Toxic pulmonary diseases
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
club cell
___________: Non-ciliated cell that produces surfactant and serves as the progenitor cell in the airways for Epithelial repair.
surfactant, progenitor, epithelial
Club cells produce _______ and serve as ______ calls in the airways to aid in ________ repair
smooth endoplasmic reticulum, club cell secretory protein (CC10), phospholipase A2
Club cells contain a lot of _________, and secrete ________ in response to adrenergic stimuli, which inhibits __________
fog fever
Acute bovine pulmonary edema and emphysema is commonly referred to as ________
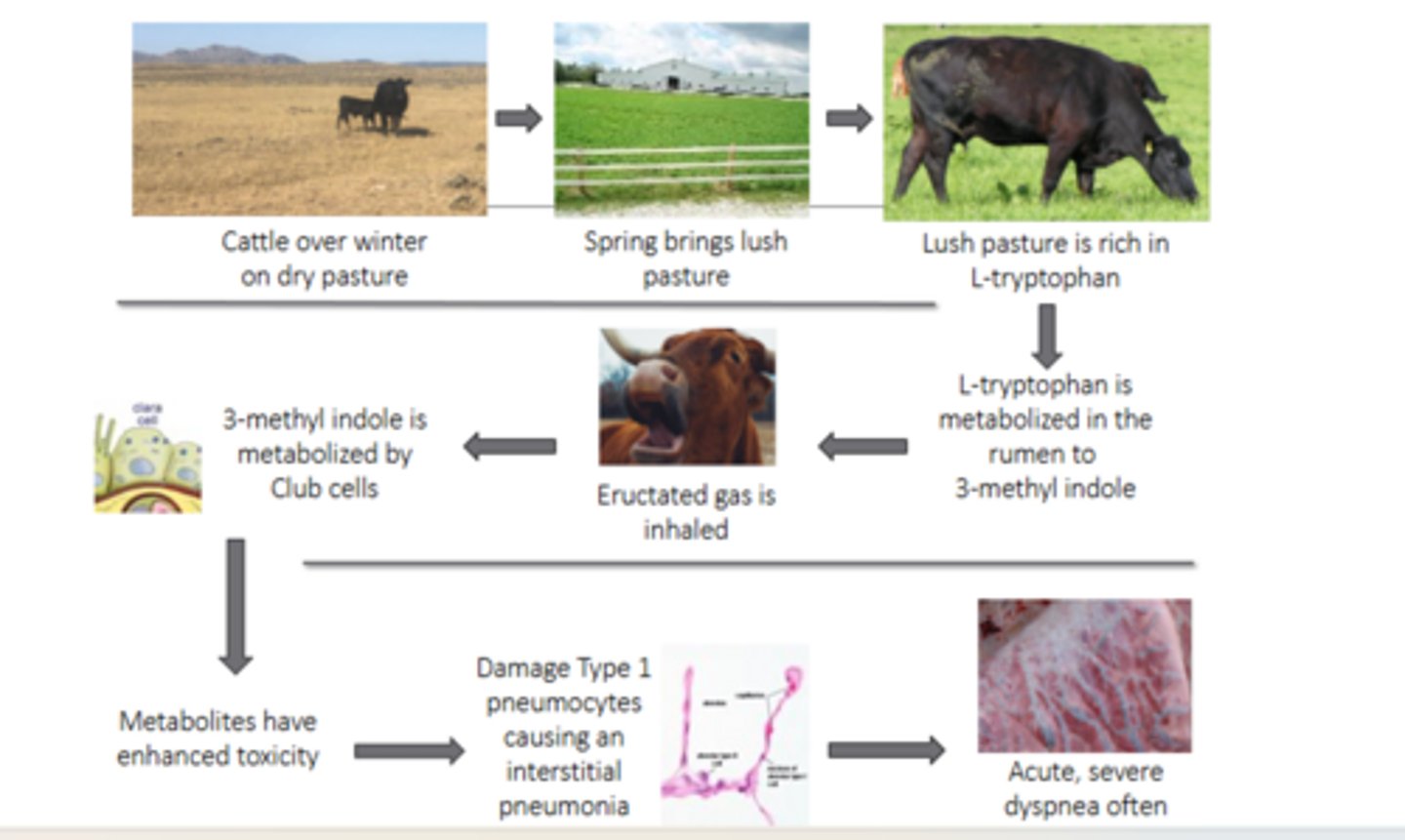
cattle no dry pasture over winter being switched to lush pasture RICH IN L-TRYPTOPHAN
What is the common inciting factor of Acute bovine pulmonary edema and emphysema?
l-tryptophan, rumen, 3-methyl indole
After being switched to lush pasture, _____________ is metabolized in the _______ to ___________
it's eructated and inhaled or absorbed through rumen wall
What happens to 3-methyl indole after its made in the rumen from L-tryptophan?
club cells, cytochrome p450, metabolites are incredibly toxic
After being absorbed into the lungs, 3-methyl indole is metabolized by _______ using _________.
Why is this bad?
type 1 pneumocytes, interstitial pneumonia
After 3-methyl indole is converted to toxic metabolites, these cause damage to __________ causing a _______________
increased permeability, pulmonary edema, interstitial emphysema, respiratory distress
The damaged lung tissue becomes leaky, leading to _________, ___________, _________ and _________, which can be fatal.
cool
She said to make sure you knew these 9 steps of "acute bovine pulmonary edema and emphysema".
It's basically the last couple terms I just went through, but the specific shortened steps are on slide 4 of lecture 11 if you want to check them.
Cool?
beef cattle in spring, 2-10 days,
Who is the prime suspect for getting fog fever?
This usually occurs ___________ days after switching to a lush pasture.
sudden death, frothing at the mouth, dyspnea, 50%
what are the clinical signs of Fog fever?
morbidity is about ________%
pale, soft and rubbery, dorsocaudal, interstitial edema, emphysema
Affected lungs (fog fever) are often ________, ______ and _______ especially in the ________ lung lobes.
There is significant _________ and ________. This correlates with the clinical signs of dyspnea and frothing at the mouth.
moldy sweet pototes, perilla mint, brassica spp
What plants are included in a differential diagnosis for toxic pneumonia in ruminants
4-ipomeanol, type I pneumocytes, S-methyl cystine sulfoxide.
Moldy sweet potatoes contain _________.
Perilla mint (perilla ketones) can also damage _______________.
Plants in the Brassica family (decorative cabbages) contain _______________________>
laryngeal and respiratory tract edema
Smoke inhalation causes thermal injury like __________________ and _______________ from inhalation of heated air and damage to epithelium
type I pneumocytes
Chemical injury from smoke inhalation includes damage to _______________________
true, duh
true/false: There are many causes for pulmonary toxicity, including chemicals, plants, etc, so obtaining a good history is necessary for diagnostics