chem midterm study guide (vocab)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/77
Earn XP
Last updated 1:53 AM on 12/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
1
New cards
solid
fixed shape and volume, particles touching, not moving
2
New cards
liquid
fixed volume, unfixed shape, particles touching and moving a little
3
New cards
gas
no fixed volume or shape, particles far apart and moving a lot, not charged
4
New cards
plasma
no fixed volume or shape, particles far apart and moving a lot, charged
5
New cards
**physical property**
anything you can see **without changing** the substance
6
New cards
**physical property ex.**
transparency, boiling point, density, elasticity, malleability, brittleness, melting point
7
New cards
**chemical property**
you can only see by **changing** the substance
8
New cards
**chemical property ex.**
flammability, ability to rust, reactivity with vinegar
9
New cards
**physical change?** (is it reversible?)
when the identity of the substance **doesn’t change (reversible)**
10
New cards
**physical change ex.**
shattering, melting, separating (sand from gravel), dissolving, mixing, evaporating
11
New cards
**Chemical change**
when the identity of the substance **changes (irreversible),** during a chemical reaction
12
New cards
**Chemical change ex.**
rusting, bleaching, cooking, burning, exploding
13
New cards
**extensive property**
**depends on how much matter** there is
14
New cards
**extensive property ex.**
mass, weight, volume
15
New cards
**intensive property**
**doesn’t matter how much matter** there is
16
New cards
**intensive property ex.**
color, combustibility, density, melting point, malleability
17
New cards
5 signs of a chemical reaction
* formation of a gas
* color change/ emission of light
* odor change
* temp change
* formation of a precipitate
* color change/ emission of light
* odor change
* temp change
* formation of a precipitate
18
New cards
**parts of a chemical reaction**
reactant, yield arrow, product
19
New cards
**Law of conservation of mass**
in a closed system, mass cannot be created or destroyed
20
New cards
the 2 classifications of matter
__pure substances__ and __mixtures__
21
New cards
pure substance
only one type of molecule, ex. water or carbon
\
\
22
New cards
compound
a __molecule__ made of different atoms, ex H20 (water)
* can be broken down into molecules using chemical charges
* compounds can be molecular, ionic, or intermetallic
* can be broken down into molecules using chemical charges
* compounds can be molecular, ionic, or intermetallic
23
New cards
element (define, examples)
an __atom__ with specific characteristics, **ex**. hydrogen, iron, copper
* can be metals or nonmetals, can’t be broken down further
* can be metals or nonmetals, can’t be broken down further
24
New cards
mixture
a combo of 2 substances, not chemically bonded
* can be __solutions__ or __heterogeneous__ mixtures
* CAN be separated physically
* can be __solutions__ or __heterogeneous__ mixtures
* CAN be separated physically
25
New cards
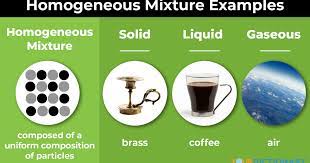
solution (aka homogenous) (how are the molecules distributed? example?)
group of molecules that are **evenly** distributed, **ex**. gasoline, air, soda
26
New cards
heterogeneous mixture
a solution (group of molecules) that is **unevenly** distributed, **ex.** salad dressing
27
New cards
accuracy
“the extent to which a measurement approaches the true value of a quantity “
* **how correct is it?**
* **how correct is it?**
28
New cards
precision
“the extent to which a series of measurements of the same quantity made in the same way agree with each other, not necessarily accurate.”
* **how close together** are your answers? (they don’t have to be right)
* **how close together** are your answers? (they don’t have to be right)
29
New cards
**percent error formula**
\[(experimental - accepted) / accepted\] \* 100
30
New cards
mass
* the **amount of matter** an object contains. Doesn’t change unless you add/remove matter
* find with a balance, use **grams**
* find with a balance, use **grams**
31
New cards
volume (define, what units?)
* the **amount of space** an object occupies
* find with liquid or a ruler, use **mL for liquids** or **cm³ for solids** or **L for gases**
* find with liquid or a ruler, use **mL for liquids** or **cm³ for solids** or **L for gases**
32
New cards
density (define)
* The **compactness** of the molecules or particles of a substance
* more compact molecules = greater density
* more compact molecules = greater density
33
New cards
density formula
**mass**/ volume
\
remember:
* mL – volume
* g – mass
* **g/mL** or**g/cm³** or**g/L**- density
\
remember:
* mL – volume
* g – mass
* **g/mL** or**g/cm³** or**g/L**- density
34
New cards
billiards ball atomic model
small, hard sphere
created by dalton in 1808
created by dalton in 1808
35
New cards
plum pudding atomic model (what? when? who?)
negative electrons in a positive atom
created by thompson in the 1890s
created by thompson in the 1890s
36
New cards
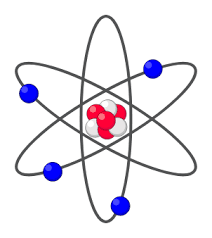
nuclear model (what? who?)
nucleus with electron shell
created by rutherford around 1911
created by rutherford around 1911

37
New cards
modern atomic model (who? what?)
discovered neutrons, current model used today
created by chadwick around 1932
created by chadwick around 1932
38
New cards
atom
the smallest particle of an element that still has the chemical properties of the element
39
New cards
nucleus
* very small thing in the center of the atom
* made of at least one proton (p+) and usually at least 1 neutron (n\*)
* surrounding the nucleus is a cloud of electrons (e-)
* made of at least one proton (p+) and usually at least 1 neutron (n\*)
* surrounding the nucleus is a cloud of electrons (e-)
40
New cards
protons (p+) (define)
located in nucleus, positive charge, big and heavy
41
New cards
neutrons (n\*)
located in nucleus, no charge, big and heavy
42
New cards
electrons (e-)
outside the nucleus, negative charge, tiny and light
43
New cards
isotopes
2 atoms with different # of neutrons
* have the same atomic #, different mass #s
\
* protons never change
* neutrons can change
* have the same atomic #, different mass #s
\
* protons never change
* neutrons can change
44
New cards
ions
* **an atom with a charge**, # of electrons change
* if atom loses electrons, atom is + and (vice versa)
* protons, neutrons, atomic # and atomic mass stay the same
* if atom loses electrons, atom is + and (vice versa)
* protons, neutrons, atomic # and atomic mass stay the same
45
New cards
1st periodic table
created by Dmitri Mendeleev, 1869
Elements arranged:
* Groups had similar properties
* Increasing atomic mass
* Spaces left for undiscovered elements
Elements arranged:
* Groups had similar properties
* Increasing atomic mass
* Spaces left for undiscovered elements
46
New cards
current periodic table
created by Henry Mosely, 1913
Elements arranged:
* By atomic #, not mass
* You already know what it looks like
Elements arranged:
* By atomic #, not mass
* You already know what it looks like
47
New cards
periodic law
*“When elements are arranged by increasing atomic #, there is a periodic repetition of physical and chemical properties.”*
* Or in simple words: **when you put elements in order by atomic #, you can see some patterns.**
* Or in simple words: **when you put elements in order by atomic #, you can see some patterns.**
48
New cards
what’s the only metal that’s liquid at room temp
mercury
49
New cards
the most reactive element groups
alkaline metals, then alkaline earth metals cause they only have 1 valance electron
50
New cards
what are the most reactive nonmetals
halogens
51
New cards
what do noble gases (except helium) bond with
nothing
52
New cards
metals (where? describe)
left side of stairsteps
* In the A block
* conduct heat, electricity
* high luster, solid at room temperature (not mercury)
* ductile, can be made into wire
* malleable, can be made into a sheet
* In the A block
* conduct heat, electricity
* high luster, solid at room temperature (not mercury)
* ductile, can be made into wire
* malleable, can be made into a sheet
53
New cards
nonmetals (where? describe, example)
right side of stairsteps
* In the A block
* Most are gases at room temperature (not bromine, it’s a liquid)
* Poor conductors, brittle, dull
* ex. chlorine and oxygen
* In the A block
* Most are gases at room temperature (not bromine, it’s a liquid)
* Poor conductors, brittle, dull
* ex. chlorine and oxygen
54
New cards
metalloids
along stairsteps
* In the A block
* Properties of metals and nonmetals
* Conductors and insulators
* Ex. Semiconductors are Selenium, Germanium, arsenide
* In the A block
* Properties of metals and nonmetals
* Conductors and insulators
* Ex. Semiconductors are Selenium, Germanium, arsenide
55
New cards
catalyst
the thing on top of the yield arrow, speeds up a chemical reaction
56
New cards
dalton
(what model? what discoveries?)
(what model? what discoveries?)
discovered the atom, did billliards ball model
57
New cards

thompson
discovered electrons, did cathode ray tube and plum pudding

58
New cards

rutherford
what experiment? what discoveries?
what experiment? what discoveries?
nucleus, protons on nucleus, discovered that the atom is mostly empty space…………
\
nuclear model (nucleus with electron shell)…………
\
gold foil experiment
\
nuclear model (nucleus with electron shell)…………
\
gold foil experiment
59
New cards

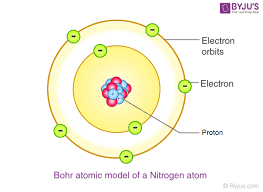
bohr (discoveries? models?)
atomic energy levels, atomic model, planetary model.
electrons shell is made of orbits/shells
electrons shell is made of orbits/shells
60
New cards

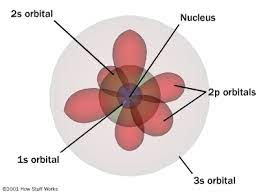
heisenberg and schroedinger (created, discovered?)
electron cloud and orbitals, heisenberg uncertainty principle, quantum model
61
New cards
hyphen notation
* (element name) dash (mass number)
* ex. uranium-235
* ex. uranium-235
62
New cards
isotope notation (nuclear symbol)
* top - mass # bottom - atomic #
* ex. U²³⁵₉₂ (pretend like that’s lined up)
* ex. U²³⁵₉₂ (pretend like that’s lined up)
63
New cards
atomic number =
\# protons (# electrons if neutral)
64
New cards
mass number =
protons + neutrons
65
New cards
atomic mass =
the decimal in the element box
66
New cards
neutrons =
mass # - atomic #
67
New cards
reactivity
**⇙ How easily an element reacts** with other elements **⇙**
68
New cards
ion
an electron with a charge
69
New cards
shielding effect
when the inner shells shield the outer shells from the nucleus’s pull
70
New cards
metallic character
**⇙** how metallic it is **⇙**
71
New cards
atomic radius
**⇙** how big the atom is **⇙**
72
New cards
ionization energy
**⇗** amount of energy required to remove an electron from the valance shell **⇗**
73
New cards
electronegativity
**⇗** how attractive an atom is **⇗ smaller atoms have higher attractivity**
74
New cards
cation
positive, lost electrons, smaller than neutral, metal
75
New cards
anion
negative, gained electrons, larger than neutral
* ex. iodide, chloride, hydroxide
* ex. iodide, chloride, hydroxide
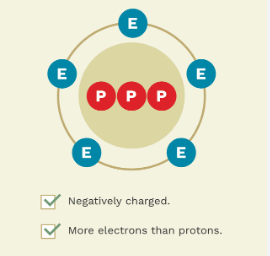
76
New cards
octet rule
usually there’s 8 electrons in a valance shell
77
New cards
ionic compounds
metal, nonmetal
when an electron is taken from another atom
when an electron is taken from another atom
78
New cards
molecular (covalent) compounds
(what are they made of, what process?)
(what are they made of, what process?)
nonmetal, nonmetal
when electrons are shared between atoms
when electrons are shared between atoms