Econ 13: Ch06 Globalization & Protectionism
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is protectionism?
When limitations are placed on a country to prevent imports from abroad
What are the 3 ways to restrict trade?
tariffs
import quotas
non-tariff barriers
What are Tariffs?
Taxes on imports. Restricts trade and increase prices on imported goods
What are Import Quotas
government-imposed trade restrictions that limit the number/value of goods that can be imported
What are Non-tariff Barriers
barriers against trade, that are different from tariffs
eg. quotas, levies, embargoes, sanctions & other restrictions
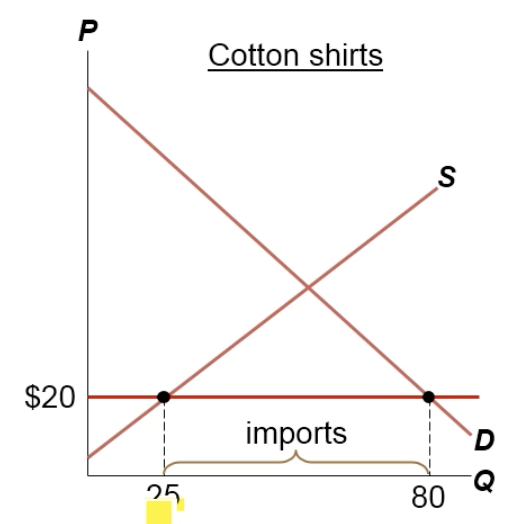
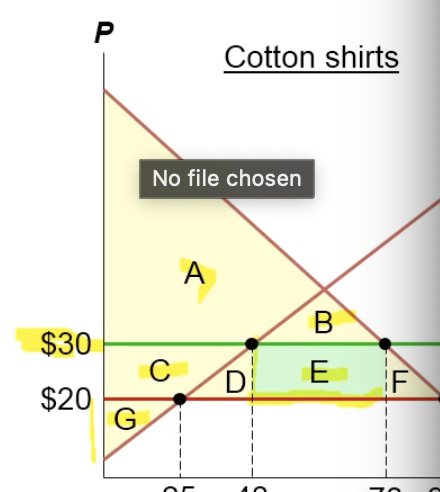
How many imports are there in this cotton-shirt economy?
80 demanded - 25 supplied = 55 imports
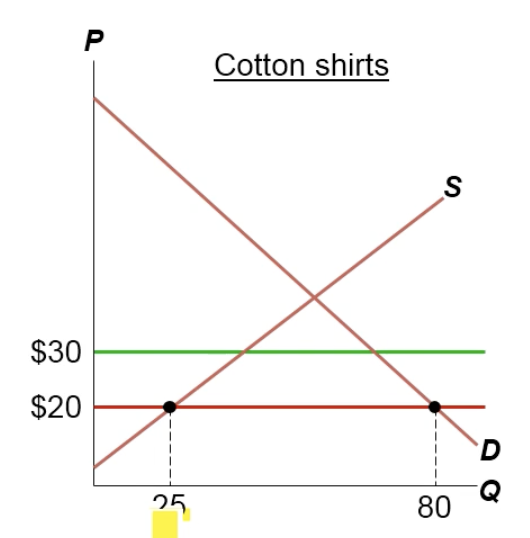
What happens to the imports when taxes are imposed on the cotton-shirt economy?
70 demanded - 40 supplied = 30 imported, taxe lowered imports
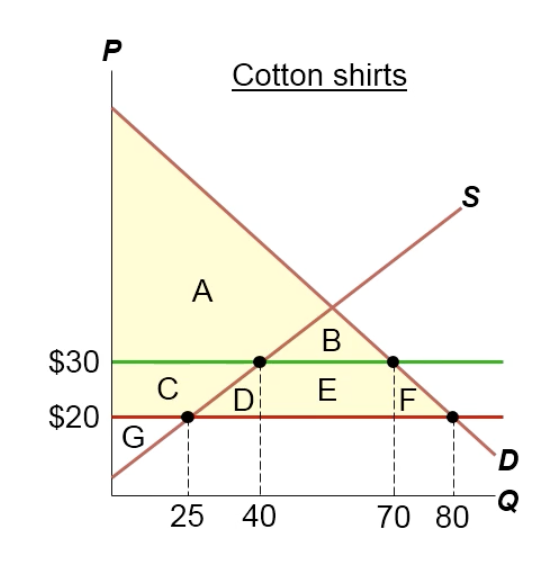
When there’s free trade, what’s CS, PS, & TS?
CS = A, B C D E F
PS = G
TS = A B C D E F G
When taxes are imposed, what’s CS, PS, TS, n dead weight loss?
CS = A B
PS = C. G
TS = A B C E G
Deadweight loss = D & F
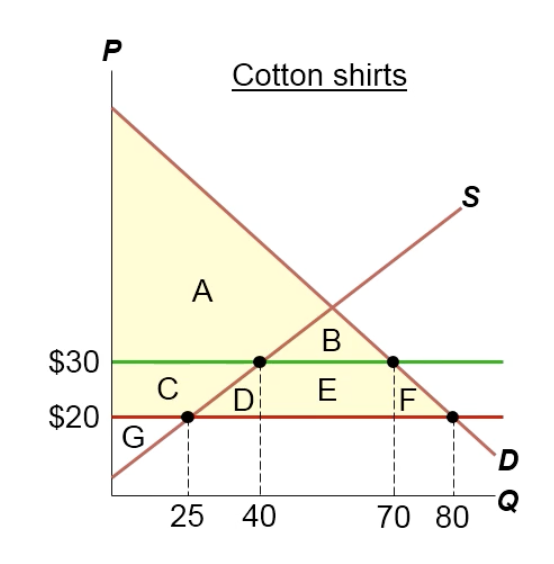
Where’s government income?
E
What is an argument against trade?
Loss of jobs
Why do economists disagree with the argument loss of jobs
But economics disagree, as the unemployment rate has not gone up as the US economy became more open to trade
job loss in one industry is compensated by job creation in another
it’s expensive to save jobs through tariffs and quotas
What happens when tariffs are placed?
They increase the price, making number of exports/imports smaller, making another countries exports/imports smaller, making their prices decrease because of lack of demand.
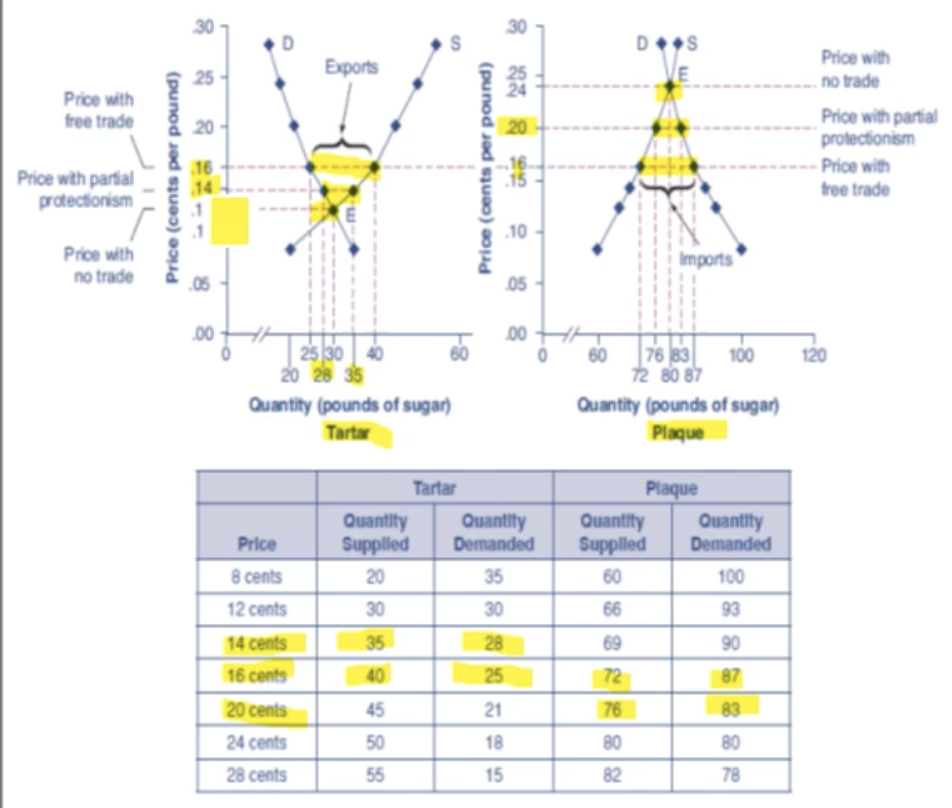
What happens when tariffs are placed on Plaque, the importer?
Plaque is importing goods because the price is below equilibrium, the demand is greater then what is supplied and they want to purchase more for a cheaper price.
When Tariffs are placed, the price increases, supply demanded decreases, supply supplied decreases, overall amount of imports are decreased. Also decreasing Tartar’s exports because they have less demand, making the prices go down
When taxes being placed on Plaque, who wins or losses, conumers and producers, on Plaque and Tartar?
Taxes imposed on Plaque: producers gain, consumers lose
Less demand for Tartar: producers lose, consumers gain
Under free trade: who wins n loses?
Importing countries: producers lose, consumers gain
Exportign countries: producers gain, consumer lose
Under protectionism/tariff: what happens to Importing country, and their consumers
Importing country: sugar farmers of Plaque are able to sell more at a higher price
Consumers who are w/ the tariffed good, they are clearly negative effects. They end p buying a lower quantity of the good and paying a higher price for what they do buy
Under protectionism/tariff: what happens to exporting country, and their consumers?
Exporting country: the Tartar won’t be able to export, and will experience lower prices, producers lose
Consumers wold benefit from these reduced prices
What happens when there is protectionism?
it hurts both countries
the cost to save jobs is high bc of tariffs
there will be a net loss of welfare to both countries (deadweight)
Does trade increase or decrease the number of jobs?
The increase in trade doesn’t have much effect on the number of jobs
there will be a shift in job s away from the industries that don’t have a comparative advantage, and it will be shifted towards those who do
What do economists say about global trade?
global trade will increase the average level of wages bc of increased productivity
but increase in wages may only be in some and losses to others
How is there downward pressure on wages bc of trade?
workers in import competing industries see their wages decrease
it affects low skilled workers
but they still benefit from lower prices because of the imports
What are arguments against labor standards and wages?
labor standards: some workers work in illegal and un-humane conditions
low minimum wage in some countries
child labor
There’s a line in labor practices between what is unpleasent to think about and what is morally wrong
Child labor, morally objectionable
long working hours in poor countries, unpleasent to think abt but good for them to make money
What is the infant industry argument?
Put taxes on small domestic industries so they can be protected from foreign large companies and grow into strong competition, but they normally dont grow
The dumping argument against trade
When prices are set at below the cost of production.
This is to drive out competition and then raise prices
What are anti-dumping laws
to block imports that are sold below the cost of production and impose tariffs that would increase the price
High Environmental Standards
Low-income countries have lower environmental standards.
Shutting off trade won’t make create a cleaner enviorment
What’s the unsafe consumer product?
countries are allowed to set any standards for product safety, but domestic products have to be the same
What’s the national interest argument?
unwise to import certain key products bc the nation could become too dependent and be vulnerable to cutoff
but its better to stockpile reasources
what’s trade conflicts
Countries experience conflict over trade issues
How does the country deal with these conflicts?
The global economy deals w/ trade issues
Global Agreements: World Trade Organization
Regional Agreements: NAFTA/USMCA
What’s the public attitude towards trade?
Pretty high
How is trade policies determined?
administrative agencies w/ government, laws passed
global negotiations thru WTO
The acronym GATT stands for:
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade.
The infant industry argument for protectionism suggests that an industry must be protected in the early stages of its development so that:
a.
it will not be subjected to a takeover from a foreign competitor.
b.
firms will be protected from subsidized foreign competition.
c.
domestic producers can attain the economies of scale to allow them to compete in world markets.
TYPE: Multiple Choice
d.
there will be adequate supplies of crucial resources in case they are needed for national defense.
c