3.1 KINESE Pelvis and Femur Bony landmarks
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Pelvis function
links the lower limbs to the axial skeleton, provides stability, provides passive and dynamic range of motion
3 parts of an os coxa bone
ilium, ischium, pubis
4 ilium spines
Anterior superior, Anterior Inferior, Posterior superior, Posterior inferior
Gluteal Fossa
Depression where the gluteal muscles attach
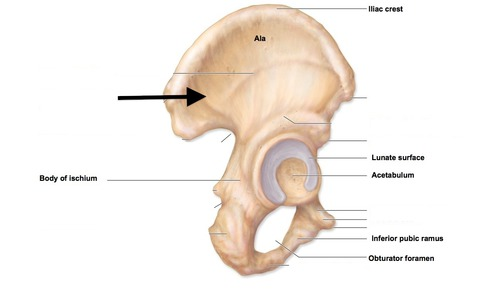
Iliac fossa
Depression where the Iliacus attaches
Posterior Gluteal line
Line on the gluteal fossa that is the most posterior to the other lines
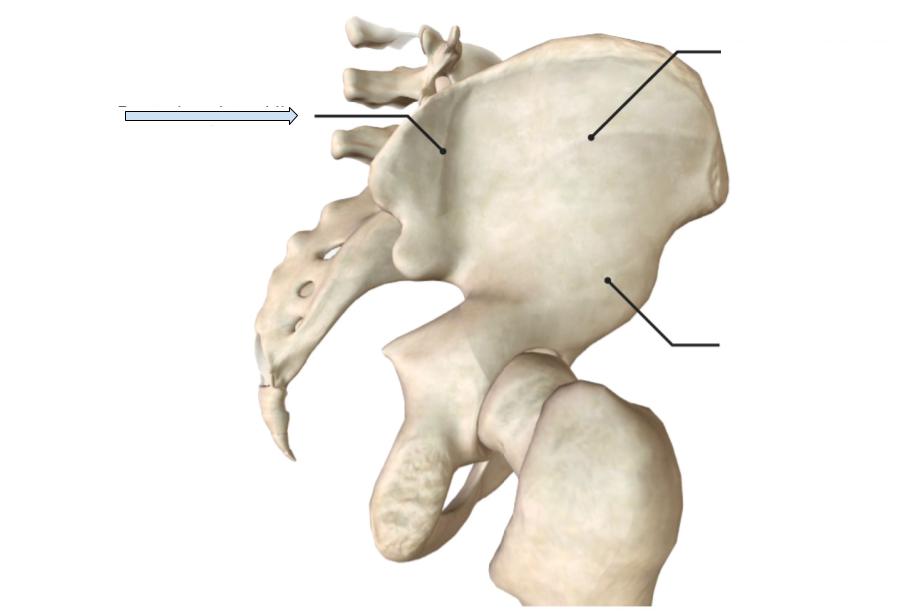
Anterior Gluteal line
Line on the gluteal fossa that is more anterior, also superior to inferior line
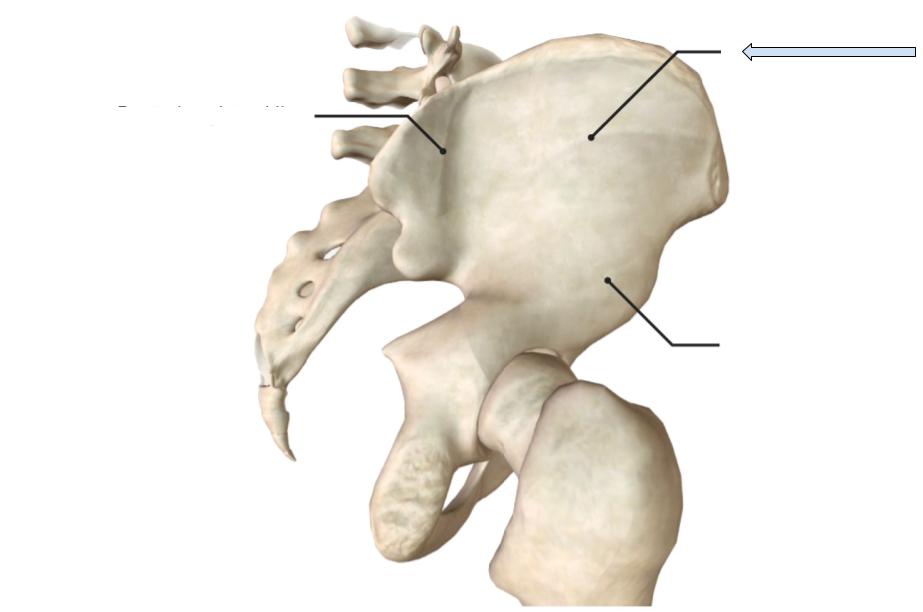
Inferior Gluteal line
Line on the gluteal fossa that is more inferior to the other lines
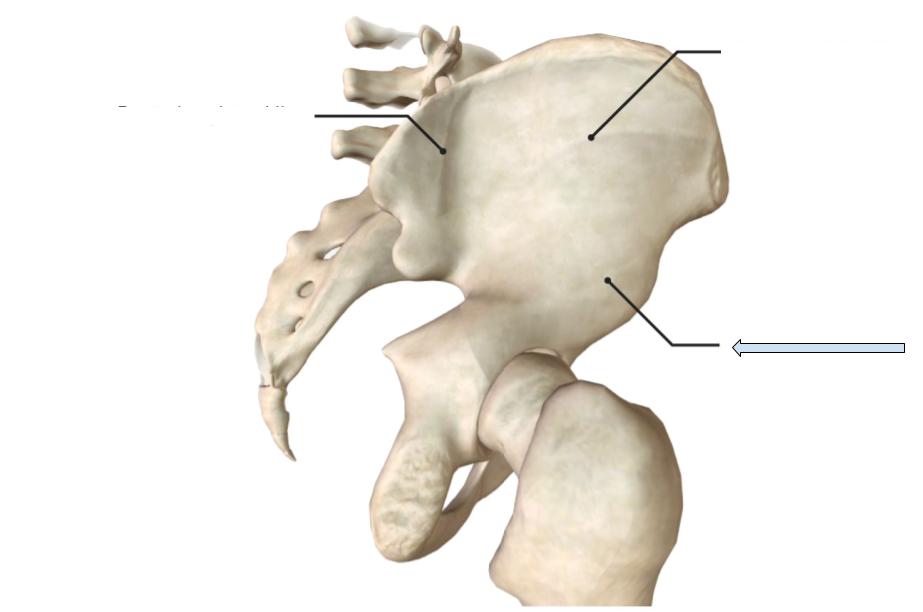
Ischial tuberosity
Medium projection found on the ischium
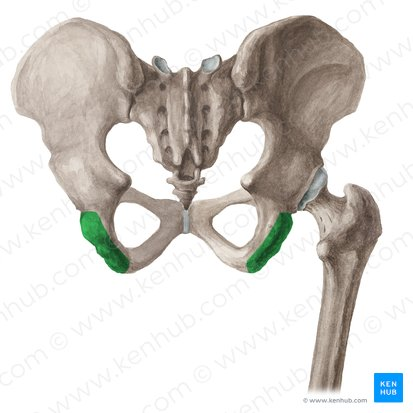
greaer sciatic notch
above ischial spine, made into a foramen by the sacrospinous ligament
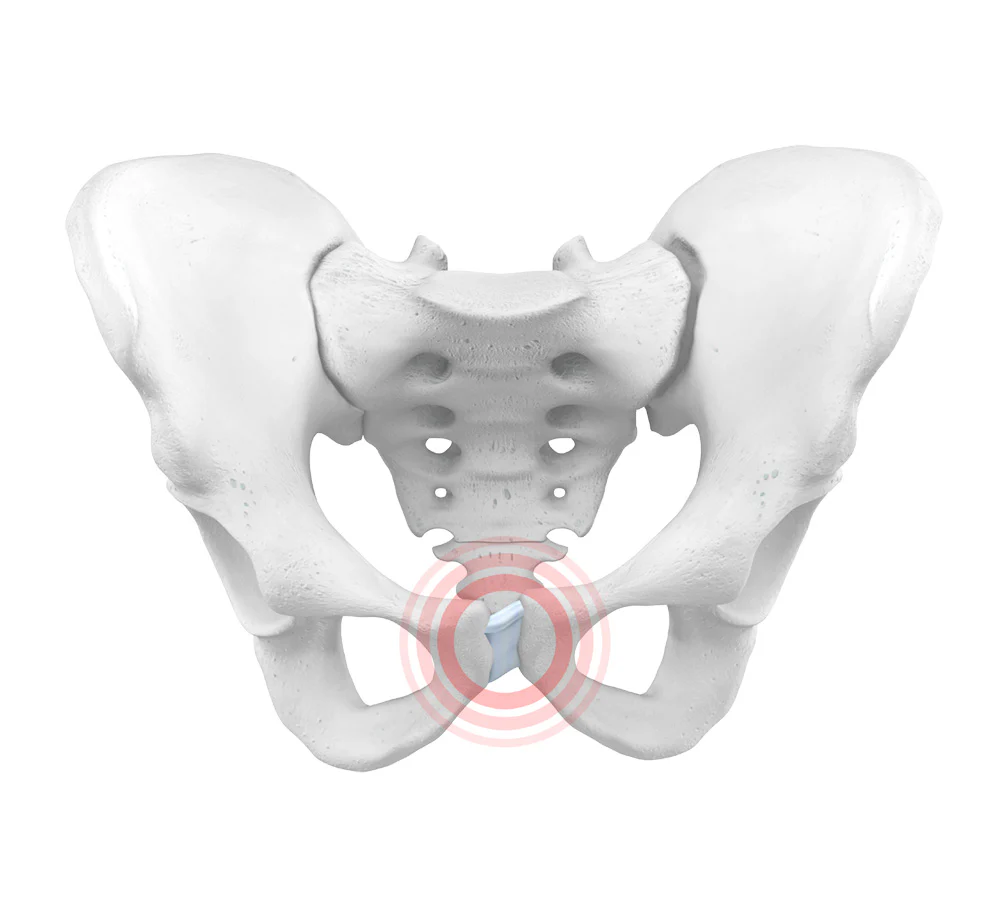
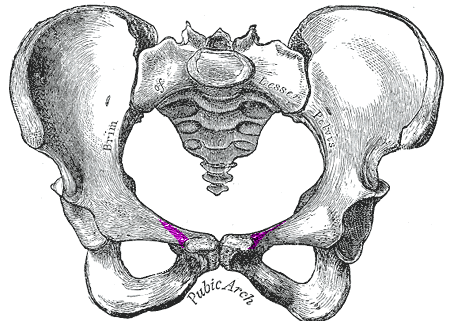
pubic symphysis
cartilagenous joint where the right and left pubis articulate
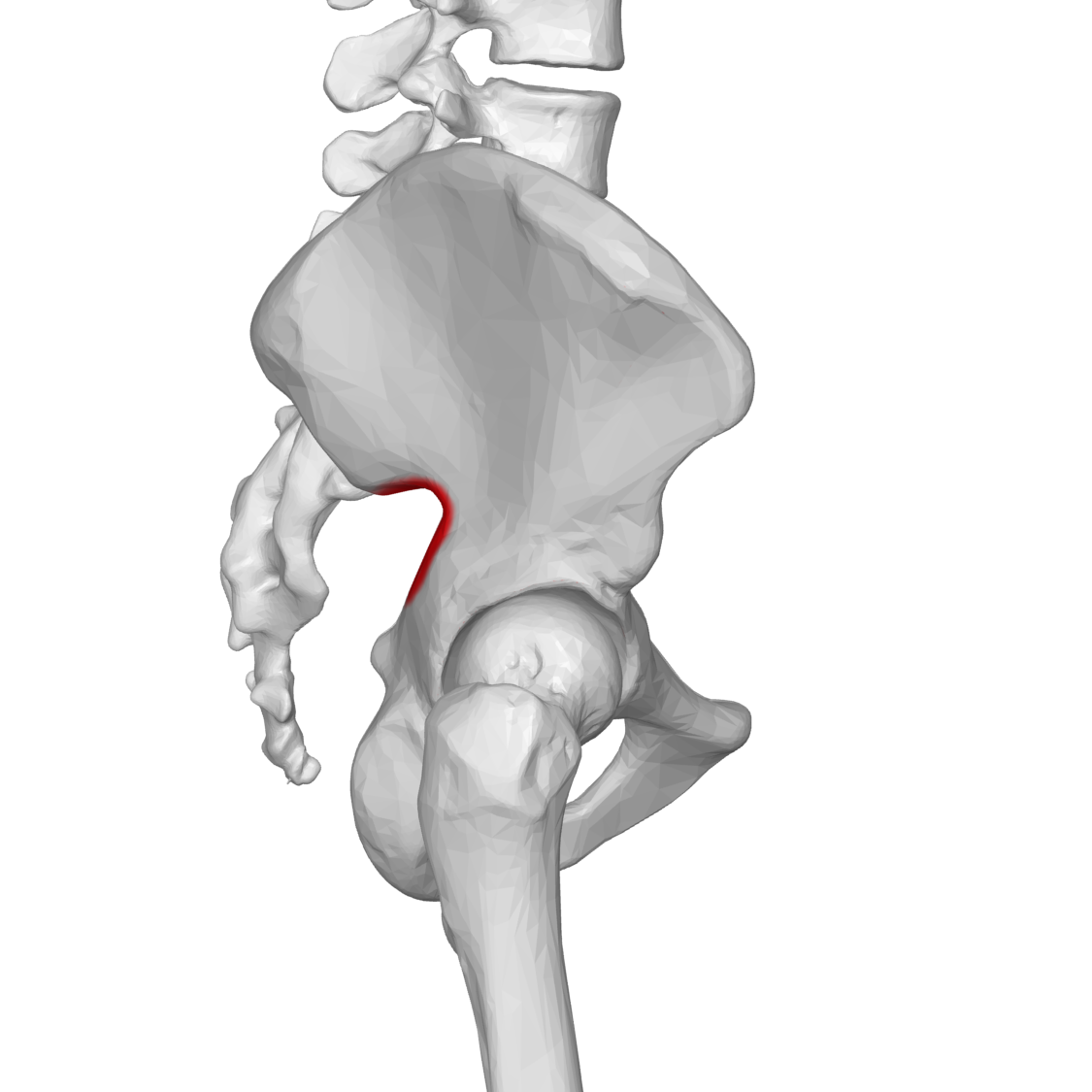
Ramus
Branch
Ascending Ramus
connects Ilium to the pubis, more superior ramus
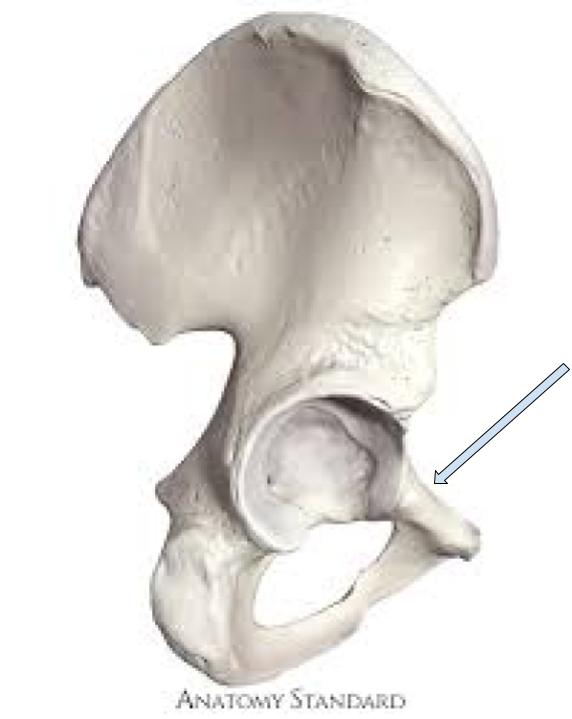
Descending Ramus
connects ischium to the pubis, more inferior ramus
Pectineal crest
superior aspect of the ascending ramus
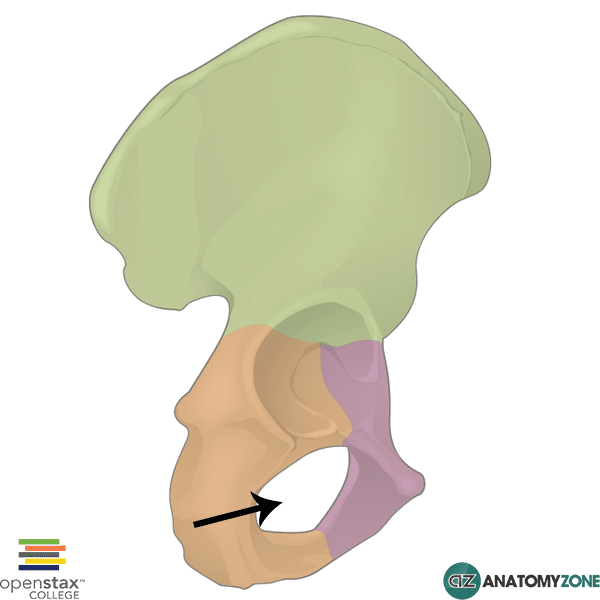
Obturator Foramen
large hole in the lower area of the pelvis
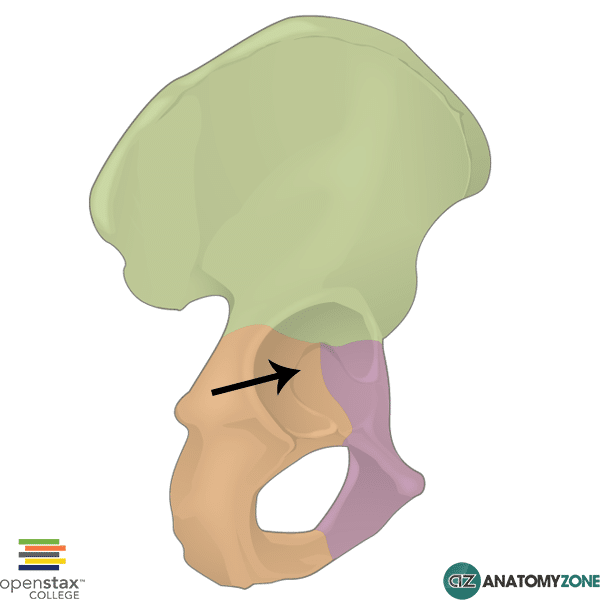
Acetabulum
articulating socket of femur
Femur Head
Proximal end of femur, articulates with acetabulum
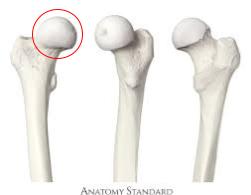
Greater trochanter
large projection at the lateral and proximal side of the femur
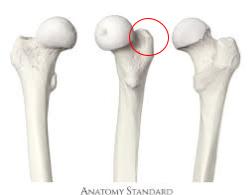
Lesser trochanter
projection on the medial and proximal side of the femur
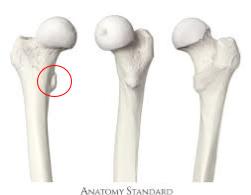
Fovea Capitis
Indentation on the femur head
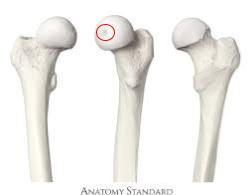
posterior
The lesser trochanteric is inferior, medial, and _________ to the greater trochanter
angle of inclination
angle made by the head, neck, and shaft of the femur
Femur neck
the area inferior to the femur head where the bone gets thinner
Femoral condyles
two projections at the distal end of the femur