earth 300 - final exam
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
earths atmosphere formed as the result of
escape of gasses from the earths interior
earths amosphere is comprised of 99% ___&__
nitrogen and oxygen
what is the relative humidity when the temperature reaches dew point
100%
why is stratospheric ozone so important
ozone absorbs harmful UV radiation
land is changes temperature more rapidly (T/F)
True
name the gas that is an effective greenhouse gas
carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor
adiabatic heating-cooling
processes where a gas's temperature changes without heat being exchanged with its surroundings. Adiabatic cooling happens when a gas expands, causing it to do work and lose internal energy, which lowers its temperature (e.g., rising air in the atmosphere). Adiabatic heating occurs when a gas is compressed, doing work on it and increasing its internal energy, which raises its temperature
cyclones
a rotating, organized system of clouds and thunderstorms that forms over tropical or subtropical waters, characterized by a closed low-level circulation. They rotate counterclockwise in the NH. Has a low-pressure center and are associated with rising air.
why is the equatorial region so wet
intense, year-round solar heating that causes constant evaporation, creating warm, moist air that rises, cools, and condenses into heavy rainfall. This process is fueled by the high energy input at the equator, which leads to a low-pressure zone where warm air is forced to ascend. As the warm, moist air rises and cools, the water vapor condenses into clouds and rain, often in the form of daily thunderstorms.
what causes monsoon conditions to develop
warm, moist air from the ocean flows onto land, causing wet conditions
what is the global scale implication of the melting of large amounts of permafrost?
massive amounts of methane will be released form permafrost, resulting in increased global warming
the amount of solar energy received over a unitarea of the earths surface is called
insolation
low latitude deserts occur near latitude 30 and are the product of ___
high-pressure zones created by descending dry air from the Hadley cell atmospheric circulation
why would oxygen gas in earths atmosphere go away if all life went extinct?
oxygen supply will be cut off with the ending of photosynthesis as iron in rocks will oxidize
name the upper limit where all the pore space in a rock are filled with water
water table
the temperature of the deepest parts of a deeplake is always near
3 degrees C
the increase concentration of ___ in the atmosphere is most responsible for global warming and the greenhouse gas effect
carbon dioxide
what is a groundwater contamination concern in coastal areas in cali
the incursion of seawater into an aquifer in response to over pumping of ground water
what is the name of the most accepted hypothesis for the formation of the earth and solar system?
nebular hypothesis
most glaciers have been ___ since 1990
retreating
valley glacier
a river of ice in mountains
ice sheets
a glacier that covers a very large area
tidewater glacier
a glacier that reaches the ocean
convection
transfer of heat by mass movement
radiation
a heat released at the surface of a hot body
conduction
transfer of heat by molecular activity
localized convective lifting
unequal surface heating causes air to rise
frontal wedging
warm air rises as cold air moves into an area
convergence
air rises as two moving air masses meet
buoyancy
rise of less dense over denser material
orographic lifting
air rises as it travels across a mountain
a sedimentary rock containing graded bedding indicates a __ environment
deep marine
the ratio of the size of a reservoir and the rate of input is called the
residence time
which of these sediment types can be biogenous?
phosphate, siliceous, carbonate
which makes up the sedimentary rock chert?
mainly of microcrystalline quartz (𝑆𝑖𝑂2), which is a fine-grained form of silicon dioxide.
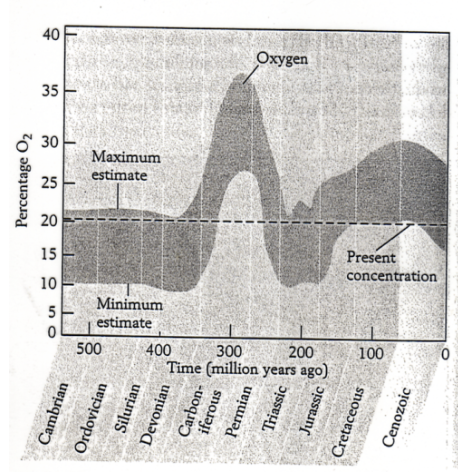
what is the level of atmospheric O2 since the acquisition of an oxygen rich atmosphere?
10-30%
which of these fossils are found in rocks as old as 3.5 billion years?
stromatolites, which are layered structures created by microbes, and are considered the oldest known evidence of life on Earth
the oceanic carbon cycle is best understood by using carbon isotopes and ___.
mass balance ?
name the factor that does not divide the ocean into distinct marine life zones
water chemistry
what is the name of the model that argues that the earth is a self regulating system held at homeostasis by the biosphere?
the gaia hypothesis
the source of coal is ___.
buried organic material
how much of the earths carbon in the near surface is currently in an inorganic oxidation state (carbonate)?
80%?
experiments by Stanley Miller and Harold Urey reacted ___ using ___ to simulate the formation of complex organic molecules from the “primordial soup”.
H2, CH4, NH3, H2O; an electrical charge
Chert is a chemical sedimentary rock that forms in __.
one hypothesized source of the organic build blocks of life is ___.
chondritic meteorites
which of the correct order of sediment deposition as a function of distance from the shoreline?
sandstone, shale, carbonate
____, made of calcite, is the most common biogenous rick.
limestone
what is the largest source of atmospheric sulfur that comes form the land (after humans)?
volcanic eruptions
the fluxes into and out of a reservoir in steady state are ___.
fluxes are equal
which of these detrital sedimentary rocks has the smallest particle size?
mudstone
the temperature of the deep ocean floor is always near __.
3 degrees C
a fine grained sediment that is well sorted and has round grains was transported a __ distance.
long
the sun was much fainter in the earliest part of Earth history. Why didn’t the earth freeze, considering it was receiving much less solar energy than today?
Atmospheric CO2 concentrations were much higher than today
a model that moves processes backwards is called a ___ model.
reconstructive ?
erosion occurs at the __ of a meandering stream.
cut bank
which of the following is not a type of change?
rotational
which of these variables do not affect the radiative balance of the earth?
wind speed
which of the following is not a source of atmospheric CO2, before humans?
chemical weathering of silicates
which statement best described carbon isotope values from carbonates during times of high rates of burial for organic material?
delta13C values increase
which of the following sedimentary rock characteristics indicates glaciation?
drop stones in an otherwise fine-grained layered sedimentary sequence
name the event responsible for the atmosphere becoming more oxygen rich.
the evolution of photosynthetic organisms
stable isotopes have ___ atomic mass and number
none of the above
the isotopes of__and__are measured in fossils of foraminifera to get information about ancient temperatures and biological productivity for a time in earths past.
carbon and oxygen
the stable isotope fractionation factor varies as a function of ___
temperature
the water standard for oxygen and hydrogen isotopes is called ___.
SMOW (standard mean ocean water)
which of these statements about stable isotopic composition of meteoric water is not true?
the delta18O and deltaD values of meteoric water increase with the degree of rainout. the values of meteoric water actually decrease with the degree of rainout
seawater delta18O values ___ during ice ages as water is removed from the ocean and accumulates on ice sheets.
increase, since the ice sheets take up the less heavy 16O.
which of these kinds of chemical reactions are most important when considering carbon isotope fractionation?
oxidation-reduction
corn is a C4 plant, so it will have a __ delta13C value.
higher (less negative)
which of these carbon species is not found dissolved in natural waters?
sugar
which of these factors do not contribute to soil erosion?
plant rotation practices
which of the following statements is true about feedback systems?
negative feedback systems resist change and stabilize a system
which of these are one of the hypotheses for the cause of snowball earth?
the position of the continents
salinity in the ocean increases in response to ___and___.
formation of sea ice, evaporation
what two factors slow down rates of chemical reaction in rocks and soils?
low temperatures and very dry
mechanical weathering adds to the effectiveness of chemical weathering because it ___the surface area exposed to water.
increases
which of these mass extinctions was the largest in earth history?
The Permian-Triassic mass extinction was the largest in Earth's history. It is often referred to as the "Great Dying" because of the immense loss of life.
assume that water filling a crack in a rock undergoes cycles of freezing and melting. Which of the following statements is true?
water expands as it freezes, causing the crack walls to be pushed apart
the permian mass extinction
Occurred 250 million years ago. At this time, amphibians ran the earth (prior to dinos). The mass extinction occurred in multiple stages. Changes in ocean chemistry led to the loss of coral reefs.
what was the most recent supercontinent during the Permian mass extinction?
Pangea. there was a loss of habitat due to lesser amounts of shallow seas and global deserts in continental interiors.
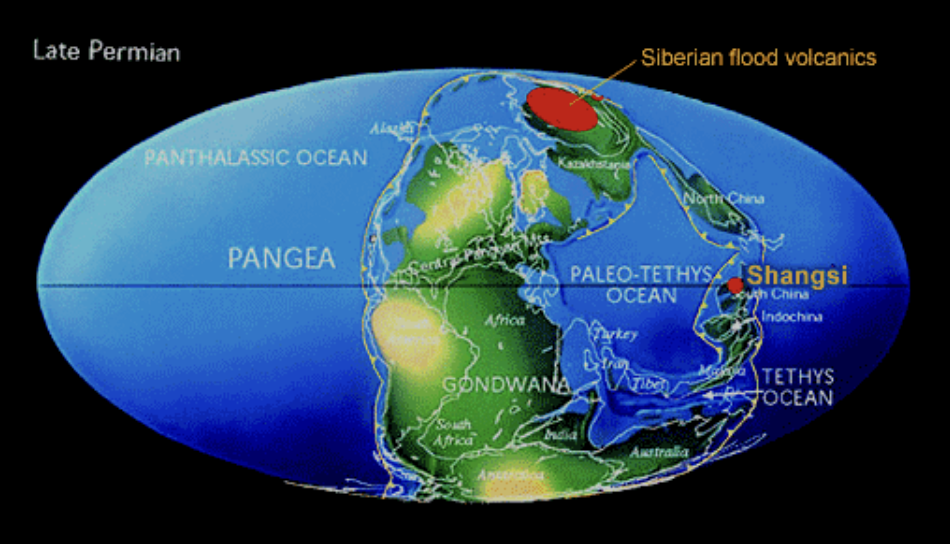
the Siberian Traps and its relation to the permian mass extinction
This was the largest volcanic eruption in geologic record that occurred almost exactly at the Permian-Triassic boundary. It covered an area half the size of the continental United States.
This created a massive flood basalt province. This is related to the emplacement of the mantle plume at the base of the crust. Sills are believed to have intruded into thick coal deposits, which results in the coal deposits warming up, CO2 is released, rapid warming occurs which then gets absorbed by the ocean, resulting in increased acidity dissolving calcium carbonates.
volcanic ash/dust can also decrease solar energy on Earth, resulting in cooling of the earth
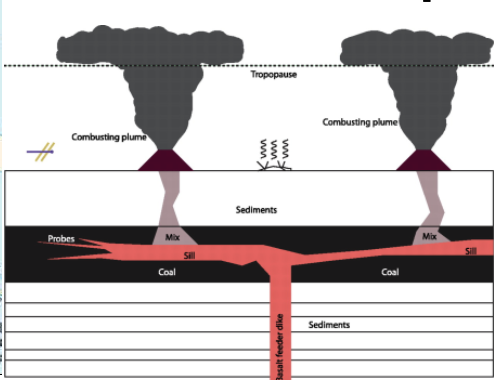
What is hypercapnia?
when CO2 builds up in the depths of a stagnant sea, resulting in acidification of oceans. This negatively effects the organisms, especially carbonate-baring ones. There are two cycles of buildup and release, accompanies by greenhouse cooling and warming
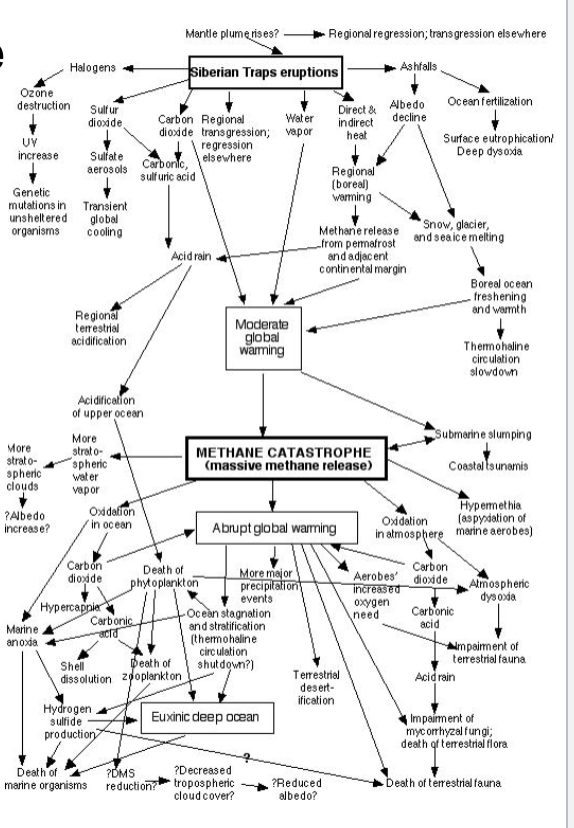
a methane catastrophe during the permian extinction
Dissociation of gas hydrates results in massive release of methane into atmosphere. Magnitude of global warming is much larger thatn if CO2 was the only GHG released.
Permian-Triassic Carbon excursion
There was a positive shift in delta13C. There was a development of vascular plants that created a new way of fixing carbon. increasing plants, resultisn in increase oxygen levels.
There was more burial of organic matter, increased free oxygen, and worldwide triassic redbeds. Much of the worlds coal deposition was just before this event due to the increase in burial of organic matter.
a Permian Impact Event
there are two candidates for this extinction theory:
bedout crater in northwestern Australia
Wilkes- land crater in Antarctica which is the largest impact event in geological records
what is the most recent hypothesis for the permian extinction?
a bloom of microbes may be responsible for the large increase in CO2 and CH4 concentrations. Anomalously high mercury concentrations are observed in sediments deposited during extinction events
summary of the permian extinction
strong correlation between impact events and large volcanic eruptions related to emplacement of plume heads. onset of continental breakup, these events trigger extreme changes in global climate
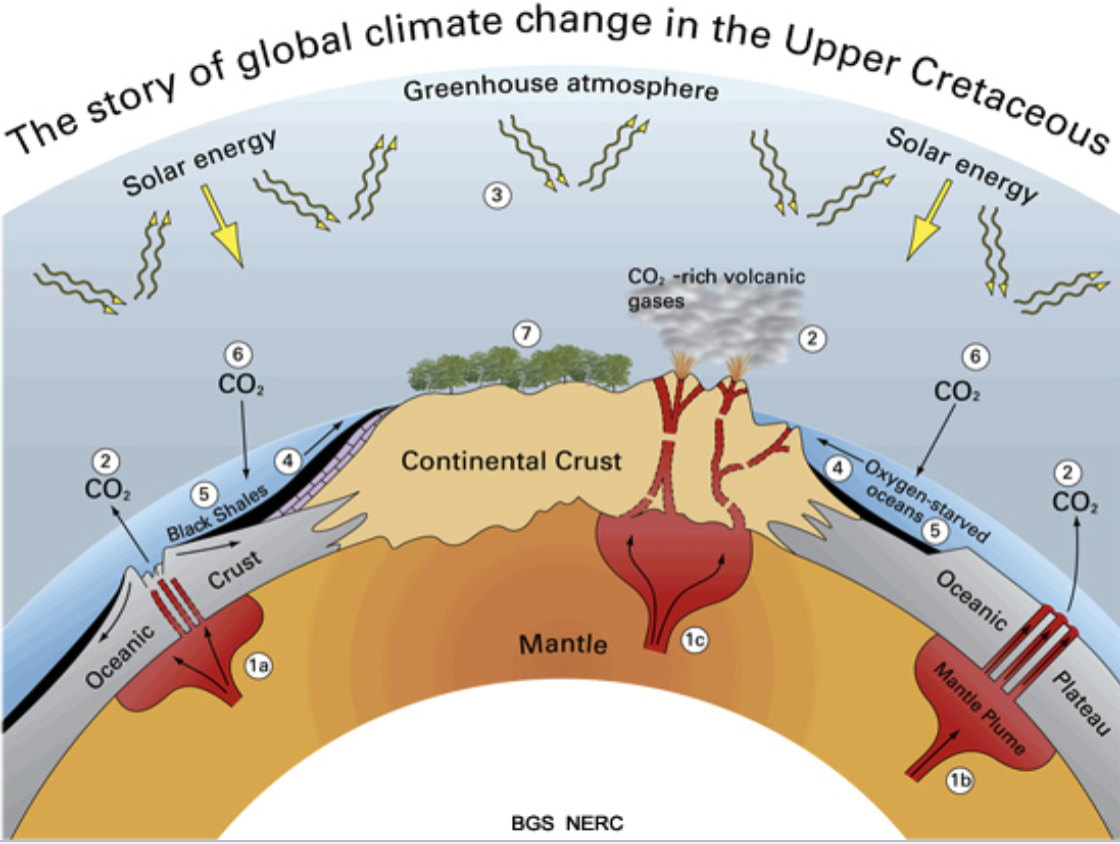
The Cretaceous Greenhouse
greenhouse conditions in which 4-8x modern atmospheric CO2 levels, resulting in increased weathering. Temperatures of tropical oceans estimated to have been 4-8 degrees warmer than today. Most petroleum was formed during this period because large areas of the ocean became anoxic for organic material to be buried.
temperature distribution during cretaceous
glaciation was unlikely because polar regions did not reach freezing (25-50 degrees C warmer than today). Temperate zones extended to poles.
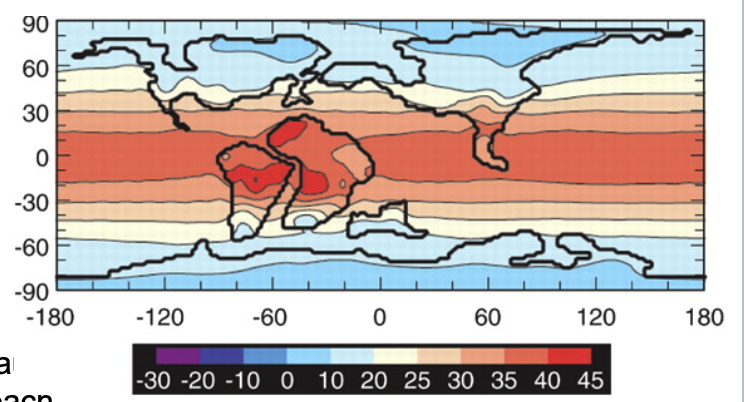
cretaceous paleogeography
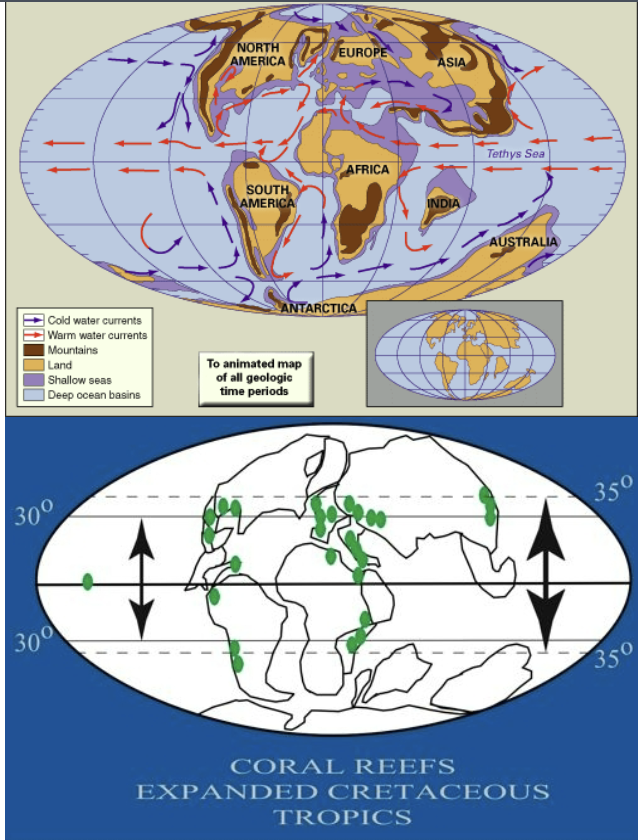
the break up of pangea is well underway. This is a time of high sea level in which much of Euroasia, NA, and Arabia is submerged with an abundance of shallow water habitat for marine life.
Gondwanaland begins to break apart, so lots of midocean ridges form
Intense magmatism along Pacifc rim where very rapid seafloor spreading in pacific ocean is taking place, as are rapid rates of subduction. This results in lots of CO2 going into atms
cretaceous ocean circulation and expanded coral reefs
Coral reefs may have extended to 35 degrees latitude (today to 30). Nearly circumglobal path for equatorial currents contributes to warmer ocean. System dominates by two very large gyres in Pacific/Tethys sea
major events in the cretaceous
numerous changes in sea level
rudist coral dominate and form reefs
ammonoids important ocean predators
giant swimming reptiles
dinos dominates land fauna
evolution and radiation of flowering plants
gymnosperms decline
mass extinction at end of period (dinos and ammonites)
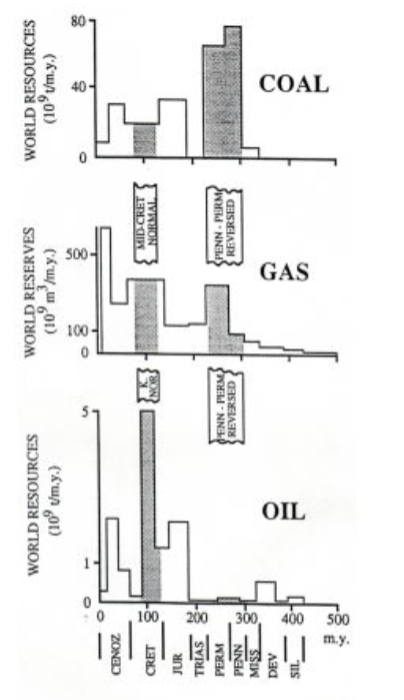
hydrocarbon accumulation through geologic time
peaks in hydrocarbon accumulation associated with times of large amounts of burial of organic materials.
coal: pennsylvanian and permian
oil: cretaceous greenhouse enviornment
both events are associated with high delta13C values.
events correlated with cretaceous thermal maximum
peak oil accumulation
peak spreading rate at midocean ridges
high sea level
deposition of black shales in anoxic basins
long cretaceous normal period of magnetism
rates of crust production during the cretaceous period
very large amounts of crust was produced during the long cretaceous normal paleomagnetic period. Increased rates of spreading resulted in higher sea level, flooding continents
black shale in the cretaceous
organic rich marine sediments deposited under anoxic, stagnant conditions
does the burial of organics (carbonates) in response to sea level ride result in increase of delta13C values?
yes. Organic matter is very 12C rich, burial removes 12C from the ocean and remaining ocean carbon becomes 13C rich.
the cretaceous mass extinction
marked by extinction of dinosaurs, ammonites, and rudist corals. This abrupt extinction was most likely due to an astroid impact at Chicxulub on Yucatan peninsula.
what do oxygen isotope records tell us?
Oxygen isotope records can be found through foraminifera retrieved for DSDP cores. high values indicate cold temperatures, low values indicate warm temperatures. Through this we discovered that the cretaceous was the warmest time, and stepwise cooling occurred since then.
position of continents and its connection with global temperatures
Temp changes are tectonic in origin. Positions of continents affects ocean circulation patterns which affect temperature patterns.