cell structure
1/286
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
287 Terms
What’s outside the cell, and what’s it made of
Extra cellular matrix made of glycoproteins
What provides support and mobility inside the cell
Cytoskeleton
What heals maintain cell shape as well as the position of organelles
Cytoskeleton
Is the cytoskeleton dynamic or not?
Dynamic
Why is the cytoskeleton dynamic
To allow rapidly changing cell shapes
What are the three components of cytoskeleton?
Microtubules, micro filaments, and intermediate filaments
What component of the cytoskeleton is largest
Microtubules
What component of the cytoskeleton is the middle sized
Intermediate filaments
What component of the cytoskeleton is smallest
Microfilaments
What component of the cytoskeleton is made of tiny tube like structures consisting of chains of proteins
Microtubules
What component of the cytoskeleton is made of two chains of actin proteins linked together?
Microfilaments
What component of the cytoskeleton is made of tightly packed, coiled, proteins?
Intermediate filaments
What component of the cytoskeleton can radiate out of the centrosome
Microtubules
What 2 component of the cytoskeleton resists pressing forces/tension
Microtubules and Microfilaments
What are the two forms of Microtubules
Cilia and flagella
What uses snake-like motion
Flagella
What provides rowing-like motion
Cilia
What can Microtubules provide for cells?
Motility/movement
Is the motility in Microtubules active or passive
Active
What component of the cytoskeleton allows vesicles and other organelles to be transported to specific targets
Microtubules
What component of the cytoskeleton are formed of either a linear strand or a 3D network of branching proteins
Microfilaments
What motor protein is in Microfilaments that supports cell movement
Myosin
What does actin-myosin interactions allow?
Muscle contraction
What component of the cytoskeleton can be made of keratins, lamins, and neurofilaments
Intermediate filaments
What component of the cytoskeleton is the hardest to break down
Intermediate filaments
What kind of cellular structures do intermediate filaments form to hold organelles in place?
Permanent
What will occur if neurofilaments aren’t functioning properly
break down, cells won’t hold shape, and can’t pass on signals
What component of the cytoskeleton can remain after cells that made them died?
Intermediate filaments
What are the three types of cell junctions
Tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions
What kind of cell junction limits space, meaning some things can go through and some can’t
Tight junctions
What kind of cell junction will prevent movement of fluid across cell layers
Tight junctions
What kind of cell junction is used as an anchoring junction
Desmosomes
Are desmosomes long or short lasting
Long
what connect desmosomes into the cell
Intermediate filaments
What kind of cell junction is a point of contact between two cells allowing ions and small molecules to pass through
Gap junctions
What kind of cell junction Allows rapid intercellular communication
Gap junctions
What do cells lie within
Extracellular matrix
What is composed of material that’s been secreted by cells
Extracellular matrix
What are most ECM proteins
Glycoproteins
What’s the most common ECM glycoprotein
Collagen
What protein has good tensile strength / won’t snap easily
Collagen
What are the proteins with extensive sugar additions called
Proteoglycans
What fibres are embedded in the proteoglycan complex matrix
Collagen fibres
What can trap water within the ECM
Proteoglycans
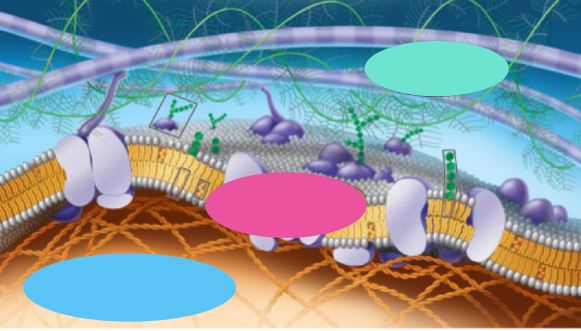
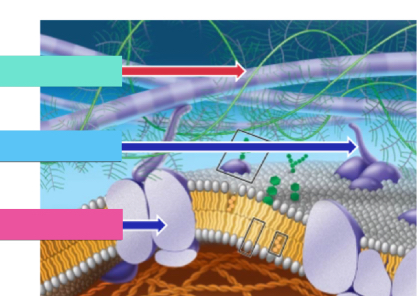
What’s pink
junctions
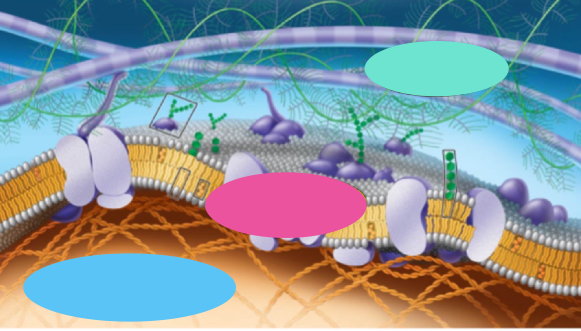
What’s blue
Cytoskeleton
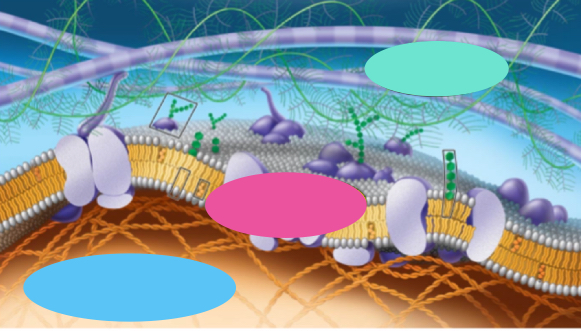
What’s teal
ECM
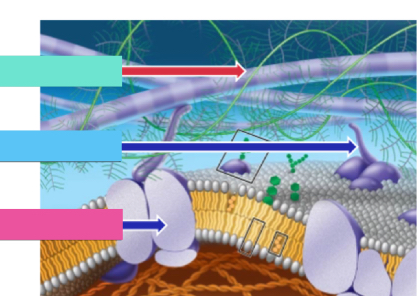
What’s teal
ECM
What’s blue
Fibronectins
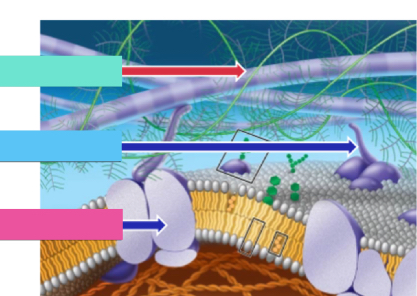
What’s pink
Integrins
energy can’t be created or destroyed, only transformed.
First law of thermodynamics
Perform mechanical work, synthesise new materials, transport molecules, and maintain order
How do cells use energy
Through cellular respiration
How do cells obtain energy
ATP
What does the breaking down of glucose generate
Generate ATP via cellular respiration
What’s the main function of the mitochondria
Outer membrane, inner membrane, cristae, matrix
What are the four key structural components of mitochondria
Controls movement of substances in and out
Function: outer membrane
Contains the electron transport chain and ATP synthase
Inner membrane: function
Folded inner membrane to increase surface area
Function: cristae
Contains enzymes for the citric acid cycle
Function: matrix
Allows compartmentalisation, enables electron transport chain to create a proton gradient
Importance of double membrane
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
Cellular respiration equation
Glycolysis, citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation
What are the three stages of cellular respiration
Cytosol
Glycolysis: location
Mitochondrial matrix
Citric acid cycle: location
Inner mitochondrial membrane
Oxidative phosphorylation: location
1 glucose, 2 ATP, NAD+
Input: glycolysis
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
Output: glycolysis
No
Is oxygen required for glycolysis
Acetyl CoA
What is pyruvate converted to before the citric acid cycle
2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, CO2
Products of citric acid cycle
CO2
Waste product: citric acid cycle
Electron transport chain, chemiosmosis
two main steps of oxidative phosphorylation
NADH and FADH2 donate electrons, which move through protein complexes, pumping protons into the intermembrane space to create a proton gradient
What happens in the electron transport chain
Oxygen
What’s the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain
Water
What does oxygen form in the electron transport chain
Protons flow back into the matrix through ATP synthase, driving ATP production
what happens during chemiosmosis
ATP
Main energy carrier in cells
Breaking down and forming phosphate bonds
How does ATP store/release energy
ATP → ADP + Pi
Release of energy using ATP
ADP + Pi → ATP
Storing of energy
Active transport, muscle contraction, protein synthesis, cell division
Uses of ATP
Chloroplasts
Where does photosynthesis occur
Glucose and oxygen
Why’s produced in photosynthesis to produce ATP in cellular respiration
Light dependent reactions, and the Calvin cycle
What are the two stages of photosynthesis
Thylakoid membrane
location: light dependent reactions
Convert sunlight into ATP and NADPH
Light dependent reactions
Use ATP and NADPH to dis CO2 into glucose
Calvin cycle
Outer membrane, inner membrane, thylakoid membrane
What are the three membranes in a chloroplast
Stroma
Location: Calvin cycle
Capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy
Function: photosystems
Photosystem II
What photosystem functions first
Photosystem I
What Photosystem functions second
Light energy excites electrons, which travel through the electron transport chain, splitting water into O₂, H+, and electrons.
What happens in Photosystem II
Build the proton gradient by moving protons into the thylakoid space
Function: cytochrome complex
ATP, NADPH, and O2
Light reactions: products
O2
Byproduct: light reactions
Fixation
Calvin cycle: first step