controlling melanin synthesis.
HERC2
controls expression of the OCA2 gene.
Albinism
No gene // No Gene =
Blue eyes
Recessive '// Recessive =
Brown Eyes
Dominant // Recessive or Dominant // Dominant =
Blue Eyes
Brown eyes + HERC2 Recessive // Recessive =
Mode of inheritance
Rules that explain the common pattern of single-gene transmission.
-Determining gene is on an autosomes or on a sex chromosomes.
-Alleles is recessive or dominant
Passing of a trait depends on whether
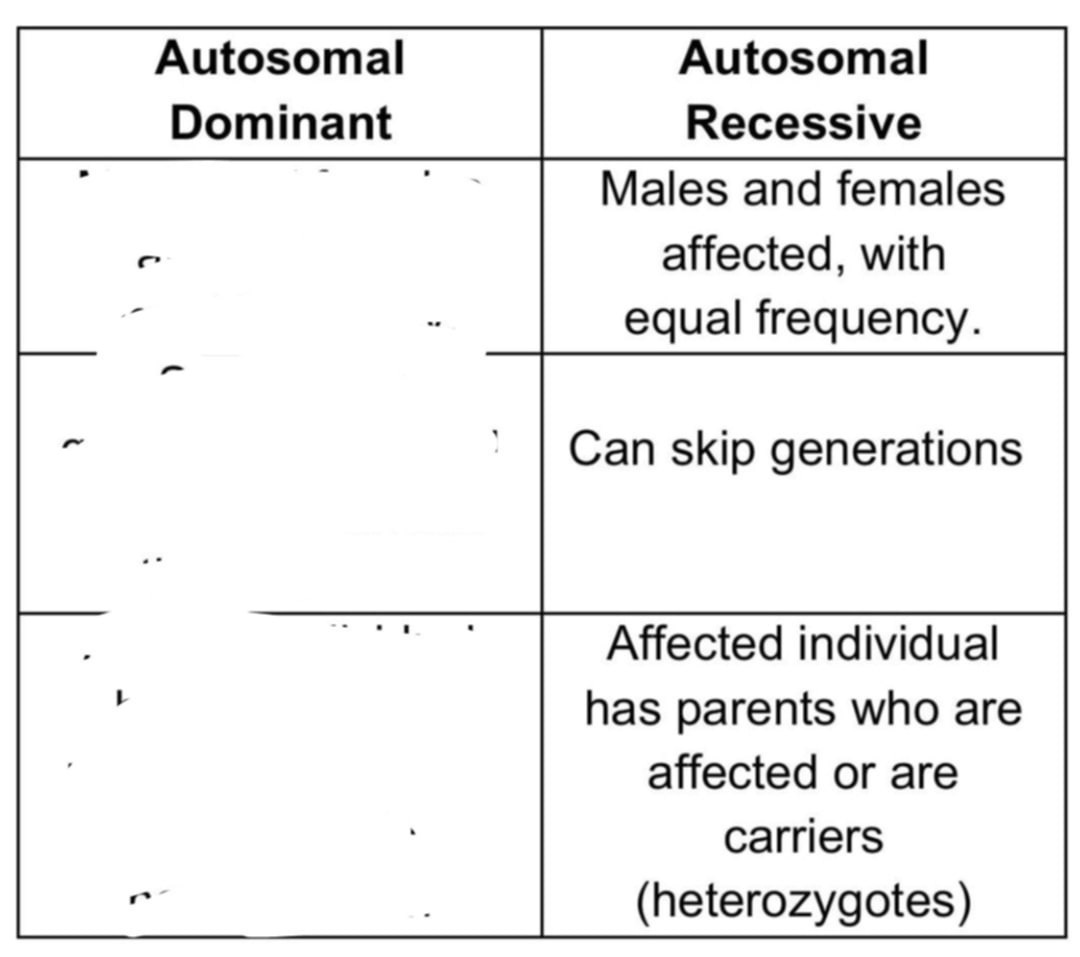
-Males and females affected, with equal frequency.
-Can skip generations
-Affected individual has parents who are affected or are carriers (heterozygotes)
Complete the missing information

-Males and females affected, with equal frequency.
-Successive generations affected until no one inherits the mutation.
-Affected individual has an affected parent unless he or she has a de novo mutation
Complete the missing information
Done illustration of mode of inheritance
Illustrate the mode of inheritance
List all genotypes and phynotypes for the trait.
- Determine the genotypes of the parents
-Derive possible alleles in gametes.
-Unite ganetes in all combinations to reveal all possible genotypes.
In solving genetic problems you must?
• Considers two genes on different chromosomes.
• The inheritance of one does not influence the chance of inheriting the other.
• Two genes that are far apart on the same chromosome appear to independently assort.
o Numerous crossovers take place between
them.
Mendel's Second Law- Independent Assortment:
Illustration Done for independent assortment
Illustrate mendel’s second law of independent assortment
Illustration Done for punnet square
Illustrate Mendel’s law of independent assortment using punnet square
Product rule
The probability of simultaneous independent events equals to the product of their individual probabilities.
Product rule?
Predicts the chance of parents with known genotypes to produce an offspring of a particular genotype.
Pedigree
are symbolic representations of family relationships and the transmision of inherited traits.