Esophagus
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
What structures does an upper endoscopy (EGD) include?
Mouth → esophagus →
stomach → duodenum
What structures does a flexible sigmoidoscopy capture?
rectum and variable portion of the L colon
What structure does a colonoscopy capture?
colon
What is the term for difficulty swallowing?
dysphagia
What is the term for a sharp substernal pain on swallowing?
odynophagia
what is the term for the feeling of substernal burning often radiating to the neck- due to reflux of acidic material into the esophagus?
heartburn
Oropharyngeal dysphagia originating from oral or pharyngeal region:
drooling, spillage of food from the mouth, inability to chew or initiate swallowing, or dry mouth- can localize to cervical area
oral origin
Oropharyngeal dysphagia originating from oral or pharyngeal region:
sense of the bolus catching in the neck, the need to swallow repeatedly to clear food, coughing or choking during meals, dysphonia, and can localize to suprasternal notch
pharyngeal origin
What is the diagnostic tool of choice for evaluating oropharyngeal dysphagia?
videoesophagography
What are some causes of mechanical esophageal dysphagia?
Schatzki ring, peptic stricture, esophageal cancer, eosinophilic esophagitis
What are some causes of motility disorder esophageal dyphagia?
achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm, systemic sclerosis, ineffective esophageal motility
Mechanical or motility disorder esophageal dysphagia:
solids worse than liquids
mechanical
Mechanical or motility disorder esophageal dysphagia:
solids AND liquids
motility disorder
What is a first line diagnostic study of choice for esophageal dysphagia because it can help differentiate between mechanical and motility disorders?
barium esophagography
What diagnostic tool helps with direct visualization, biopsies, and therapeutic?
endoscopy
What diagnostic tool measures peristalsis and contractility of sphincters?
esophageal manometry
What diagnostic tool aids in the assessment of esophageal acid or nonacid reflux?
pH/impedance testing
What esophageal issue has thin, diaphragm-like membranes of squamous mucosa seen in the mid to upper esophagus that occurs in esophagitis and iron deficiency anemia (Plummer-Vinson syndrome)?
esophageal webs
What esophageal issue has smooth, circumferential, thin mucosal structures located in the distal esophagus at the squamocolumnar junction commonly associated with hiatal hernias?
esophageal rings (Schatzki rings)
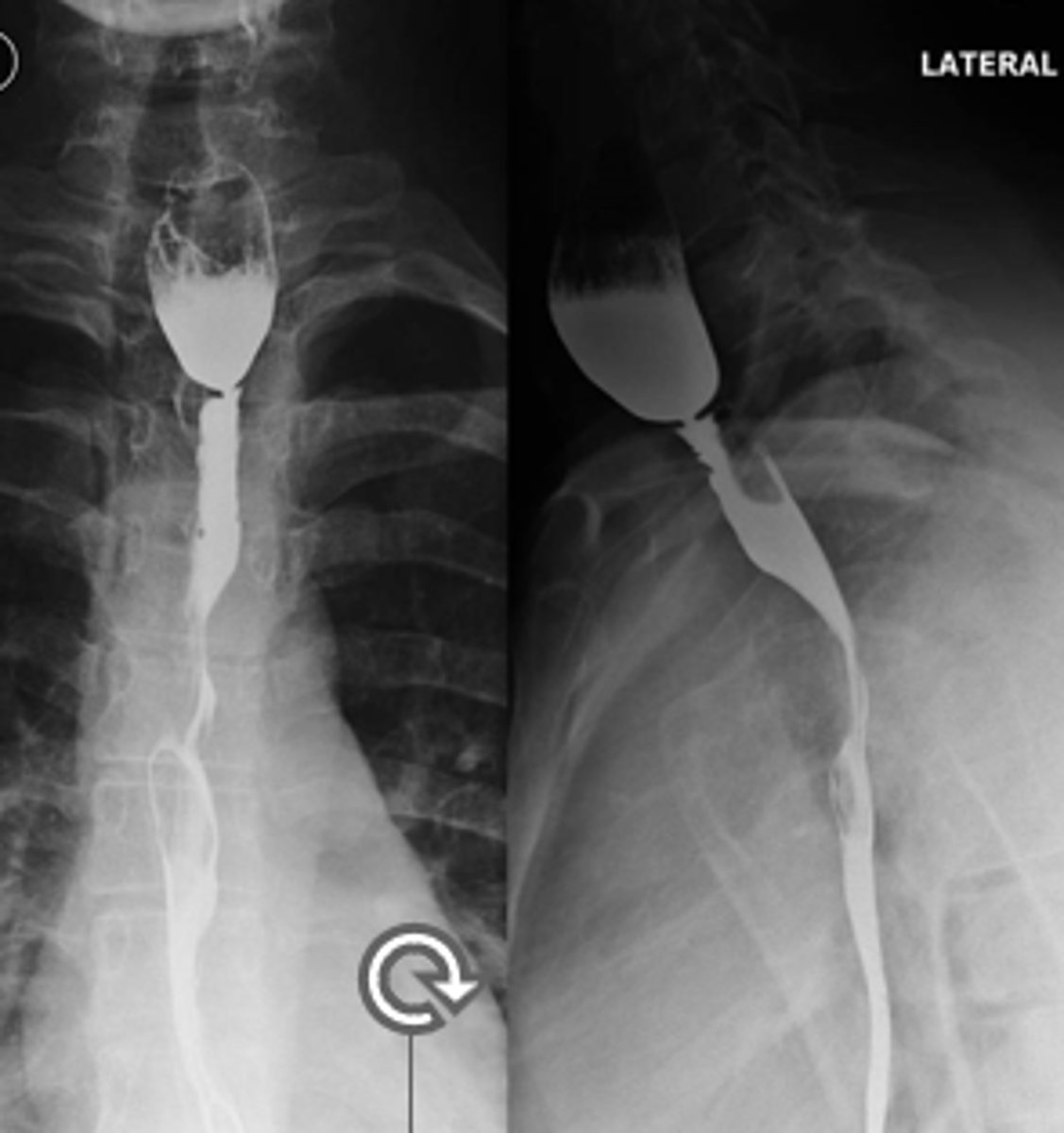
A pt presents with GERD like symptoms (solid food dysphagia). Upon taking a History you find out he has iron deficiency anemia. You decide to do a barium swallow -- you see thin, diaphragm like membranes of squamous mucosa in the mid to upper esophagus.
---- what is the likely dx and how are you treating this pt?
esophageal webs
tx: esophageal dilation or electrosurgical incision with long term PPI therapy
A pt presents with GERD like symptoms (solid food dysphagia). Upon taking a History you find out he recently had a hiatal hernia. You decide to do a barium swallow -- you see smooth, circumferential, thin mucosal structures located in the distal esophagus at the squamocolumnar junction
---- what is the likely dx and how are you treating this pt?
esophageal rings (schatzki)
tx: esophageal dilation or electrosurgical incision with long term PPI therapy
What are the diagnostic tools to aid in diagnosing esophageal webs and rings?
barium swallow (esophagram)
EGD
How do you treat esophageal webs and rings?
Esophageal dilation (may need multiple) or electrosurgical incision
Long-term PPI therapy
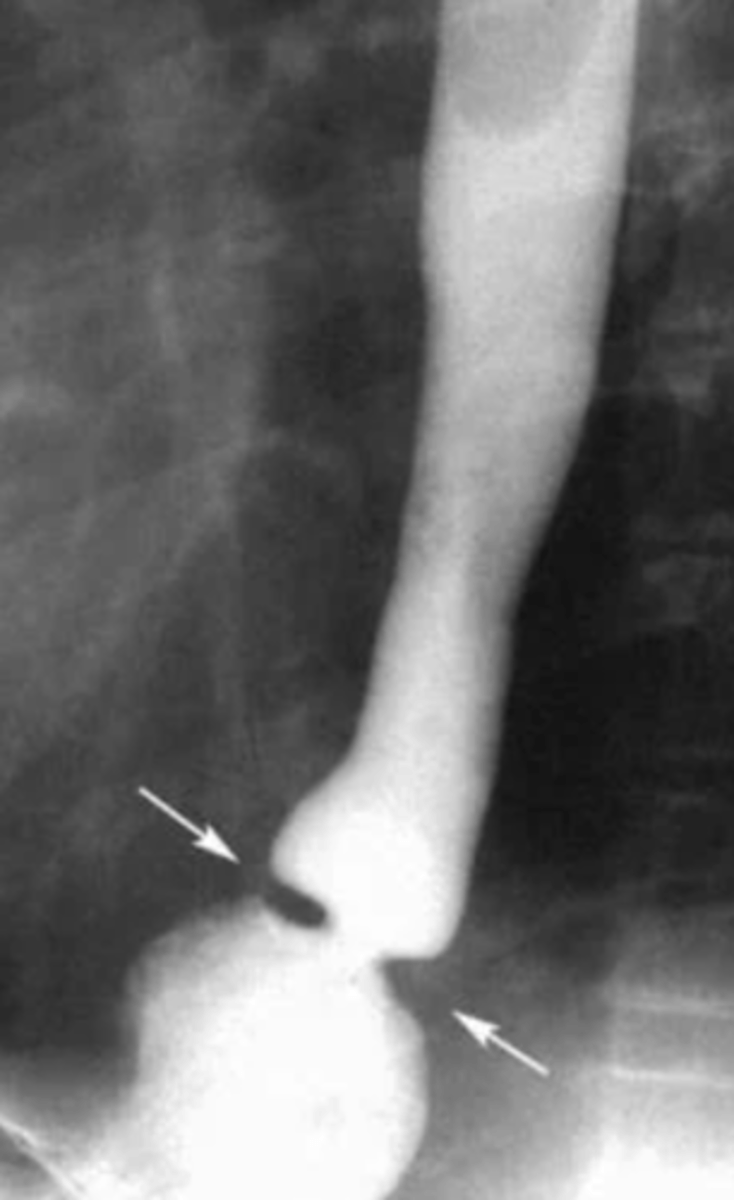
What occurs due to a protrusion of the pharyngeal mucosa at the pharyngoesophageal junction?
zenker diverticulum
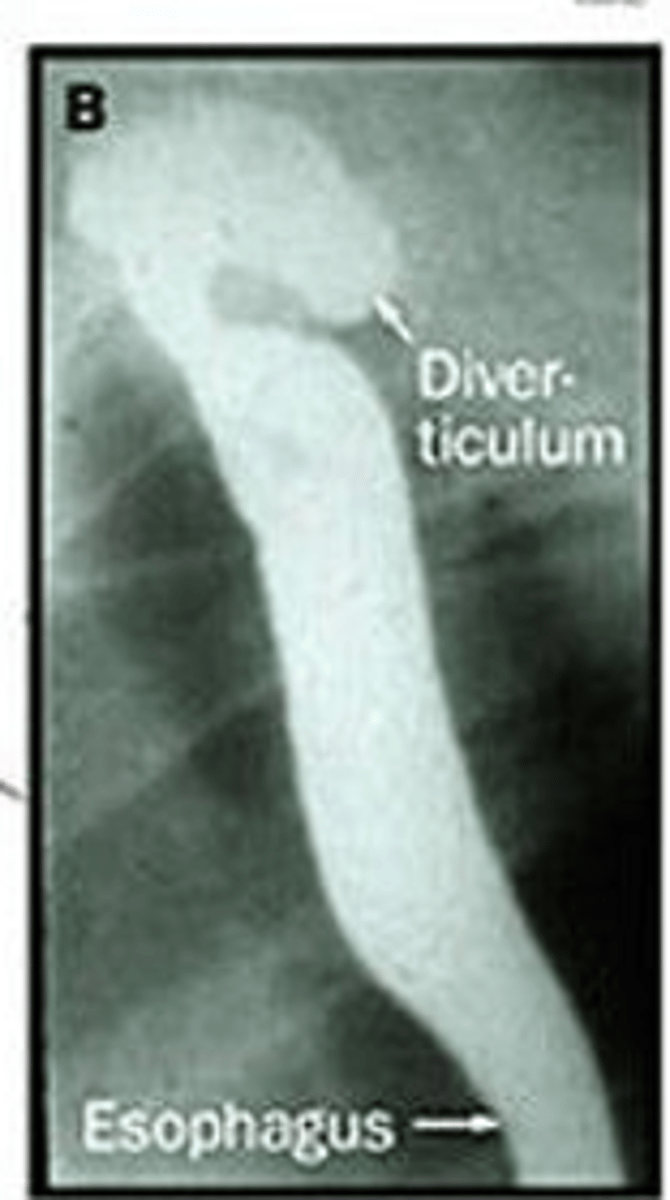
A pt presents with oropharyngeal dysphagia and cough. He was put in observation and as time went he experienced nocturnal choking, gurgling in the throat, and protrusion of the neck. The imaging is shown. -- what is the likely dx?
zenker diverticulum
What are some complications that can arise from zenker diverticulum?
aspiration pneumonia, bronchiectasis, and lung abscess
Symptomatic patients with suspected zenker diverticulum-- require what treatment?
esophageal myotomy
What is the tx for zenker diverticulum?
symptomatic- esophageal myotomy
asymptomatic- observe
What is the MC congenital esophageal anomaly?
esophageal atresia
What occurs when there is a failure of fusion between the proximal and distal esophagus?
esophageal atresia
What is the MC esophageal atresia?
distal
What is the tx for esophageal atresia?
surgically corrected within the first few days of life
What are some complications that can arise from esophageal atresia?
Dysphagia from anastomotic strictures
Absent peristalsis --> Reflux
What esophageal motility disorder occurs due to the loss of peristalsis in the distal two-thirds (smooth muscle) of the esophagus + impaired relaxation of the LES-- causing idiopathic degeneration of Auerbachs plexus ?
achalasia
The esophageal motility disorder- achalasia occurs due to idiopathic neuronal degeneration of what?
Auerbachs plexus
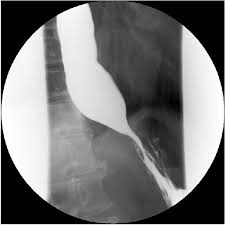
A pt presents with gradual onset of dysphagia for solid foods AND liquids. She complains of nocturnal regurgitation and cough. She also complains of substernal discomfort/fullness after meals. There is impaired LES relaxation. Upon diagnostic testing of a barium study you see esophageal dilation with loss of peristalsis and a "birds beak" tapering of the distal esophagus ------ what is the likely dx?
achalasia
If you see "birds beak" tapering of the distal esophagus on a barium study--- what is the dx?
Achalasia
What is the 1st test when suspecting achalasia and what key sign will you see?
barium esophagram
•Esophageal dilation, loss of peristalsis, poor emptying, smooth/symmetric “bird’s beak” tapering of distal esophagus
What is the GS for confirming the diagnosis of achalasia and what will you see?
manometry
Absence of normal peristalsis and impaired GEJ relaxation after swallowing
What esophageal motility disorder occurs because of abnormal esophageal contractions with normal LES relaxation and presents with intermittent and non-progressive dysphagia (solid foods and liquids) ?
diffuse esophageal spasm (DES)
What are some possible treatments for Achalasia?
Botulinum toxin injection
Pneumatic dilation
Surgical Heller cardiomyotomy
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM)
If you see "corkscrew esophagus" or "rosary beads esophagus" on a barium study-- what is the likely dx?
diffuse esophageal spasm (DES)
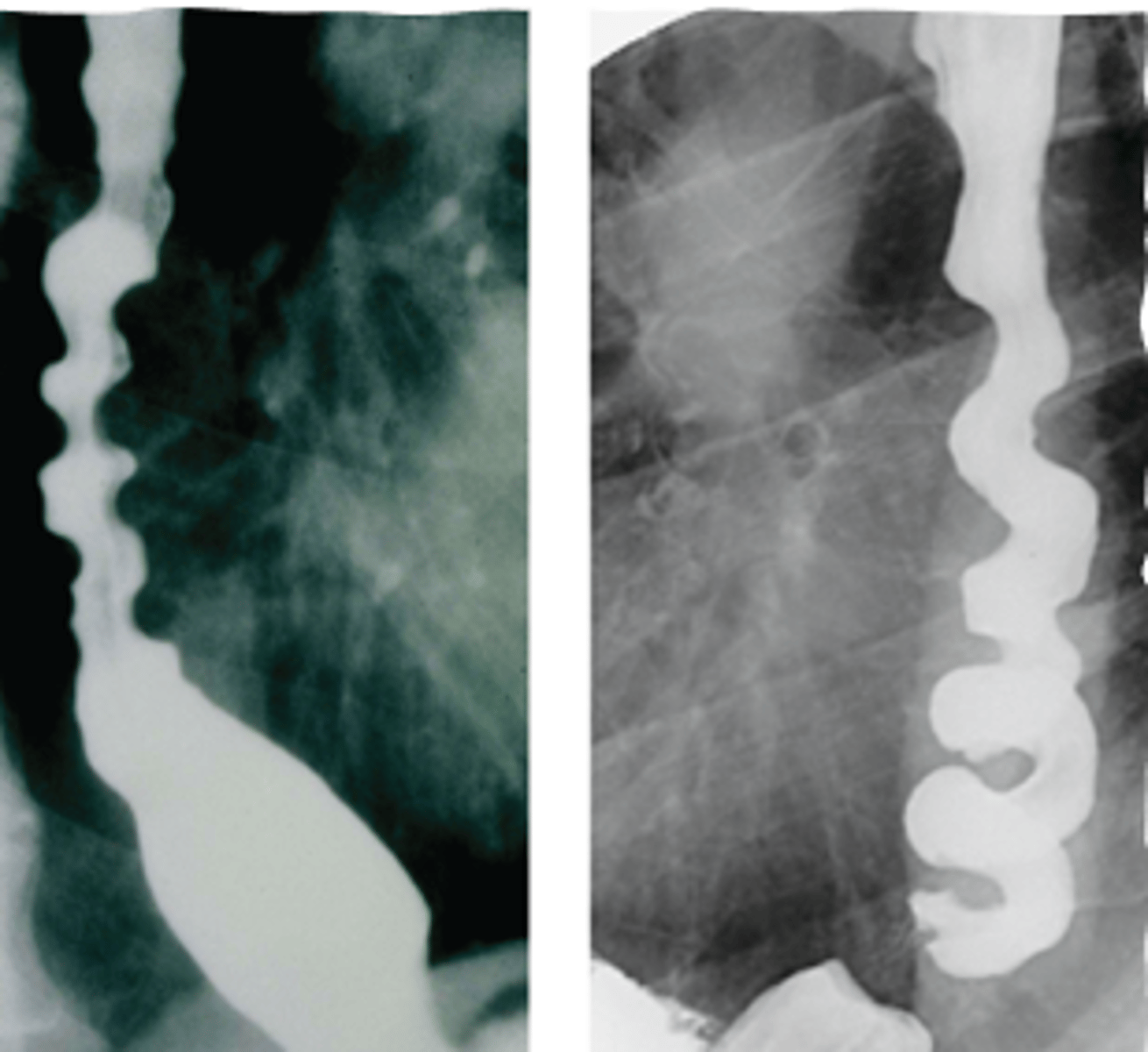
A pt presents with intermittent and nonprogressive dysphagia of solid foods and liquids and chest pain. Upon taking the history she stated to have a lot of stress recently. There is normal LES relaxation. A barium study if preformed and the image is shown "corkscrew esophagus"--- what is the likely dx?
diffuse esophageal spasm (DES)
What is the treatment for DES (diffuse esophageal spasm)
Instruct pt to eat more slowly and take smaller bites, maybe have a warm liquid at the start of a meal
Trial of PPI for 4-8wks
What occurs due to protrusion of a part of the stomach upward through the opening in the diaphragm?
hiatal hernia
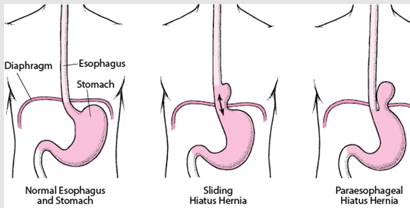
What type of hernia is a sliding hiatal hernia?
I
What type of hernia are all subtypes of paraoesophageal hernias?
II, III, IV
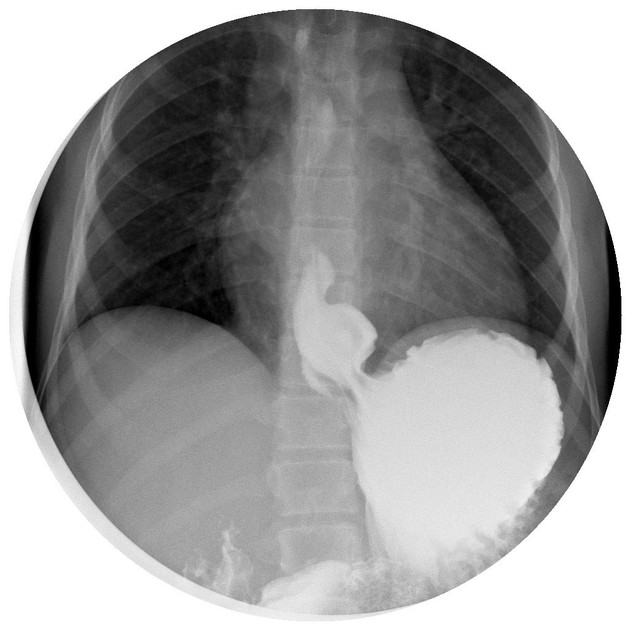
A pt presents with pain/pressure in their lower chest after eating and then vomiting. Upon PE you find decreased breath sounds with bowel sounds in the L chest. A CXR shows air fluid level behind the cardiac shadow and an upper GI contrast study shows cephalad displacement of the stomach---- what is the likely dx?
hiatal hernia
What is the most useful diagnostic test for hiatal hernias because it demonstrates the herniation pattern?
endoscopy
What is the treatment for hiatal hernias?
asymptomatic- no tx
symptomatic- WL, diet, avoidance of tight clothing, elevated sleeping position, PPI
persistent/complicated- surgery
What type of GERD occurs with:
hypotensive peristalsis (<30mmHg), failed peristalsis, impaired salivation
abnormal clearance
What type of GERD occurs with:
gastroparesis and outlet obstruction
delayed gastric emptying
A pt presents with complaints of heartburn that usually occurs an hour after eating. She states it usually occurs with spicy foods and certain types of alcohol. She also has symptoms of dysphagia, regurgitation, and a chronic cough. --- What is the likely dx?
GERD
What is the tx for GERD?
Trial of H2RA or PPI for 4-8 weeks
What are some diagnostic tools for GERD?
not warranted with typical symptoms, if red flag or persistent symptoms SCOPE them and do more testing
Standard screening for adults with GERD is NOT recommended, unless 1 or more risk factors for adenocarcinoma are present. What are the risk factors?
-GERD > 5 years w/ age >50
-obesity
-white race
-male sex
-tobacco use
-family hx
What are red flag symptoms?
Dysphagia, odynophagia, weight loss, iron deficiency anemia, bleeding, vomiting*******
What is the tx for mild/intermittent GERD?
Lifestyle modifications (eating smaller meals, elimination of acidic/trigger foods, WL, avoid lying down within 3 hrs after meals)
PRN antacids or H2RAs
Long term use of PPIs has an increased risk for what?
infectious gastroenteritis (including C difficile), SIBO, and micronutrient deficiencies (iron, vitamin B12, magnesium)
What is the tx for persistent/complicated GERD?
Initial: daily PPI
Long term (SCOPE THEM FIRST): PRN PPI or try H2RA
What is the tx for unresponsive GERD?
compliance?
--->
endoscopy/manometry/pH impedance testing
-->
Dx of "functional heartburn:
A pt presents with hoarseness, cough, and complaints of sleep disturbances. Upon taking a hx-- pt has asthma-- what is the likely dx and how are you treating?
extraesophageal GERD
tx: trial 2x daily PPI for 2-3mo
What are some surgical treatment options for GERD?
Fundoplication
Magnetic sphincter augmentation (MSA)
What are two possible complications of GERD?
Barret esophagus
and
Peptic Strictures
What complication of GERD occurs due to an injury in the esophageal squamous epithelium → normal epithelium → metaplastic columnar epithelium?
barrett esophagus
What can occur due to an increased risk of dysplasia in barrett esophagus?
esophageal adenocarcinoma
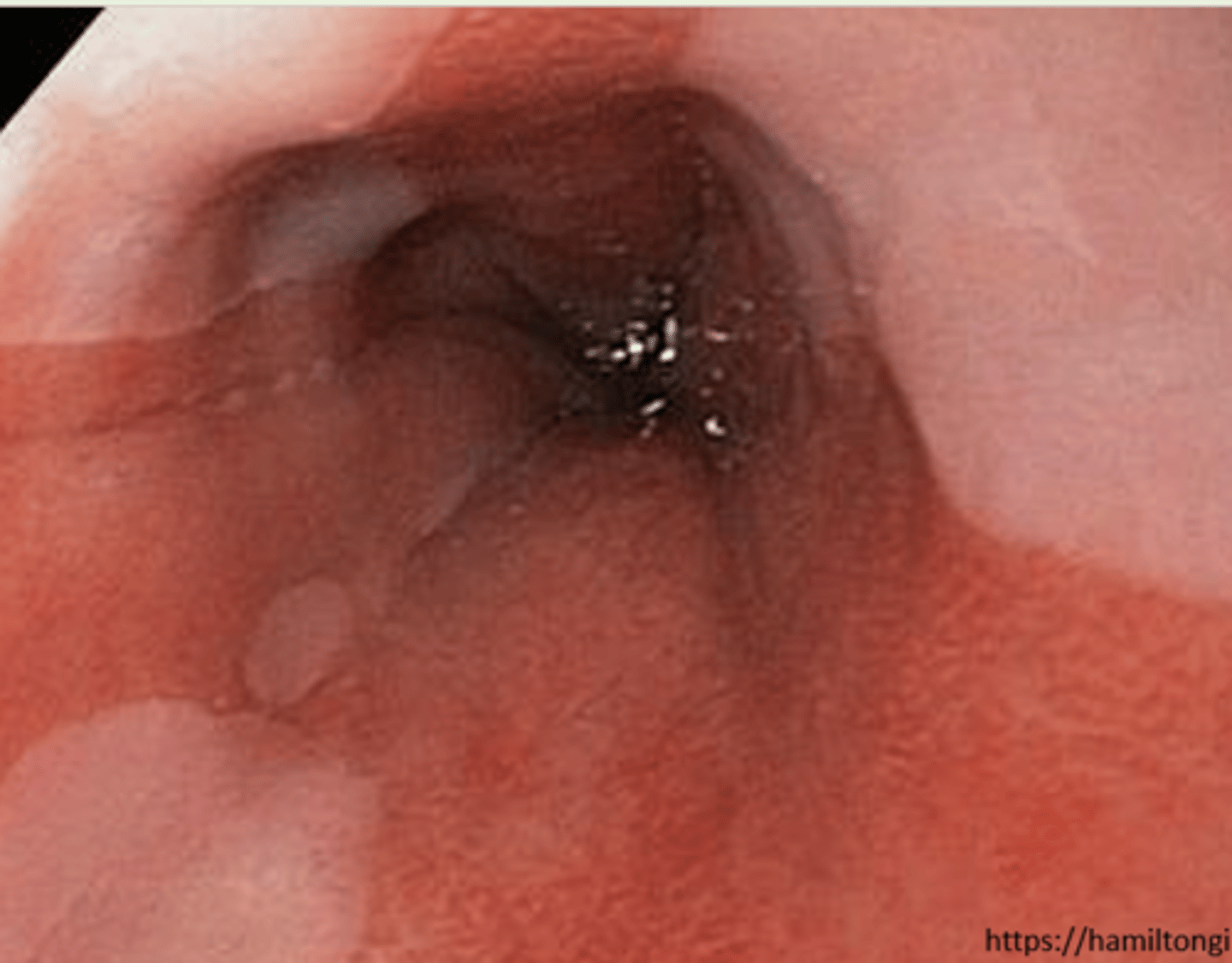
A pt presents with a history of GERD and worsening symptoms. Upon doing an endoscopy you see circumferential orange, gastric type epithelium extending > 1cm from the GEJ---- a biopsy would confirm what likely dx?
barrett esophagus
What are the possible treatments for barretts esopagus?
PPI (long term)
no dysplasia- endoscopy every 3-5yrs
dysplasia- endoscopic therapy
What GERD complication occurs in 5% of patients with esophagitis, typically at the GEJ and is treated with balloon dilation?
peptic strictures
A pt with a history of GERD presents with gradual development of solid food dysphagia. You decide to do an endoscopy with biopsy and diagnose the pt with Peptic stricture. --- How are you treating them?
Balloon catheter dilation
Long term PPI therapy
An immunosuppressed pt presents with dysphagia and odynophagia. Upon endoscopy w/ biopsy and brushing, you see diffuse, linear, yellow-white plaques adherent to the mucosa -- what is the likely dx?
candida esophagitis
An immunosuppressed pt presents with dysphagia and odynophagia. Upon endoscopy w/ biopsy and brushings, you see small, deep ulcerations--- what is the likely dx?
herpes esophagitis
An immunosuppressed pt presents with dysphagia and odynophagia. Upon endoscopy w/ biopsy and brushing, you see one to several large, shallow, superficial ulcerations?
CMV esophagitis
How do we treat infectious esophagitis: candida, CMV, and herpes strains?
Candida: PO Fluconazole, x14-21 days; Itraconazole suspension, PO Voriconazole, or IV Caspofungin if refractory
CMV: IV Ganciclovir (myelosuppression)àPO Valganciclovir once symptoms resolve, x3-6 weeks; IV Foscarnet (AKI)
Herpes: PO Acyclovir or Valacyclovir, x14-21 days; IV Foscarnet if refractory (AKI)
What is the diagnostic tool of choice for infectious esophagitis?
endoscopy --> biopsy and brushings
What are the MC pathogens of infectious esophagitis?
Candida albicans, herpes simplex, and CMV
What are MC causes of pill induced esophagitis?
NSAIDs, biphosphonates, doxy, and tetracycline
A pt presents with retrosternal chest pain, odynophagia, dysphagia and complaints of taking a pill 4 hours ago. -- what is the likely diagnostic tool, diagnosis, and treatment for this pt?
endoscopy, pill- induced esophagitis
Tx: 4 ox water and remain upright for 30 min
What type of esophagitis occurs due to a food or environmental antigens that stimulate an inflammatory response?
eosinophilic esophagitis
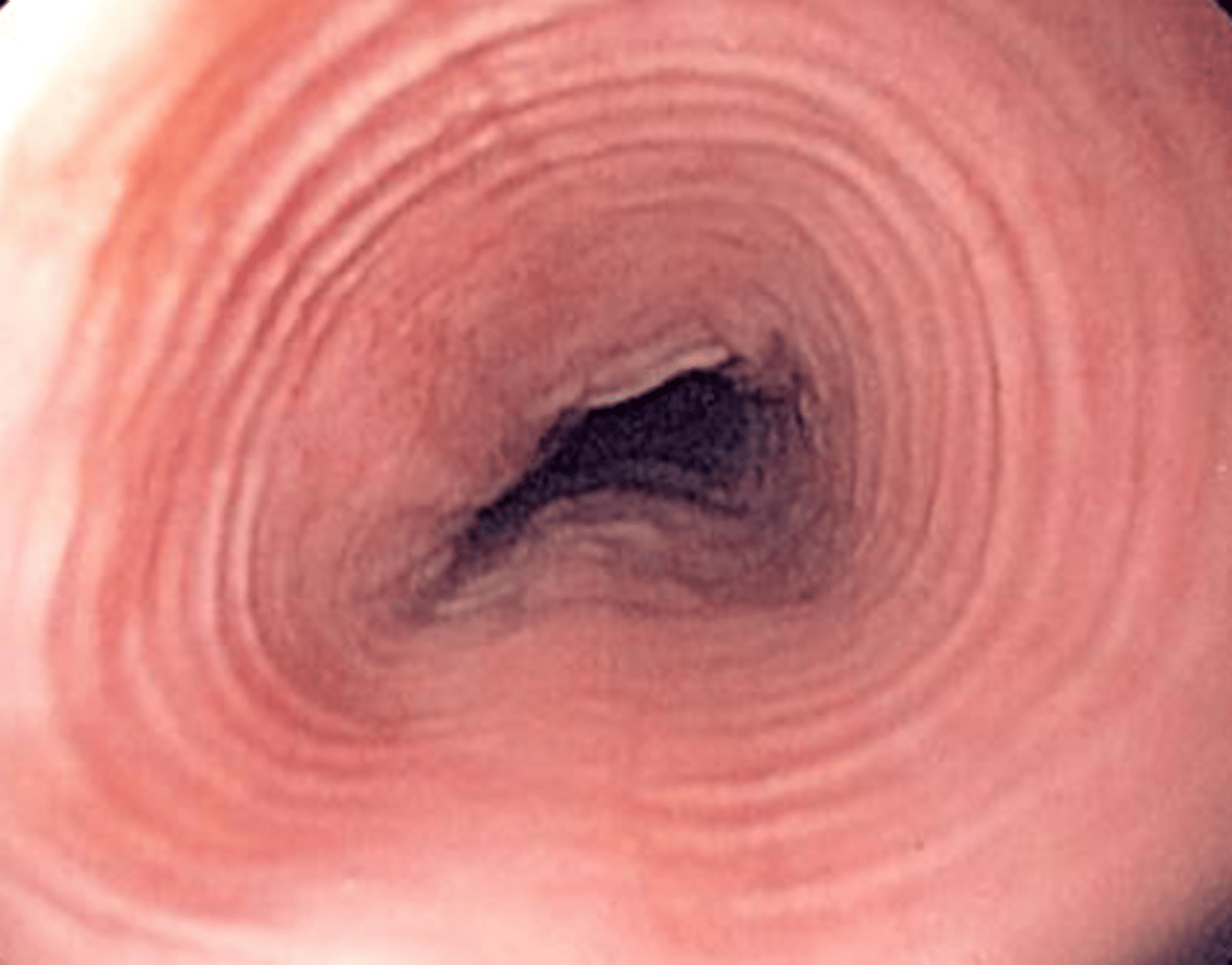
A pt presents with dysphagia for solid foods, heartburn, and chest pain. Upon Hx you find he has allergies. You decide to do an endoscopy with biopsy to confirm the dx.--- you see edema, concentric rings, exudates, furrows (vertical lines), and strictures-- labs show elevated IgE levels--- what is the likely dx?
eosinophilic esophagitis
What is the treatment of choice for eosinophilic esophagitis?
PPI PO twice daily
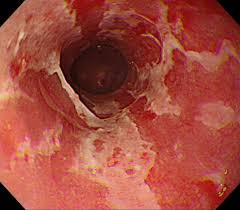
A pt presents with odynophagia and dysphagia. Taking the Hx you find she is a current breast cancer pt and completing radiation. Upon endoscopy you see: mucosa that is erythematous, edematous, and friable --- what is the likely dx?
radiation esophagitis
What is the tx for radiation esophagitis?
supporative: PPI, viscous lidocaine, dietary modification
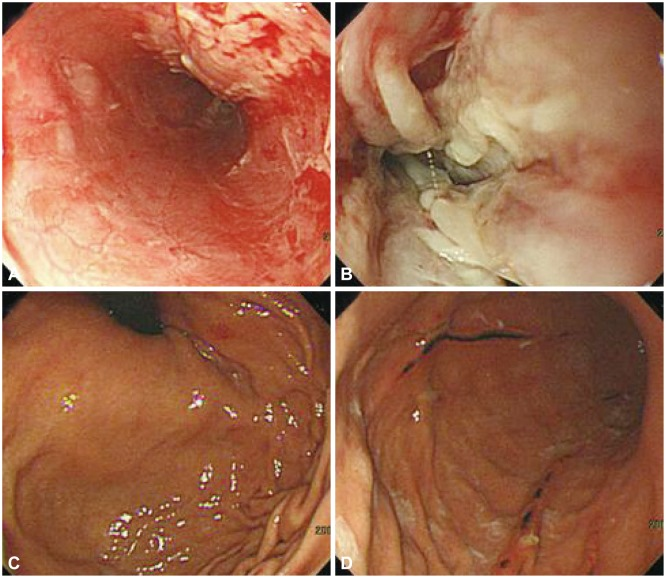
What type of esophagitis is due to a caustic injury due to the ingestion of chemical agents, mainly alkaline substances that in severe cases can cause esophageal perforation, bleeding, and death?
corrosive esophagitis
What is the diagnostic tool for corrosive esophagitis?
early endoscopic eval
What is the treatment choice for corrosive esophagitis?
supporative
NO corticosteroids
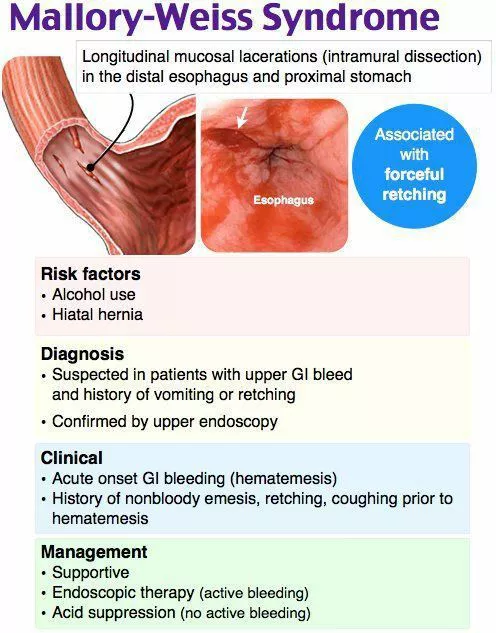
What occurs due to a mucosal tear at the gastroesophageal junction usually due to sudden raise in transabdominal pressure--- history of retching, vomiting, or straining?
mallory weiss syndrome
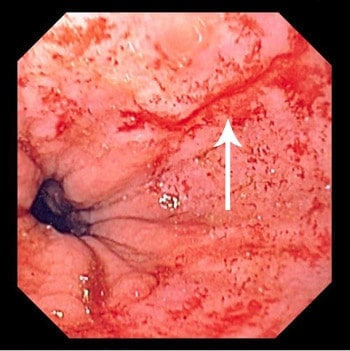
A pt presents with complaints of dark red blood from the rectum (hematemesis with melena). Upon taking a history there was recent violent vomiting due to alcohol. You scope them and find a small linear mucosal tear just below the GEJ---- what is the dx?
mallory weiss syndrome
What is the treatment for mallory weiss syndrome?
resuscitate with fluids and blood transfusion
- endoscopic therapy
- Epi injection, cautery, mechanical compression
Wat are some causes of esophageal perforation?
endoscopy, NGT placement, stricture site during dilation, forceful vomiting or retching, corrosive esophagitis, neoplasms
What type of esophageal perforation has these signs and symptoms:
odynophagia, dyspnea, sepsis, tenderness to palpation of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and crepitation due to the presence of cervical subcutaneous emphysema
cervical
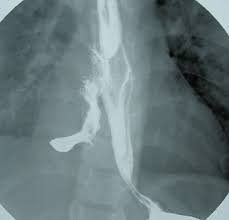
What type of esophageal perforation has these signs and symptoms:
Mediastinal emphysema, mediastinal crackling with each heartbeat may be heard on auscultation especially if the patient is in the left lateral decubitus position (Hamman's sign)
thoracic
What type of esophageal perforation has these signs and symptoms:
epigastric pain with radiation to the shoulder, back pain, inability to lie supine or present with an acute (surgical) abdomen
intra-abdominal
What is the diagnostic tool of choice for esophageal perforation?
gastrograffin and/or barium esophagography CT scan
What are treatments for esophageal perforation?
NGT, BS ABX, prompt surgical drainage of fluid, endoscopic clipping
What are some possible complications with esophageal perforation?
Mediastinitis, necrosis, empyema, sepsis. Very high mortality untreated (100%), 25% of thoracic perforation will die.
What can lead to complete obstruction causing inability to handle secretions and severe chest pain
foreign body and food impaction
How do you treat food impaction?
glucagon 1mg IV
What is the treatment for foreign bodies?
endoscopic removal
Gastric distension, sudden temperature changes, alcohol, and heightened emotion are all benign causes of what?
Hiccups