Internet Computing T2
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
Does OOP overloading apply in PHP
No, PHP is not a compiling language
How does PHP implement overloading
uses variable-length arguments (also called variadic functions) to accept flexible number of arguments

How does overrriding work in PHP
same as OOP

How to override inherited methods
by redefiining methods using same name (overriding) in child class and with the final keyword

Abstract classes vs methods
class: contains at least one abs. method
method: method that is declared but not implemented
Abstract Classes Rules
child class methods must be defined with same name
child class method must be defined with same or less restricted access
number of required arguments must be the same, but child class can have optional arguments aditionally
What are interfaces
defined in same way as a class, but says interface instead of class.
to implement interface, class needs to use implements keyword
Interface vs. Abstract Classes
interfaces cannot have properties, but abstract classes can
all interface methods must be public, while abstract classes can be public or protected
all methods in an interface are abstract, so abstract keyword is not necessary, but all methods in an abstract class do not have to be abstract
classes can implement an interface while inheriting from another class at the same time.
Methods that connect PHP to MySQL
MySQLi
PDO
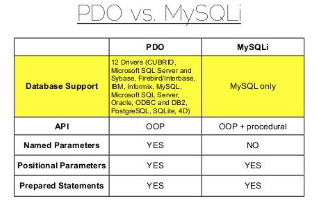
difference: PDO suppords various databases and MySQLi supports only MySQL. MySQLi also a bit faster. PDO supports 12 different drivers, opposed to MySQLi (MySQL only)
MySQLi code demo

PDO code demo

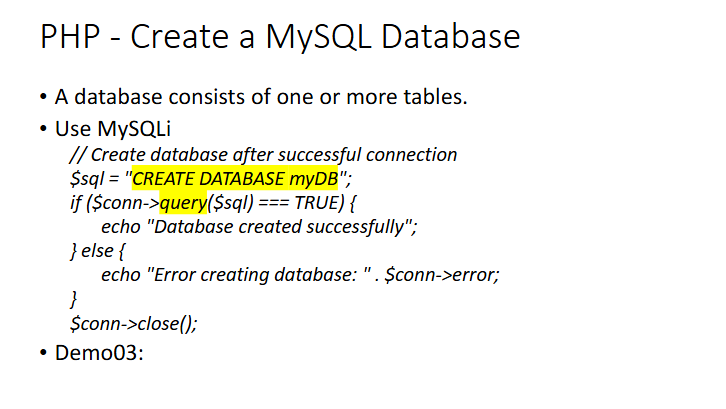
create DB with MySQLi
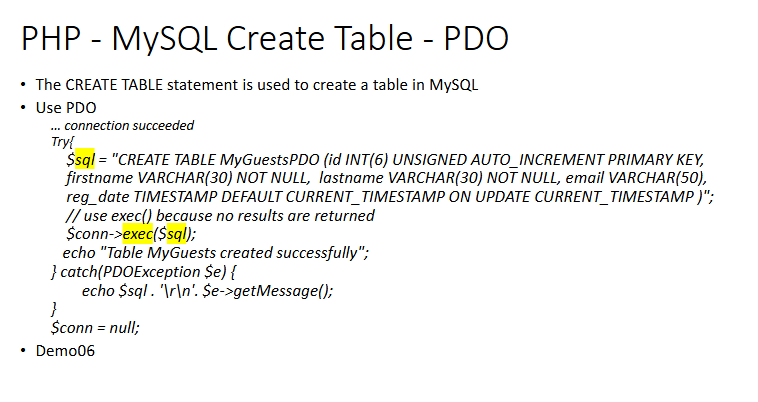
Create DB with PDO

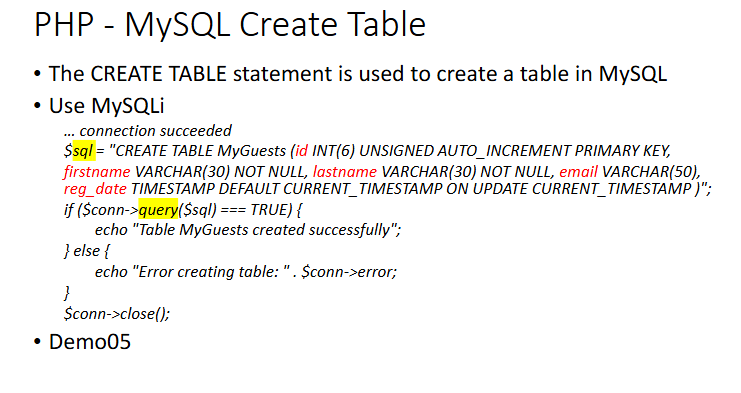
Create Table MySQLi
Create Table PDO
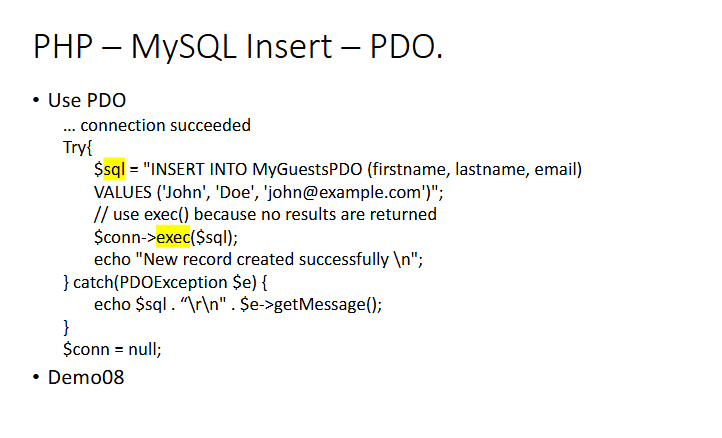
MySQLi Insert

PDO Insert
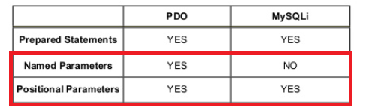
Prepared Statement MySQLi vs. PDO
prepared statements procedures
prepare sql query with empty vals. as placeholders with “?” or variable name (ex. “INSERT INTO MyGuests VALUES(?, ?, ?)”)
bind values or variables to placeholders
execute query simultaneously
MySQLi prepared statement procedure

benefits of using SQL prepared statments
useful against SQLi attacks
reduce parsing time since preparation is done only once
minimizes bandwidth to server since you need only params each time
PDO prepared statement procedure

PDO vs. MySQLi
What is PDO
an extension that defines lightweight consistent interface for accessing databases in PHP
What classes does PDO contain?
PDO class: represents connection between PHP and DB server
PDOStatement class: represents prepared statement and, after statement is exectured, an associated result test
PDOException class: represents error rasied by PDO (dont raise from ur own code)
Types of prepared statments
named parameters
positional parameters
when should you use prepared statments
SQL statements contain user inputs or SQL statments run repeatedly
When should you use direct execution APIs
SQL statements do not contain user inputs and SQL statments run one time
How to use direct execution (PDO statment)
$pdo→exec(…)
Steps for PDO prepared statement
two param methods (named param, positional param)
$pdo→prepare(…)
$pdo→bindParam(…)
$pdo→bindValue(…)$pdo→execute(…)
SQL templates for named parameters and positional parameters
named parameters: the form :name
positional parameters: ?
PDO prepared syntax
PDO::prepare(string $query, array $options = []): PDOStatement|false
$query: a valid SQL statement template
$option: set attribute values for PDOSStatement object
bindValue() function
PDO::bindValue(string|int $param, mixed $value, int $type = PDO::PARAM_STR): bool
$param: for prep. statment with named placeholder will be in form :name , ? placeholder statements will be the 1-index position of param
ex
Example:
$stmt1 -> bindValue (':name ','Ben’, PDO :: PARAM_STR );
$email = ‘shaun@gmail.com';
$stmt1 -> bindValue (':email ',$email );
bindParam() function
bindParam()
bool PDO::bindParam(string|int $param, mixed &$var, int $type = PDO::PARAM_STR, int $maxLength = 0, mixed $driverOptions = null): bool
ex
$name = 'Ben ';
$stmt1 -> bindParam (':name’, $name ,PDO::PARAM_STR );
named parameter example

positional parameter example
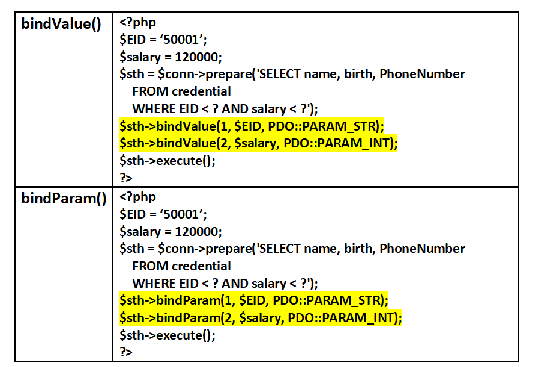
difference between bindValue() and bindParam()
similar from user perspective, differ in implementation
bindParam() binds param exclusively to specified variable name, bound as reference
bindValue() binds value that could be a varaible, integer or string to parameter
Debug tools for PHP
visual studio
Xdebud
Debug techniques
dump variables to standard output (stdout)
switching error reporting level - update php.ini
main uses of PHP
server side scripting
requires: PHP parser, web server, web browser
PHP code not visible to browser users
how to define variables and check data types in PHP
variables start with $, case sensitive
var_dump() checks data types
Method for data type conversion
Settyype(mixed &$var, string $type)
<?php
$count = "5";
echo gettype($count); // before datatype conversion: $count is a string
settype($count,'int’);
echo gettype($count); // after datatype conversion: $count is an integer
?>
Comparision Operators in PHP
Operator | Name | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
== | Equal |
| Returns true if |
=== | Identical |
| Returns true if |
!= | Not equal |
| Returns true if |
<> | Not equal |
| Returns true if |
!== | Not identical |
| Returns true if |
< | Less than |
| Returns true if |
> | Greater than |
| Returns true if |
>= | Greater than or equal to |
| Returns true if |
<= | Less than or equal to |
| Returns true if |
<=> | Spaceship |
| Returns an integer less than, equal to, or greater than zero, depending on whether |
how do Arrays in PHP work
indexed array
associative array (paired key → value)
accessing items in array with foreach
syntax: foreach ($array as $key => &$value)

If we remove the sign “&” in foreach, what the output will be?
values inside array will not be modified bc $value is just a copy of each elemt, not reference to original element
PHP variable scopes
local
global
static
PHP anon function
$fn = function (int $x, int $y)
do not inherit variables from parent scope → need to use use keyword
can be assigned to variables, passed as arguments to other functions, or returned from functions.
$factor = 10;
$multiplier = function($x) use ($factor) {
return $x * $factor;
};
echo $multiplier(5); // Outputs: 50PHP arrow function
$fn = fn (int $x, int $y)
automatically inherit variables from parent scope
used for simpler one liner functions
$factor = 10;
$multiplier = fn($x) => $x * $factor;
echo $multiplier(5); // Outputs: 50function declaration
declare(strict_types=1)
how to accept variable number of arguments
function functionName(...$args) { ... }superglobal variables
associative arrays that are always accessible, regardless of scope
provide information about server, request, and environment
nodejs
open source back-end javascript runtime environtment
allows developers to use javascript for server side scripting
event driven architecture capable of asynchronour I/O
how to start javascript code
<script>…</script>
is JS case sensitive
yes
how do JS comments work
supports both C and C++ style comments
any text between // and at end of line is treated as comment
any text between /* and */ is treated as a comment
how is JS data type determined
dynamicaly based on value stored
Difference between function_name and function_name() in
JavaScript
function_name refers to the function object while function_name() refers to
the function execution result.
display function exec results example

scopes in javascript
block scope: decalred inside {} block with either let or const cannot be accessed outside the block
function/local scope
global scope
variable scope diference between PHP and JS?
ways to declare a javascript varaible
var - function scope
let - cannot be redeclared afterwards, have block scope
const - cannot be chaned after assigned valueble scope difference between PHP and JS?
what are identifiers in JS
unique names JS variables are identified by
JS hoisting
varaibles defined with var are hoiseted to the top anc can be initialized at any time
with let you cannot use a varaible before its declared
JS functions to extract string parts
slice(start, end) - start, end are indexes
substring(start, end) - does not accept negative indices
if start > end, substring will swap arguments
substr(start, end) → DEPREACTED
how to replace parts of string in JS
replace(searchValue, newValue)
What kind of number does JS have
64-bit floating point
Symbol in JS
represents unique identifier
ever symbol call is guaranteed to return a unique symbol
how to create an object in JS
using Object Literal/Initializer Syntax
var p1 = { name:“John" }; // object literal syntax
using new operator
var p2 = new Car(‘BMW’, ‘red’); //Car can be either a function or a class
such that an objectusing the Object() Constructor function with new keyword or create()
var p2 = Object.create(car); // Object() constructor function
p2.name = “John"; // property
JS object creation limitation
a property name that has a space or a hyphen, or that starts with a
number) can only be accessed using the square bracket notation.
what is a JS object property and types of properties
characteristic of an object, often describing attributes associated with data structure
instance properties: hold data specific to object instance
static properties: hold data shared among all other instances
what does a property have in JS
a name (string or symbol)
a value (primitive, method, or object reference)
how to access object properties JS
objectName.property
ex. person.age
objectName[“property”]
ex. person[“age”]
objectName[expression]
ex. x=”age”; person[x]
JS methods
JS methods can be located at value location in key:value
JS method is property containing function definition
how to access object methods JS
objectName.methodName()
JS accessors
gettters: get property()
setters: object.property = “x”
JS class
program code template for creating objects
class ClassName {
constructor() { ... }
method_1() { ... }
method_2() { ... }
...
}
//"constructor“ is a special method
// constructor does not have a name
// there is no destructor() in JavaScriptJS class example

JS inheritance
uses extends, inhetits all methods from parent class
super() method in constructor meands parent property is called
JS encapsulation
public/private
by default all methods/vars are public
private members can be created using # prefix
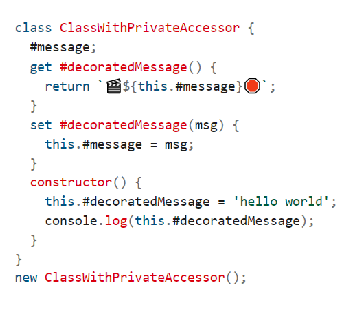
getter and setter syntax
{get prop() { return property; }}
{set prop(val) { ... }}
Do not use parentheses when calling a getter (e.g., rect.area, not rect.area()).
get and set can be used both inside and outside of classes
getter example
class Rectangle {
constructor(height, width) {
this.height = height;
this.width = width;
}
get area() {
return this.height * this.width;
}
}
const rect = new Rectangle(5, 10);
console.log(rect.area); // Outputs: 50setter examples
const language = {
set current(name) {
this.log.push(name);
},
log: []
};
language.current = 'en';
language.current = 'jp';
console.log(language.log); // Outputs: ['en', 'jp']this keyword in JS vs PHP
JS:
this refers to object that is executing in curr function
in global scope, refers to global object
in functions, refers to hlobal object or undefined (nonstrict vs. strict)
in methods, refers to object that owens the method
in event handlers, refers to element that recieved event
in arrow functions, inherited from parent scope
PHP
this is used within class methods tp refer to current object instance
used to access properties and methods of class
cannot be used in static methods, since they are called on class itself and not instance
not used in global scope
function declaration vs function expression
declaration:
function declarations load before any code is executed,
hoisted on top of other code,
cannot define anon func
expresson:
function expressions load only when the interpreter reaches that line of code,
not hoisted,
can define anon func

What are the basic syntax forms of JavaScript arrow functions?
param => expression
//ex
param => {
let a = 1;
return a + param;
}(param1, paramN) => expression
//ex
(param1, paramN) => {
let a = 1;
return a + param1 + paramN;
}arrow functions limitations
does not have its own bindings to this or super and should not be used as methods
does not have new.target keyword
noy suitanle for call, applu, and bind methods which rely on scope
cannot be used as constructors
What are the key differences between traditional functions and arrow functions?
Traditional functions use the
functionkeyword, while arrow functions use=>.Arrow functions are more concise, especially for single-expression functions.
Traditional functions are more versatile (e.g., can be used as constructors), while arrow functions are ideal for short, non-method functions.
what do JS function parameters not do
function definitions do not specify data types for parameters.
functions do not perform type checking on the passed arguments.
functions do not check the number of arguments received ←→ PHP
what are the arguments object in JS functions
array of arguments used when function called
default parameters in JS
if function is called with missing arguments, the missing valuesa re set to undefined and JS keeps running
how to invoke a function as a method of an object
objName.methodName()
ex. console.log(employee.fullName());
how to invoke function with a function constructor
new Function(functionBody)
new Function(arg1,…argN, functionBody)
call() method JS
predefined method of function objects
useful when you want to reuse a function with different objects or explicitly set value of this
function is not a method of object you want to use with
want to borrow method from one object and use with another object
call() method example
const person = {
fullName: function() {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
}
};
const person1 = {
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe"
};
// Using call() to set `this` to person1
console.log(person.fullName.call(person1)); // Outputs: John DoeHere, fullName is a method of the person object, but we want to use it with person1. By using call(), we explicitly set this to person1, allowing the function to access person1's properties (firstName and lastName).
when to use call()
borrowing methods
const person2 = { firstName: "Jane", lastName: "Smith" }; console.log(person.fullName.call(person2)); // Outputs: Jane Smithexplicitly setting this
function greet() { console.log("Hello, " + this.name); } const user = { name: "Alice" }; greet.call(user); // Outputs: Hello, Alice
When is call() necessary in JavaScript, and when is it unnecessary?
Unnecessary:
When a function is already a method of the object you're calling it on. Useobject.method()directly.
Example:employee.fullName().Necessary:
When you want to reuse a function with a different object or explicitly setthis. Usefunction.call(thisArg).
Example:person.fullName.call(person1).
JS apply() function
The
apply()method is similar tocall(), but it allows you to pass arguments to the function as an array (or array-like object).It is used to invoke a function with a specific
thisvalue and arguments provided as an array.
synatx: functionName.apply(thisArg, [argsArray]);
JS bind() function
The
bind()method creates a new function with the same body as the original function but with a fixedthisvalue.Unlike
call()andapply(),bind()does not immediately invoke the function. Instead, it returns a new function that can be called later.