Ch 19 - International Trade and Finance
(Macroeconomics)
@@The Balance of Trade@@
- ^^Net Exports:^^ when a nation’s balance of trade is equal to its exports minus imports
- ^^Trade deficit:^^ When the balance of trade is negative. A trade deficit could be the result of many things, such as poorer quality of products, or a nation’s currency may be overpriced to foreigners, or that a country may have nothing to export.
- ^^Trade Surplus^^: Excess of a nation’s exports over its imports.
@@Trade Restrictions@@
Comparative advantage of free trade enables the countries involved to consumer more than under restricted trade.
^^Infant Industry^^: Industries that are just getting started (baby steps). It is important to keep an economy diverse in terms of where they import products from. Diversity is health, and trade barriers can promote diversity.
^^Dumping^^: The practice of foreign products selling in the domestic market for less than it cost to produce it. This is a well known term in international trade. Trade barriers can prevent dumping
Arguments for Trade Restrictions:
- Promote Domestic employment
- Infant industry argument
- Diversity of production
- Prevent dumping
@@Instituting Trade Restrictions@@
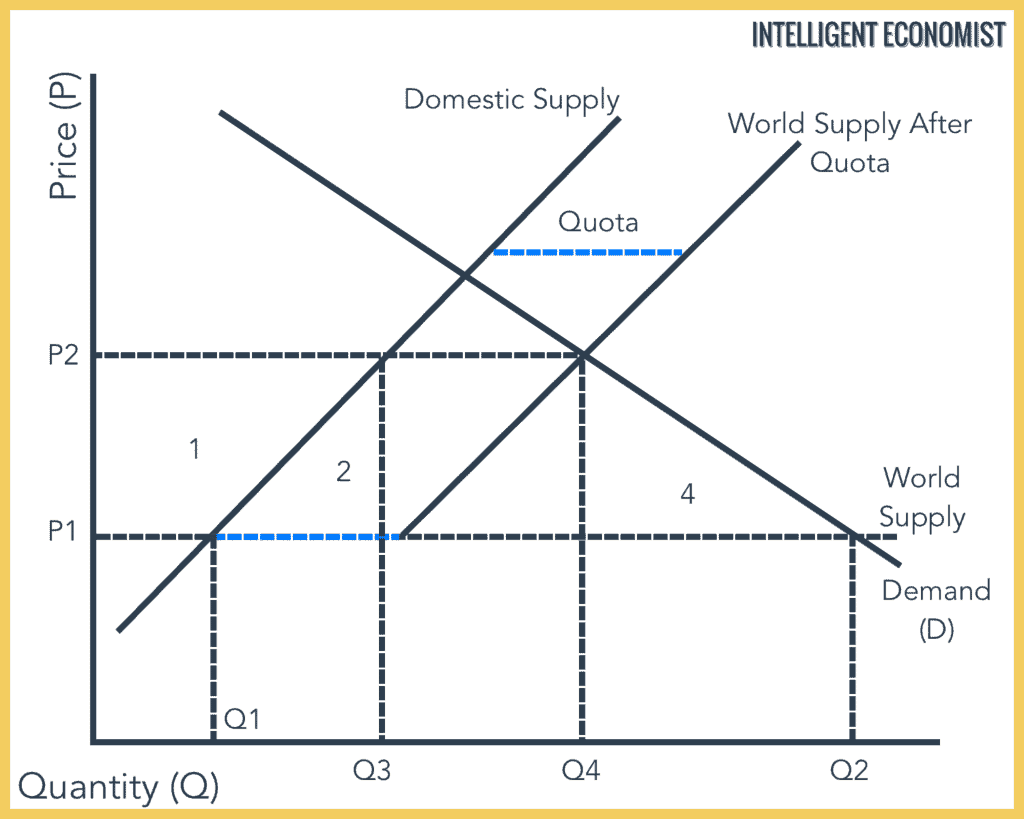
An ^^import quota^^: is a limit on the amount of a product that can be imported. When the import quota is set at zero, domestic producers are completely protected from foreign competition.
- If free trade is allowed, then prices will be set at world price. Compared to free trade, the quota raises the domestic price of goods and consumers will consume less of that good. It can be shown that consumer surplus is reduced by the quota as is total surplus.
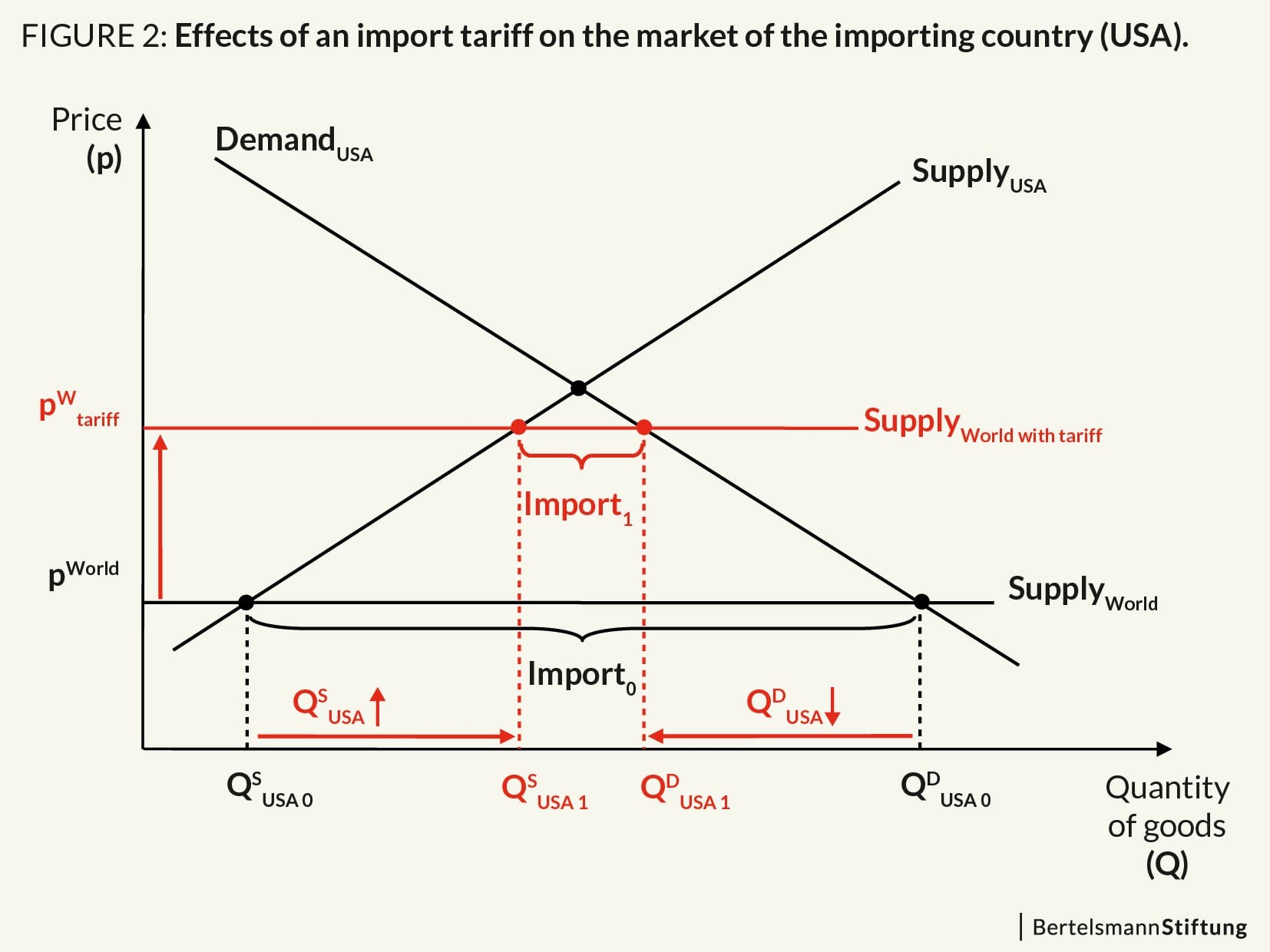
An ^^Import Tariff^^ is a tax on the specific imported product. The tariff serves to raise the price of the imported products in the eyes of domestic consumers. The gives the edge to domestic producers.
- Life quota, tariffs raise the domestic price of goods and lowers the amount bought and sold. The higher prices and reduced amounts of consumption are the costs of trade restrictions. (higher price decreases quantity demanded)
Other restrictions:
- Arcane rules and regulations are often developed with no other purpose in mind than to discourage competition. The effects of licensing agreements and rules and regulations that stifle trade are shown in exactly the same manner as the import quota in Fig. 1.
- Comparative advantage suggests that free trade allows nations to consume more goods and services than if trade was restricted. The arguments for trade restrictions are dubious while the costs in terms of higher prices and less competition are more definite.
- Trade restrictions are bad for consumers since they raise prices and limit their choices.
@@The Balance of Payments@@
- ^^Balance of payments:^^ an accounting of the funds that flow into and out of a country comprised of a capital account, the current account, and the financial account.
- The current account is primarily net exports with some additional items
- The financial account measures investment dollars flowing into the united states minus investments by the US entities abroad.
- The current, financial, and capital accounts should equal to zero. The financial account plus the capital account must be positive by the same magnitude.
- %%Trade restrictions:%% Quotas, Tariffs, and Licensing requirements.
- %%Balance of Trade:%% Net exports = Exports - Imports
- %%Balance of Payments:%% Current account + capital account + financial account
@@Exchange Rates@@
^^Exchange rates^^: The value of one country’s currency in terms of another’s. The demand for dollars in the foreign exchange market is not the same as the demand for money. The demand for dollars in the foreign market is downward sloping.
- The supply curve for dollars reflects how many dollars are available in exchange for euros, it is upward sloping. This implies that the quantity of dollars supplied will be greater when the dollar price is higher.
Two things that could cause the demand for dollars by foreigners to increase:
- Foreigners want more American products
- Foreigners want to invest more in America
Two things that could cause the supply of dollars to increase:
- Americans want more foreign products
- Americans want to invest more abroad
^^Appreciation^^: The increase of the value of a currency in terms of another country
^^Depreciation^^: the decrease of the value of a currency in terms of another currency
- The second factor that could increase the demand for dollars is foreigners wanting to invest their money in America.
- The number of dollars traded on the international exchange has increased as well.
Determinants of Exchange Rates:
- Demand for a nation’s exports (tastes)
- Relative interest rates
- Political stability
- Relative Level of income
- Relative prices (theory of purchasing power)
- Speculation
^^Net Investment income:^^ amount US citizen earns as interest and dividends from abroad minus how much was paid to foreigners in interest and dividends
^^Net transfers:^^ Money our government and citizens send as gifts or aid to foreigners mius how much foreigners send to us in gifts and aid
- ^^Official reserves:^^ government’s holdings of foreign currencies.
@@Exchange Rate Regimes@@
^^Gold standard:^^ kept exchange rates between countries fixed, a unit of currency that is equivalent to a stated amount of gold. The gold standard was one of the main methods of exchange of money. Economists believe that the gold standard led to balance of payments crisis and the great depression.
^^Managed float:^^ the current system for determining international exchange rates.
- Supply and demand determine exchange rates between currencies. If exchange rates change in a detrimental way, nations will intervene.
- ^^Intervention^^ involves coordinated buying and selling of currencies in order to adjust their equilibrium values determined by supply and demand
@@Monetary and Fiscal Policy in an Open Economy@@
^^Monetary and fiscal policy^^: can be used to fight inflation or recession. The impacts of monetary and fiscal policy in the context of an open economy are more complicated. Monetary and fiscal policy are less than effective when the economy is more open as opposed to closed to foreign trade.
- An expansionary monetary policy stimulates the economy in the short run by increasing the quantity of output and putting upward pressure on prices.
- Rising incomes tend to drive imports, worsening the balance of trade. The rising prices tend to discourage exports, and again leading the balance of trade into a worse position.
In a closed economy, an increase in the money supply stimulates output and income in the short run. In an open economy, these effects will be dampened because imports will rise.
- The stimulatory effect will be spent overseas, and exports will fall because of the inflation resulting from the increase in the money supply.
The exchange rates are impacted by the relative level of income and the relative level of prices in a nation.