Muscular System
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Muscle
a tissue that contracts (shortens) to facilitate locomotion and support
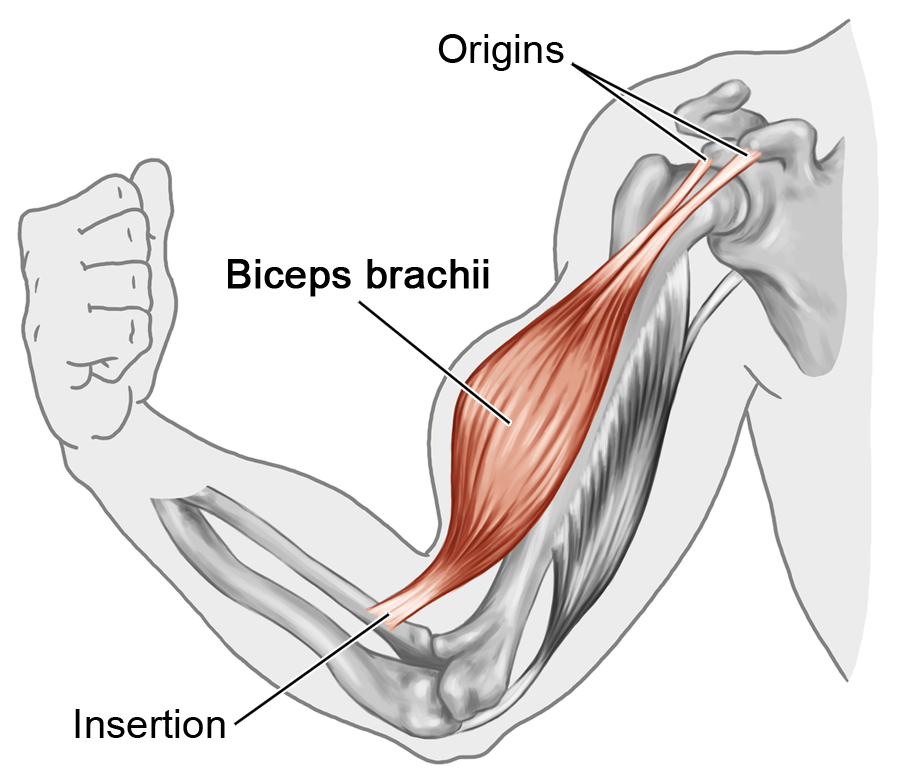
Origin
fixed proximal end of a muscle
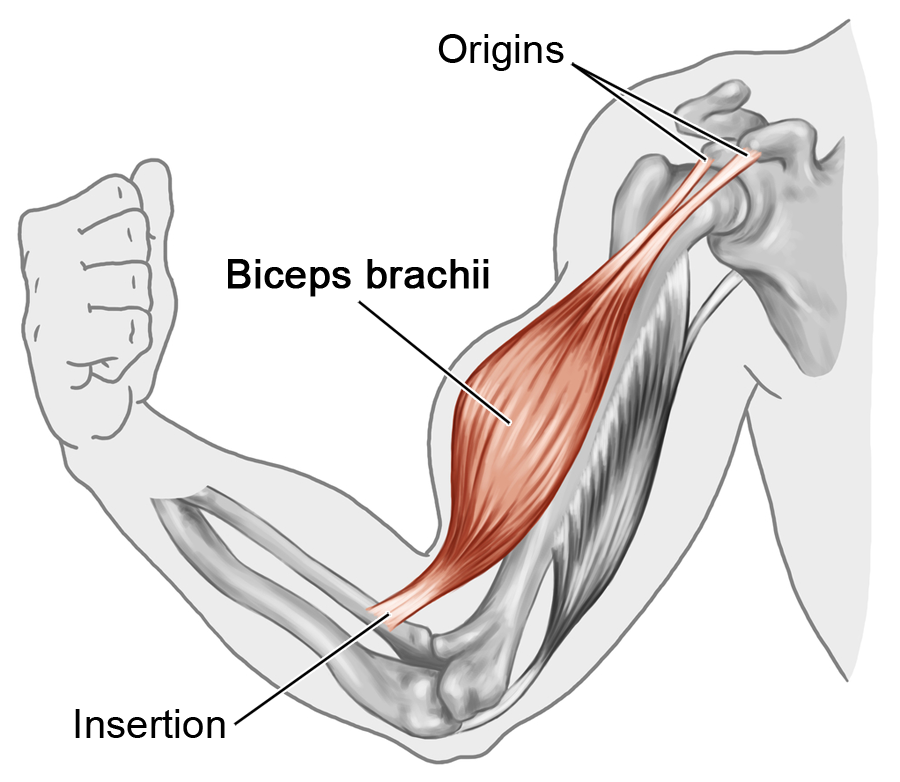
Insertion
distal moveable end of a muscle
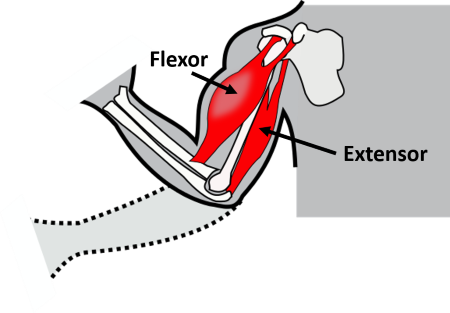
Flexor
closes/angulates a joint
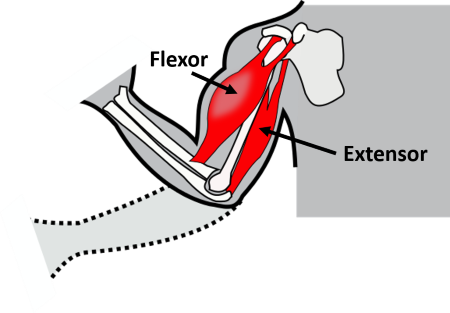
Extensor
opens/straightens a joint
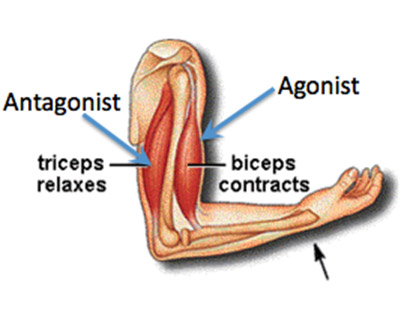
Agonist
muscle that produces desired movement
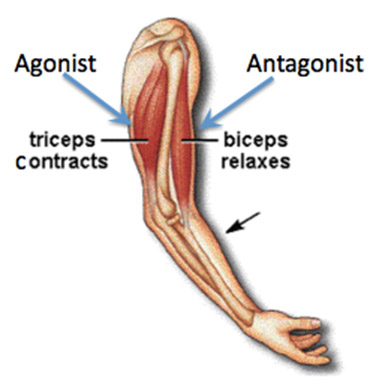
Antagonist
opposes movement of agonist
Which skeletal muscle group…
Produces skin twitch
Has little to no attachment to bone
cutaneous
Which skeletal muscle group…
Controls facial expression
Facilitates neck and sensory structure movement
head and neck
What skeletal muscle group…
Supports organs
Flexes the back
Facilitates defecation and urination
Aids in parturition
abdominal
What skeletal muscle groups…
Aid in locomotion
Provides abduction and adduction of the shoulder and lower limbs
thoracic and pelvic limbs
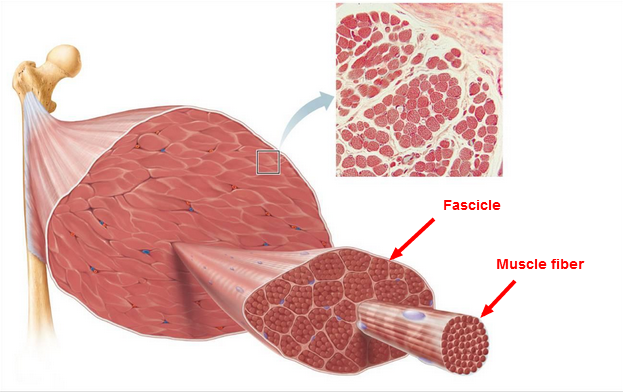
Muscle fiber
single muscle cell
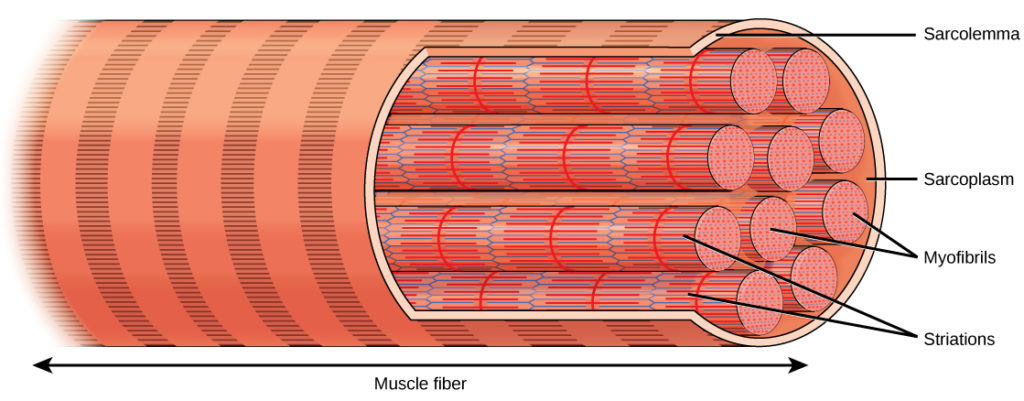
Muscle myofibril
composed of myofilaments; hundreds run together lengthwise to make up muscle fibers
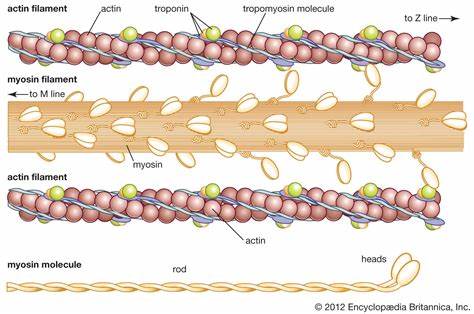
Protein filaments
actin and myosin; contractile proteins
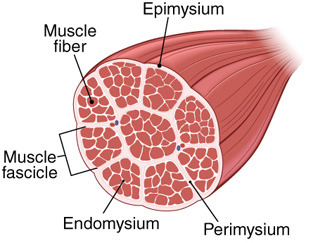
Fascicle
bundles of skeletal muscle fibers within a muscle
Endomysium
connective tissue around individual muscle fibers
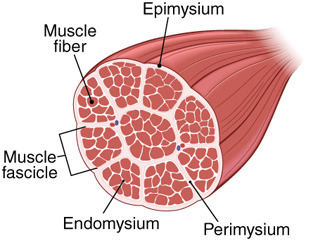
Perimysium
connective tissue around a bundle of muscle fibers
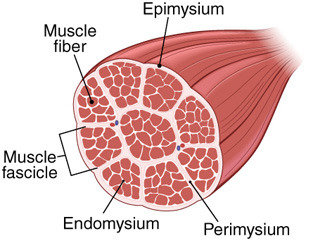
Epimysium
dense connective tissue sheet covering a whole muscle
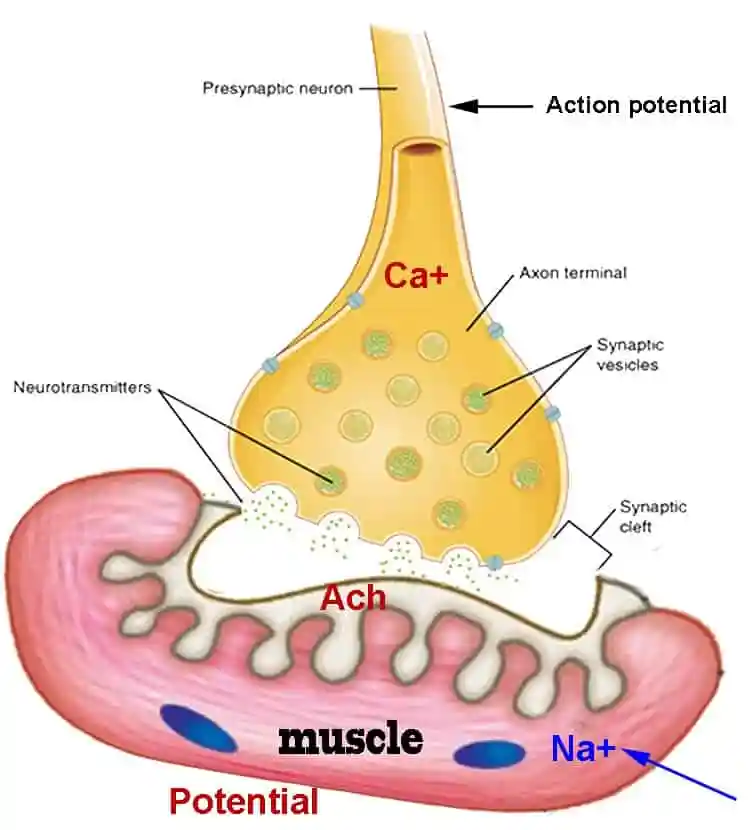
Neuromuscular junction
where motor neuron terminal axon meets muscle fibers with a chemical synapse
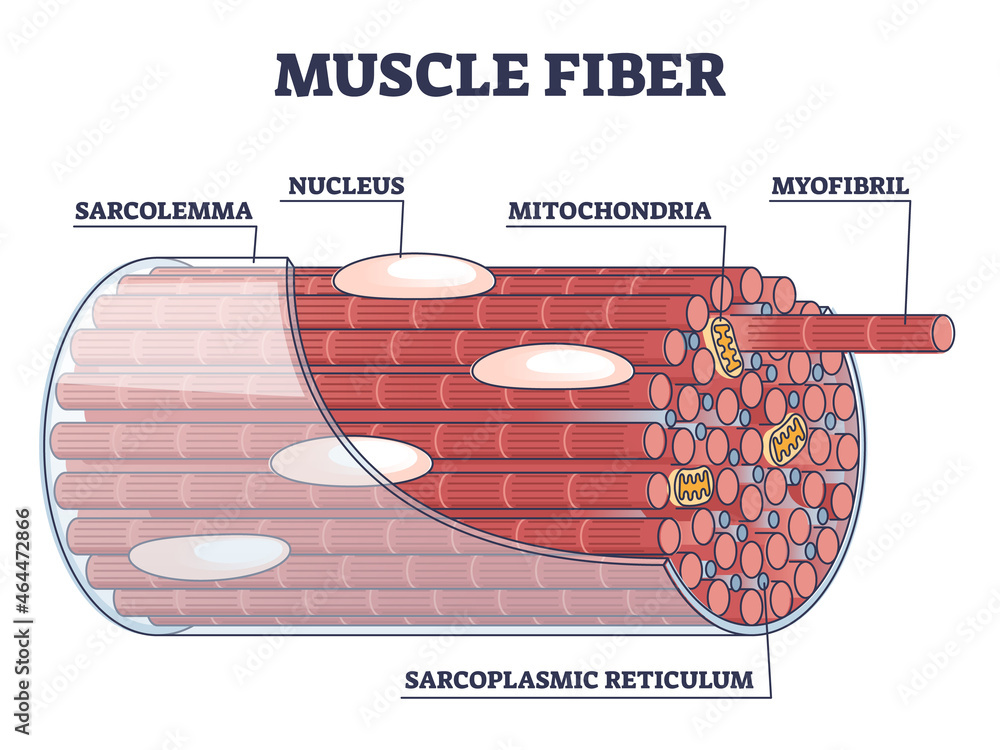
Sarcolemma
muscle cell membrane
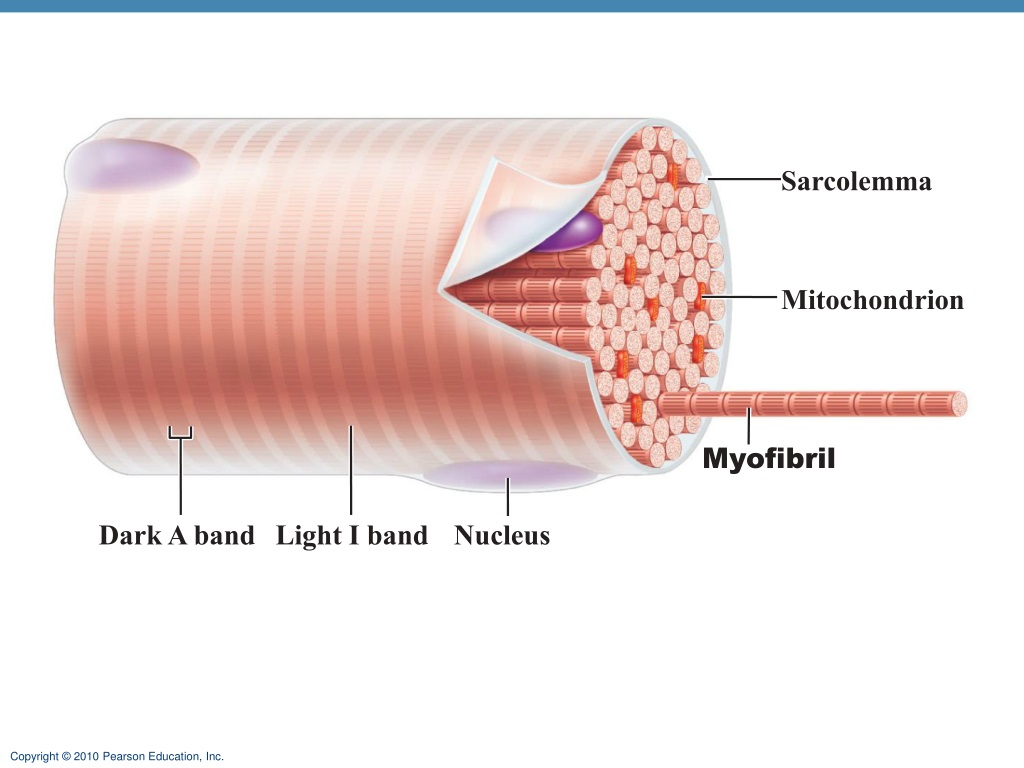
The sarcolemma is a site for…
nervous system interaction
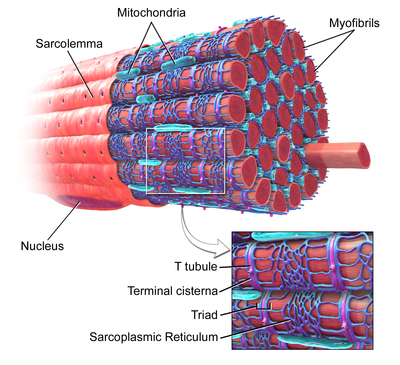
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
muscle equivalent to ER; stores calcium
T-tubule
extend inward from sarcolemma to carry nerve impulses into the cell
energy stores
Glycogen acts as _____________ for muscles.
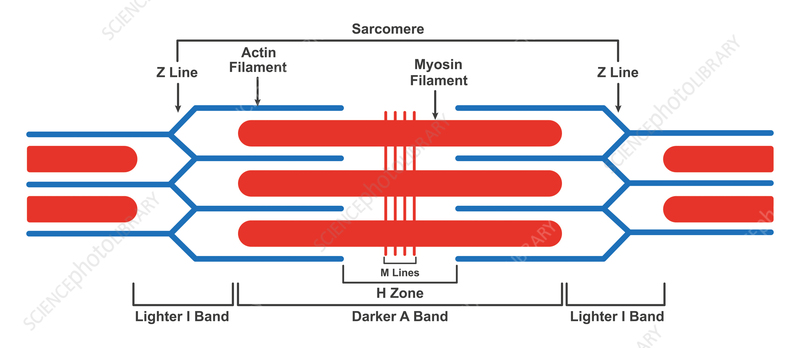
Sarcomere
repeating contractile unit
multinucleated
In terms of nuclei, skeletal muscle cells are….
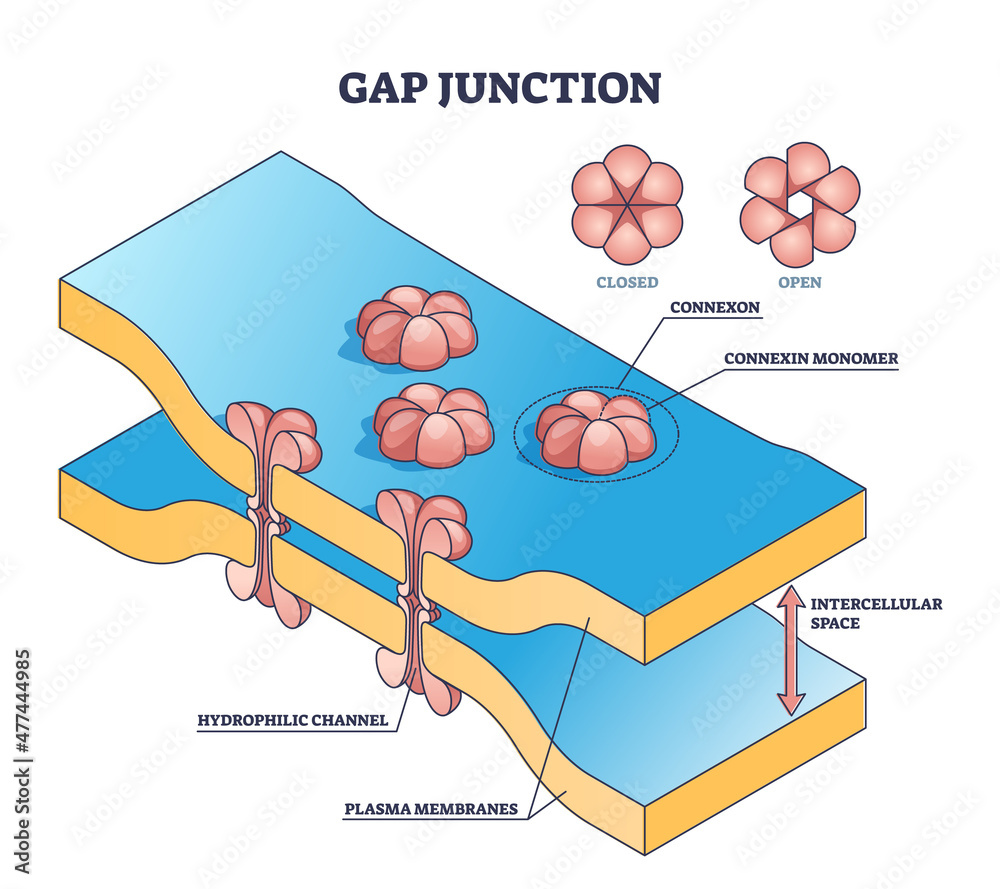
Gap junctions
connect cardiac muscle cells, allowing electrical impulse to flow rapidly and ensure synchronized contractions
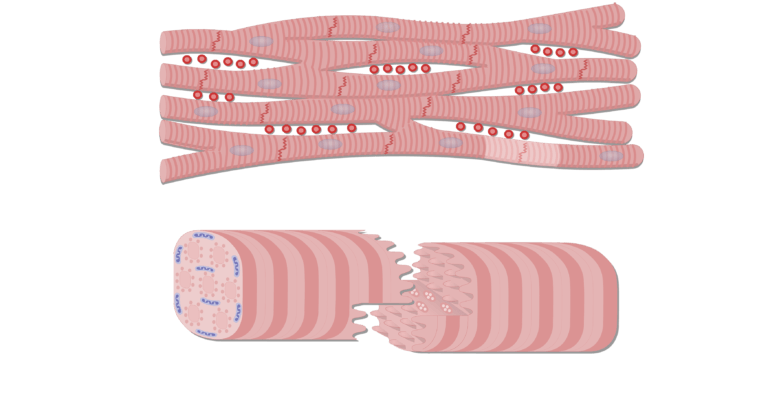
Intercalated discs
attachment sites between cardiac muscle cell network
Sinoatrial node (SA) pacemaker
The impulse that triggers the involuntary contraction of cardiac muscle is controlled by the…
increases heart rate and blood pressure
What does norepinephrine do for the muscular system?
waves
Smooth muscle cells produce large, rhythmic ______ of contraction.
visceral
Smooth muscle cells are __________; they’re found in large sheets inside organ walls.
Peristalsis
series of wave-like contractions that push substance through tube-like structures, especially in the digestive or urinary systems
increases
As tissue stretches, contraction strength _________.
Smooth muscle cells are not capable of fine movement, with the exception of…
multiunit smooth muscle (ex. blood vessels, air passages)
Crossbridge
where actin and myosin come into contact and pull Z lines together
Acetylcholine
neurotransmitter for specified action potential
maximizes muscle longevity and endurance
What is the function of creatine phosphate?
phosphates
In order to turn ADP into ATP, the body needs…
shorten
When Z lines are brought together, muscle fibers _________.
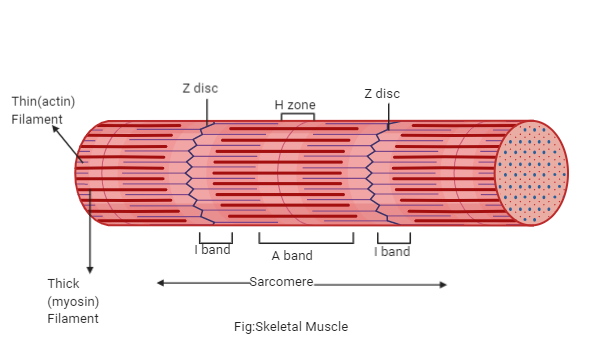
Band H
“disappears” during muscle contraction
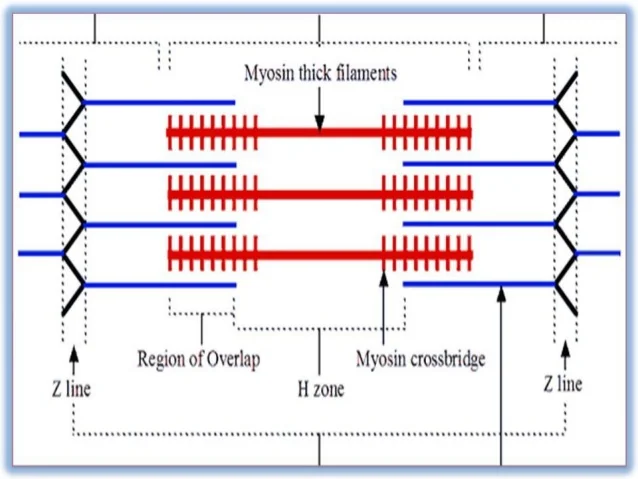
Band A
length of myosin within sarcomere
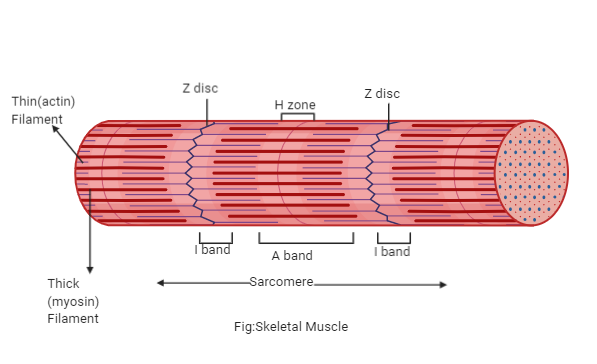
Band I
sarcomere region containing only thin myofilaments
List the steps of muscle contraction and relaxation. (Hint: 6 steps)
Electric impulse arrives through chemical synapse
Calcium ions release from SR
Troponin binds to calcium, changing shape and pulling tropomyosin away to expose myosin’s binding sites
Myosin, using ADP and Pi, binds with actin and the H-band disappears
ATP binds with myosin’s head and it releases actin (relaxation)
Calcium returns to SR through active transport
Summation
whole muscle contracting at various lengths
Spacial summation
several excitatory postsynaptic potentials travel down MULTIPLE presynaptic neurons and arrive at axon at the same time as an action potential
Temporal summation
several excitatory postsynaptic potentials travel down a SINGLE presynaptic neuron in quick succession
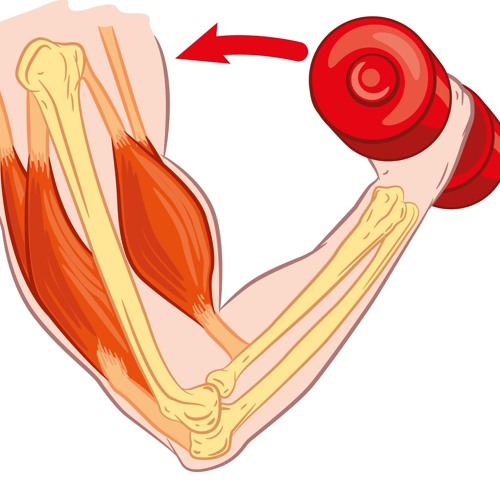
What type of muscle contraction…
Shortens muscle (flexes)
concentric
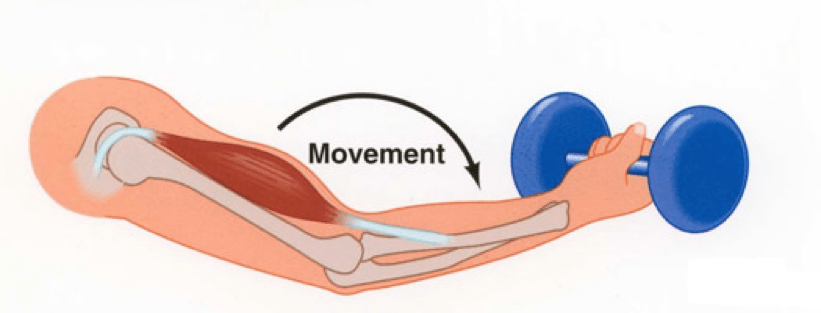
What type of muscle contraction…
Lengthens muscle (extends)
eccentric
What kind of muscle contraction…
Stays the same length
Changes in tension
Produces no movement
isometric
What kind of muscle contraction…
Changes length
Maintains the same tension
Produces movement
isotonic
adaptive
Muscle is the most __________ tissue in the body.
Hypertrophy
enlargement; increase in muscle cell size
Hyperplasia
enlargement of muscle by increase in number of muscle fibers
Atrophy
muscle shrinkage due to lack of use or denervation
Classify the muscle fiber. (Think: long distance)
Dark
Aerobic
Slow twitch
Type I
Classify the muscle fiber. (Think: 400/800m run)
Fast twitch
Intermediate
Anaerobic
Type IIA
Classify the muscle fiber. (Think: short sprints)
Light
Fast twitch
Aerobic
Type IIB
Skeletal
Identify the muscle type.
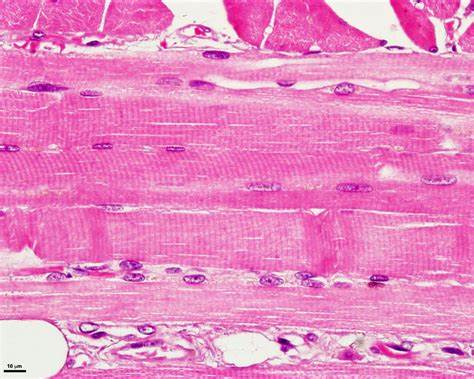
Cardiac
Identify the muscle type.
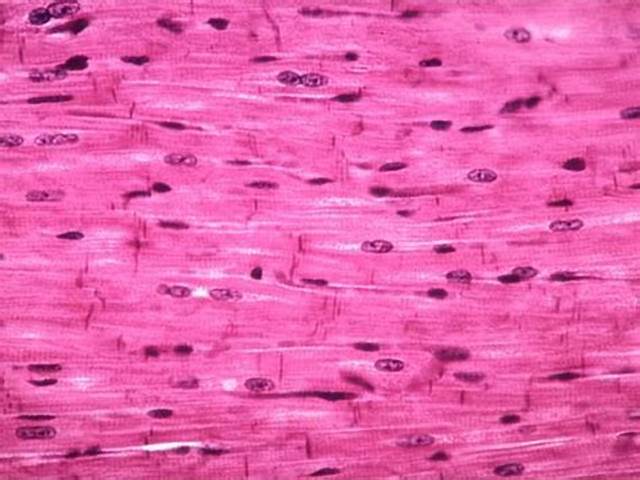
Smooth
Identify the muscle type.
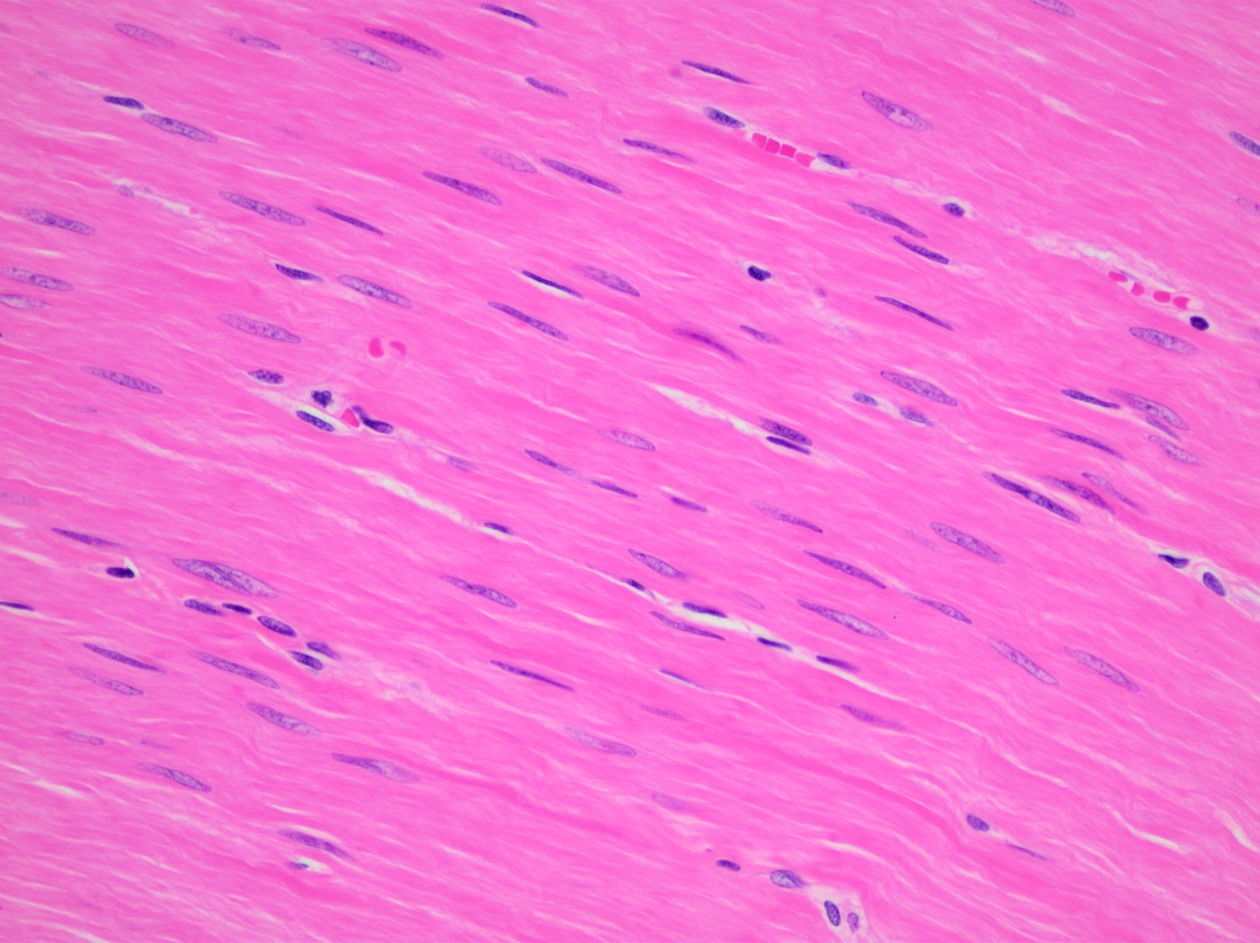
latissimus dorsi
Identify the muscle indicated by the green dot.
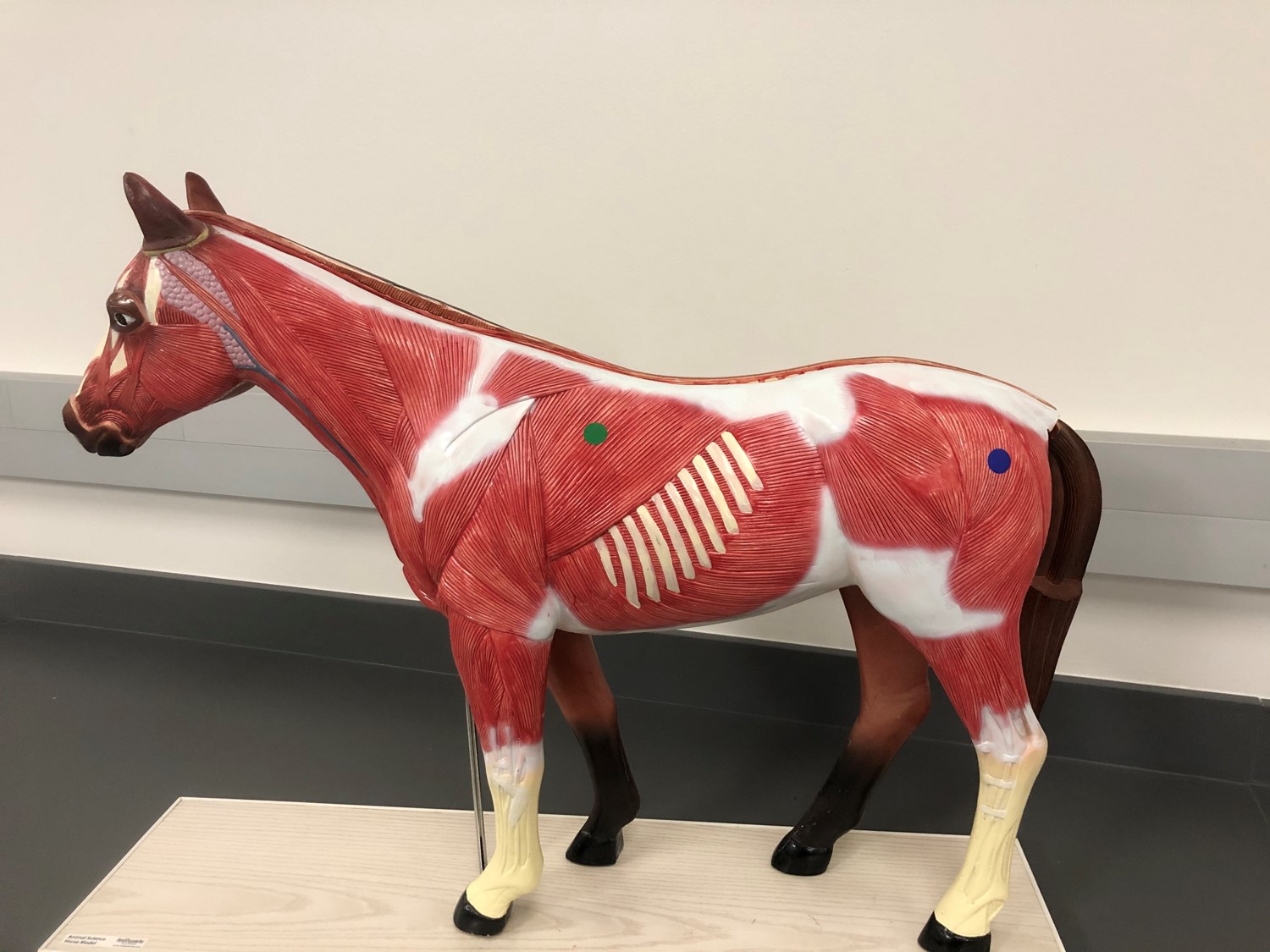

superficial gluteal
Identify the muscle indicated by the blue dot.
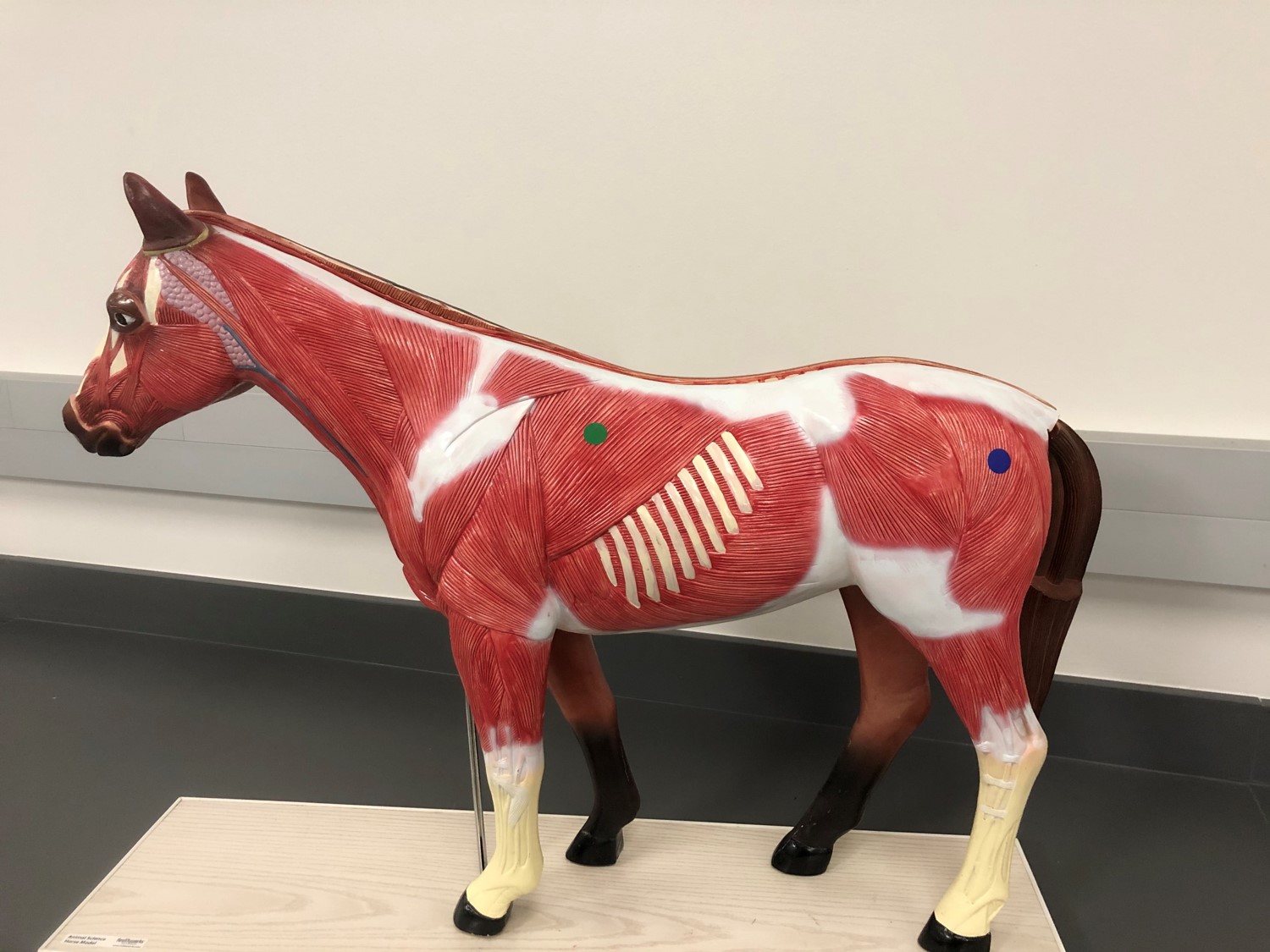

trapezius
Identify the muscle indicated by the green dot.

semitendinosus
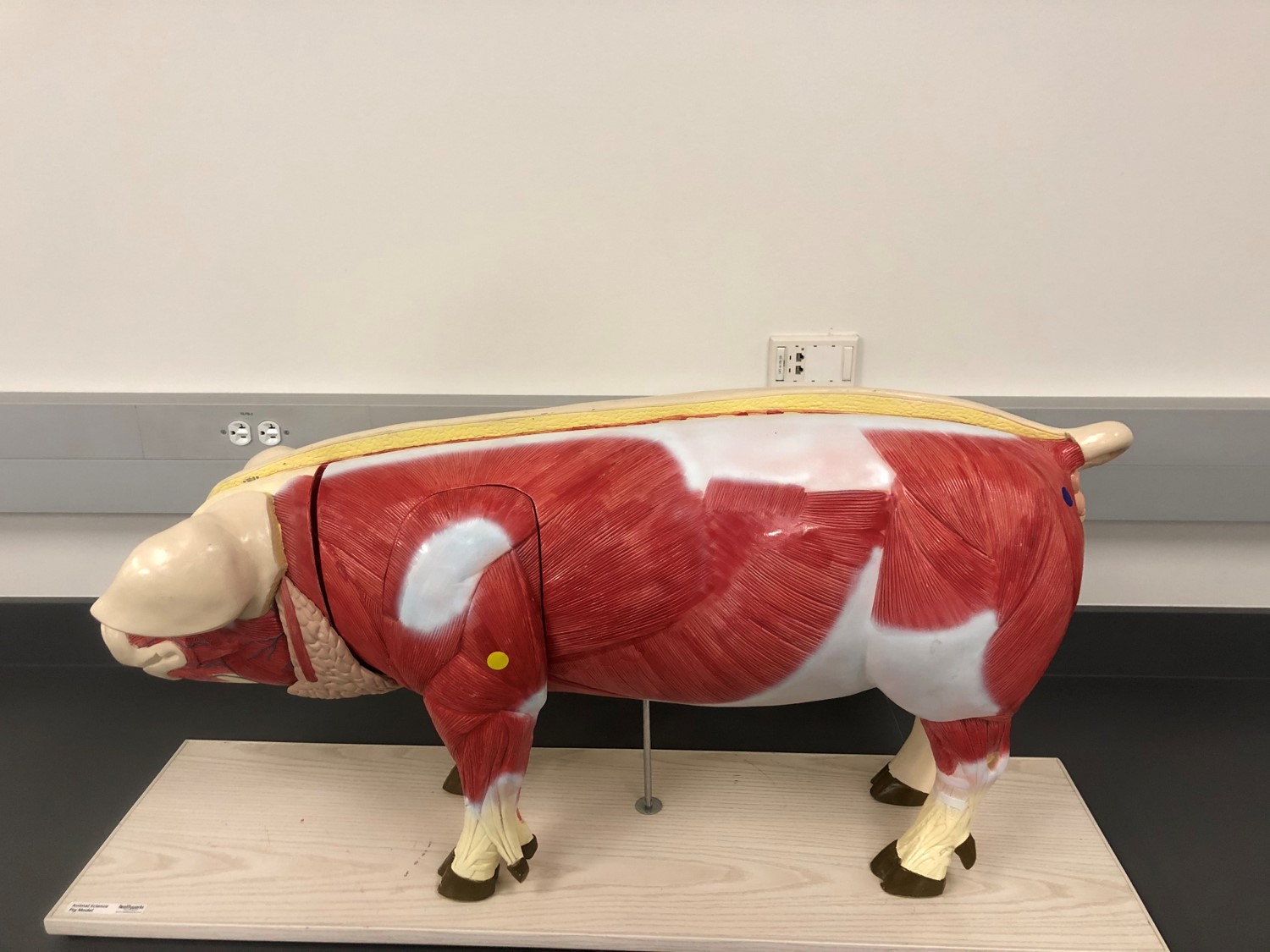
Identify the muscle indicated by the blue dot.
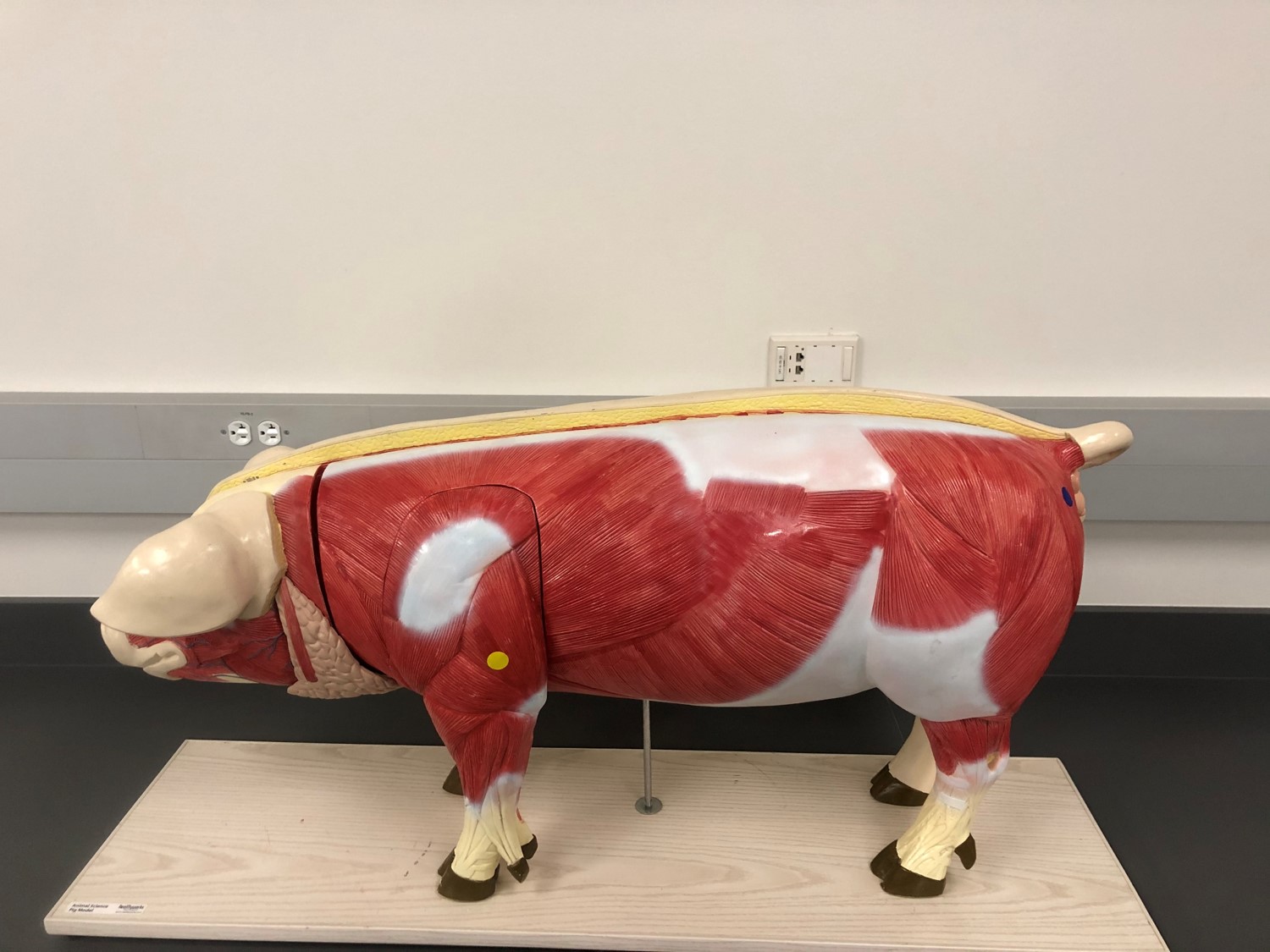

deltoid
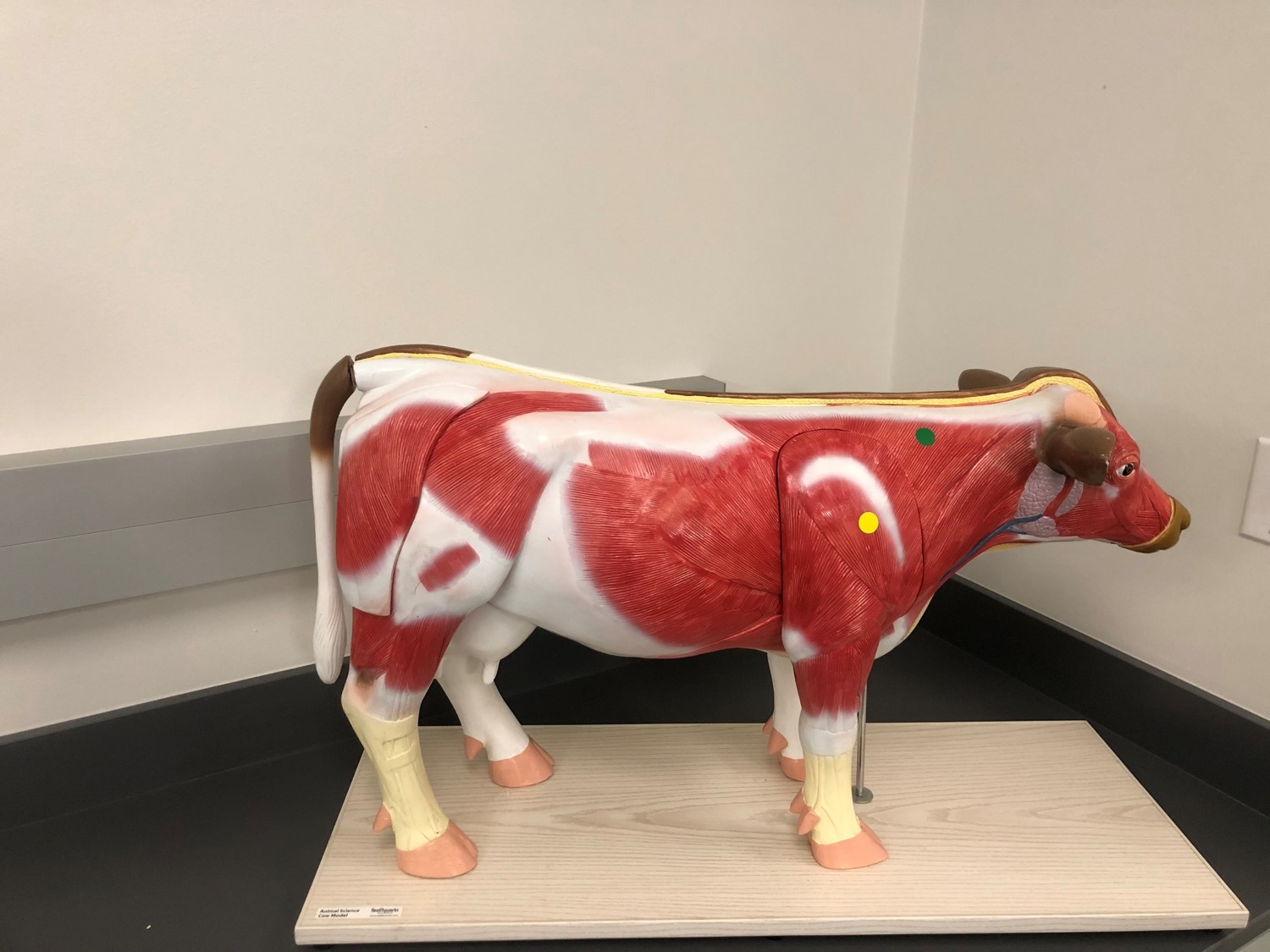
Identify the muscle indicated by the yellow dot.
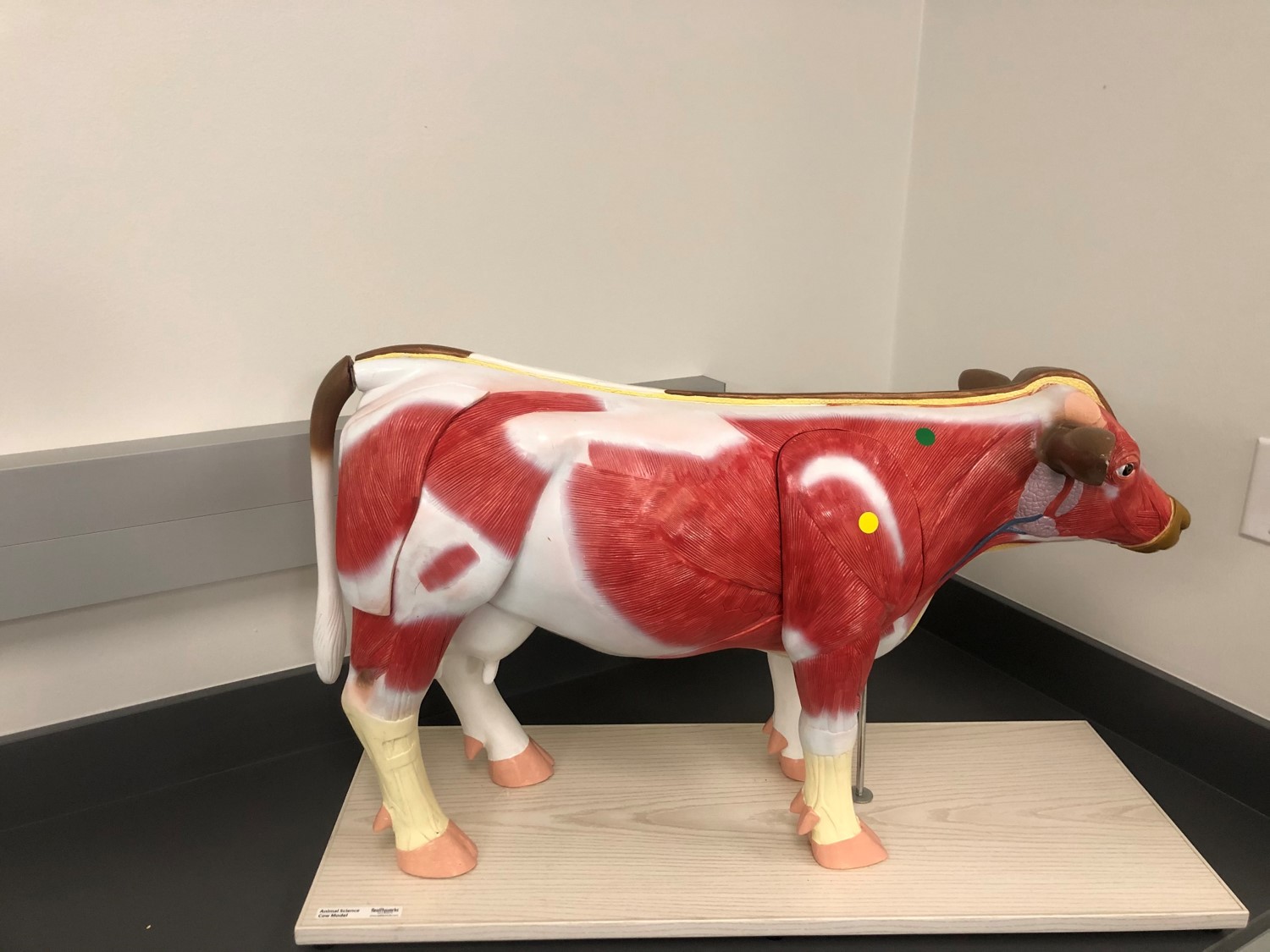

triceps brachii
Identify the muscle indicated by the yellow dot.

What is the cheek muscle known as?
Masseter
gluteobiceps
In small ruminant animals, the biceps femoris is known as the…