Facial, Skull, and Brain Anatomy Overview
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Cerebrum
Largest portion of the brain.
How many cranial nerves come from the brain stem
10 out of the 12!!! Cn1 and cn2 dont come from the brain stem
Where does cranial nerve 1 and 2 originate from if it's not the brain stem then?
The Cerebrum!!!!!
Brainstem
Small mass of tissue packed with motor and sensory nuclei; 10 of the 12 cranial nerves originate from the brainstem.
Cerebellum
small brain
Major regulator of motor activities; maintains balance, regulates muscle tone, and coordinates voluntary movement.
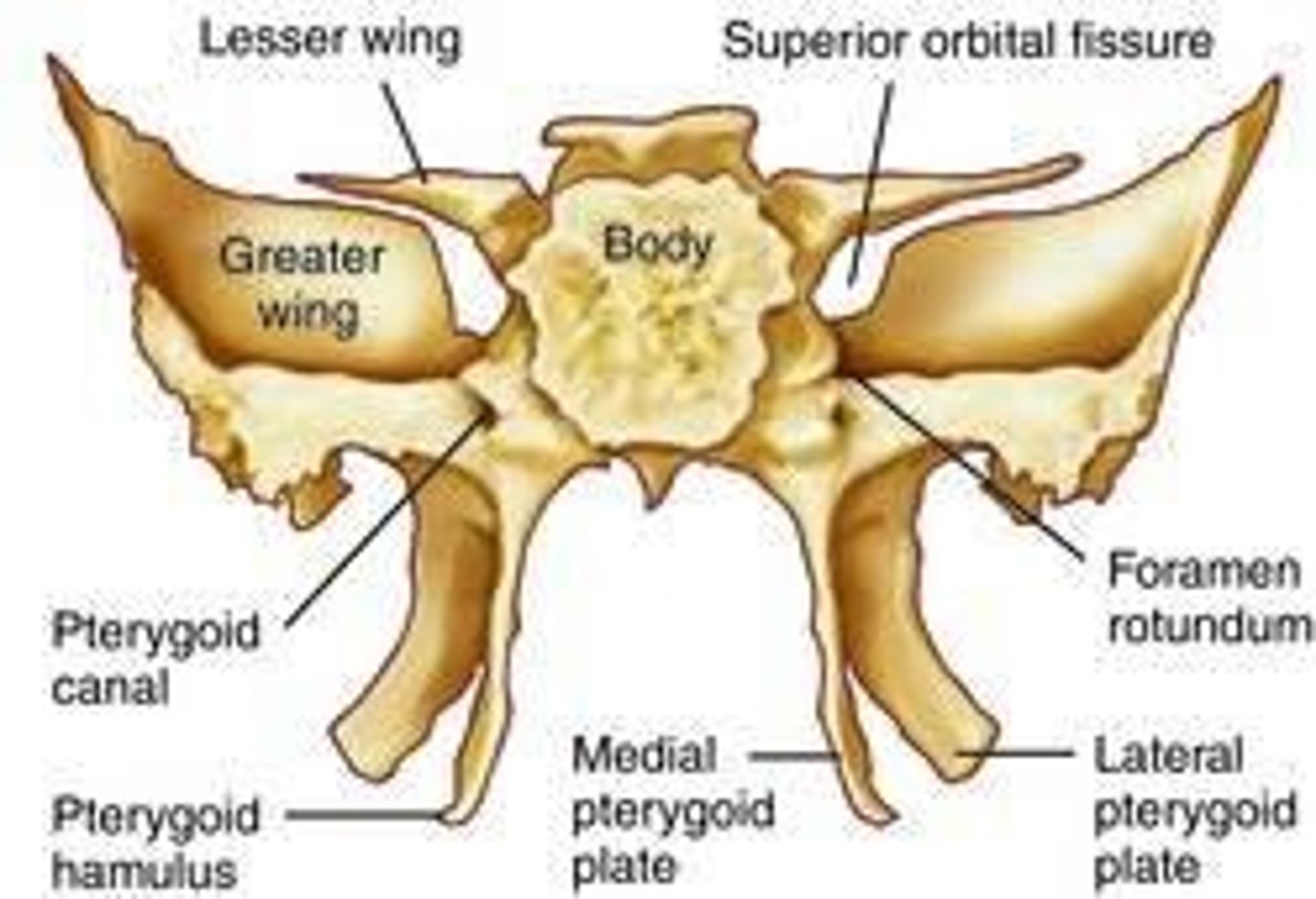
Sphenoid Bone
Called the 'keystone' of the cranium; articulates with all other cranial bones.
Facial Bones
14 bones including Nasal (2), Lacrimal (2), Maxilla (2), Palatine (2), Zygoma (2), Inferior Nasal Conchae (2), Vomer (1), Mandible (1).
Maxilla
Formed by two maxillary bones; makes up the upper part of the mouth and anterior ¾ of hard palate.
Zygoma
Cheek bones; form the inferior and lateral walls of the orbits.
Nasal Conchae
Project medially and inferiorly along the nasal cavity; have a scroll-like appearance.
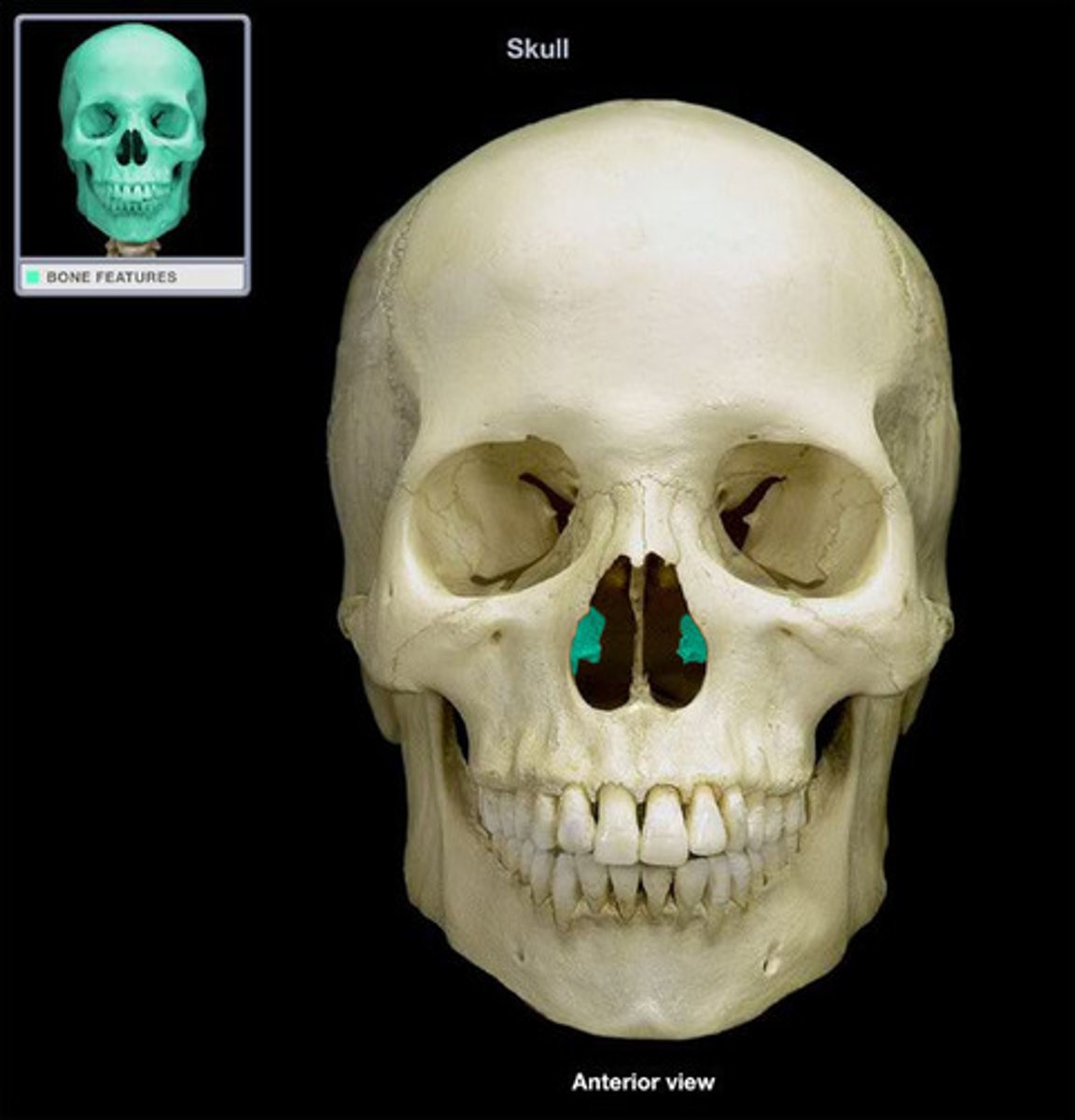
Vomer
Projects superiorly from the base of the nasal cavity to form the inferior portion of the nasal septum.
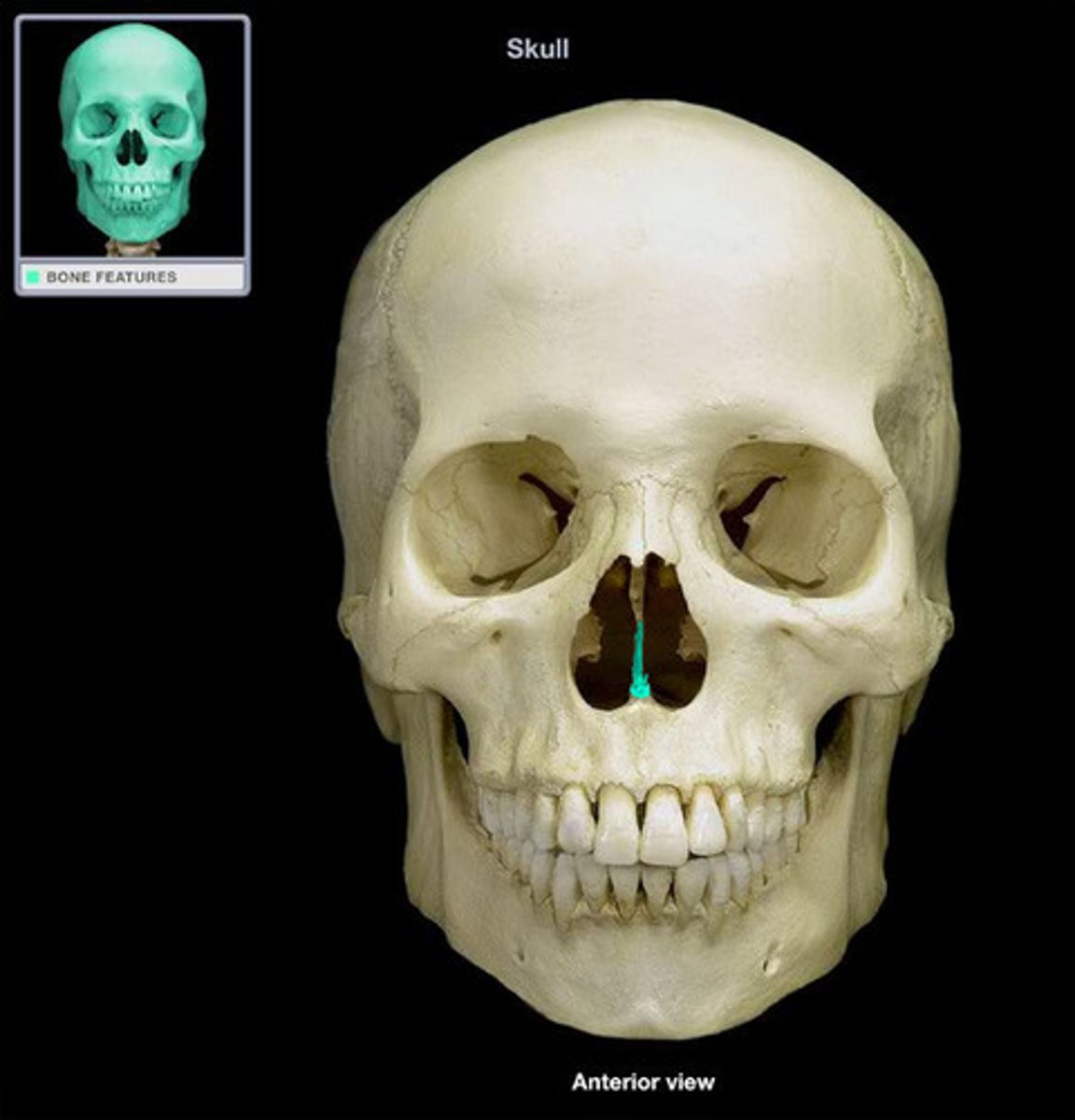
Mandible
Jaw bone; only moveable bone in the skull and the largest and strongest facial bone.
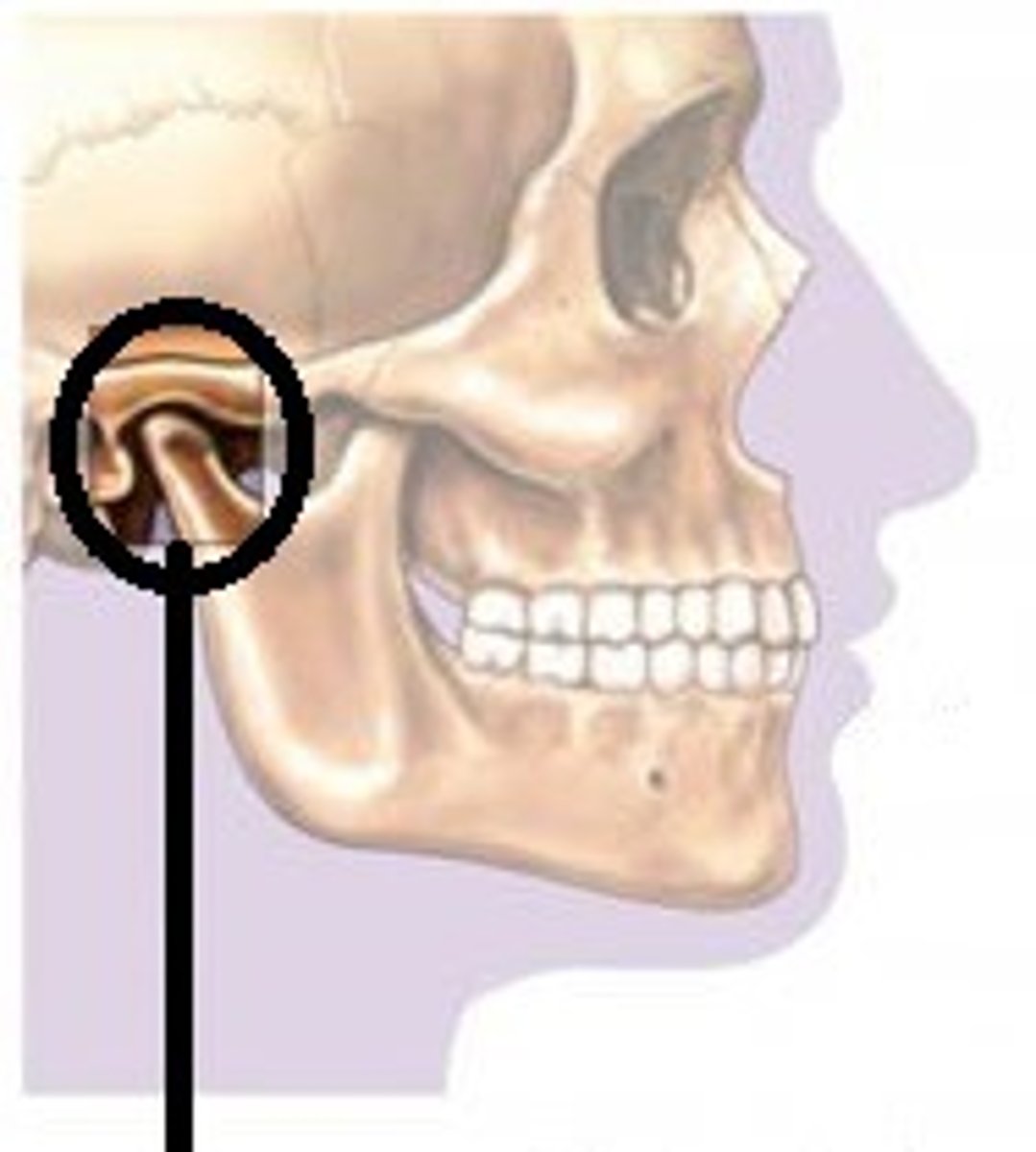
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
Hinge joint that allows for the necessary motions of mastication (chewing).
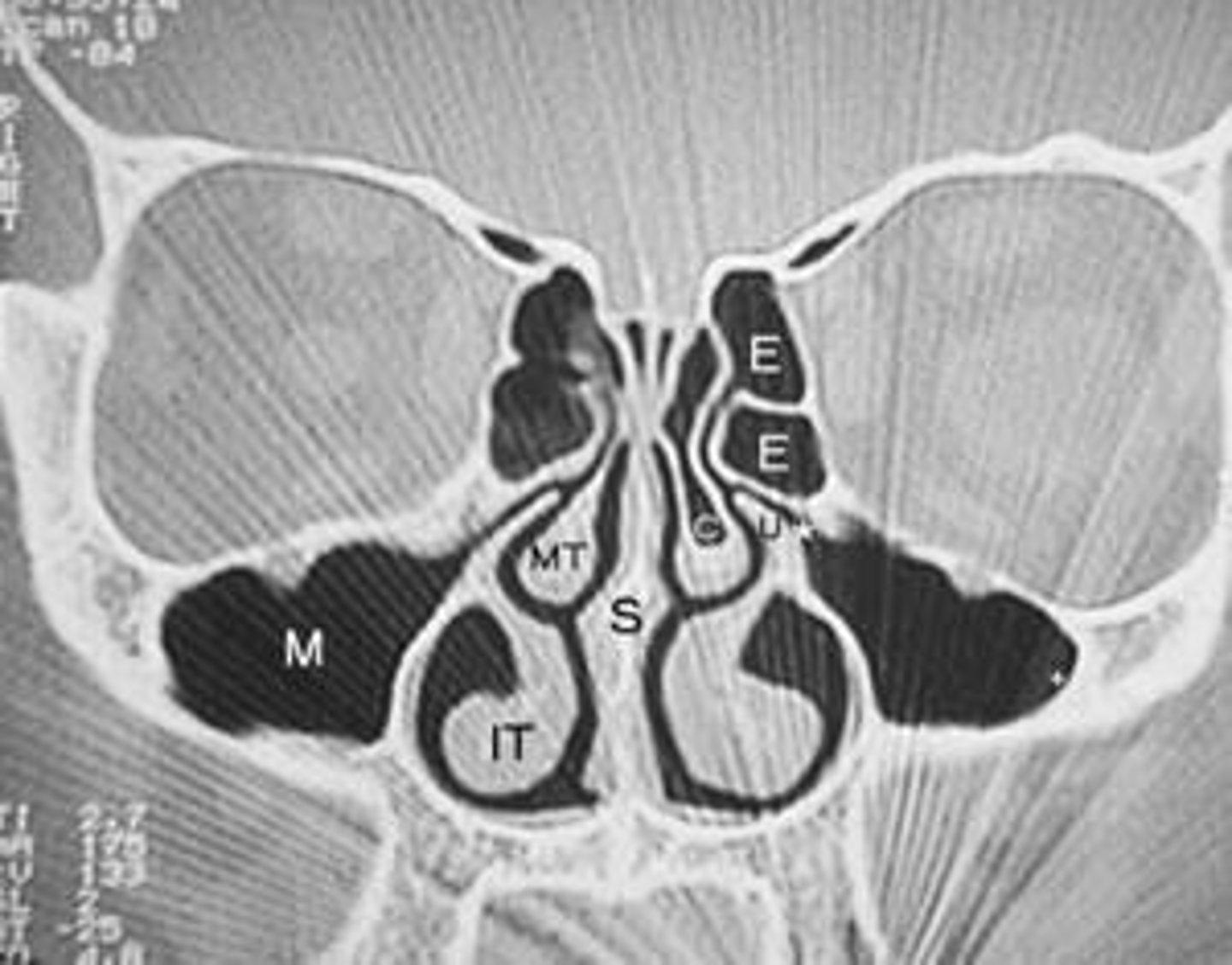
Paranasal Sinuses
Include Ethmoid, Maxillary, Sphenoid, and Frontal; lined with cuboidal epithelium composed of ciliated and mucus producing cells.
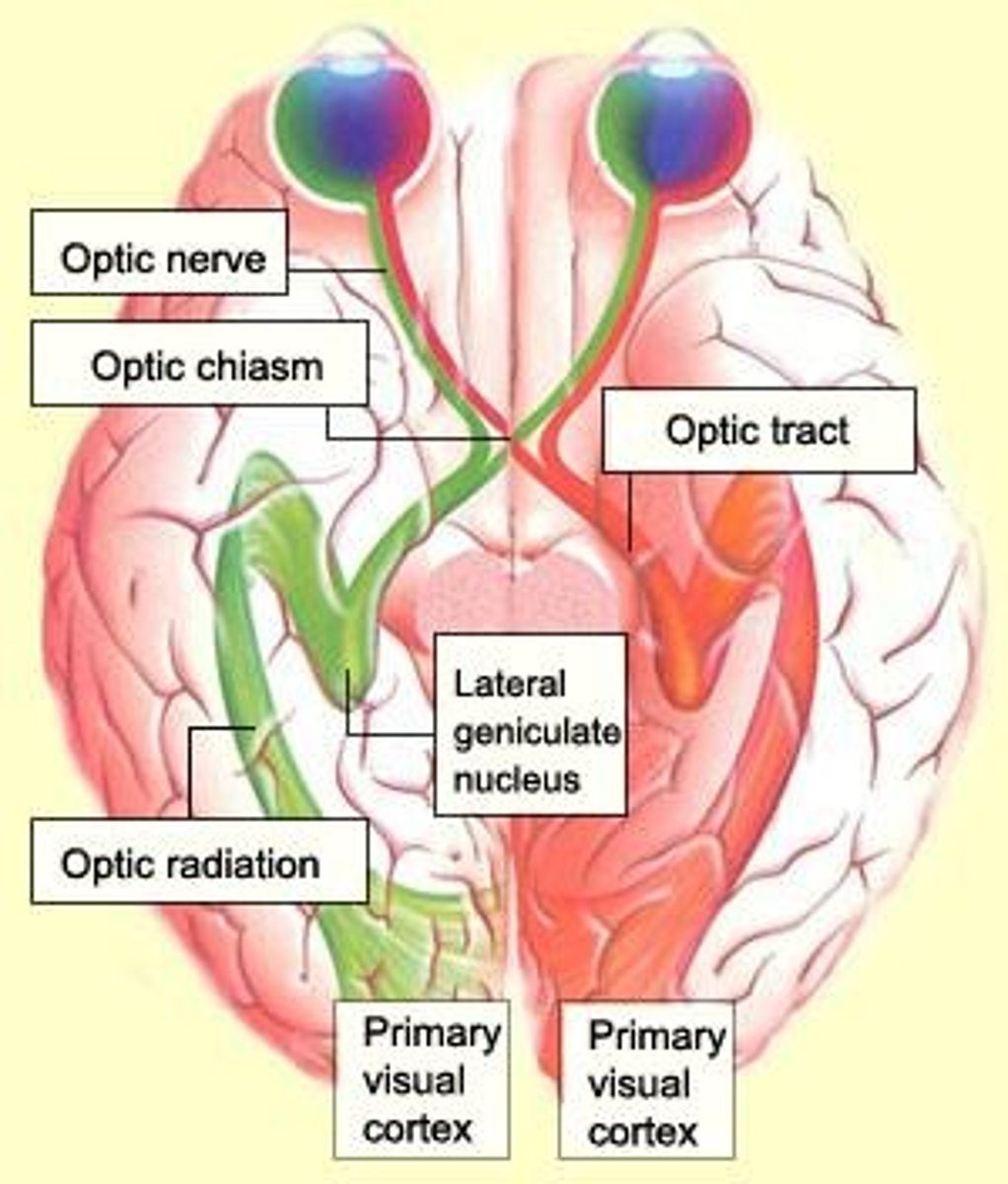
Optic Nerve (II)
The nerve of sight; blindness at 5000 cGy. (td55 5000cgy)
Optic Chiasm
Where the optic nerves from both eyes cross, located near the dorsum sella; blindness at 5000 cGy. (td55 = 5000cgy)
Cranium
Composed of 8 bones: Occipital (1), Temporal (2), Sphenoid (1), Ethmoid (1), Parietal (2), Frontal (1).
Frontal Bone
Forms the forehead, the anterior part of the skull, and roof of the orbital cavities.
Ethmoid Bone
Located between the orbits; contains the cribiform plate that transmits the olfactory nerves.
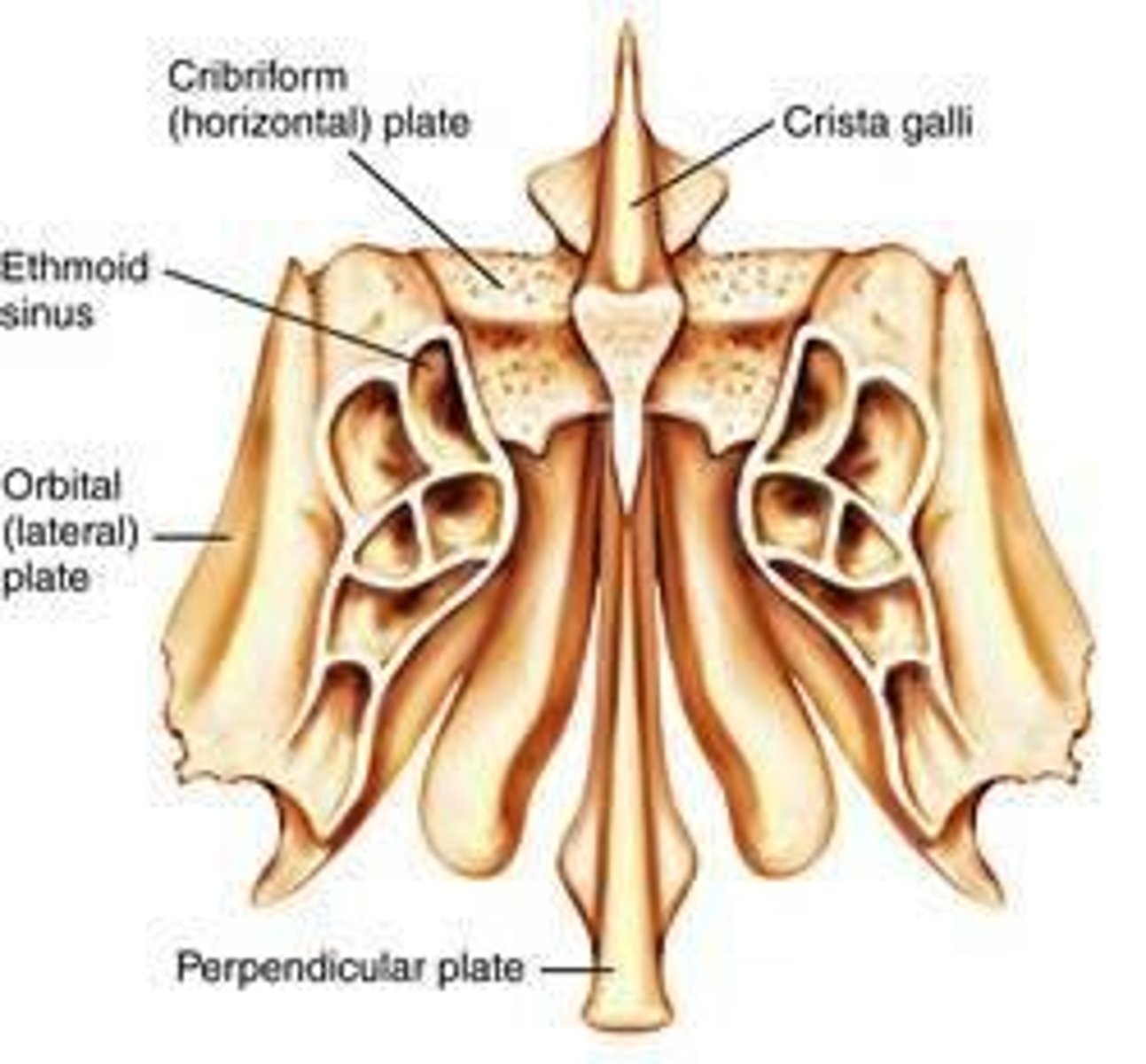
Crista Galli
Provides attachment to the falx cerebri.
Falx cerebri ( also called midline falx)
Separates the cerebral hemispheres; attaches to the crista galli of the ethmoid bone.

Sella Turcica
Located within the sphenoid bone; houses the pituitary gland.
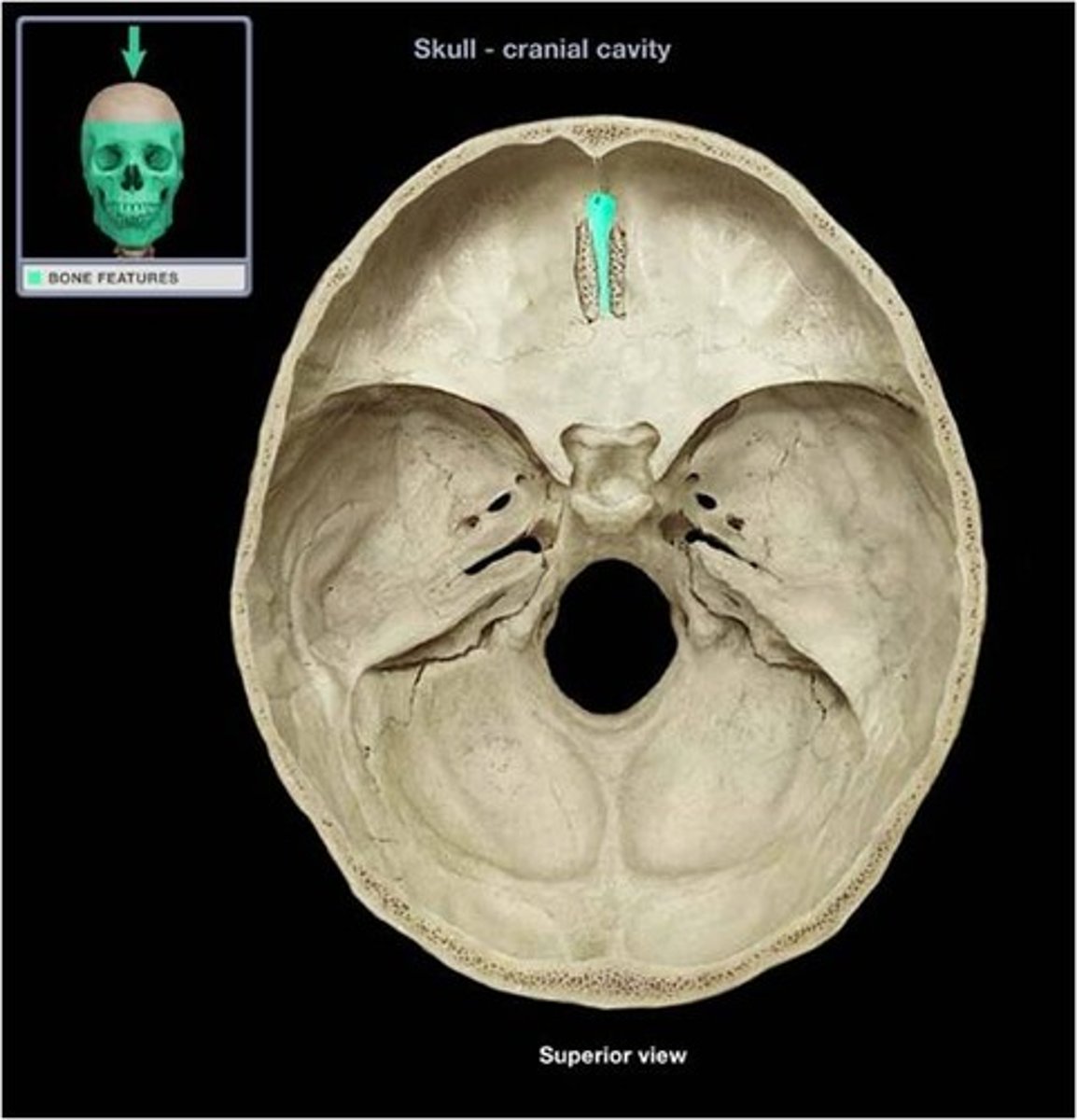
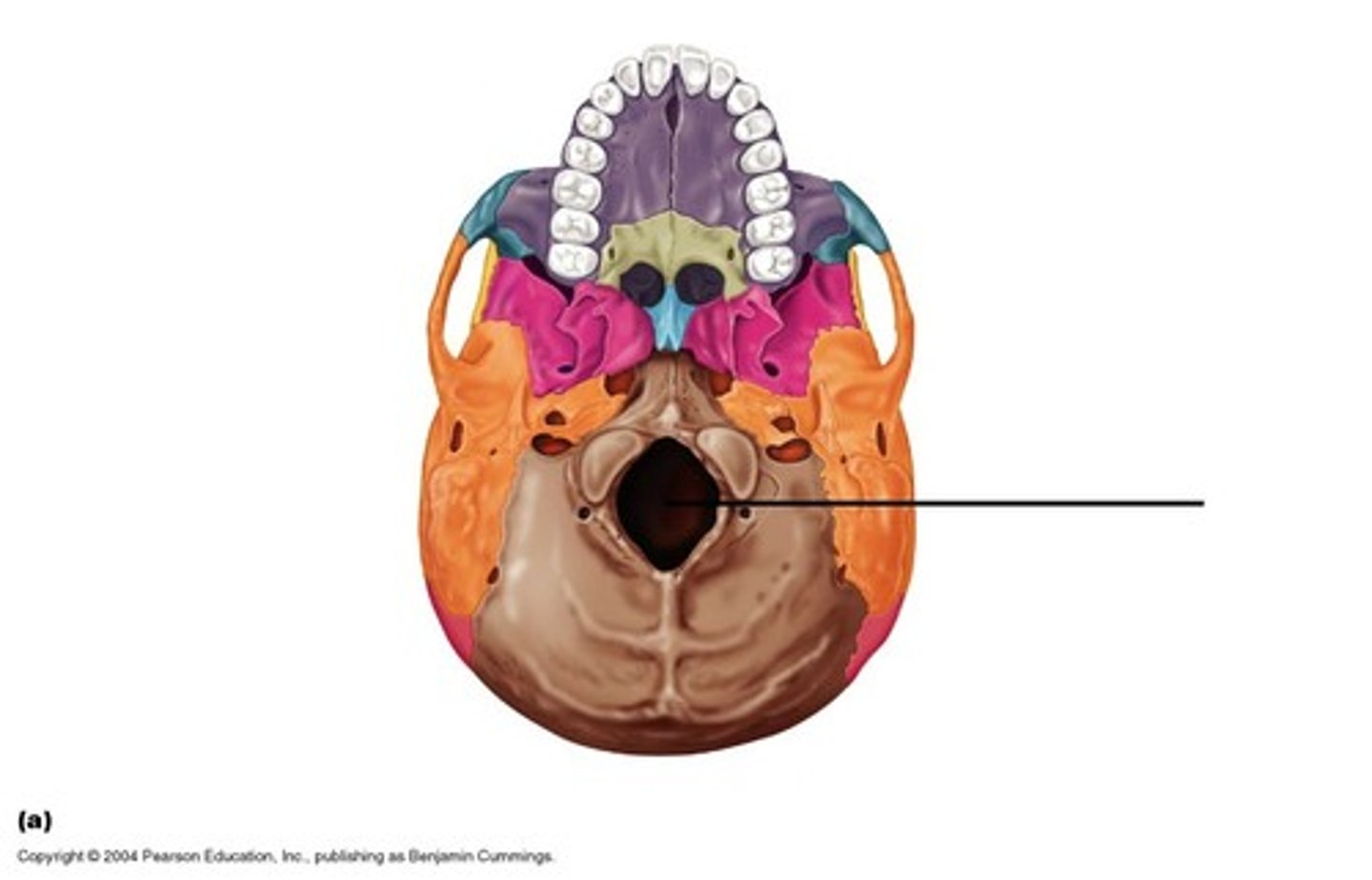
Foramen Magnum
Passage for the brain stem into the spinal canal.
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Cushions the brain from injury; produced in the choroid plexus of the ventricles.
Circle of Willis
Located within the subarachnoid space; supplies arterial blood to the cerebrum.
Cranial Nerves
Includes Olfactory (I), Optic (II), Oculomotor (III), Trochlear (IV), Trigeminal (V), Abducens (VI), Facial (VII), Acoustic (VIII), Glossopharyngeal (IX), Vagus (X), Accessory (XI), Hypoglossal (XII).
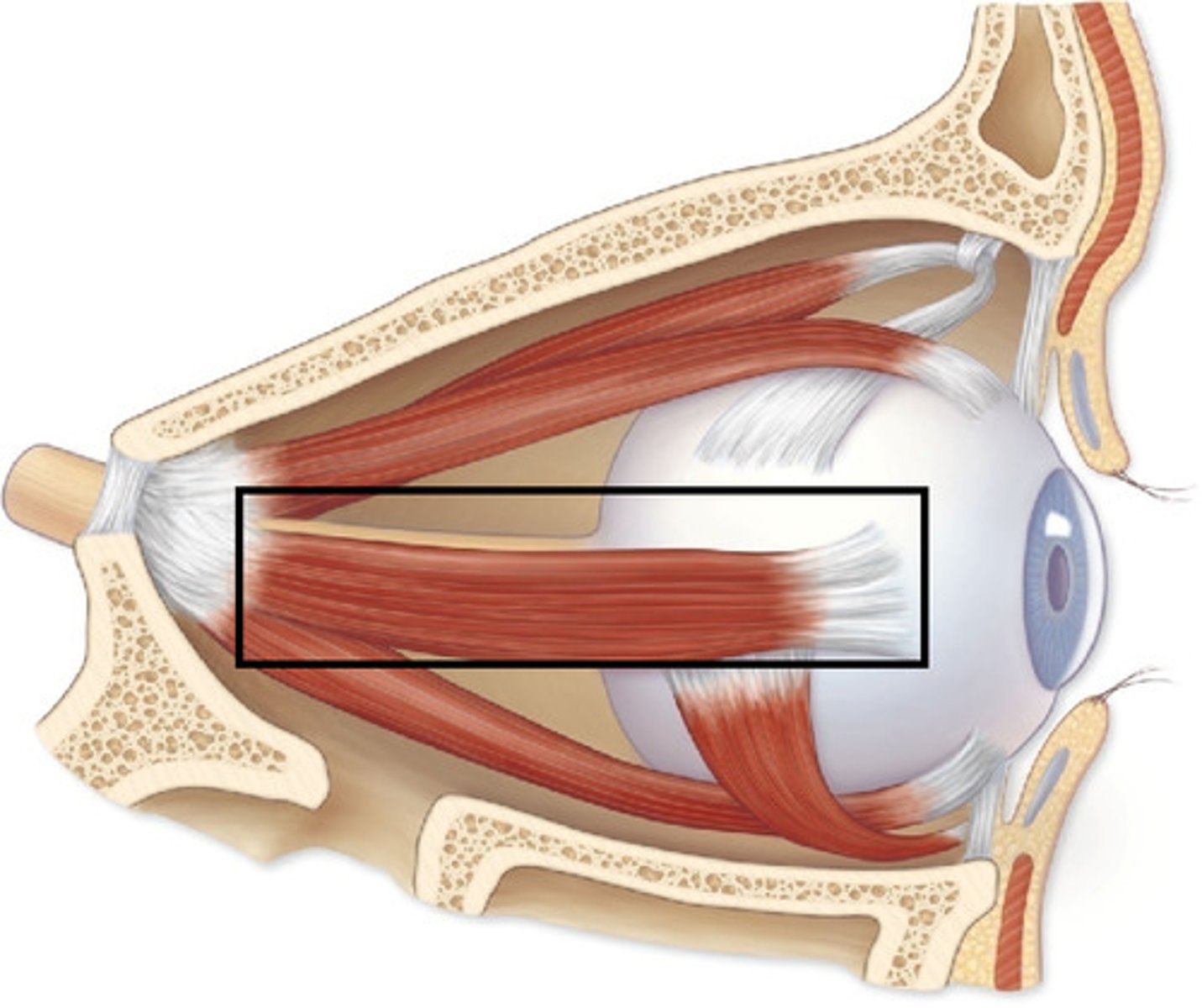
Lateral Rectus
One of the muscles of the eye.
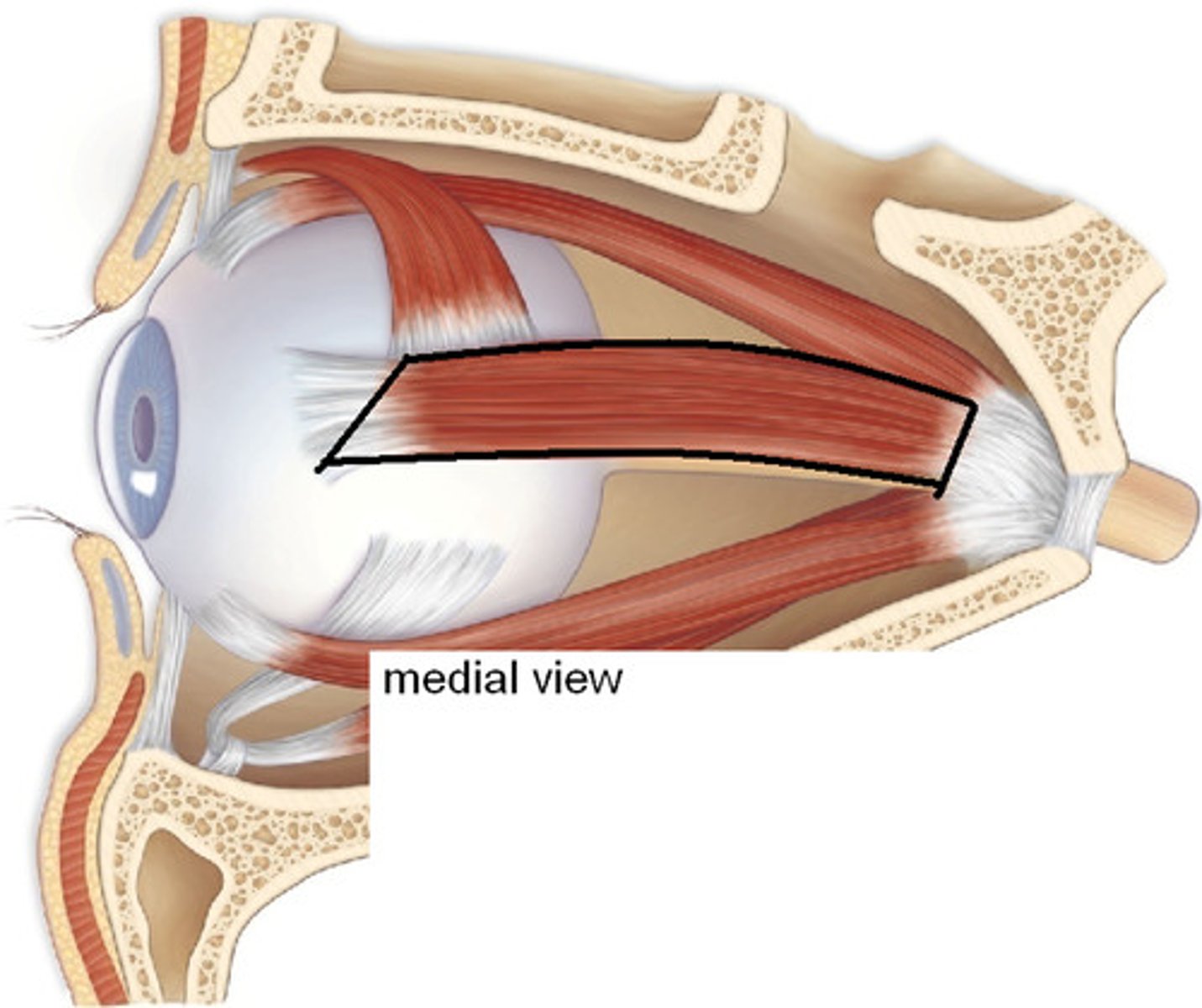
Medial Rectus
Another muscle of the eye.
Ventricles of the Brain
Include Lateral, Third, Cerebral Aqueduct, and Fourth Ventricle.
Cerebral Aqueduct
Passage of CSF from the lateral and third ventricles to the fourth ventricle.
Fourth Ventricle
Rests on the pons and medulla oblongata; receives CSF through the cerebral aqueduct.
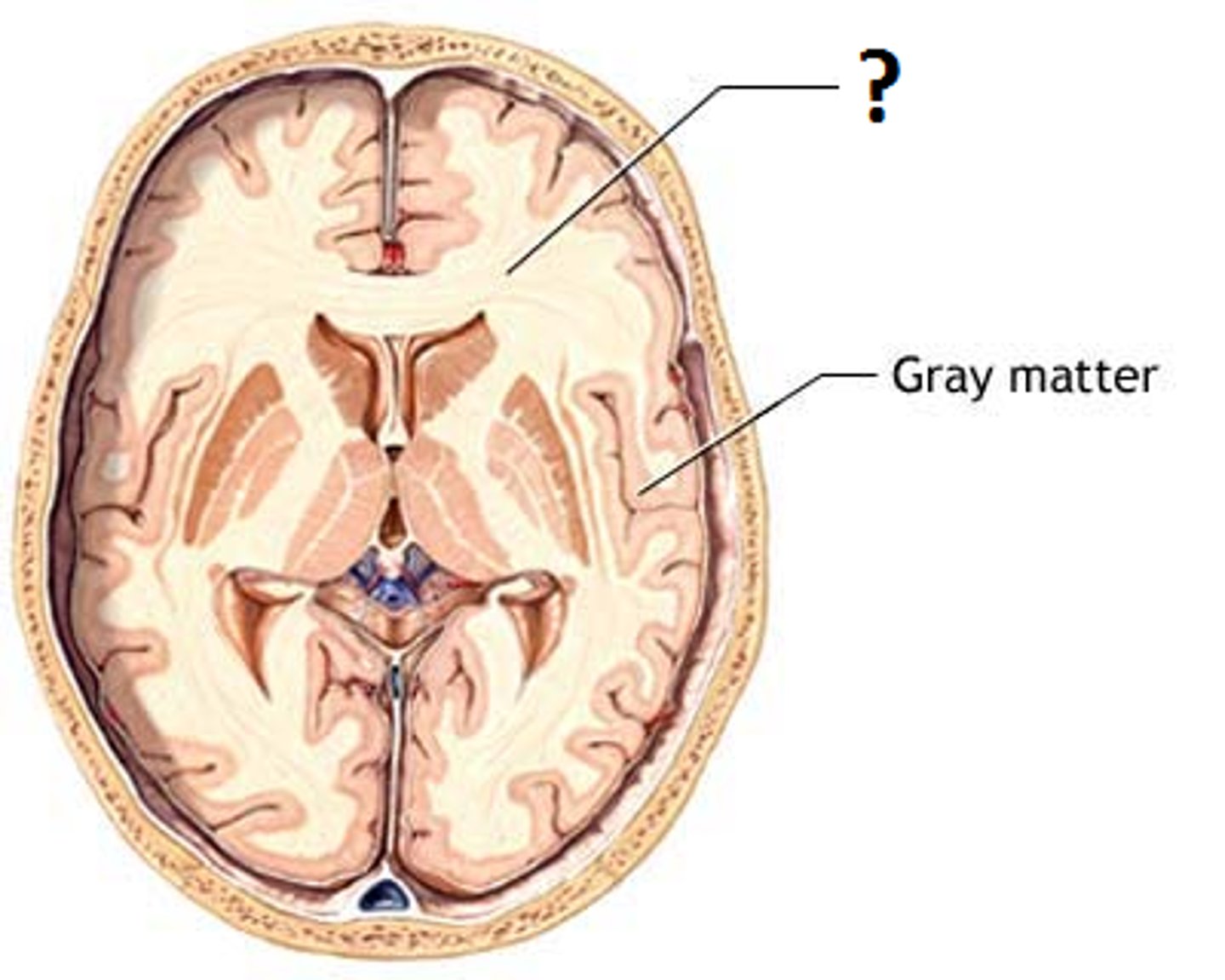
Gray Matter
The cortex of the brain.
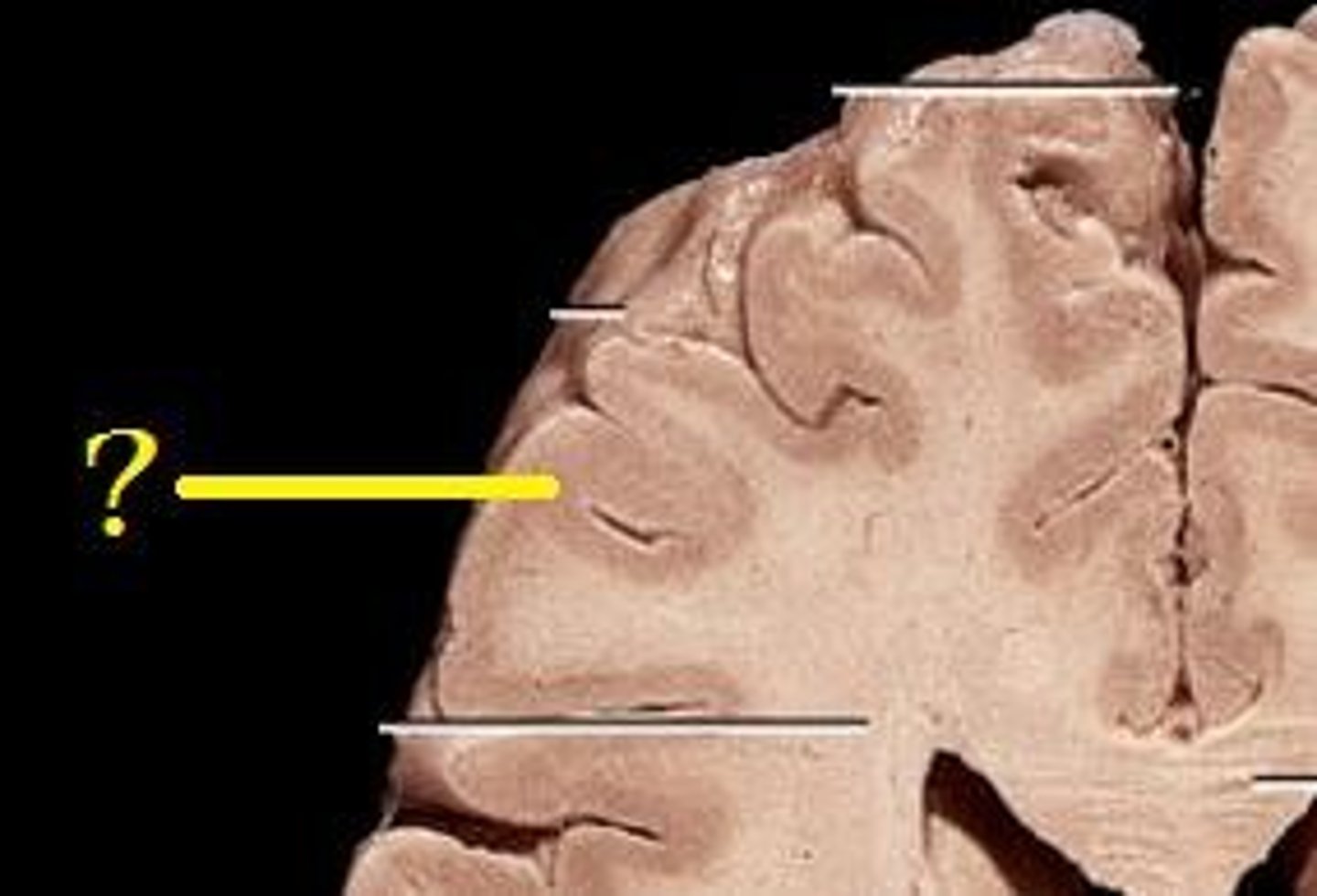
White Matter
Located beneath the cortex of the brain.
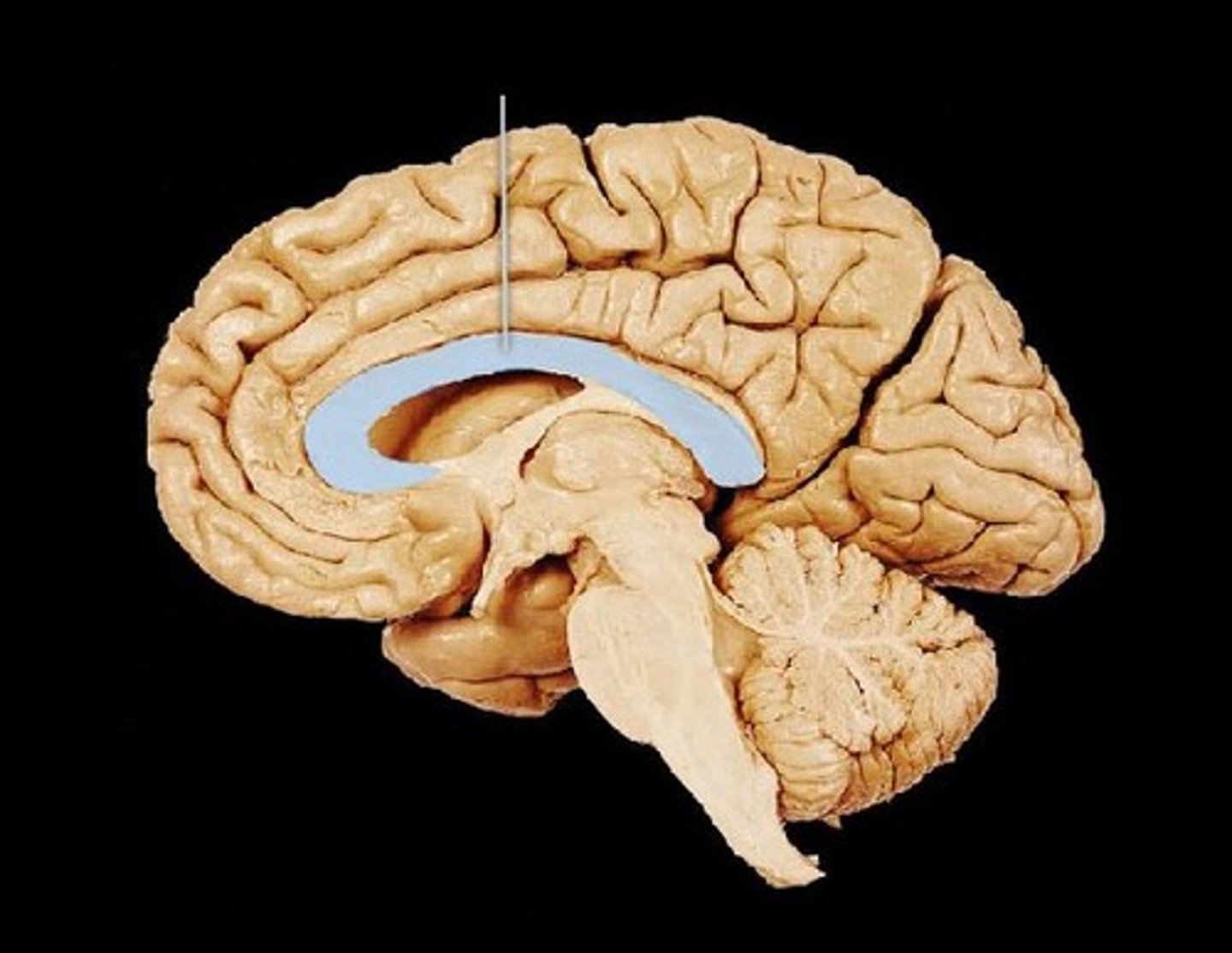
Corpus Callosum
White matter connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
oh oh oh to touch and feel a girls vagina, ah heaven
(I AM SO SORRY SO(F/PH)IA BUT IT’LL HELP ME REMEMEBER)
Jk we only need 1,2,5,7 and 10 rn
Olfactory (I)
Optic (II)
Oculomotor (III)
Trochlear (IV)
Trigeminal (V)
Abducens (VI)
Facial (VII)
Acoustic(VIII)
Glossopharyngel(IX)
Vagus (X)
(Spinal) Accessory (XI)
Hypoglossal (XII)
(absolutely insane)
Check body habitus stuff from the previous tests!!!
BODY HABITUS MEMORIZE PLS
Most common brain diagnostic
Brain Mets
Most common primary brain in adult
Astrocytoma
Most common pediatric brain
Medullarblastoma
Where is astrocytome/glioblastlma normally in adults
Cerebrum
Where is medullarblastoma found
Cerebellum
What is the vertex setup
Beam is coming from top of the head
Where is the superior orbital margin
The bony Part behind eyebrow
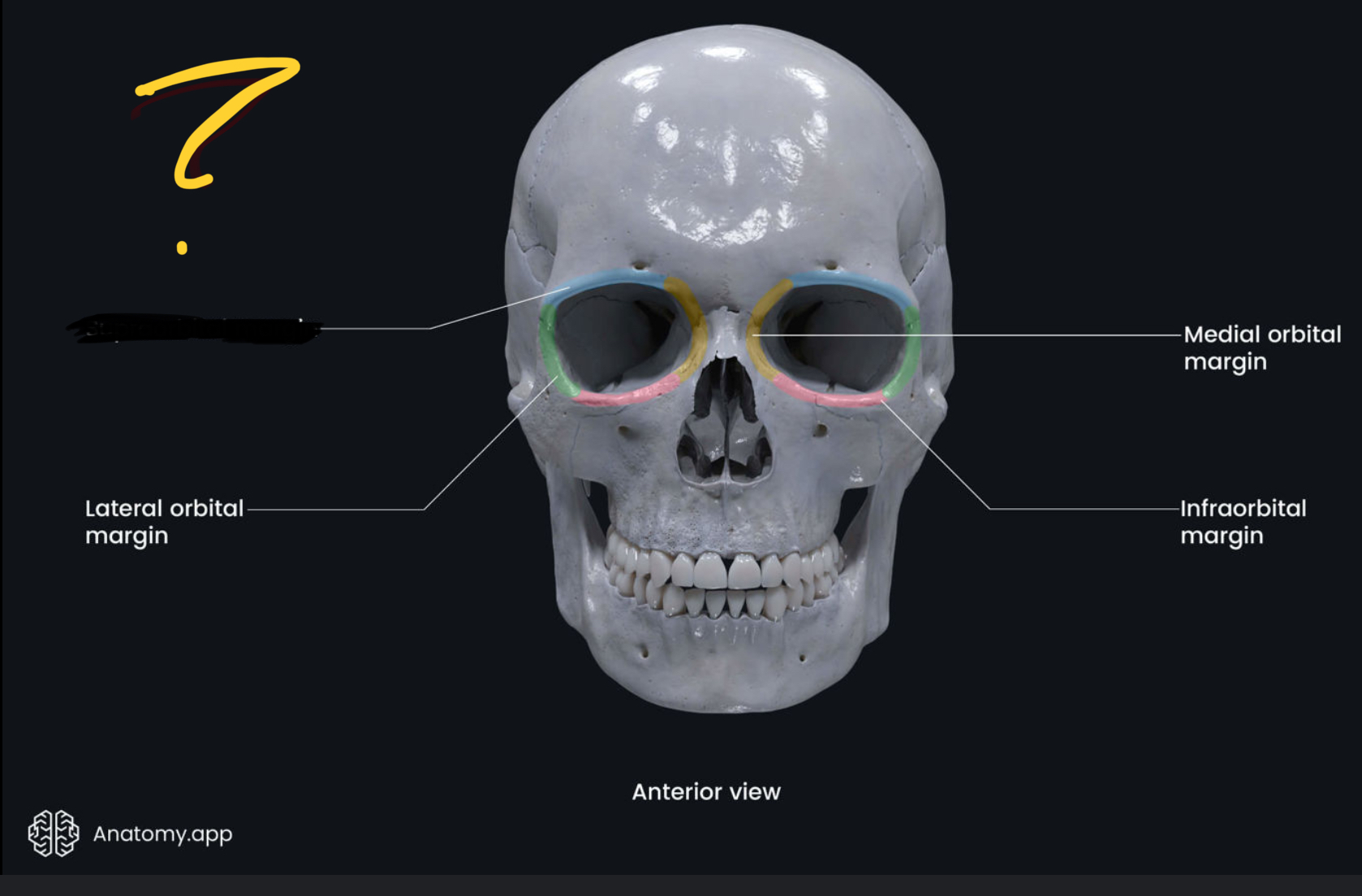
What bones r behind the inner canthus
Lacrimal bones
What part of the ear is good for leveling
The Tragus
Is the vermillion sensitive to radiation
Yes!!
What is the off cord field
Rad field.that is away from spinal cord
What is Off axis
Rad field that is going away from the central axis of the beam
Look at common metastatic areas
On previous dragon
If a adult primary brain goes infra tentorium does that mean a better or worse prognosis
It means a worse prognosis because the cancer has moved from Cerebrum to the cerebellum
If a pediatric patient's primary cancer grows supratantorium Does that mean a worse or better prognosis for them?
It means a worse prognosis because the cancer has moved from the cerebellum to the cerebrum
What is the blood brain barrier made out of?
The blood brain barrier is a line of astrocytes around the inner part of the brain
The blood brain barrier acts as what
A Filter allowing only certain things thru
Temodar is what type of drug
Nitrosaurous drug
What does the drug Temodar do?
Breaks the blood brain barrier and acts as a radiosensitizer
The mastoid tip is on what bone
TEMPORAL BONE
What two things are looked at to determine prognosis with brain cancers
Whether the cancer has passed the tantorium And whether there's a lot of necrotic tissue inside of the tumor
If it’s whole brain is it palliative or curative
Palliative 30-40 gy treatments
When u treat whole brain how do u set up the gantry
Parallel opposed laterals
90 and 270 degrees
Where do they like to treat down to for brain
Around c2 cause that’s where the fourth ventricle is
If the collimators angle on one side is 340 degrees what is the angle needed on the opposite side so the collimators become mirrored
360-340=20
20 degrees
What is flash
The light field beyond area being treated
It means u have the entire area covered (in case of like movement)
What is a keystone structure?
A structure that holds other things so if you take away that structure all the things around, it would fall out of place
What's an example of a keystone structure in the head?
Sphenoid bone
Why do they tend to go down to C2 when doing a whole brain radiation?
Because the fourth ventricle ends at C2
What is the external part of the ear called
Pinna, auricle, helix
What is an acoustic neuroma?
Benign tuber that grows behind the tympanic membrane, Will usually get treated with radiation can’t b removed surgically
What happens if you over radiate the cochlea?
The cochlea has fluid in it so the fluid will dry out, The fluid helps maintain balance
What is the bony base of the skull called?
Petrous ridge
The crista galli is part of what bone
Ethmoid bone
What is the vertex
Top of head
When kids have a medullarblastoma, what is the tumor usually pushing on? That causes hydrocephalus
The fourth ventricle of the brain
Gives them instability when standing up and nausea
With structure sends the signals to the pituitary gland to secrete hormones
Hypothalamus
What are the layers of the Menengies from outer to inner
Dura matter
Arachnoid matter
pia matter
The tentorium and falx cerebri r both an extension of what
The dura matter
Is the sella Turcica/ sella dorsum a supratentorial or infratentorial?
Supra tentorial
Where does the brain metastasize to?
Brain usually doesn't metastasize, but if it does, it will be to other parts of the brain or the cerebral spinal fluid
When treating a brain, where don't you want flash
Over the nasion because that means that you're gonna treat the contra lateral eye
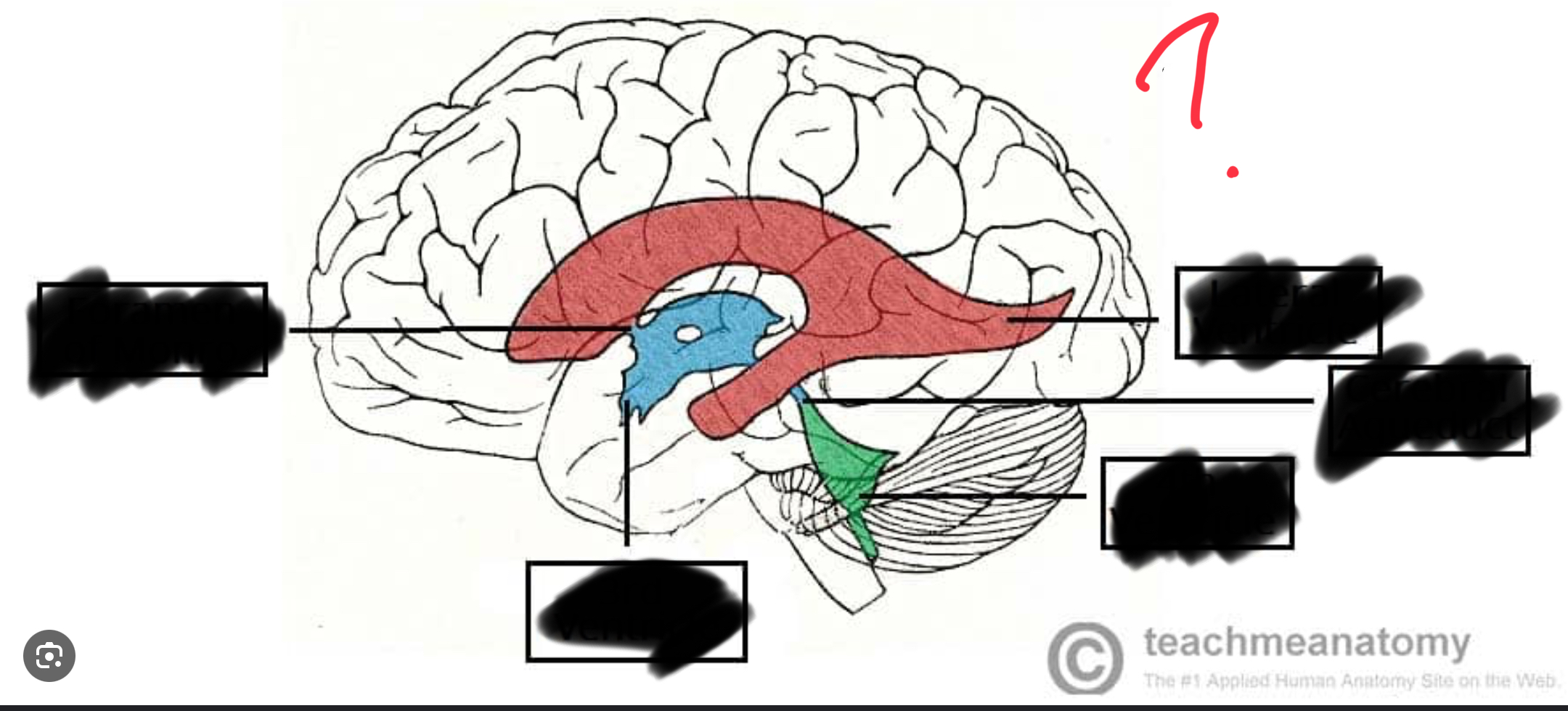
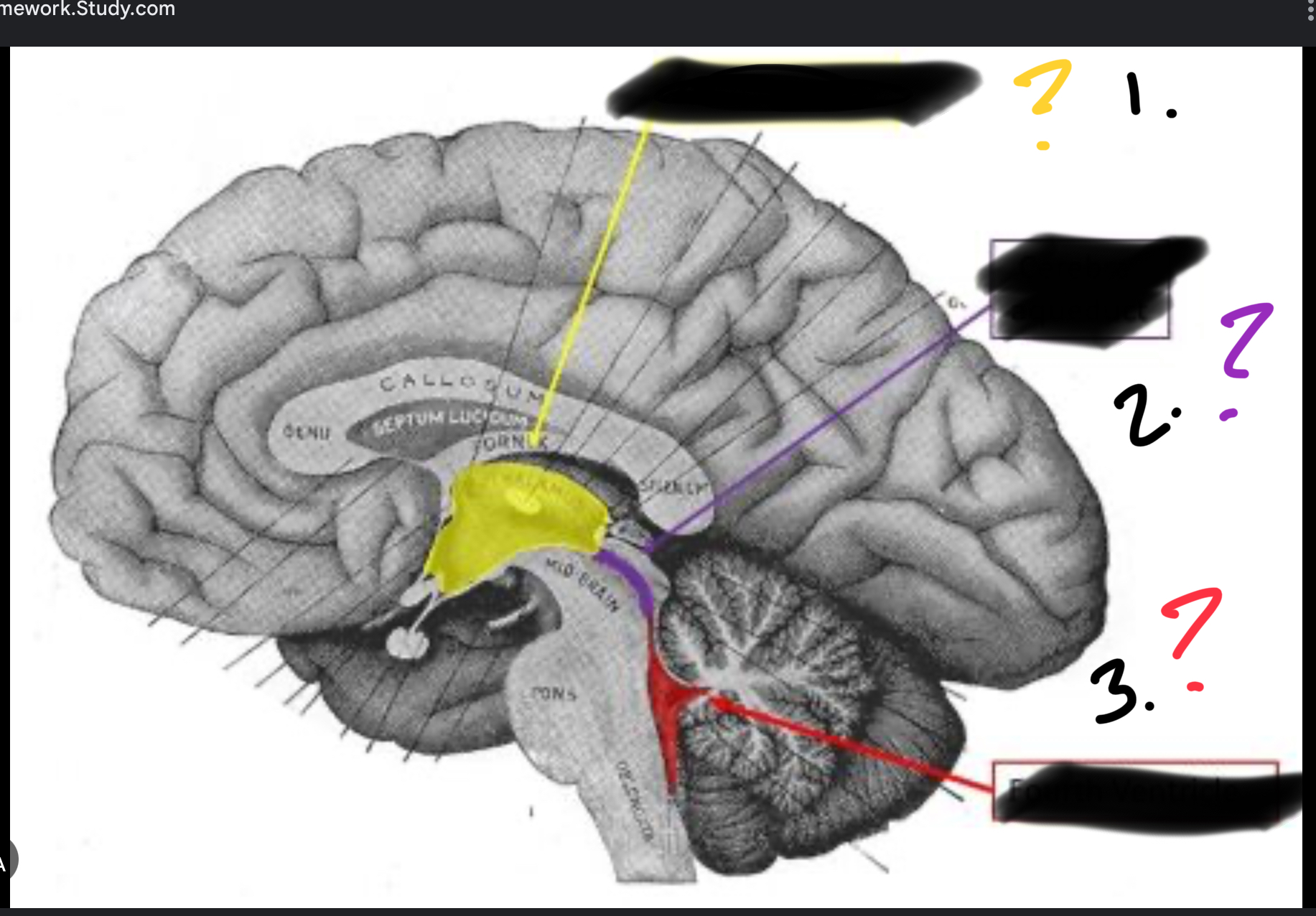
Red
Lateral ventricle
(The blue is the third ventricle)

Third ventricle
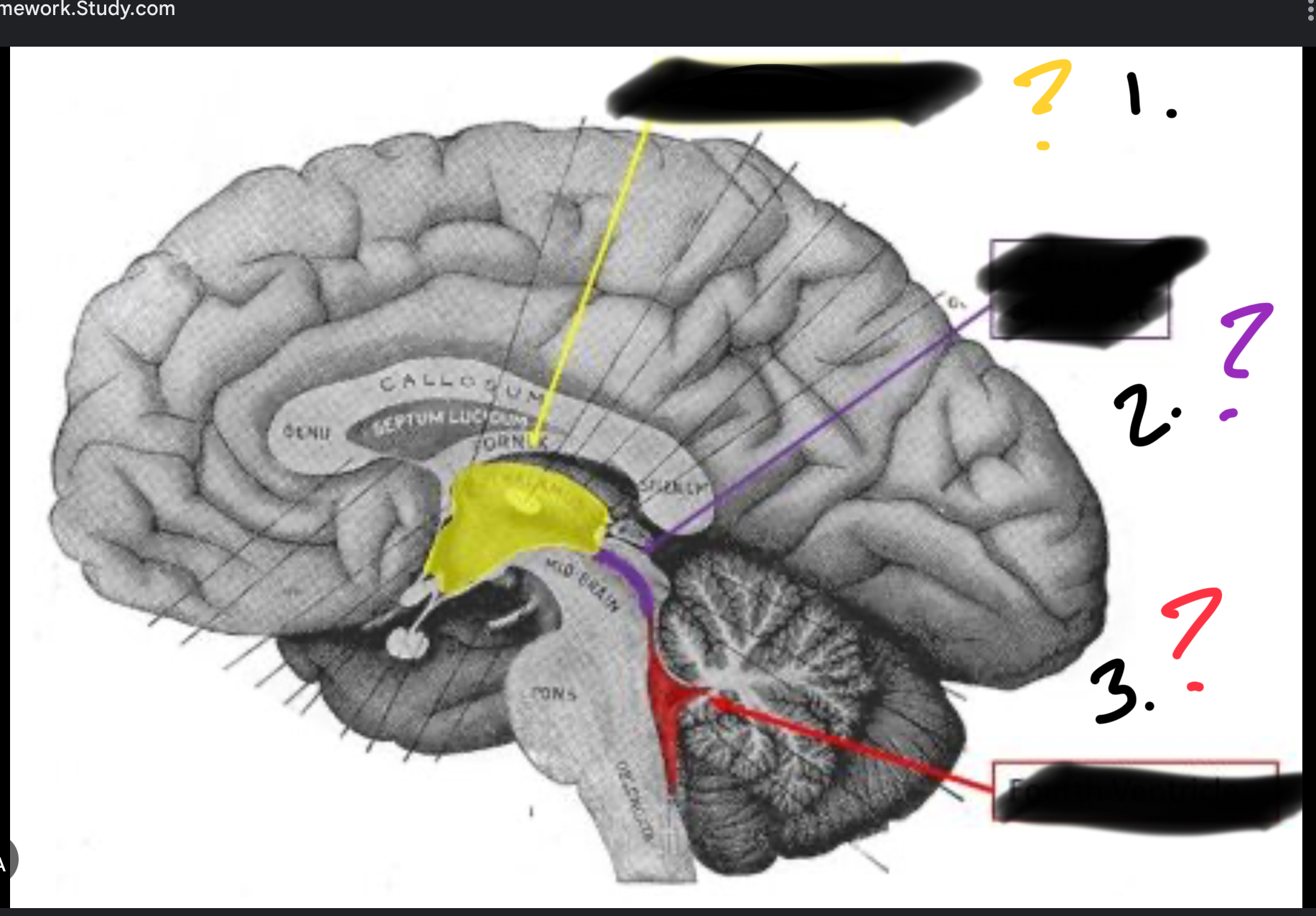
Purple
Cerebral aquaduct
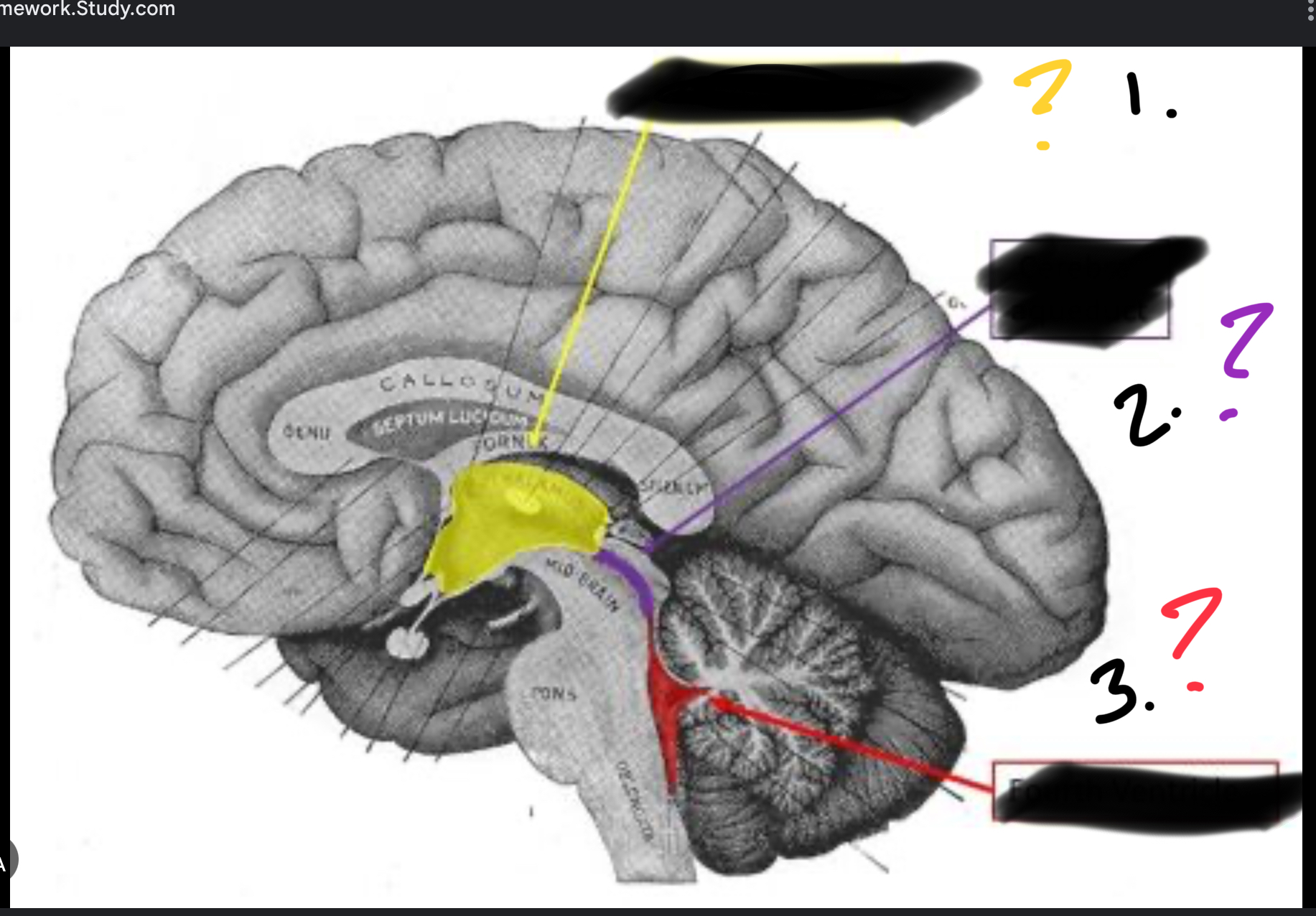
Red
Forth ventricle
What makes the cerebral spinal fluid?
The choroid plexus
What makes up the choroid plexus
The inner lining of the ventricles that makes the cerebral spinal fluid
What connects the lateral and third ventricles
Intraventricular foramen aka foramen of Monro
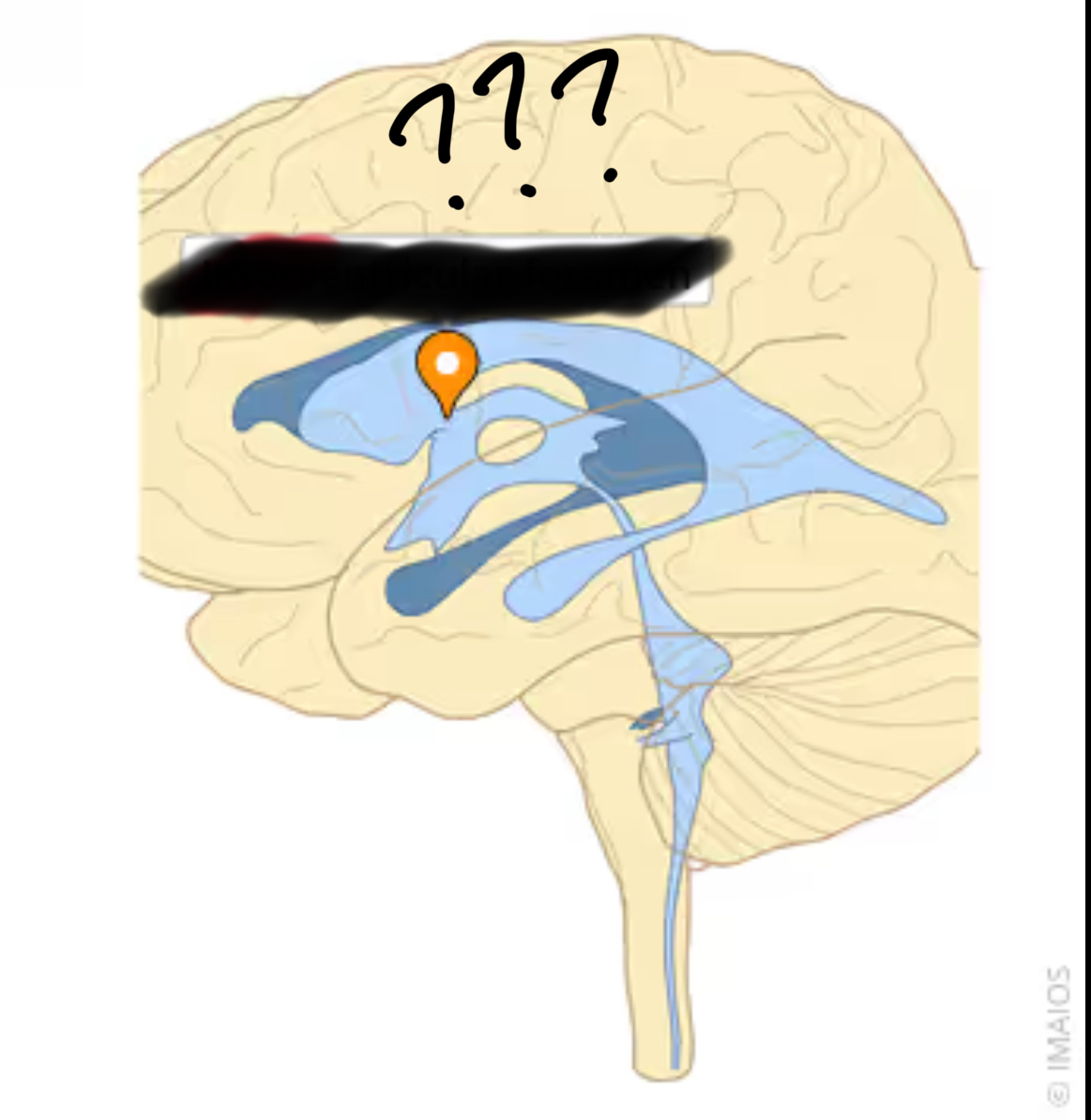
Intraventricular foramen
What connects the third ventricle to the forth ventricle
Cerebral aqueduct
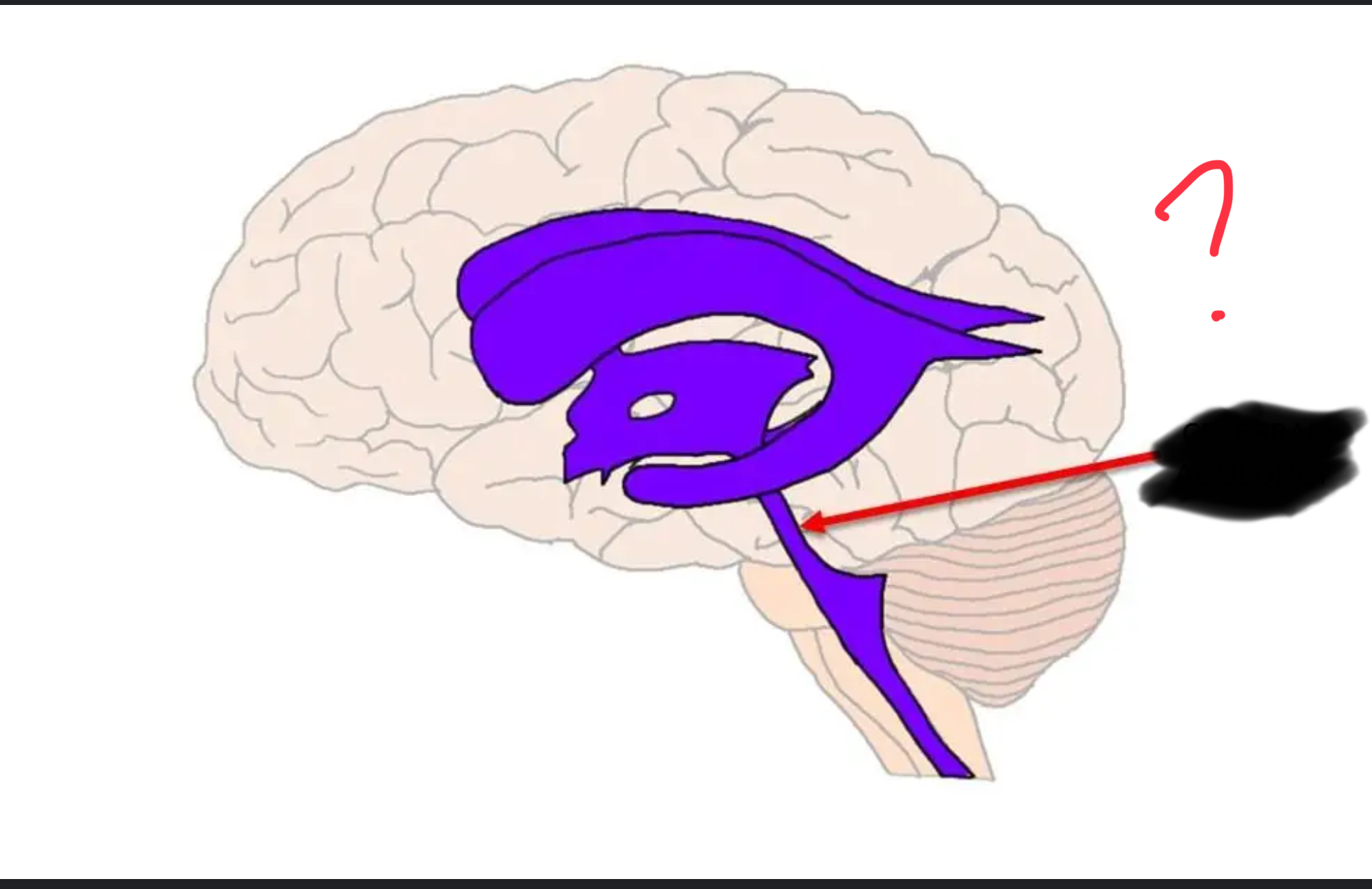
Cerebral aqueduct
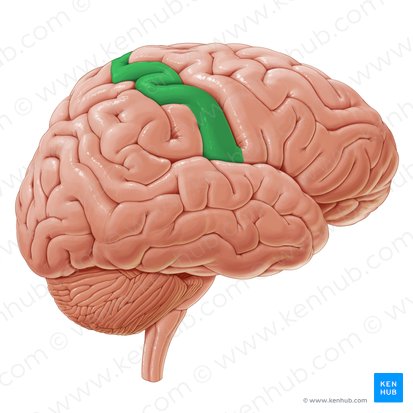
Gyrus
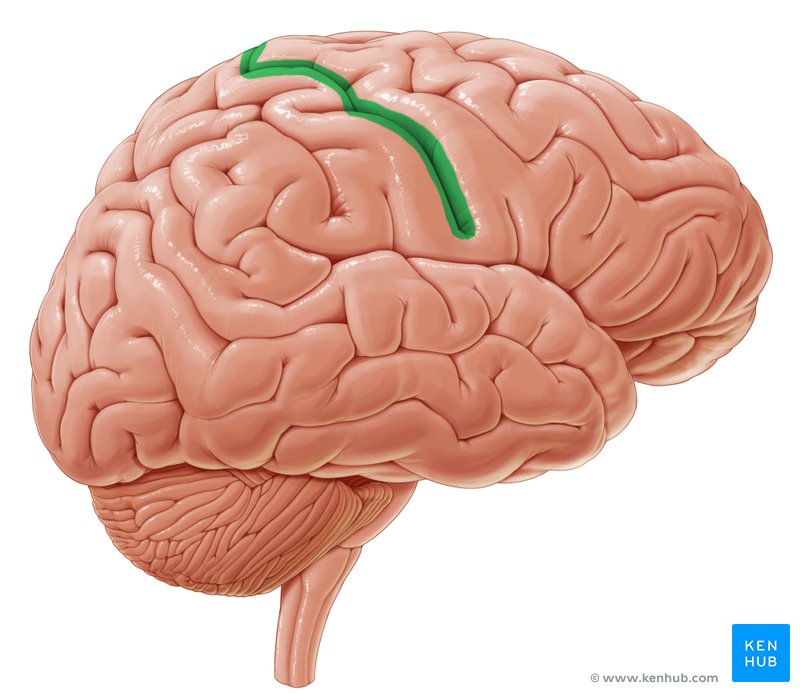
Sulcus
Cortex of brain is
Grey matter
Beneath the cortex is
White matter
The corpus callsosum is white or grey matter
White matter
The brain stem is made up of
The midbrain pons and medulla oblongota
What is the function of the midbrain
Visual and auditory reflex center
What is the function of the pons
Regulates relaxation
Relay signal between spinal cord and brain
What is the function of the medulla oblongota
Contains a vital center
Responsible forCardiac vasomotor and respiratory
When does the medulla oblongota Become the spinal cord
Once it passes the foramen Magnum
What is cranial nerve one
Olfactory nerve
What is cranial nerve two
Optic nerve