Reactivity Series
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the reactivity series
An order of how reactive a group of metals are with water, steam, oxygen and each ther (displacement reactions)
Order of reactivity series
Potassium,
sodium,
calcium,
magnesium ,
aluminium,
zinc ,
iron ,
copper
List of all diatomic elements
+state of substance
Iodine I - = solid
Hydrogen Have -Gas
Nitrogen No - Gas
Bromine Bright - liquid
Oxygen Or -gas
Chlorine Clever - gas
Fluroine Friends -gas
What determines how reactive a metal is
the tendency of the metal to lose electron(s) and form a positive ion/ more reactive metals lose electrons more easily e.g potassium and sodium lose electrons easily and from ions while copper does not lose electroms easily therefore is very unreactive
metal + oxygen →
metal + oxygen → metal oxide
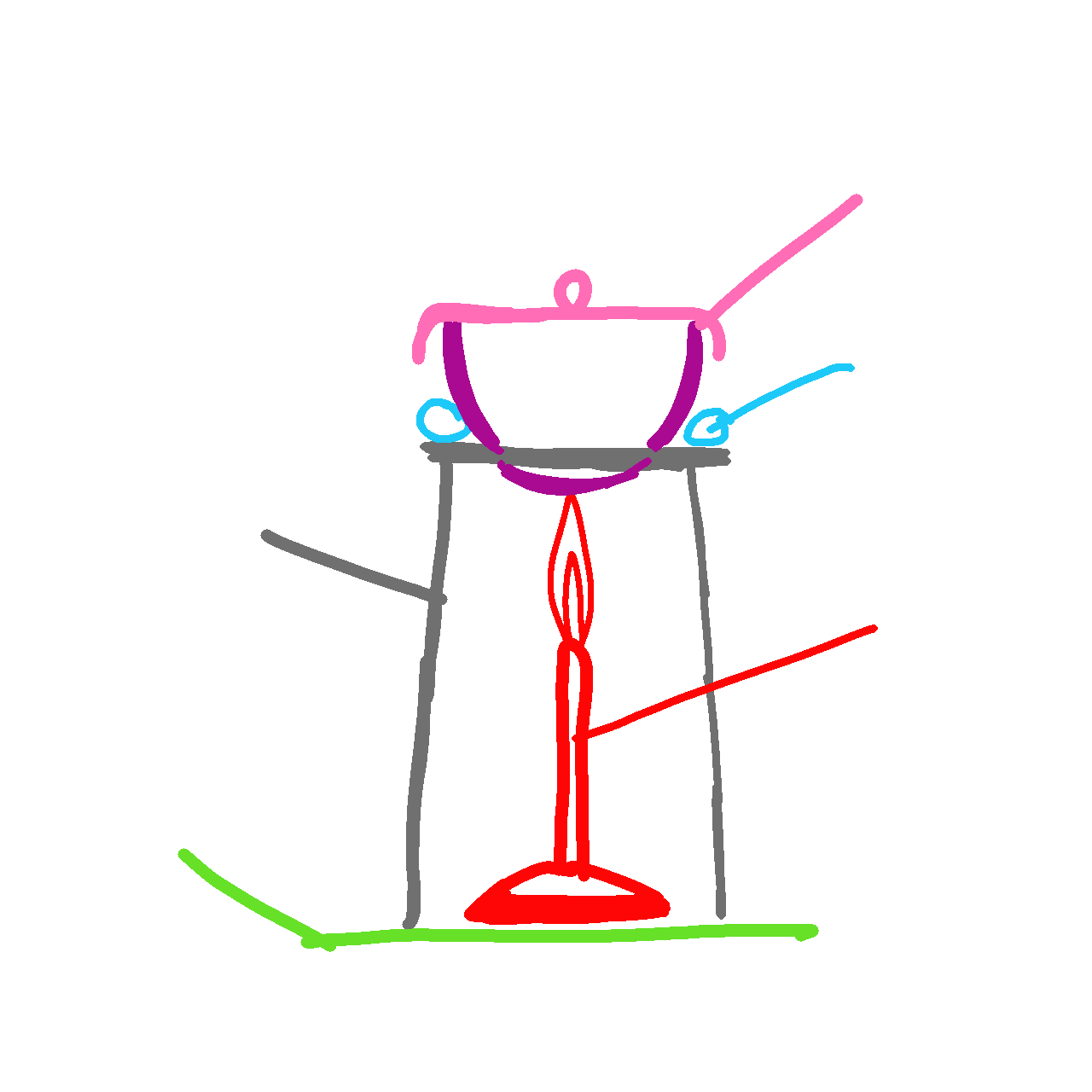
reaction with air
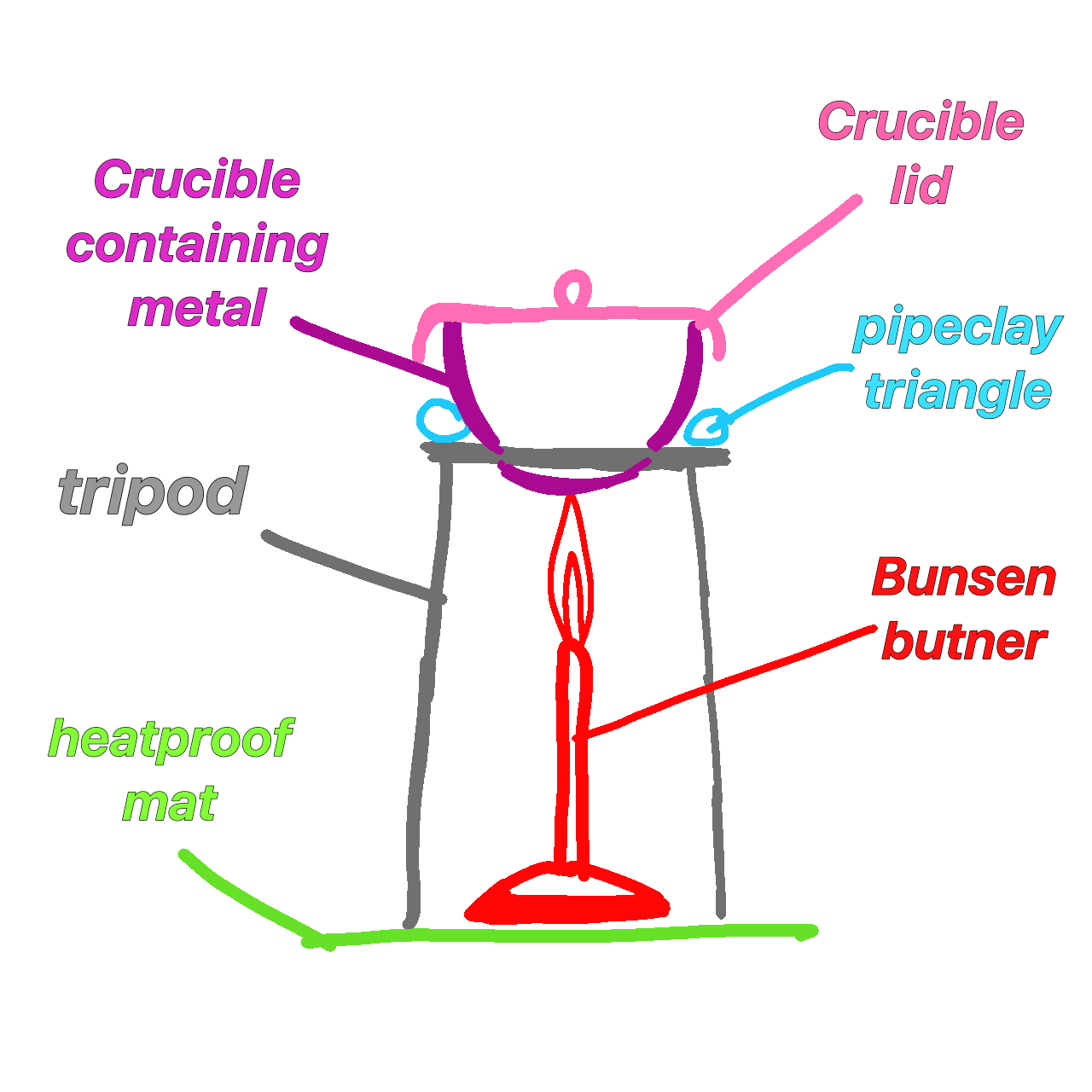
potassium reaction when heated in air
burns with a lilac flame
Forms a white solid
4K + 02 → 2k20
sodium reaction when heated in air
burns with a yellow flame
forming a white soli
4Na + 02 → 2Na20
calcium reaction when heated in air
Burns with a red flame
forming a white solid
2Ca+ 02 → 2Ca0
Magnesium reaction when heated in air
Burns with a bright white light
Forming a white solid
2Mg + 02 → 2Mg0 ( magnesium oxide)
Aluminium reaction when heated in air
Burns only when a fine powder
Forming white solid
4Al + 302 → 2Al203
zinc reaction when heated in air
burns in air
forming yellow solid which changes to white on cooling
2Zn + 02 → 2Zn0
Iron reaction when heated in air
Iron fillings burn with orange sparks
Forming black solid
3Fe + 202 → Fe304
copper reaction when heated in air
does not burn but becomes covered in black layer
2Cu + 02 → 2Cu0
Ionic compounds are all white
metal + water →
metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
lithium observations with water
equation
floats and moves on the surface
fizzes gas is given off
eventually disappears
heat given out
colourless solution is formed
2Li+2H20 → 2LiOH+H2
sodium observations with water + equation
FFEHC
melts into a silvery ball
burns with a yellow flame
2Na+2H20 → 2NaOH+H2
potassium observations with water
FFEHC
burns with a lilac flame
2K+2H20 → 2KOH+H2
group 2 less reactive metals with water
Calcium Reaction with water
Fizzing
Sinks then rises
Heat released
Calcium disappears
Cloudy solution is formed
Ca+2H20 → Ca(OH)2+H2
magnesium reaction with water
Slow reaction
Few bubbles
Mg+2H20 → Mg(OH)2+H2
How do you test did hydrogen gas
lit splint into test tube of hydrogen then hear squeaky pop
metal + steam →
metal + steam → metal oxide + hyrdogen
Magnesium reaction with steam
Bright white light
White solid forms
Heat given out
aluminium reaction with steam
powdered aluminium reacts to form a white solid. Heat given out
no reaction in foil form- aluminium only reacts when the protective layer of aluminium oxide is removed
zinc reaction with steam
glows to form a yellow powder which changes to white on cooling. Heat given out
iron reaction with steam
powdered iron glows to form a black solid
What is a displacement reaction
A more reactive metal takes the place (displaces) of a less reactive metal in a compound
Magnesium + copper (4) sulfate →
observations and how to carry out
a solid metal reacting with a solution of a metal ion
magnesium powder is added to blue copper sulphate solution
Blue solution fades to colourless
Magnesium disappears
Black specks at bottom
Heat given off
Mg + CuSO4 → MgSO4 +Cu
Aluminium + iron (III) oxide →
Solid metal reacting with a solid metal ion
aluminium + iron (III) oxide → iron aluminium oxide
Fe2O3 + 2Al → 2Fe + Al2O3
THERMIT REACTION
Produces sparks
Very exothermic
Molten iron produced
SAM CID
Same - Control
Alter - Indepentend
Measure - Dependent
what is an ore
an ore is a rock that contains a metal compound from which the metal can be extracted.
oxygen must be removed
what metals are reduced from it’s ore by electrolysis
Potassium
sodium
Calcium
Magnesium
Aluminium
how is zinc , iron, copper reducted from its ore
reduction of the metal ore by heating with carbon