Exam 3
1/402
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
403 Terms
Timing and percentage of loss due to embryo wastage in domestic species
bovine
ovine
porcine
equine
bovine
days of gestation: 8-16
embryos lost: 25-40%
ovine
days of gestation: 9-15
embryos lost: 25-40%
porcine
days of gestation: 8-16
embryos lost: 25-40%
equine
days of gestation: 30-36
embryos lost: 30-40%
Ectoderm (Inner cell mass) develops
skin, hair, hooves, horns, sweat glands( including mammary glands), nervous system, oral and nasal cavity, outer repro tract (vulva, vestibule, clitoris, glans penis)
Mesoderm (Inner cell mass) develops
heart and blood vessels, renal system, skeleton (including muscle), internal repro tract (gonads: female including ovaries, oviduct, uterus, cervix, and vagina & male including epididymis, vas deferens, and accessory glands
T/F: yolk sac does play a role in waste removal
true
Endoderm (Inner cell mass) develops
digestive system (including liver and pancreas), pulmonary system, major glands
Site of semen deposition in cow and sheep
vagina
site of semen deposition in horses
cervix
site of semen deposition in pigs
cervix or uterus
T/F: oogenesis can proceed without folliculogenesis
false
Stage of embryo development w/ first defined cells
a) morula
b) syngamy
c) blastocyst
d) zygote
e) none of the above
c) blastocyst
T/F: the second meiotic division takes place after ovulation in most farm species
true
a single cell embryo is called a
a) morula
b) syngamy
c) blastocyst
d) zygote
e) none of the above
d) zygote
which parts of the female would be a potential barrier to sperm movement
a) vagina
b) cervix
c) uterotubular junction (UTJ)
d) all of the above
e) none of the above
d) all of the above
T/F: under normal conditions, 99.5% of all oocytes will never be ovulated
true
T/F: heart is the first tissue to form in the embryo, but nervous system is the last to become fully functional
false
which of the following might be responsible for embryo mortality
a) genetics
b) low progesterone
c) uterine crowding
d) all of the above
e) none of the above
d) all of the above
the last organ to begin functioning is the
a) heart
b) lungs
c) brain
d) liver
e) none of the above
b) lungs
T/F: oogonia originate in the yolk sac
true
[what] is the placental hormone that regulates the growth of the fetus
a) progesterone
b) estrogen
c) relaxin
d) all of the above
e) none of the above
e) none of the above
T/F: in cattle, we would we have a retained placenta if animal has not passed placenta within 2 hours after birth of neonate
false
Which species we have talked about has a normal gestational length of ~280d
a) bovine
b) equine
c) ovine
d) porcine
e) none of the above
a) bovine
Which species we have talked about has a normal gestational length of ~114d
a) bovine
b) equine
c) ovine
d) porcine
e) none of the above
d) porcine
T/F: milk letdown is due to an arc reflex of oxytocin from mother due to neonate suckling
true
Which species we have talked about has a normal gestational length of ~340d
a) bovine
b) equine
c) ovine
d) porcine
e) none of the above
b) equine
Which semen analysis measures movement of sperm cells
a) volume
b) motility
c) morphology
d) concentration
e) none of the above
b) motility
Which semen parameter examines the shape of the sperm cells
a) volume
b) motility
c) morphology
d) concentration
e) none of the above
c) morphology
T/F: cryopreservation is currently the best method available for long term storage of male genetics
true
Which species routinely produces semen volumes around 1mL
a) porcine
b) canine
c) ovine
d) equine
e) none of the above
c) ovine
T/F: normal semen analysis has been assoc. w/ higher pregnancy rates
true
Which species requires surgical embryo transfer
a) cattle
b) pig
c) horse
d) sheep
e) none of the above
d) sheep
Which species shows no detectable signs of heat in absence of an intact male animal
a) cattle
b) sheep
c) horse
d) pig
e) none of the above
b) sheep
Which of the assisted reproductive technology (ART) procedures should be used as a routine treatment for infertile female domestic animals?
a) cryopreservation
b) superovulation
c) embryo transfer
d) all of the above
e) none of the above
e) none of the above
T/F: winking of the vulva is a common sign of standing heat in pigs
false
T/F: to be efficient, estrus detecting should be done during feeding
false
Oocyte is the
female gamete (inside of follicle)
spermatogenesis
physiological process of growing and maturing spermatozoa
what are the 2 similarities bt Oogenesis and Spermatogenesis
phase where chromosomal numbers are reduced (meiosis cell division)
undergo a metamorphic change in structure
Males have billions of copies (of sperm cells) per [what] while females have a few million eggs in her [what]
ejaculate; ovary
Embryo transfer
process of super-ovulating and retrieving embryos from a donor animal and transferring those embryos into a recipient
How about many embryos are retrieved when attempting embryo transfer
10-15
Follicles are located where and make functional eggs
on the ovary
T/F: of the 75,000 to 2 million primordial follicles only .05% will reach the point of developing into a Graafian follicle and ovulation
true
Steps of folliculogenesis
primary follicle (primary oocyte inside)
secondary and tertiary stages
Graafian follicle
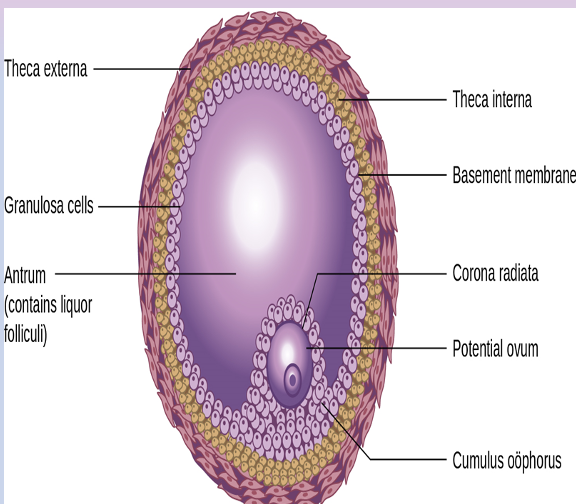
Graafian follicle has several structures. Describe them
highly structured relationship bt outer layers of theca and inner layers of granulosa separated by basement membrane
basement membrane creates a physical barrier that allows fluids to pool and final structures of follicle to form, creates a blood barrier
as follicle develops, egg develops its own barrier, Zona Pellucida
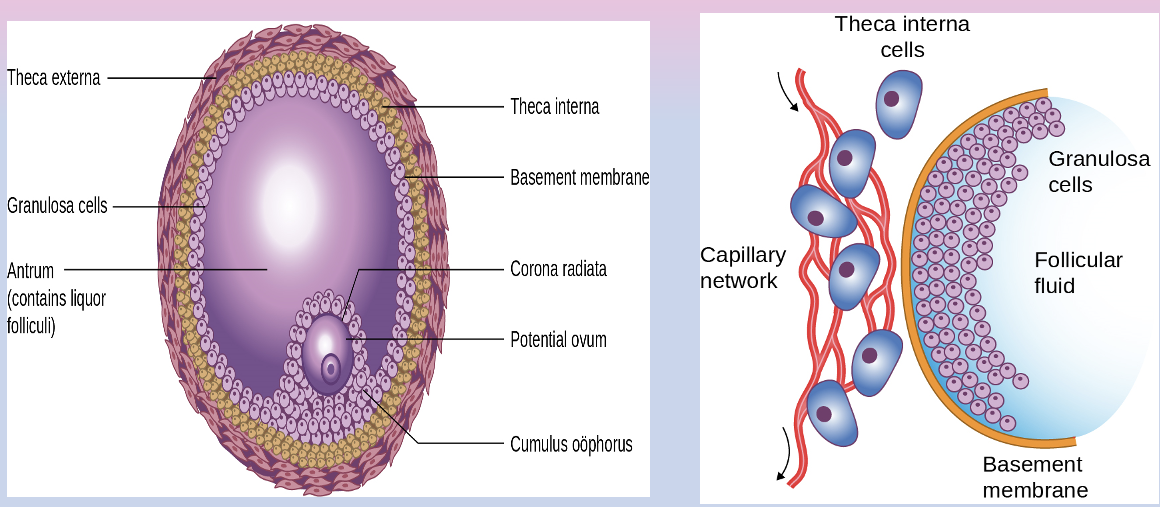
Zona Pellucida
protein structure surrounding oocyte that serves a barrier to fertilization
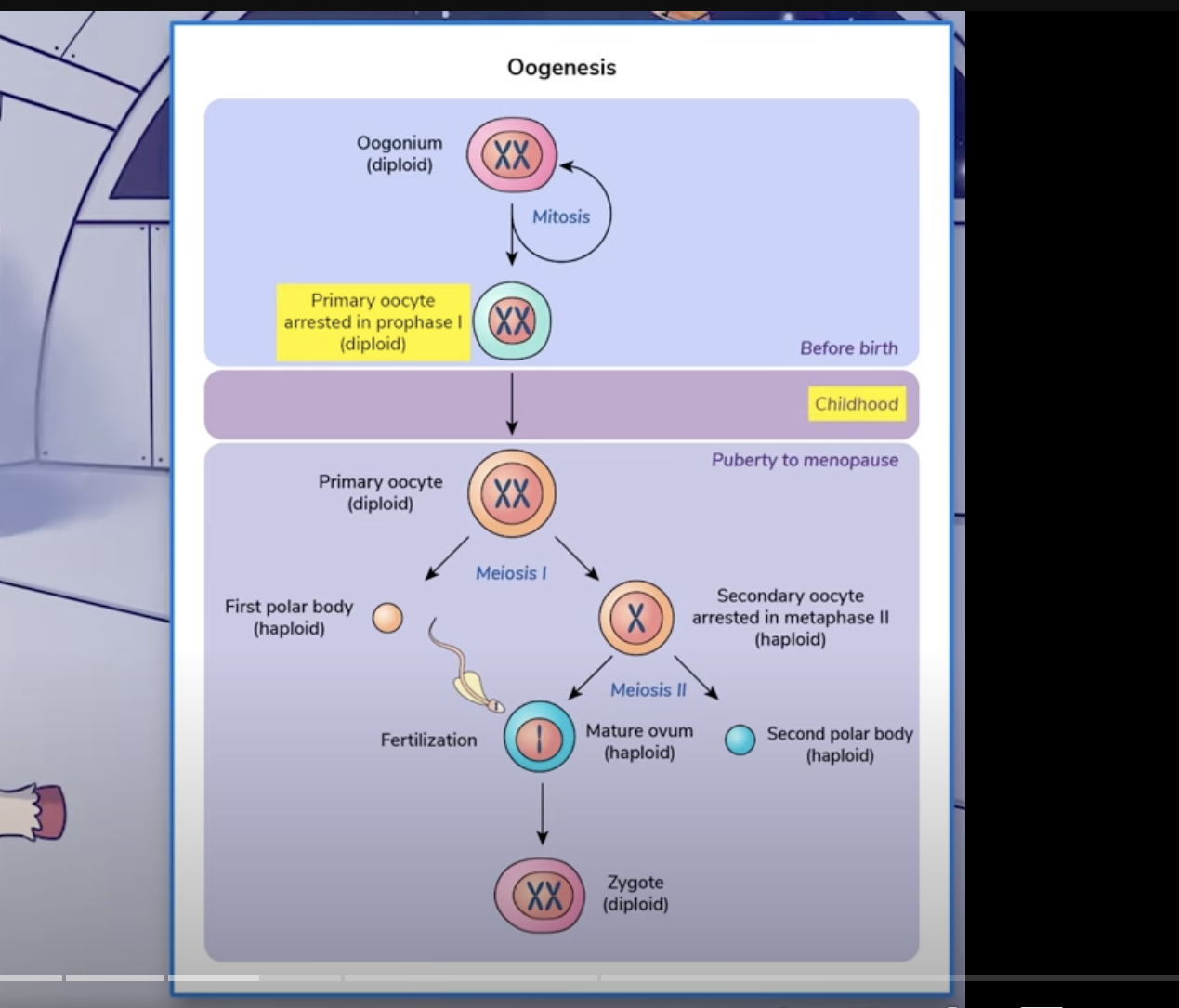
During embryo development (i.e embryonically), the first form of egg cells which contain 2 sets of chromosomes identical to other cells of the body is called what
Oogonium
Oogonium undergo [mitosis or meiosis?] to create 75,000 to 2 million primary oocytes
mitosis
T/F: the mitotic divisions in oogonium continue after birth and number of potential oocytes increases
false;
the mitotic divisions CEASE BEFORE BIRTH
potential oocytes becomes FIXED and begin decreasing even before birth
What is one of the reasons why a female only has a set amount of oocytes (most before birth)
the mitotic divisions underwent by oogonium to create primary oocytes CEASES
once this stops, there will ONLY be meiosis from this point
T/F: females will lose eggs before birth (once mitotic divisions cease!) because the hormone-independent phase has primordial follicles trying to grow and develop and they will become atretic esp if they are trying to grow before puberty
true
T/F: some oocytes that attempt to continue development before puberty will become atretic and some will be viable
false; ALL of the oocytes will become atretic if they try to develop before puberty
If the female has hit puberty and has the right set of hormones, will the follicles and oocytes continue to develop in a normal fashion
yes
What is a large difference in male and female reproductive systems (spermatogenesis and oogenesis)
Order in which they go through meiosis and metamorphosis
males go through spermatocytogenesis first then through spermiogenesis
Spermatogonia goes from 2N to N (chromosomal change) → sperm shape (metamorphic change)
Oogonia go from small to bigger shape (metamorphic change) → 2N to N (chromosomal shape)
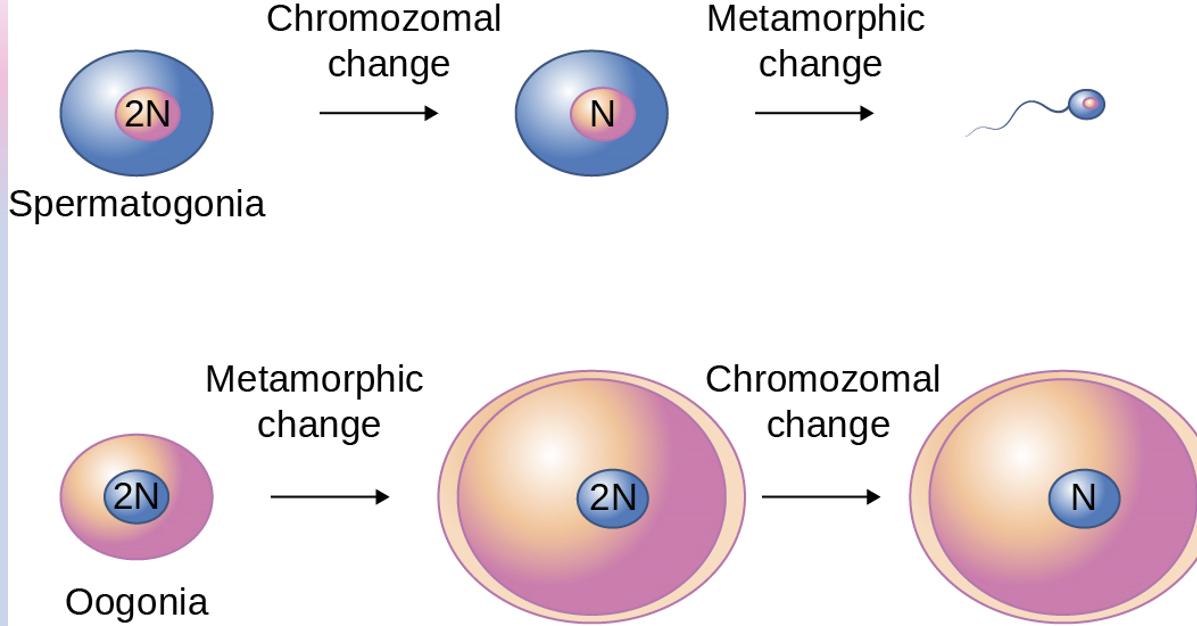
Male reduces gametes’ chromosome number first then transforms its shape to look like a sperm cell which means what
a) nothing
b) makes more copies
c) can’t make more copies
d) none of the above
b) makes more copies
Female changes shape of gamete first (zona pellucida around the structure) and then goes through what
a) meiosis
b) mitosis
c) spermatocytogenesis
d) none of the above
a) meiosis
T/F: the difference bt the order of meiosis and metamorphosis in male repro and female repro leads to both males and females having limited gametes
false;
males remain fertile for their entire lives
chromosome reduced (meiosis) then sperm shape made → more copies of sperm being made
females have limited gametes
changes shape with zona pellucida going around the structure then meiosis
Metamorphic change of the oocyte (Females)
follicle is developing from primary to secondary stage of development, egg will begin to enlarge; increase cytoplasm and organelles
once 2X or 3X bigger: develop the zona pellucida, granulosa cells known as corona radiata
this arrangement = very large cell, only nutrients the embryo will have until the outer wall, zona pellucida, attaches to the uterine wall
Meiosis in the egg is how many steps
2 step
2 part meiosis: cell is waking up
Meiosis I in oocyte
cell begins growing w/o duplication of chromosomes
arms of paired chromosomes will exchange genetic material in process called crossover: exchange of genetic material bt paired chromosomes
ends with production of 2 nuclei each w/ 1 set of chromosome (haploid)
these nuclei are genetically diff
one of these nuclei will be “thrown out”
polar body
remaining nuclei is called secondary oocyte
Crossover
exchange of genetic material bt paired chromosomes
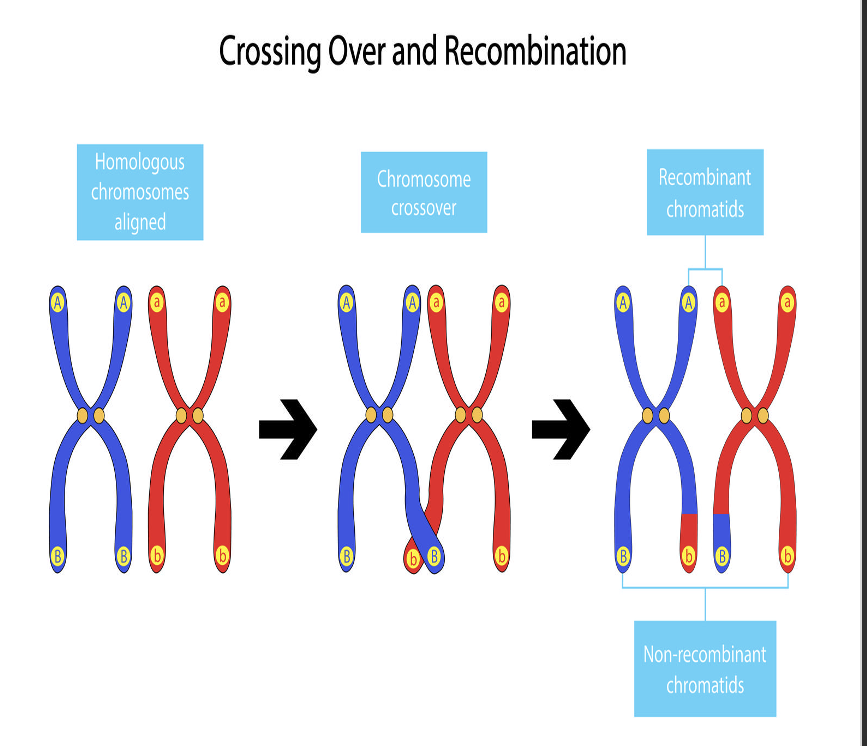
T/F: crossover leads to genetic recombination → survival of fittest
true
T/F: many high tech procedures require healthy, mature oocytes
true
Meiosis II in oocyte
still need to become mature
there will be no meiosis 2 and we are kinda stuck until next part!
as sperm is crossing vitelline membrane, this triggers second meiotic division, and 2 haploid nuclei, called pronuclei, form
one will be expelled and form a second polar body
second one (mature ovum; haploid) will fuse w/ DNA from sperm during fertilization
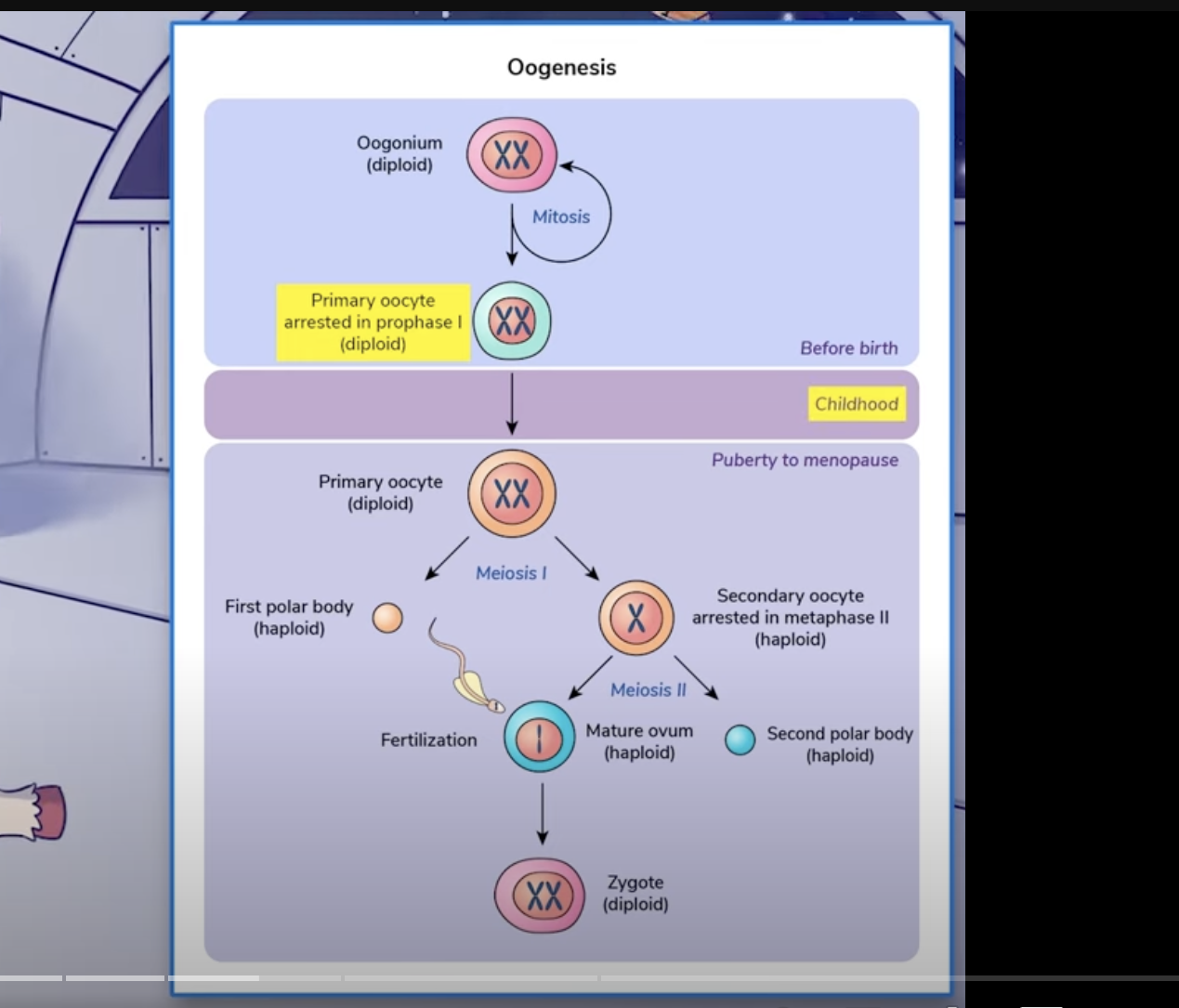
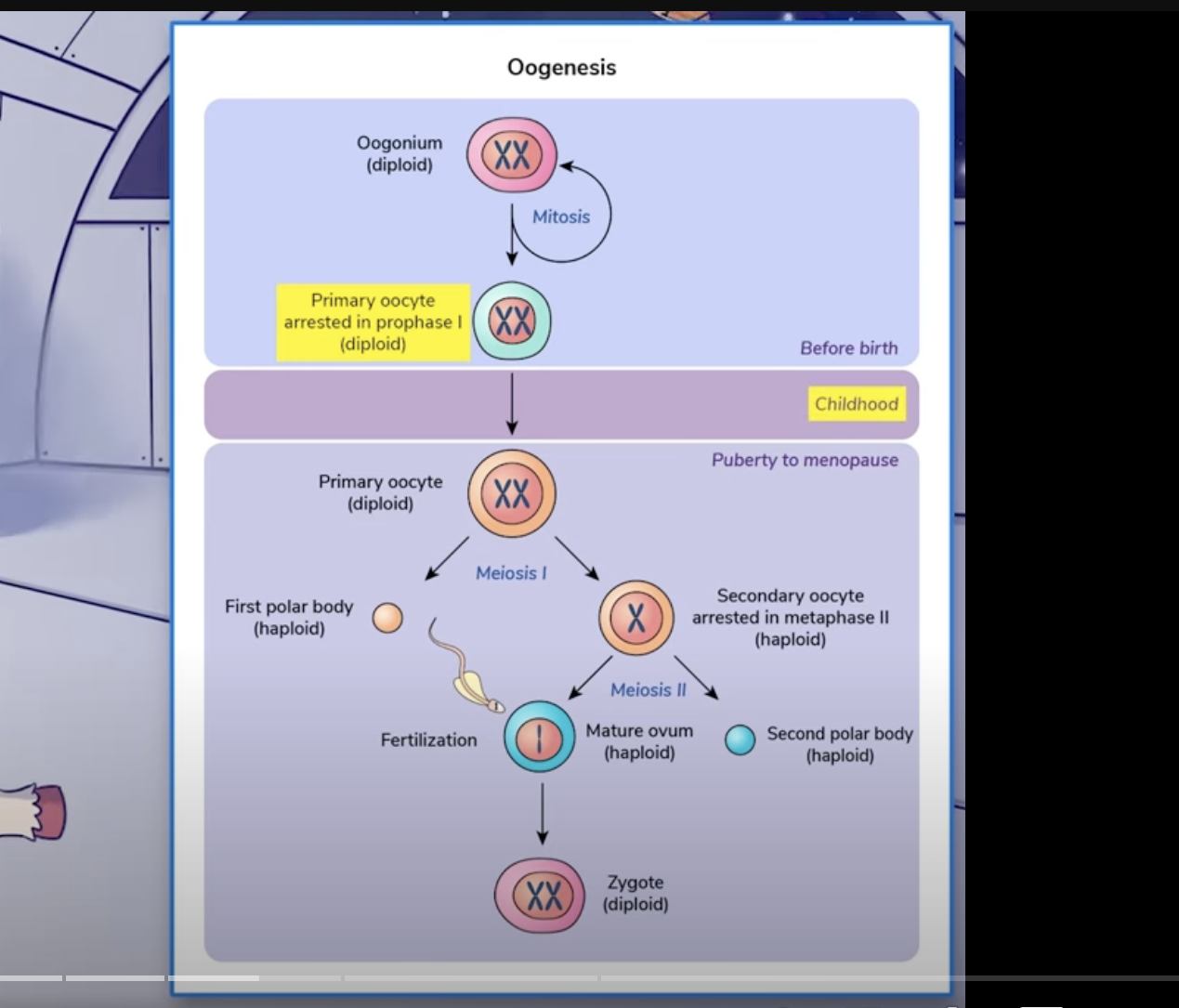
Ooogenesis Picture and link to yt video
Usually, ovulation occurs after the peak of LH surge except for what species
a) bears
b) pigs
c) dogs
d) horse
d) horse
ovulation occurs before peak of LH surge and will occur 1 or 2 days prior to end of estrus
Timing of ovulation in cow
10-12 hrs after end of estrus
Timing of ovulation in ewes
24-30 hrs from start of estrus
Timing of ovulation in sow
35-45 hrs from start of estrus
Timing of ovulation in mare
1-2 days before end of estrus
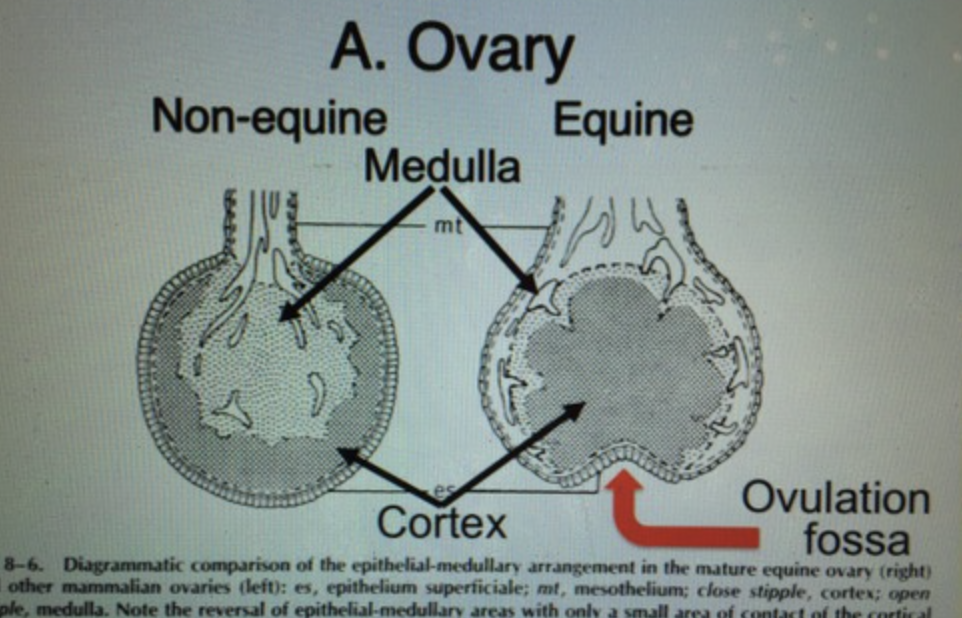
Medulla of the ovary
that portion of the ovary containing nerves and blood supply
Cortex of the ovary
that portion of the ovary containing the follicle and hormone production
T/F: in most domestic species, cortex is on the outside and medulla is on inside
true
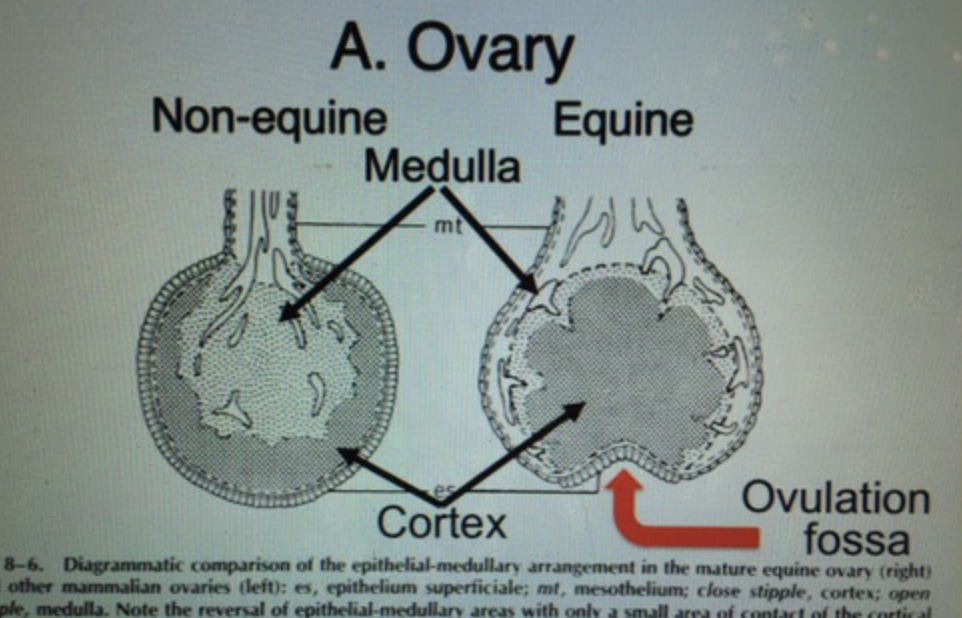
T/F: Mares have the medulla on the outside and cortex on the inside
true
ovulation fossa
Pattern to ovulation in species who ovulate after LH surge
LH surge triggered by high lvls of estrogen (from the ovary)
LH triggers 4 important changes within follicle
saturation of LH receptors on theca cells will begin their transformation from theca to luteal cells
binding will trigger these converting cells to release proteolytic enzymes, weaken the bond bt follicular cells and basement membrane
trigger the local release of prostaglandins, which will stimulate contractions at the base of the follicle and cause shifts in blood flow
maturation of the oocyte cytoplasm, nucleus, and vitelline membrane to make fertilization possible
Rupture of follicle caused by (steps of ovulation)
pressure from contractions
weakened basement membrane
rift in follicle wall
oocyte will be extruded
oocyte into the waiting fimbria
Where will the rupture of the follicle occur
anywhere in the cortex*
*except the hilus: depression or pit at the part of an organ where vessels and nerves enter
Where will the rupture of the follicle NOT occur
the hilus of the cortex
T/F: single ovulators, the maturation and ovulatory event is totally random bt 2 ovaries and cannot be predicted by previous cycle
true
Where do the female’s gametes go before fertilization
AIJ
Sperm cell pathway in male tract
epididymis → vas deferens → pelvic urethra → penile urethra before introduced to female tract
What causes movement of the sperm through the female repro tract (towards AIJ for fertilization)
contractions of the female tract
NOT the sperms’ tail!
T/F: contractions of muscles of female tract move sperm cells to AIJ and not the sperm cells’ tail
true
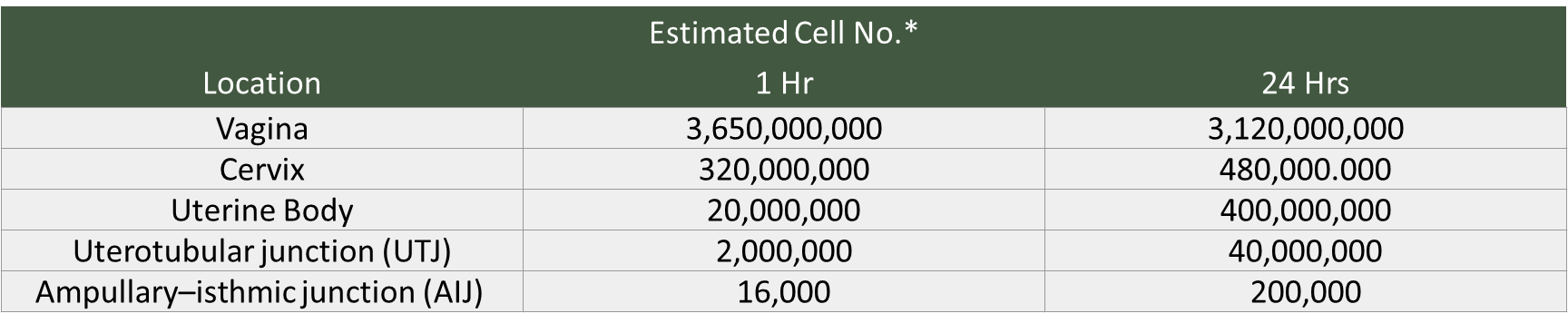
T/F: Female tract creates barriers for sperm and facilitate its movement.
true
ex: cow, male deposits 4-5 billion sperms in vagina, only few 100-1000 arrive at the AIJ
Sperm move up what structure (specifically) to wait for an egg
AIJ (remember this is a physiological location not PHYSICAL)
T/F: Sperm can swim for days in female tract but 24-48hrs become biochemically nonfunctional
true
oviduct is the most ideal environment for prolonging sperm shelf life → sperm can wait up to 96 hrs waiting for oocyte to fertilize
In the female tract, the sperm will undergo what type of reaction and capacitation
acrosome rxn
T/F: once the sperm cells have gone through acrosome rxn and capacitation, the sperm has forever to fertilize the oocyte
false; it only has a limited number of hrs to fertilize the oocyte
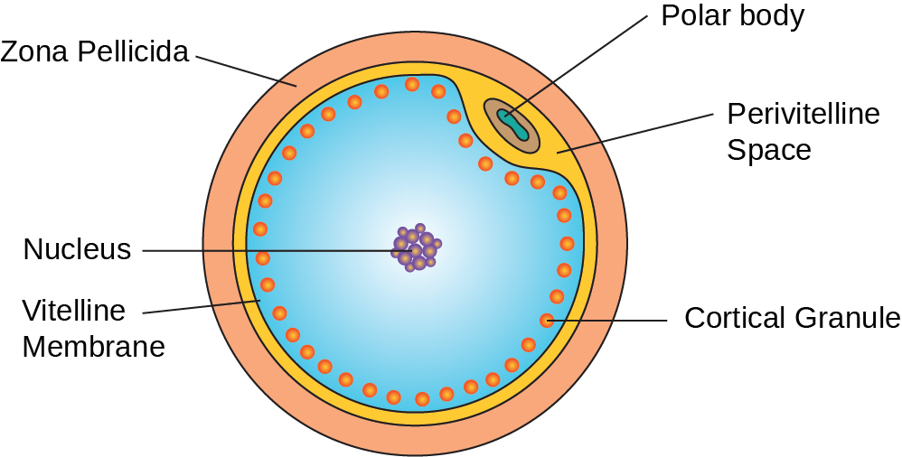
What is the function lifespan of an oocyte and what will happen to the oocytes that aren’t fertilized within this lifespan
the lifespan of a functional oocyte is bt 6-10 hrs
after this, egg cells that aren’t fertilized will be phagocytized (absorbed by the body)
Mature Oocyte Ready to be Fertilized Picture
Where does the final maturation of a sperm cell happen
within the female repro tract
Final Maturation of Sperm (Fertilization)
Step 1-5
sperm cells undergo acrosome rxn and capacitation
hypermotility of sperm cells (maybe induced by chemical agents from egg) as it approaches egg
sperm cell forms loose assoc. w/ zona pellucida
enzymes in the acrosome digest a hole through the zona as the tail pushes the sperm head through into the perivitelline space
function of motility
several sperms could enter perivitelline space
What is the main function of the sperm cell’s tail
function of motility during fertilization
tail will push sperm head through perivitelline space
under normal circumstances, how many sperm cells will lay down on the vitelline membrane and form an assoc. w/ membrane surface
1 sperm cell
What will the sperm cell laying down on vitelline membrane and forming an assoc. w/ membrane surface trigger
triggers membrane to phagocytize sperm (at least sperm head)
this step is species dependent*
Fill in the Blanks
3 important events in fertilization
cortical granules will migrate and fuse with the vitelline membrane, releasing their enzymes into perivitelline space and change [1.What] structure
enzymes will functionally change the zona because [2. Why?]
trigger [3. What process] in the oocyte nuclei. The first 2 events will lead to vitelline block, both the membrane and the zona will become resistant to any other sperm cells crossing their structure, preventing more than one sperm cell from entering the egg
vitelline membrane
no other sperm can get across it and into the perivitelline
meiosis 2
T/F: activation of the egg nuclei is essential for final steps of fertilization
true
Activation of egg to forming a zygote (Fertilization)
Steps 1-6
Nuclei forms a visible nuclear membrane → duplicate in chromosomes → briefly returning oocyte to 2N cell
Meiosis II: nuclei splits to form 2 pronuclei (each haploid)
One of the 2 pronuclei migrates to become second polar body; the DNA from sperm will form male pronuclei
2 remaining pronuclei (one from sperm and one from egg) will align together toward middle of oocyte
Remember there were 2 pronuclei from the egg
one of them becomes the second polar body and is EXPELLED
Male and female aligned fuse together in a process called Syngamy
Fertilization is complete: single cell w/ combo of male and female’s genetics → new genetic combo
Zygote: a single cell formed at fusion of an egg and sperm cell
T/F: sometimes, you can see the the pronuclei from sperm and other pronuclei from the egg aligning together toward the middle of the oocyte under a microscope
true
Syngamy
fusing of pronuclei during fertilization
Zygote
a single cell formed at fusion of an egg and sperm cell