SSEH1103 Module 1
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Health and Wellness, Physical Fitness, Motivation, Self-Determination and Need-Supportive Behaviour, Exercise and Training Principles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Health
a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity - World Health Organisation
Wellbeing
a multidimensional state of being describing the existence of positive health in an individual as exemplified by quality of life and a sense of wellbeing - Corbin and Pangrazi (2001)
Characteristics of Wellness
Multidimensional
Integrated Components
Non-binary and Dynamic
Wellness Dimensions
Emotional
Intellectual
Physical
Social
Spiritual
Environmental
Vocational
Wellness Internal Environment Factors
Hereditary
Congenital
Attitudes and Values
Personal behaviour-acquired risk factors: smoking, eating, driving habits
Wellness External Environment Factors
Physical: living and work environment, pollution
Biological: micro and macro organisms
Socio-Economical: education, income, health services
Fitness
the quality of being suitable to fulfil a particular role or task
Physical Fitness
an ability function effectively in meeting the physical demands of the day's work and to use free time effectively
Characteristics of Physical Fitness
Health-related physical fitness
Skill-related physical fitness
Health-related Physical Fitness
a fitness component that has direct influence on your physical health and wellness
Skill-related Physical Fitness
the aspects which are fundamental to athletic or work skills. Not essential for development and maintenance of physical fitness for health benefits
Cardiovascular Endurance
the ability of the heart, lungs, and vascular system to deliver O2 to working muscles during sustained physical activity
Muscular Strength
the ability to exert force against a resistance
Muscular Endurance
the ability to apply force repeatedly, or to sustain a contraction for a period of time
Flexibility
the capacity of a joint to move freely through a full range of motion without undue strain
Body Composition
the relative amount of fat and fat-free tissue that comprises body weight
Self-Determination Theory
the motivation by stating that people are driven when they feel autonomy (control over choices), competence (capable and effective), and relatedness (connected to others).
Broad Forms of Motivation
Intrinsic
Extrinsic
Amotivation
Purpose of Self-Determination Theory
helps explain how humans grow and thrive, aiming for happiness and a fulfilling life (eudaimonia)
Self-Determination Continuum
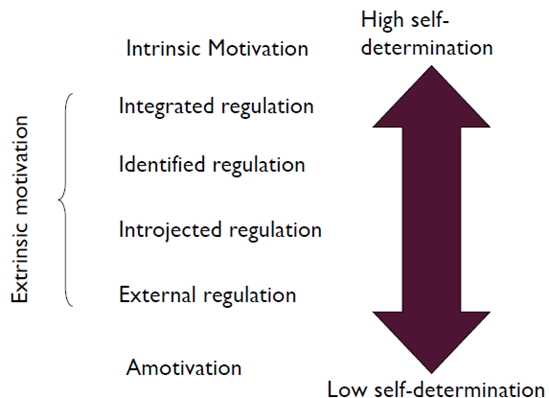
External Regulation
action performed to satisfy an external demand or reward
Introjection Regulation
taking in a regulation, but not fully accepting or endorsing is as one’s own
behaviours that require self-control, are performed to avoid guilt, or attain some kind of ego enhancement
Identified Regulation
identifying with the value of a behaviour or behavioural goal
the action itself is personally important, but the activity may not be pleasant
Integrated Regulation
the behaviour is a part of you, it’s fully assimilated to the ‘self’
the behaviour is in line with your values and needs, nonetheless, the behaviour is still performed for reasons other than inherent enjoyment
Intrinsic Motivation
the ‘gold standard’ of motivated states
the endorsement of behavioural engagement is completely internalised
engaging in a behaviour for the inherent pleasure or satisfaction
Need-Supportive Behaviour
actions that foster a person's intrinsic motivation by supporting their needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness, leading to better engagement and wellbeing
autonomous motivation is highly desirable in exercise
Importance of Autonomous Motivation
Improved exercise adherence, wellbeing
Positive relationship between autonomous motivation and exercise behaviour
How to Support Autonomous Motivation
Autonomy support
Structure
Interpersonal involvement
Autonomy Support
helping individuals feel in control and motivated
What does Autonomy Support Involve?
Offering choices, like exercise variations or intensity levels
Using supportive, non-controlling language (avoiding "should" or "must")
Exploring their personal goals and values
Giving constructive feedback to enhance understanding
Structure (Competence)
building competence by offering clear guidance and support
What does Structure (Competence) Involve?
Giving clear and constructive feedback, framed positively
Recognising effort and progress, not just outcomes
Tailoring challenges and demonstrations to fit individual needs
Interpersonal Involvement
building strong, supportive connections with others
What does Interpersonal Involvement Involve?
Showing empathy and care, especially during challenges
Taking an interest in others by learning about them and sharing a bit about yourself
Encouraging questions, being non-judgmental, and offering positive, unconditional support
Major Exercise and Training Principles
Individuality
Specificity
Progressive Overload
Recovery
Principle of Individuality Considerations
Tolerance of training loads
Responsiveness to training load
Recovery from training
Training needs
Environmental tolerance
Physical Characteristics
Life-Style variations
Preference
Principle of Specificity
the adaptations which occur are specific to the type of training performed
SAID stands for
Specific Adaptation to Imposed Demands
Principle of Progressive Overload
the gradual increase of stress placed upon the body during exercise training, essential for improving fitness
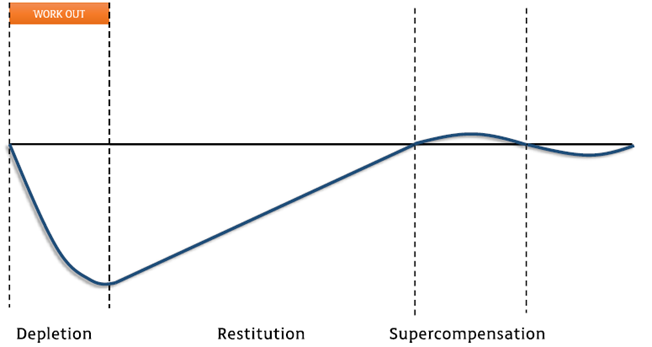
Principle of Recovery
the time required for the body to recover after exercise training, crucial for adaptation and performance improvement
Stress-Recovery Model
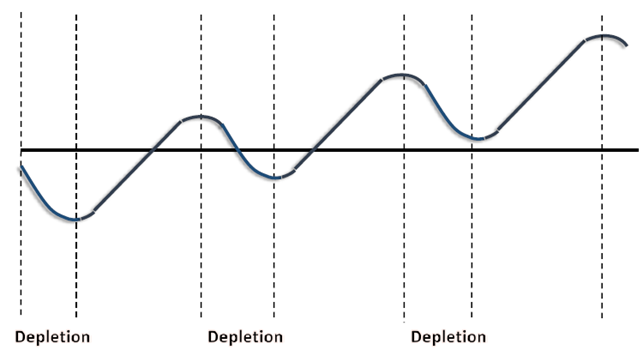
Repeated Stress-Recovey Model
Intensity vs Volume Graph