Genetics Honors bio
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Genetics
branch of biology that is concerned with how characteristics are transmitted from parents to offspring
Heredity
passing on of a characteristic from parents to their offspring
traits
consist of two genes
1 from each parent
gene
segment of DNA that codes for a trait
Allele
a single gene
Gregor Mendel
used pea plants
they're able to self pollinate and cross pollinate
reproduce very quickly
can study several generations in a short period of time
They had 7 contrasting traits
1. pea textures ( smoothed or winkled)
2. Flower color (purple or white)
3. Color of pod (green or yellow)
4. Pea height (height of plant )(tall or short)
5.Pea color (Green or Yellow)
6. Pod Texture (inflated or Constricted)
7. Flower Position (axial or deminal)
very accessible to him
Mendel's Experiments
1. He grew plants that were pure for each trait by allowing them to self pollinate through several generations
2. He crossed a pure tall plant and a pure short plant
P1 generation
the original parents
The results
offspring's were all tall
Tall was dominant
All tall is P1 generation
F1 Generation
offspring of the P1 generation
3. Cross two plants from the F1 Generation
Results
offspring's were 3/4 tall, 1/4 short
Recessive gene have been hidden
F2 Generation
offspring of F1 Generation
Mendel called genes factors or units
Dominant gene
represented by a capital letter

Dominant trait
if the dominant gene is present, the dominant trait will show
Ex
RR or Rr
recessive gene
represented by a lowercase letter
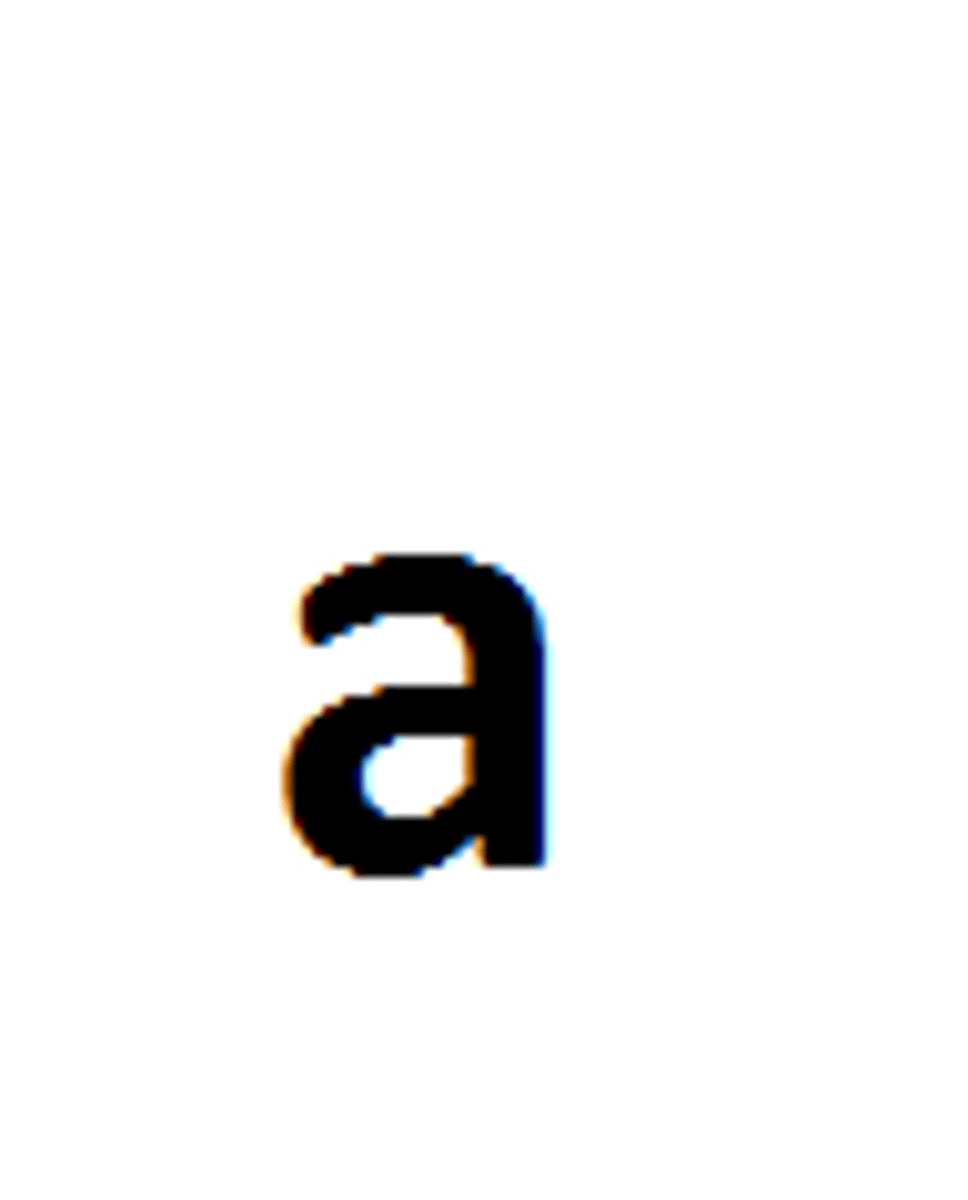
Recessive trait
only expressed if two recessive genes are present
Ex
rr
Homozygous trait (purebred trait)
trait that contains two genes that are the same
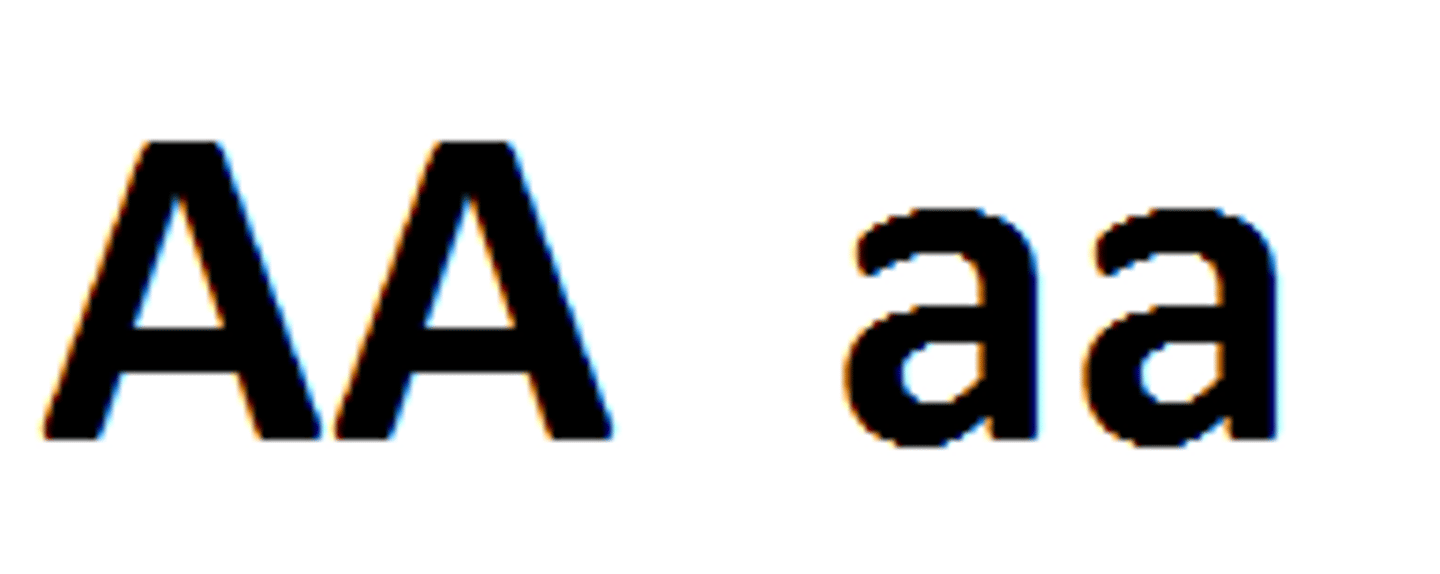
Heterozygous trait (hybrid trait)
a trait that has two different genes

Phenotype
actual visible physical characteristics a genotype produces
ex
Brown hair, Blue eyes, Purple flowers, wrinkled pea, green pea
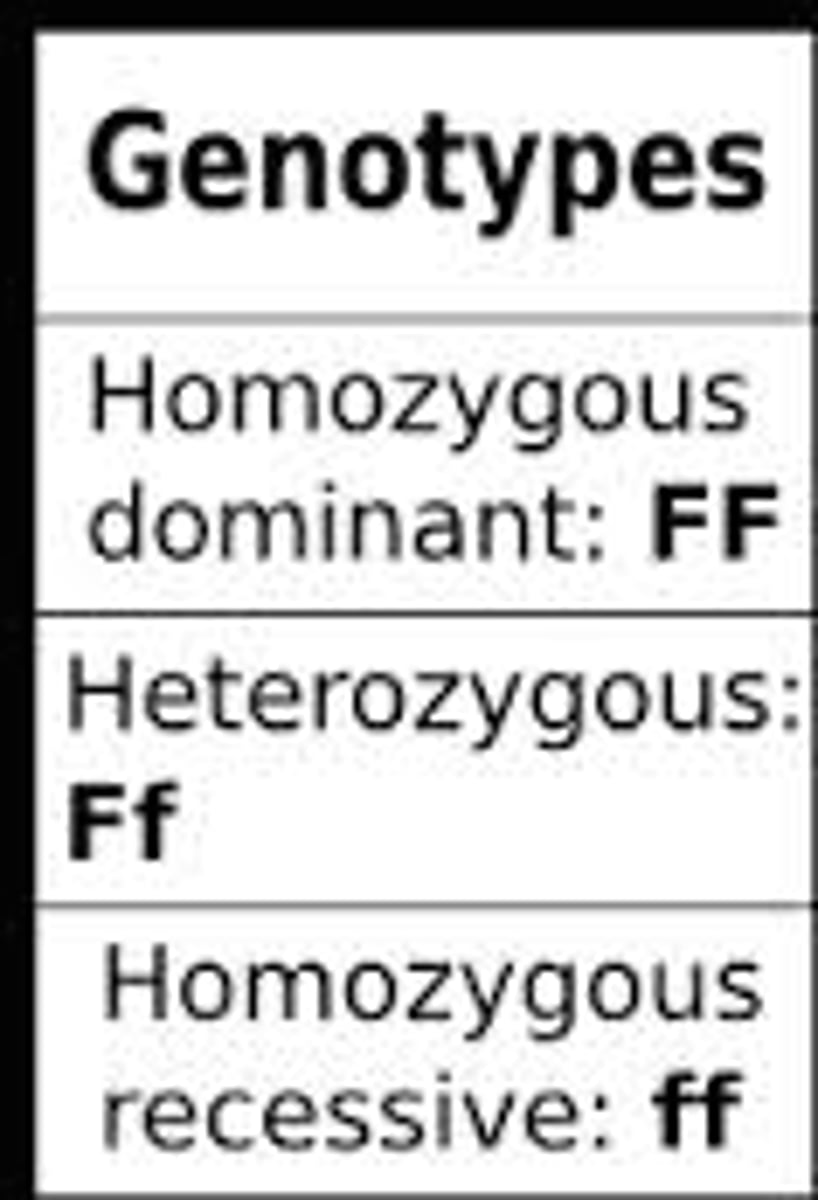
Genotype
the actual allele combination
Mendel's Laws
Law of Dominance
if the dominant gene is present, the dominant trait will show
ex
Bb
law of seggregation
during gamete formation gene pairs for every trait will separate
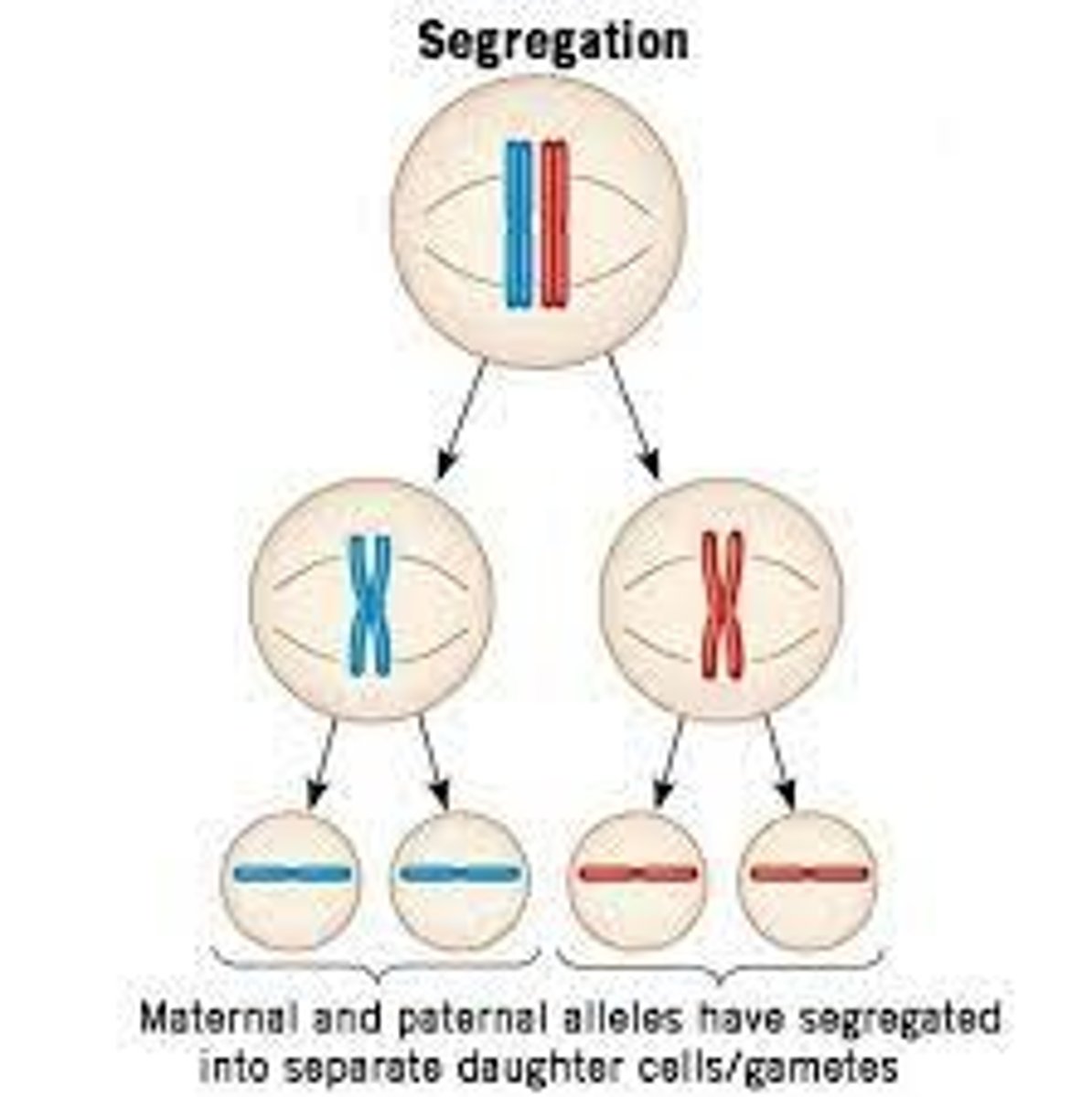
gamete
sex cells (egg in sperm)
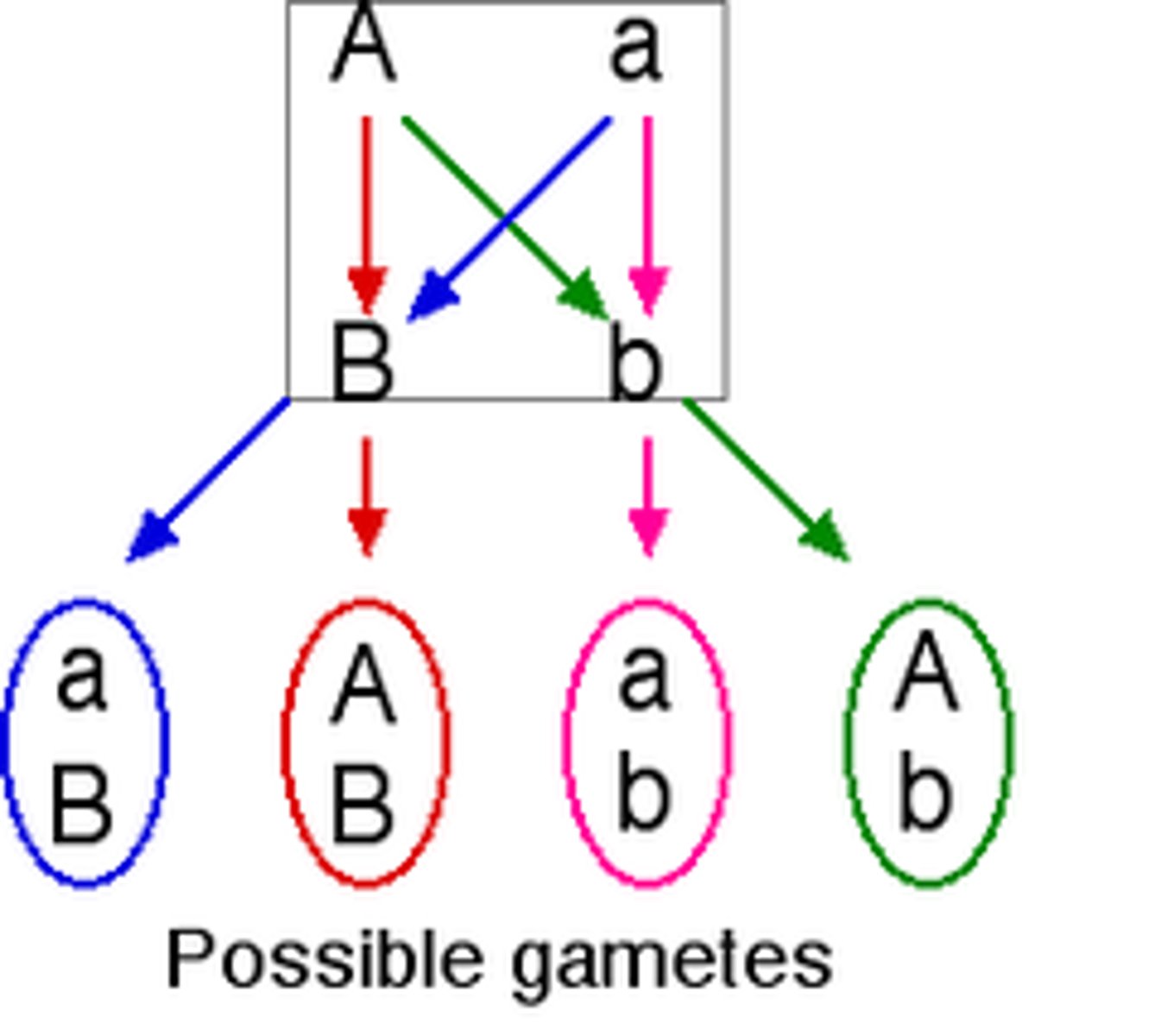
law of independent assortment
during gamete formation genes for every trait will separate independently from one another
Probility
The chance will or will not happen
1. Percent
2. Fraction
3. Ratio
ex
chances of coin being heads
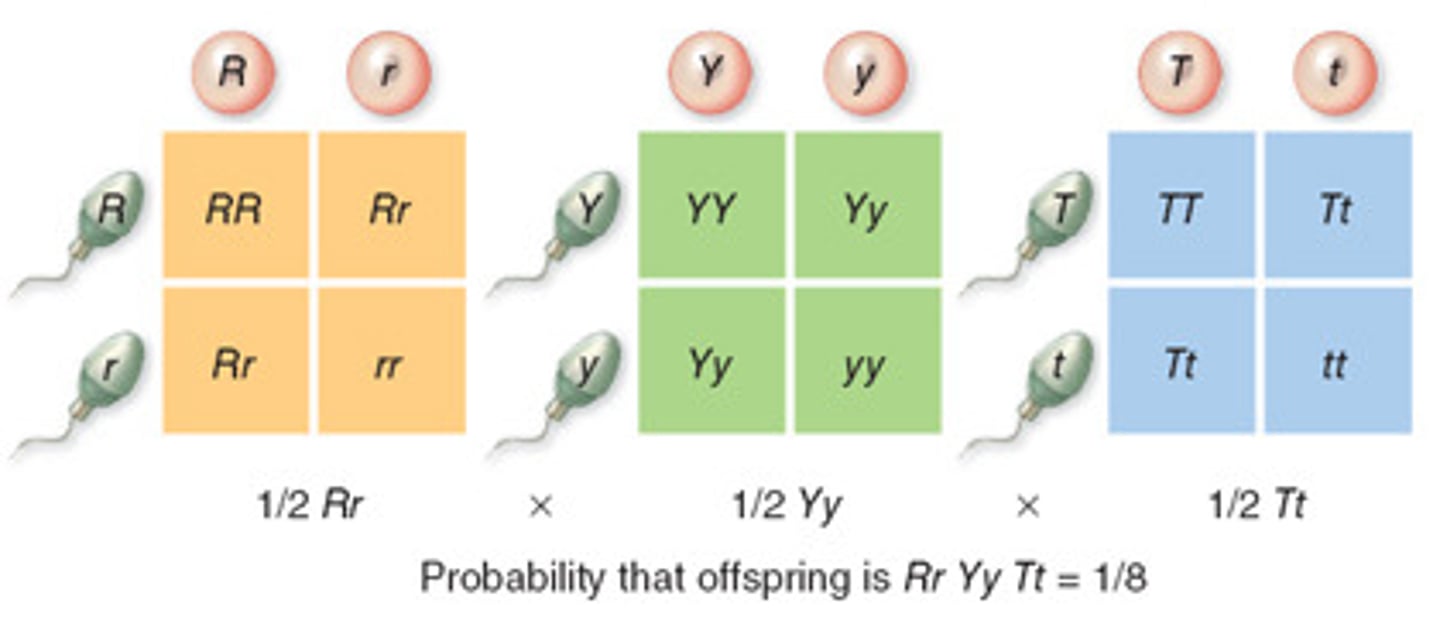
product rule
probability of more then one thing happening at the same time
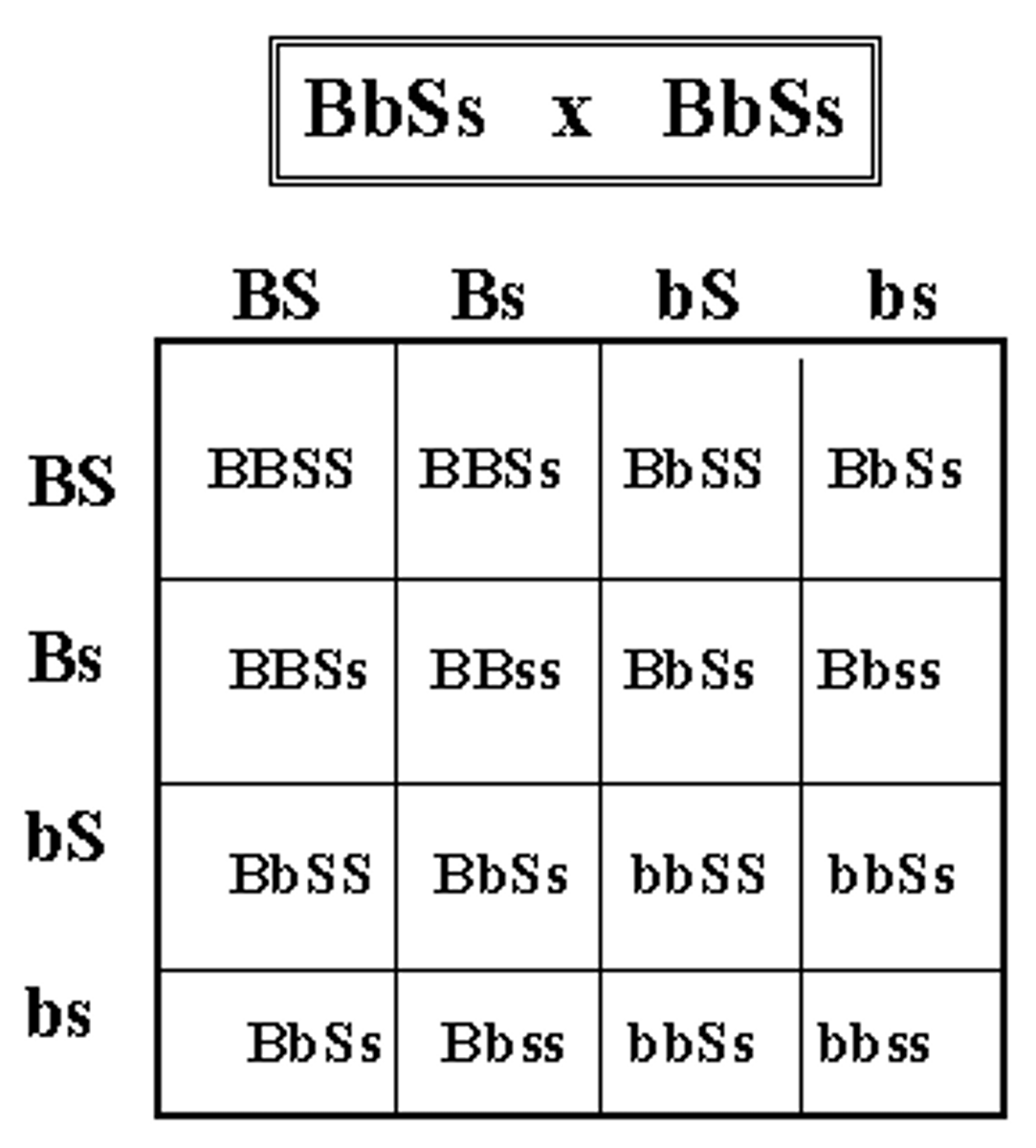
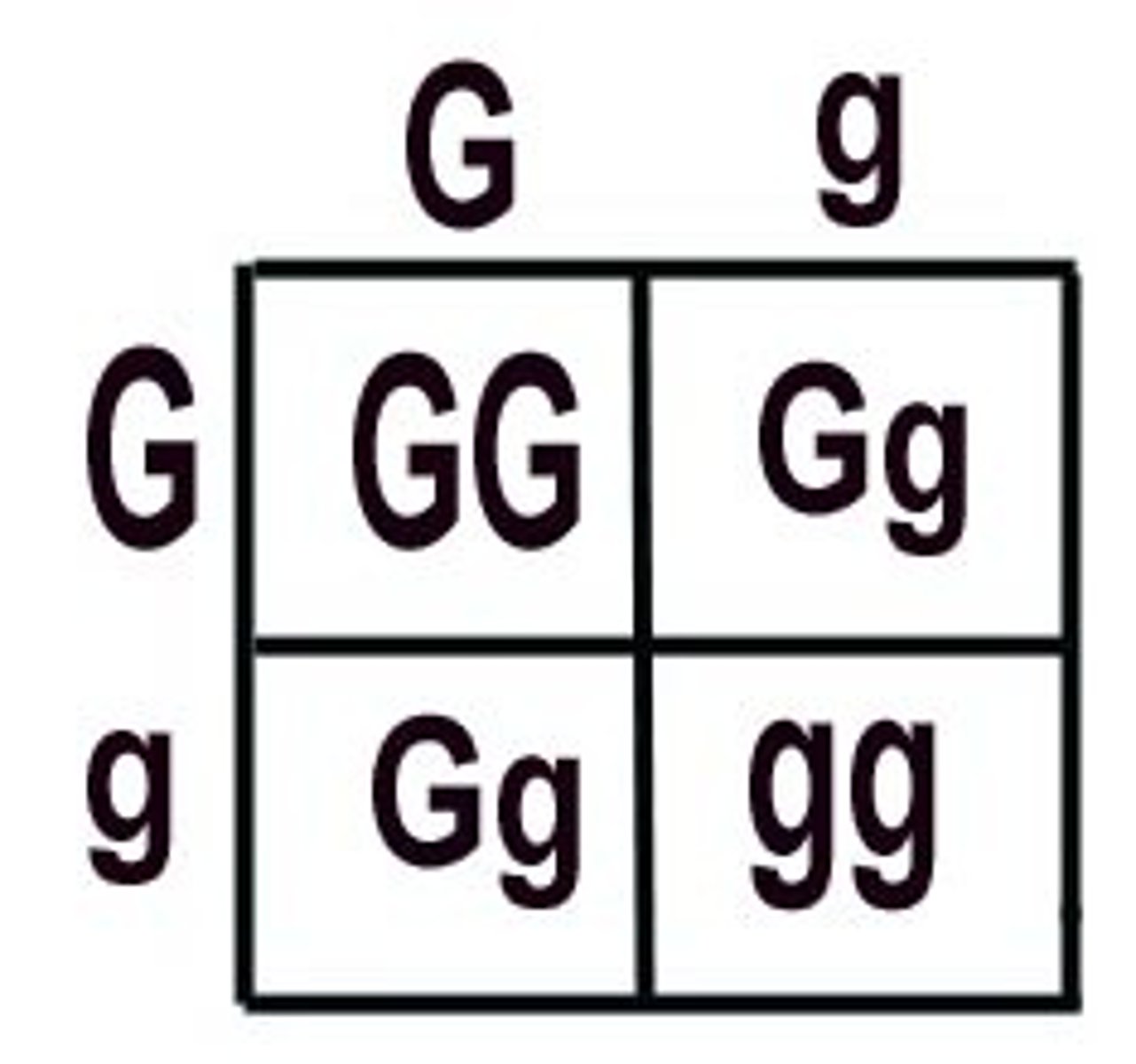
Punnett square
used to determine the probability of possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring
Monohybrid cross
cross that involves one trait
Genotype ratio
Number of offspring with the same allele combination
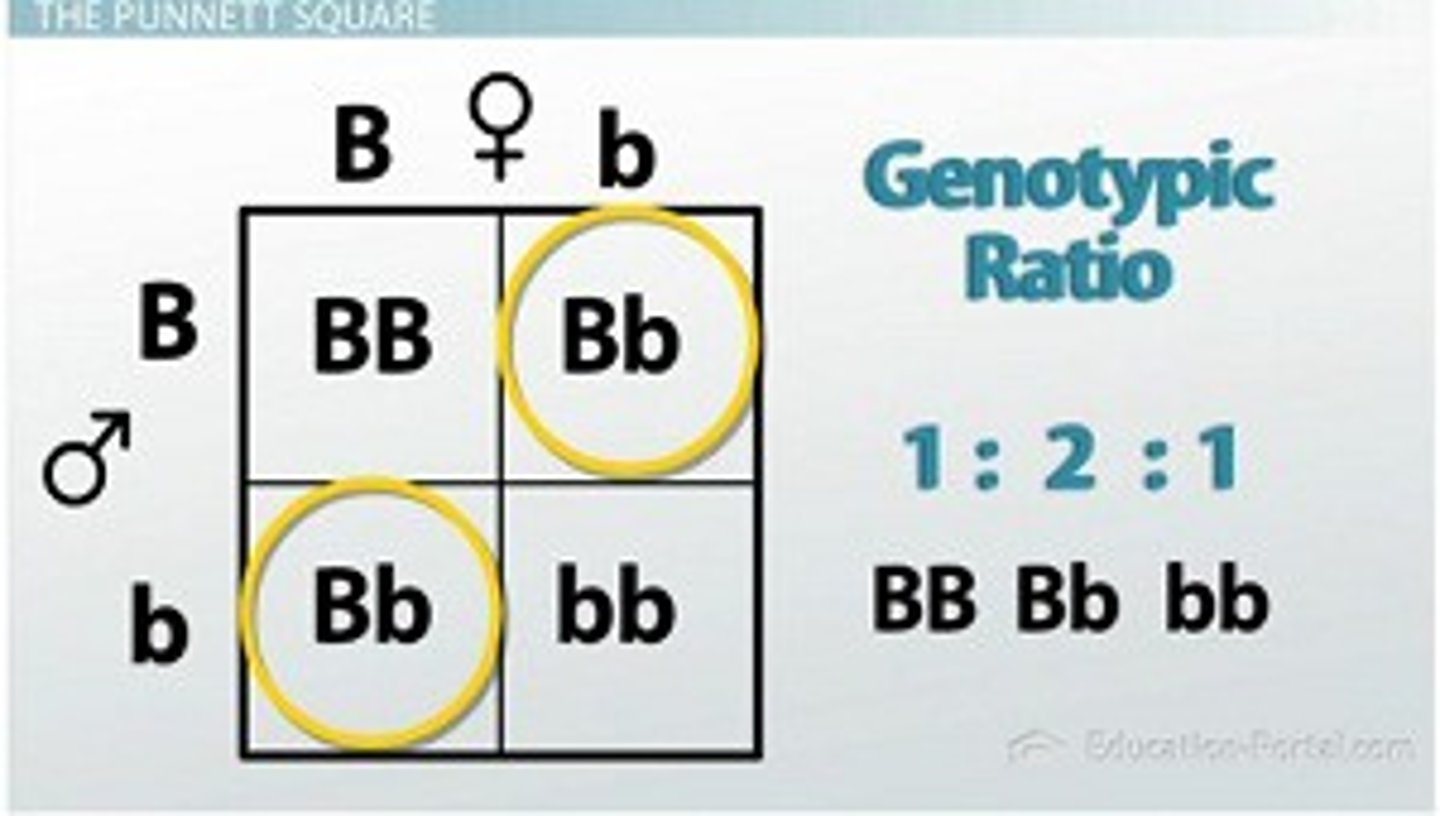
Phenotype ratio
Number of offspring that look the same physically
Dihybrid cross
cross that involves two different traits