plant diversity exam 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:39 AM on 2/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
what is taxonomy?
the science of classifying and naming plants
2
New cards
main goals of taxonomy:
identification, nomenclature, classification
3
New cards
how do the three components of systematics inform and depend on each other?
4
New cards
what are the four primary goals of systematics?
1) Inventory of Earth’s Biota
2) Identification and Communication: Nomenclature
3) Orderly, Logical Sequence of Classification
4) Demonstrate Evolutionary Implications of Biodiversity
2) Identification and Communication: Nomenclature
3) Orderly, Logical Sequence of Classification
4) Demonstrate Evolutionary Implications of Biodiversity
5
New cards
advantages of common names:
* descriptive, colorful
* easy to remember
* only names for most people
* easy to remember
* only names for most people
6
New cards
disadvantages of common names:
* one species can have many common names
* one common name = same for more than one species
* names can be confusing
* most plants dont have a common name
* one common name = same for more than one species
* names can be confusing
* most plants dont have a common name
7
New cards
why do we use scientific names?
* all species need names
* uniform system on naming = avoid confusion
* facilitates information - retrieval
* uniform system on naming = avoid confusion
* facilitates information - retrieval
8
New cards
who developed the binomial system of nomenclature?
carolus linnaeus
9
New cards
species name
* species: binomial name (Genus and epithet)
10
New cards
what are species synonyms and why do they exist?
* duplicate name
* discovered by two different people around the same time
* discovered by two different people around the same time
11
New cards
what is the type method and what is the purpose of a type species?
* every species name must be linked to a herbarium specimen
* type species sets “the standard” of the species = holotype
* type species sets “the standard” of the species = holotype
12
New cards
Process for naming a species
* find a binomial not taken (Genus + epithet)
* make type specimen and deposit at herbarium
* latin / english description of new species
* publish in journal or visible paper product
* THIS MAKES IT VALID not directly accepted
* make type specimen and deposit at herbarium
* latin / english description of new species
* publish in journal or visible paper product
* THIS MAKES IT VALID not directly accepted
13
New cards
epithets
* descriptive term
* label that associates species w a certain group
* label that associates species w a certain group
14
New cards
scientific name
* scientific: species name + authority
15
New cards
authority
the name of the person or persons who provided the binomial for the species
16
New cards
process of renaming
* put OG authority into parenthesis
17
New cards
5 basic rules of botanical nomenclature
1. name based on nomenclatural types (genus type etc)
2. only one accepted name for a taxonomic group
3. names must be treated as latin but a lot of latitude
4. nomenclature based on rule priority
5. independant from zoological nomenclature
18
New cards
rule of priority
1st published binomial for a species in a genus is the accepted name ( start 1753 )
19
New cards
artificial classification system
* habitat is an essential character to naming (essentialism)
* logical, efficient, easy, but rigid
* logical, efficient, easy, but rigid
20
New cards
artificial classification groups
* theophrastus - 372-287 BC
* herbalists-physicians - alphabetical or medicinal property for classification 15-16 centuries
* herbalists-physicians - alphabetical or medicinal property for classification 15-16 centuries
21
New cards
natural classification system
* 1580-1800
* lots of new plants coming in
* Andrea Caesalpino
* focus on flowers and fruits (reproductive parts)
* John Ray
* all parts of plant shoudl be used to classify
* dicots and monocots
* Pierre Magnol
* families
* Carolus Linnaeus
* created the sexual system
* lots of new plants coming in
* Andrea Caesalpino
* focus on flowers and fruits (reproductive parts)
* John Ray
* all parts of plant shoudl be used to classify
* dicots and monocots
* Pierre Magnol
* families
* Carolus Linnaeus
* created the sexual system
22
New cards
Sexual Systems
* carolus linnaeus
* workable “natural” classification system
* backward step to artificial
* Species Plantarum (systema sexuale)
* classification based on reproductive features
* selective and features chosen a priori simply on workability
* workable “natural” classification system
* backward step to artificial
* Species Plantarum (systema sexuale)
* classification based on reproductive features
* selective and features chosen a priori simply on workability
23
New cards
Species Plantarum
* arranged as systema sexuale
* 1st level: number of stamens
* 2nd level: number of pistils
* intense criticism ( johan siegesbeck )
* more concerned w mechanics (usable, predictable…) = lots of issues
* 1st level: number of stamens
* 2nd level: number of pistils
* intense criticism ( johan siegesbeck )
* more concerned w mechanics (usable, predictable…) = lots of issues
24
New cards
why was the sexual system an advancement and a step back?
* considered backwards bc it was artificial (mechanics of reproductive parts?)
* an advancement bc focused on reproductive parts
* an advancement bc focused on reproductive parts
25
New cards
Natural Classifications 1760-1880
* linnaeus did good w cataloging but unrelated plants were being grouped
* taxonomist reconsidered purpose of classification = look at older natural ideas
* de Jussieu family created most complete natural classification
* natural system came from taxonomic gardens
* replanting @ Trianon Garden by grouping most similar looking
* published Genera Plaantarum
* taxonomist reconsidered purpose of classification = look at older natural ideas
* de Jussieu family created most complete natural classification
* natural system came from taxonomic gardens
* replanting @ Trianon Garden by grouping most similar looking
* published Genera Plaantarum
26
New cards
Phylogenetic Classifications
* 1859 to publication of Origin of Species
* to darwin natural meant that two species looked similar because they shared a features from a common ancestor
* must include: genealogy + amount of change (similarity)
* descent w modification = evolution
* “common ancestry is a fact - the outcome is a phylogenetic tree
* Ernst Haeckle publish the first TREE OF LIFE
* to darwin natural meant that two species looked similar because they shared a features from a common ancestor
* must include: genealogy + amount of change (similarity)
* descent w modification = evolution
* “common ancestry is a fact - the outcome is a phylogenetic tree
* Ernst Haeckle publish the first TREE OF LIFE
27
New cards
Engler-Prantl classification system (phylogentic)
* 1915 their system had phylogenetic flavor w simple plants listed first then more complex plants
* standard in the early 20th century
* simple (salix) = primitive
* amentiderae = primitive
* standard in the early 20th century
* simple (salix) = primitive
* amentiderae = primitive
28
New cards
Charles Bessey Phylogenetic System
* classification of angiosperms w ideas on ancestral vs derived characters
* looked at the ancestral vs derived state of many pllant characteristics
* bessey’s dicta = basis of his system
* formed the basis for all subsequent modern systems
* looked at the ancestral vs derived state of many pllant characteristics
* bessey’s dicta = basis of his system
* formed the basis for all subsequent modern systems
29
New cards
Besseys dicta
1. floral parts -
1. all present (ancestral state)
2. loss of parts (derived state)
2. Floral fusion
1. parts separate
2. parts fused
3. floral symmetry
1. actinomorphy
2. zygomorphy
4. ovary position
1. hypogynous
2. epigynous
30
New cards
molecular classifications
* AGP (angiosperm phylogeny group) uses DNA to establish relationships and morphology to ID groups
* goal of groups is to include common ancestor and descents
* goal of groups is to include common ancestor and descents
31
New cards
tips
* extant individual in a population
32
New cards
nodes
* inferred ancestors
33
New cards
branches
* unique history of linages
34
New cards
topology
* overall branching pattern of tree
35
New cards
clade or monophyletic group
* a group of tips w node (common ancestor) and all of the descents
36
New cards
goal of modern taxonomic ?
* for all generas/families/orders etc to be monophyletic
37
New cards
sisters
* tips or clades that share a common ancestor that is not shared by others
38
New cards
synapomorphy
* a trait derived from the most recent common ancestor of a clade and shared by all taxa in the clade
39
New cards
paraphyletic
* some but not all descendants of a common ancestor are included
* need revision
* need revision
40
New cards
polyphyletic
* species derived from more than one ancestor
* need revision
* need revision
41
New cards
Challenges of terrestrialization
* desiccation
* UV radiation
* temperature fluctuation
* novel pathogens
* pressure change
* UV radiation
* temperature fluctuation
* novel pathogens
* pressure change
42
New cards
Adaptations during movement to land (???)
develop a symbiotic relationship
43
New cards
Mycorrhizae
* symbiosis between plant roots and fungi
* represents ancestral state for land plants
* represents ancestral state for land plants
44
New cards
how did symbioses with bacteria and fungi help plants overcome these challenges?
* mycorrhizae: between plant roots and fungi
* help obtain nutrients in roots from the soil
* help with water uptake
* bacteria:
* nitrogen fixing
* alter soil temp. and moisture = impact heterotrophic respiration
* help obtain nutrients in roots from the soil
* help with water uptake
* bacteria:
* nitrogen fixing
* alter soil temp. and moisture = impact heterotrophic respiration
45
New cards
how do non-vascular plants differ from vascular plants?
* non-vascular: lack true vascular tissue = xylem and phloem
46
New cards
what is meant by “vascular plant” and how does this differ from bryophytes with hydroids and leptoids?
* Bryophytes don’t have vascular tissues ( xylem ) to help them transport water ( get thru leaves instead)
* hydroids: water and mineral conducting specialized cells
* leptoids: sugar-conducting specialize cells
* hydroids: water and mineral conducting specialized cells
* leptoids: sugar-conducting specialize cells
47
New cards
Can vascular plants undergo desiccation?
no, vascular system and waxy cuticle prevent it.
48
New cards
Why is water so fundamental to bryophytes?
* since bryophytes do not have a structure to keep and transport water, they must live near water so they can use it when they need it
49
New cards
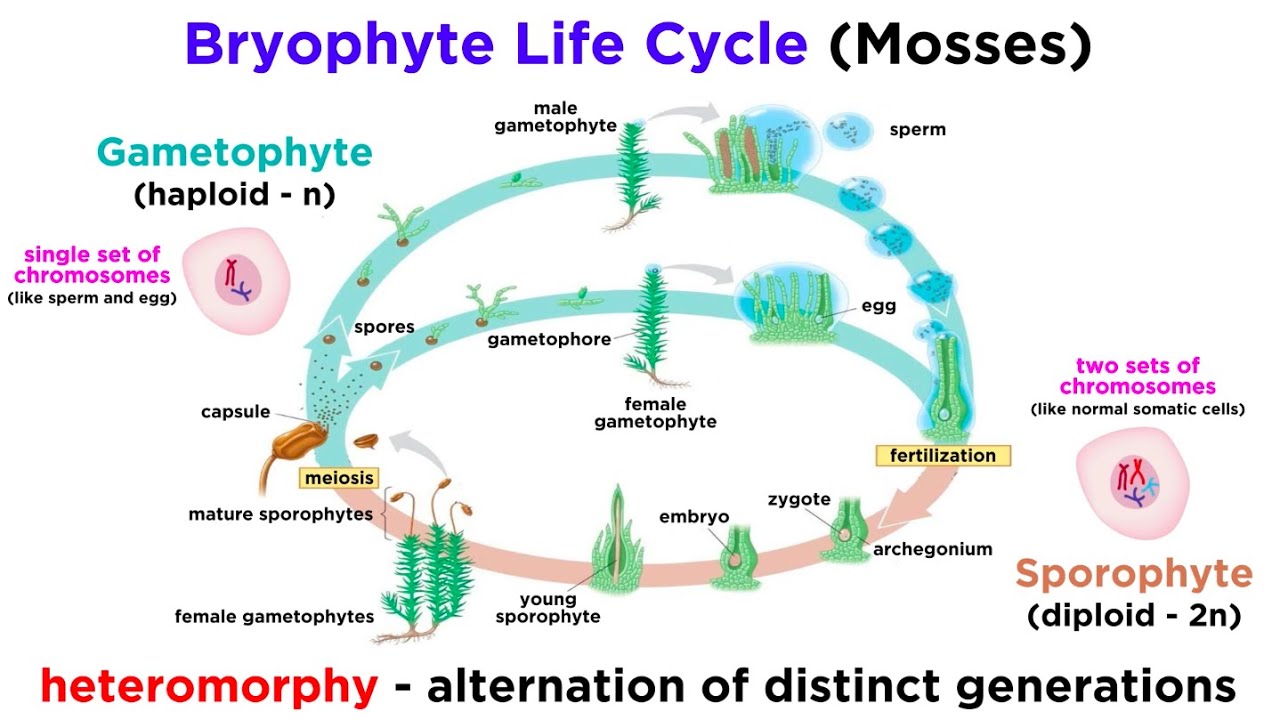
alternation-of-generation life cycle (non-vascular)
1. haploid produces antheridia (male) and archegonia (female) bits.
1. these produce gametes via mitosis
2. two come together = fertilization of ovum via biflagellate sperm
3. fertilization results in diploid zygote that develops into a sporophyte
1. sporophyte is dependent on gametophyte
4. sporophytes produce haploid spores through meiosis
5. spores disperse and germinate into a protonema (baby gametophyte)
\
\
50
New cards
gametophyte
* the body
51
New cards
sporophytes
* the tips w them sporangium capsules
52
New cards
Anthocerotophyta
* the hornworts
* lack seta
* simple thallus
* lack gemmae
* lack water conducting cells
* stomata on both gametophyte and sporophyte (don’t close)
* 215 species
* lack seta
* simple thallus
* lack gemmae
* lack water conducting cells
* stomata on both gametophyte and sporophyte (don’t close)
* 215 species
53
New cards
Thallus
* plant body lacking roots, stems, or leaves
* complex thallus: containing multiple strata, with marked differentiation of tissues
* simple thallu: undifferentiated thallus
* complex thallus: containing multiple strata, with marked differentiation of tissues
* simple thallu: undifferentiated thallus
54
New cards
Leafy
* terete and bearing leaf-like appendages
55
New cards
rhizoids
* filamentous structures that anchor the plant
* can be used in some species for water uptake via capillary action
* can be used in some species for water uptake via capillary action
56
New cards
hydroids
* water conducting cells. not in hornworts
57
New cards
leptoids
* sugar conducting cells
* only in moss family polytrichaceae
* only in moss family polytrichaceae
58
New cards
capsule
* contains sporangium (produces spores)
59
New cards
Operculum
* in mosses, the lid that blocks the capsule mouth
60
New cards
calyptra
* a little hat (absent in hornworts)
61
New cards
seta
* sporophyte stalk
* absent in hornworts
* absent in hornworts
62
New cards
Marchantiophyta
* the liveworts
* nicholas marchant
* gametophyte thalloid or leafy
* lack stomata
* 7300 species
* noble taxa = marchantia = very common = model system
* nicholas marchant
* gametophyte thalloid or leafy
* lack stomata
* 7300 species
* noble taxa = marchantia = very common = model system
63
New cards
Bryophyta
* the mosses
* gametophyte a leafy shoot
* stomata on sporophyte capsule
* complex sporophyte capsule
* gametophyte a leafy shoot
* stomata on sporophyte capsule
* complex sporophyte capsule
64
New cards
Bryophyta (Body Plans)
* Acrocarpous
* upright w terminal sporangia (all upright)
* unbranched
* Pleurocarpous
* produce their sporangia on short lateral branches or buds
* prostrate - forming freely branches mats (sporophytes upright rest sideways)
* complex sporophyte capsule
* peristome = a ring of teeth surrounding the mouth of the capsule (teeth move in response to changes in humidity)
* upright w terminal sporangia (all upright)
* unbranched
* Pleurocarpous
* produce their sporangia on short lateral branches or buds
* prostrate - forming freely branches mats (sporophytes upright rest sideways)
* complex sporophyte capsule
* peristome = a ring of teeth surrounding the mouth of the capsule (teeth move in response to changes in humidity)
65
New cards
Sphagnum (Bryophytas Notable Taxas)
* Major component of peatlands
* fuel producation // horticulture
* 3% of global land surface
* peatlands = contain up to 44% of all soil carbon
* fuel producation // horticulture
* 3% of global land surface
* peatlands = contain up to 44% of all soil carbon
66
New cards
Dawsonia superba (Bryophytas Notable Taxas)
* big boys
* tallest self-supporting bryophhyte
* tallest self-supporting bryophhyte
67
New cards
Physcomitrella patens (Bryophytas Notable Taxas)
* first seedless plant to have genome sequenced
* model system for evolution / genomics
* model system for evolution / genomics
68
New cards
Super cute (Bryophytas Notable Taxas)
* Ulota
* Macromitrium
* Macromitrium
69
New cards
homosporous
* one kind of spore is produced
70
New cards
heterosporous
* different spores are produced
71
New cards
Microspore
* give rise to male gametophytes
72
New cards
Megaspore
* give rise to the female gametophytes
73
New cards
megaphylls
* complex leaves with branches veins
74
New cards
microphylls
* small, simple, one veined leaves
75
New cards
Circinate vernation
* vernation is the arrangement of folded leaves in a bud, forming a crozier or fiddlehead
76
New cards
indusium
* falp-like structure that protects the sorus
77
New cards
Sori (plural), Sorus (singular)
* Sporangia borne on the margin or the lower surface of the leaf
78
New cards
double fertilization
* the sperm cell has two nuclei - one fertilizes the ovule, the other fertilizes two polar nuclei
79
New cards
Tracheid
* a type of water-conducting cell in xylem which lacks perforations in the cell wall
80
New cards
Whorl
* a whorl arrangement of leaves, sepals, petals, stamens, or carpels that radiate from a single point and wrap around the stem/stalk
81
New cards
Sporangia
* an enclosure in which spores are formed
82
New cards
Strobilus
* a reproductive system of gymnosperms
* hold the sporangia that produce the spores
* cone like structure (kinda light brown / orange)
* hold the sporangia that produce the spores
* cone like structure (kinda light brown / orange)
83
New cards
terete
* cylindrical // rounded
84
New cards
prostrate
* laying down
85
New cards
dichotomous branching
* branching by forking in airs, can be irregular or equal
86
New cards
sporophyte
* the spore-producing individual or phase in the life cycle of a plant having alternation of generations
* a diploid phase in the life cycle
* MEIOSIS produces spores diploid
* a diploid phase in the life cycle
* MEIOSIS produces spores diploid
87
New cards
sporophyll
88
New cards
gametophyte
* stage of sexual reproduction process that produces HAPLOID gametes
* MITOSIS produces egg and sperm haploid
* MITOSIS produces egg and sperm haploid
89
New cards
antheridium
* male sex organs
* diploid side
* diploid side
90
New cards
archegonium
* female sex organs
* diploid
* diploid
91
New cards
spiral arrangment
* leaves are opposite and alternate
92
New cards
monomorphic
* leaves on flower plant = leaves on non-flowering plant
93
New cards
dimorphic
* plant organs that appear in two distinct forms or shapes on the same plant or in closely related species
94
New cards
sheath
* a protective covering on the lower part of the stem
95
New cards
Blade
* leafy part
96
New cards
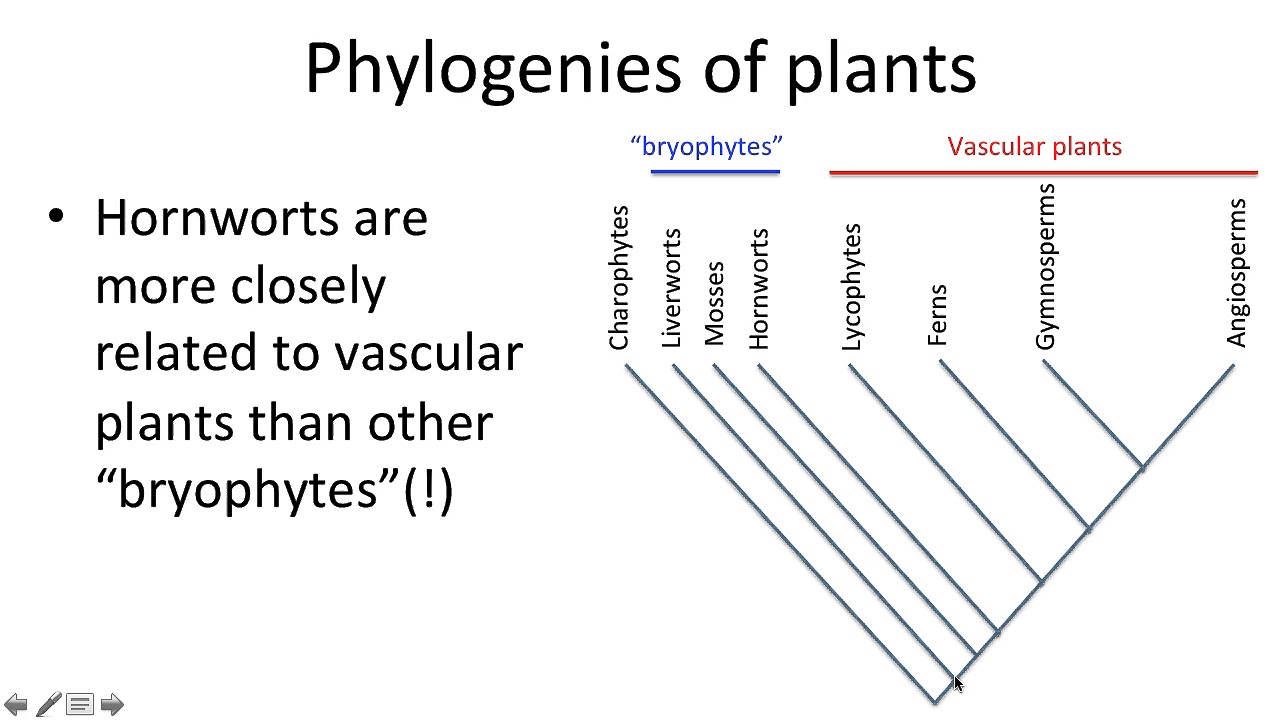
phylogeny w lycophypts, ferns, gymnosperms, angiosperms
97
New cards
when were lycophytes dominate? How does this relate to reproductive traits
* carbonniferous period
* very wet period
* water needed for fertilization of lycopod gametophytes
* they had no protective coating
* very wet period
* water needed for fertilization of lycopod gametophytes
* they had no protective coating
98
New cards
what is darwin’s abominable mystery?
* the origin and rise of angiosperms
99
New cards
when did angiosperm begin to arise in the geological record?
jurassic / early cretaceous
100
New cards
are angiosperms relatively recent?
yes relatively recent