Chapter 1: Measurements and Units
- Physical Quantity is a ==quantity that can be measured==. It consists of a numerical magnitude and a unit.
Numbers and Units
Prefixes for SI units
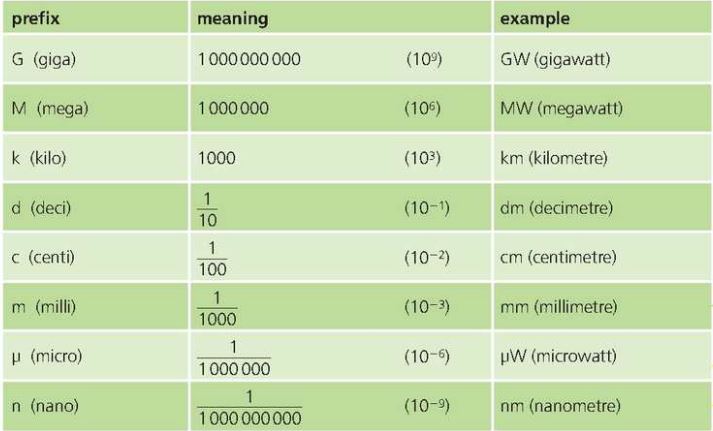
Powers of 10

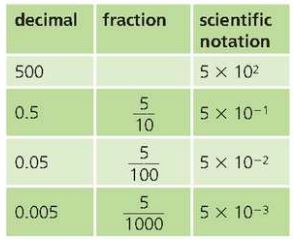
Scientific Notation
- Numbers written using powers of ten are in scientific notation or standard form.
- For example;
 System of Units
System of Units
SI Units
- Are set ==systematic international units,== for measuring mass, time, and other base units and derived quantities.
Mass
- Is the ==measure of the amount of substance in an object.==
- Has the following effects:
- all objects are attracted to the Earth. The greater the mass of an object, the stronger is he Earth’s gravitational pull on it.
- all objects resist attempts to make them go faster, slower, or in a different direction. The greater the mass, the greater is the resistance to change in motion.
- SI base unit is kilogram (kg).
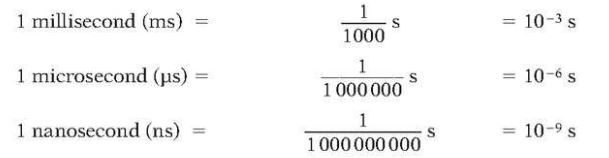
Time
- SI base unit is second (s).
- Following are some of other units for second:
 Length
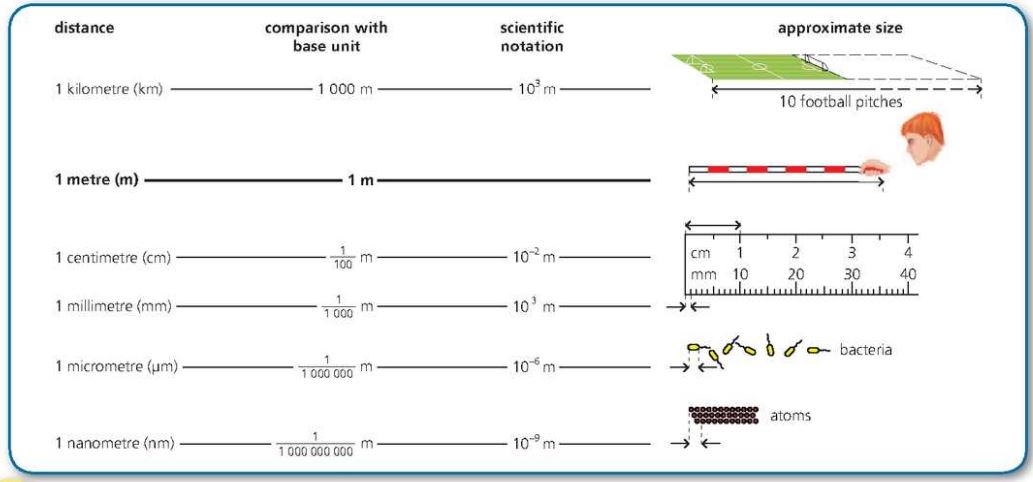
Length
SI base unit is metre (m).
Measuring Length and Time
Measuring Length
- Ruler can be ==used to measure small distances== of a few centimetres (cm).
- They are able to measure to the nearest millimetre (mm).
- Can measure upto one metre.
- Example of usage:
- height of the table
- Micrometer is ==used to measure objects that are too small to be measured== with vernier calipers
- Gives a precision of 0.01 mm
- Can measure measurements of less than 25 cm.
- Example of usage:
- diameter of a wire
- Vernier Calliper is a ==useful tool for measuring both internal and external diameters==.
- They are able to measure to a precision of 0.01 cm.
Measuring Time
- Time intervals of many seconds or minutes can be ==measured using a a== ==stopwatch.==
- Some instruments have analogue or a digital display.
Volume and Density
Volume
- It is the quantity of space an object takes up.
- It’s SI unit is cubic metre (m^3).
Density
- It is the ==quantity of mass per unit volume of a substance.==
- Formula:
- Density= Mass/Volume
- ρ=m/v
- ρ is a greek letter ‘rho’ .
- (both equations are same, written in different ways; i.e first one is the word equation and the other one is symbolic equation.
- SI unit of density is kilogram per cubic metre (kg m^-3).
- Objects that are %%less dense than water will float on water; and objects that are denser than water will sink.%%
Measuring Volume and Density
Measuring Volume
Liquid
- Its volume ==can be measured using a measuring cylinder.==
- Most cylinders have scale marked in millilitres (ml) or cubic centimetres (cm^3).
Regular Solid
- If an object has a simple shape, its volume can be calculated through formula. For example:
- volume of a regular block = length x width x height
Irregular Solid
- ==If the shape of the object is too awkward to calculate its volume, then immerse the object in a measuring cylinder filled with water and then calculate the increase in water level. This value will be the volume of the object.==
Measuring Density
Once volume of the object is obtained through one of the above methods suitable, find the mass of the object using a balance.
Following is one of the example:

Checking the mass and density of a liquid
An easy method of finding the density of a liquid is by using a small float called hydrometer.
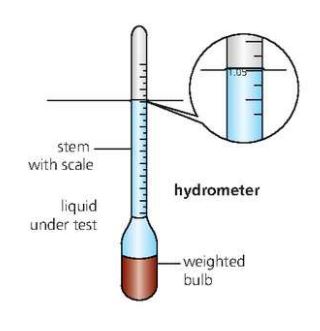
The relative density on a hydrometer indicates the ^^relative density^^ of the liquid.
Checks like these are important in some production processes.