Abrasives, Abrasion, and Polishing
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
finishing is to put a final surface on; the _____ of ____ prior to ____
the refinement of form prior to polishing
polishing is to make ___ and ____ by _____
smooth and glossy usually by abrasion
what casting technique can you use for indirect restorations? process?
lost-wax casting technique; via spruing, investing, burnout
what are three types of investments contributing to surface roughness?
nodules, ridges / veins, or fins
what three factors contribute to a FINE surface roughness?
low W / P ratio (decreases investment adaptation or flow)
prolonged burnout (increases investment decomposition)
overheating alloy (increases investment decomposition)
a high W / P ratio ____ surface roughness
increases
what are the 13 steps of a streamlined direct restoration?
diagnostic
tissue management
isolation
decay removal
cavity prep
sectional matrix
lingual matrix
bonding
composite
place, shaping, blending, curing
finishing
polishing
procedure systems
define abrasion
wear or material loss from a surface as a result of scratching or other mechanical means
define the substrate and abrasive
substrate is ABRADED (passive)
abrasive CAUSES wear (active)
what is the first type of dental abrasion procedure?
two body abrasion;
abrasive particles are tightly bonded to the abrasive instrument that is removing material from the substrate surface
what is the second type of dental abrasion procedure?
three body abrasion;
involves the use of non-bonded abrasives, particles are free to translate and rotate between two surfaces
what is the third type of dental abrasion procedure?
airborne particle abrasion;
abrasive particles are propelled (sandblasted) against a substrate by air pressure to remove surface material
what factors affect the rate of abrasion?
hardness between abrasive and substrate
abrasive particle size
abrasive particle shape
speed & pressure
lubrication
the hardness between the abrasive and the substrate is the …
relative hardness of minerals using a Mohs scale (1812) which indicates the resistance to scratching of one material by another
what does the Mohs Hardness Test compare?
compares the resistance of a mineral by scratching with ten reference minerals known as the Mohs Scale Materials
what are the 10 Mohs Scale Materials? Hardness increases 1 - 10.
Talc
Gypsum
Calcite
Fluorite
Apatite
Orthoclase
Quartz
Topaz
Corundum
Diamond
The Gecko Couldn’t Fight Against One Quail, Too Catty, Damn!
how is the Mohs Hardness Scale determined?
by scratching the surface of the tile with different minerals and subjectively assigning a “Mohs” number
how is pumice created? Mohs number?
super-heated, highly pressurized rock ejected from a volcano, 6
what is another test to determine the hardness between the abrasive and the substrate?
indentation hardness test for surface hardness;
surface hardness (Brinell, Knoop, Vickers hardness tests)
what does the indentation hardness tests determine?
the size or depth of the indentation and the amount of force are used to calculate a hardness value
WHAT ARE THE FIVE FACTORS AFFECTING RATE OF ABRASION?
hardness between abrasive and substrate
abrasive particle size
abrasive particle shape
speed & pressure
lubrication
how does the particle size of the abrasive affect abrasion?
for the same applied pressure, larger particles leave larger scratches in the substrate and smaller particles leave smaller scratches
what are the four different sizes of abrasive particles?
superfine (<10 um)
fine (10-20 um)
medium (20-100 um)
coarse (100-500 um)
how does the particle shape of the abrasive affect abrasion?
a sharp particle (pointy) produces deeper abrasion than a rounder (blunt) particle under the same applied force
how does abrasive speed & pressure affect abrasion?
deeper and wider scratches are produced with increasing force.
equivalent sized scratches can be produced by different sized particles if you vary the applied pressure.
how does lubrication affect abrasion?
it reduces heat build up and helps wash away debris to prevent clogging of the abrasive instrument.
ex: oil in an engine to stop metal to metal contact
when does the most efficient abrasion occur?
when the difference in hardness between the abrasive and substrate is LARGER
what is the step-down approach to finishing and polishing?
gross reduction using diamond or carbide burs
finish (refinement of substrate surface)
polish (make smooth and glossy)
rotary grinding instruments!
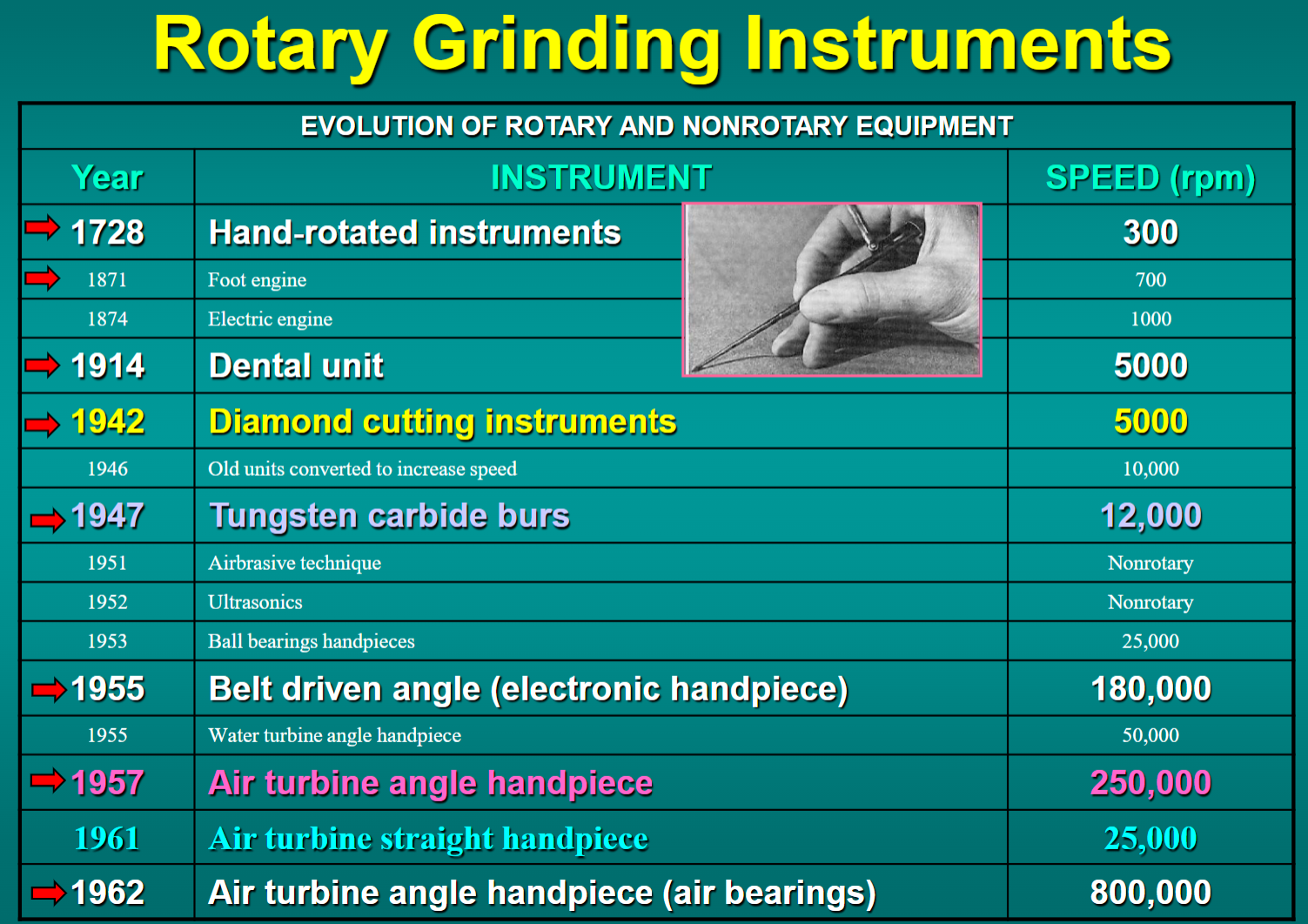
what are the three speed ranges of rotary grinding instruments?
low speed <20K rpm
medium speed 20K - 200K rpm
high speed >200K rpm
the high speed handpiece utilizes what?
it is air-driven; air turbine
balance between speed and torque, faster and consistent cutting and grinding
what type of handpieces are electric vs air-driven?
electric = 100K - 200K rpm (medium speed), greater initial cost, 60 watts
air-driven = 400K rpm (high speed), louder sound, high pitched, 20 watts
what are five types of finishing and polishing instruments?
carbide burs
diamond burs
dental stones
rubber wheels
disks & strips
what are the three basic parts of a dental bur?
shank, neck, head
shanks can very to accommodate either contra-angle or straight handpieces
shanks can be friction grip (high speed) or latch type (high or low)
what type of shank and cutting blade are used for CARBIDE burs?
bur shank is stainless steel
cutting blade is tungsten carbide
carbide burs are available in a variety of shapes that can be used for ____ and ____
contouring & finishing
the most commonly used burs range from ___ to ____ ____ blades which can be straight or twisted
range from 8 to 30 fluted blades which can be straight or twisted
what is the difference between straight and spiral blade design?
straight blade design have one blade on tooth, spiral blade design have multiple blades on tooth
READ THRU THE 13 STEPS OF STREAMLINED DIRECT RESTORATIONS
READ THRU THE 13 STEPS OF STREAMLINED DIRECT RESTORATIONS
finishing diamond instruments are used to __ , __ , and __ composites or porcelain
contour, adjust, and smooth
what is the structure of a diamond bur?
shank: stainless steel
abrasive: powdered diamond with a metallic bonding material that holds the powder onto the shank
what is the bur shank and bur cutting end of a diamond bur?
bur shank is stainless steel
bur cutting end is stainless steel w diamond particles cemented
diamond burs also come in disk form, what is the structure of the disk?
stainless steel metal disk with diamond particles cemented
three considerations with diamond particle use
usually applied in sequence, starting with coarser and progressing to a finer grit
diamond burs used WITH water spray
other polishing instruments (ex: rubber) will usually follow the use of diamond
carbide burs are better for ____, the produce lower heat, and have more _____ for cutting
better for end-cutting, produce lower heat, have more blade edges
diamond burs are more effective for ____, ____, and __
1) tooth preparation
2) beveling enamel margins
3) enameloplasty
carbide vs diamond bur $$$
$ 1 vs $$$ 3
5 recommendations for cutting
use contra-angle handpiece to cut
use air-water coolant system
use higher-operating speed >200K
use light pressure
use carbide or diamond bur
what are the procedures for finishing & polishing?
original rough surface
1) gross reduction & contouring
2) finishing
3) initial polishing
4) final polishing
final smooth restoration
what do dental stones consist of?
consist of abrasive particle that have been sintered together or bound with an organic resin to form a cohesive mass
available in fine, medium, and coarse grades
stones are used for ___ and ____ when ___ abrasion is needed
used for contouring & finishing when maximum abrasion is needed
three examples of dental stones include
silicon carbide (carborundum)
aluminum oxide
diamond
what are rubber wheels used for?
fine grinding to remove coarse scratches from rough grinding
how are rubber wheels made?
made by molding the fine abrasives (AlO, SiC, CrO) into a rubber matrix
what are rubber polishers used for?
adjusting and polishing acrylic material
come with variety of shapes since they are flexible to reach more tooth surfaces
when using rubber polishers…
use light pressure! (avoid friction heat because it can be deleterious to the restoration, rubber, and tooth)
why are polishing strips useful?
particularly useful in finishing and polishing interproximal areas
what is the peak-to-valley height?
the scratches. we want to reduce this height 9and active SA of restoration) with proper polishing.
finishing and polishing sequence! woohoo!
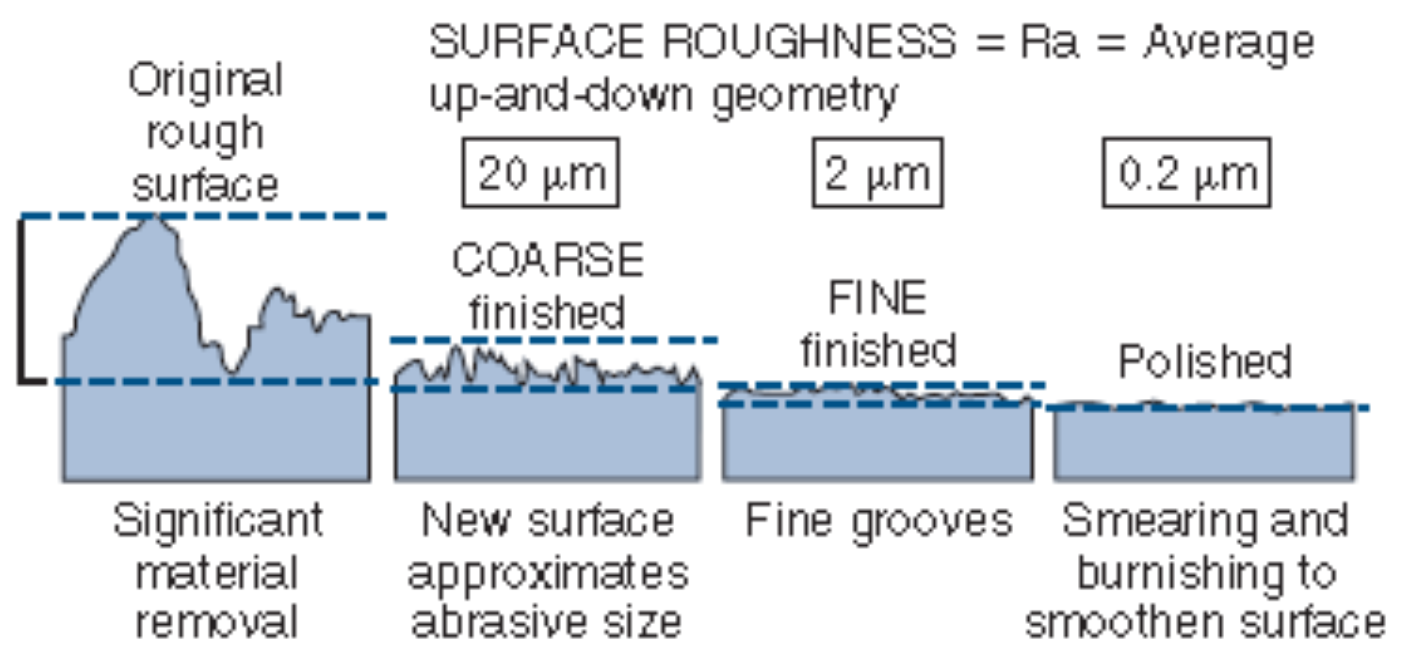
if the polished surface is DULL,
the scratches are GREATER THAN 0.5 um
if the polished surface is SHINY,
the scratches are LESS THAN 0.5 um (500 nm vis light)
the tongue can feel scratches. when can the Pt feel rough? smooth?
scratches GREATER than 20 um deep are ROUGH
scratches LESS than 2 um deep are SMOOTH
what is the importance of coolants?
control frictional heat at cutting site (vital tissue)
what are the three most common types of coolant?
air, water, & air-water spray
when does an air coolant work?
used when visibility is a problem
used with low speed and light intermittent application
when do you use water coolant?
it is very effective, but clouds visibility
if cutting is continuous though, the water might be deflected
why is air-water spray the most common type of coolant?
maximizes visibility, lubricates and cleans which increases cutting efficiency and instrument life
dental prophylaxis paste should be carefully chosen and applied to _______ without ______
applied to remove exogenous stains and particles
without damaging tooth structure or adj. restoration
why is dentifrice/toothpaste used?
used to remove debris and residual stains from teeth and for polishing the tooth surface and restoration
abrasivity values for dentifrice products are reported as
abrasivity index (AI)
what is the abrasivity index (AI) a measure of?
the amount of material abraded from a dentin surface in a given time period
higher AI means more wear in a set amount of time
when you polish amalgam, use ____
copious amounts of coolant
key polishing concepts and tips
work from larger grit to smaller grit
coarse - medium - fine - superfine
use slower and optimal speed
light pressure
5 characteristics of a well polished restoration
maximize esthetic appearance
resist staining & plaque formation
minimize soft tissue irritation
decrease wear on opposing dentition
increase durability and service life
how are disks made?
made by a stiff plastic or paper backing coated with abrasive particles
what are disks used for?
used for gross reduction, contouring, finishing, and polishing
Enhance Finishing (aluminum oxide) and PoGo Polishing (diamond) systems are designed to
finish and polish all types of composite restoration surfaces
what is a flute?
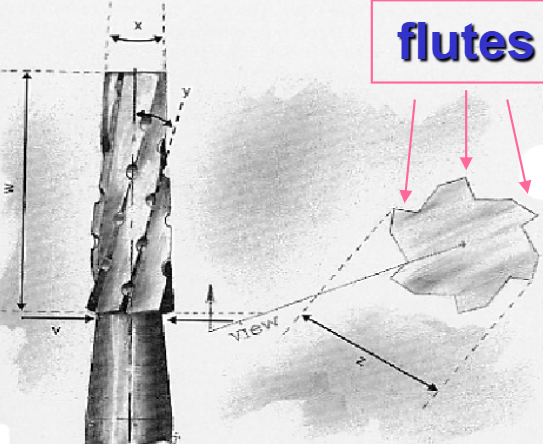
what is the rake angle?
the angle made between the rake face and the line connecting the edge to the axis of the bur