business exam unit 2
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Legal and government regulations
Business name registration
- ASIC is responsible for national business name registration.
- a MUST, optional if name is owner’s name and nothing else is added
- Registration doesn’t protect rights to name but prohibits others from trading under similar name. - To protect rights, register as trademark.
Registering domain name
- Key element of online website - domain name = website address
- Should be unique + clearly represent business activities
- Can register more than one - easier for customers to find, prevents others from registering similar domain name that might confuse customers
- Registered by visiting Australian Domain Administration website
- Costs $10-$100 per year
Legal and government regulations - Taxation compliance/regulations
Income tax: type of tax govs impose on income generated by businesses and indivs within their jurisdiction
- Companies pay 30% (28.5% if business turnover is <10Mil)
- Individuals pay progressive tax rate
GST (Fed tax): a tax of 10% on most goods & services
- Businesses only register for GST if earning $75k or more in financial year
PAYG (Fed tax): tax taken from an employee’s salary/wage directly
FBT (Fed tax): tax that employers pay on the benefits paid to an employee (eg car for private use, business pays tax)
Land tax (State tax): tax levied annually on owner of land
Stamp duty (State tax): tax that state and territory govs charge for certain documents that give evidence to transactions.
Business Activity Statement (BAS): an ATO form issued to all GST registered entities
- It reports a businesses’ GST activity for the period.
Local government legal requirements
Zoning regulations: ensures business activities don’t impact residential areas
- Each council has local planning scheme that describes type of business activities/developments that are allowed in different areas of suburbs/district
- Land can be zoned as residential, industrial, business or other.
- Owner must consult with local council if using a premises/land, must seek local government approval/find out which zoning regulations will affect business.
Fire regulations: requires employers to identify risks & take steps to remove/reduce them. EG fire extinguisher
Parking regulations: ensures locals don’t trespass properties & are able to get it safely. EG parking
Business signs: ensure size, location, and shape of business signs don’t past the standards of an expected sign.
Health regulations: ensures compliance with health regulations. - EG the food act 1984 (VIC)
- Local council supply businesses with regulations and standards.
- Health officers.
- Council can also register to inspect other businesses to ensure they meet hygiene and safety requirements.
WH&S regulations
These laws provide a consistent framework nationally to protect workers. Objectives:
- Protect workers against harm to health, safety and welfare arising from work.
- Encourage unions and employer organisations to promote improvements in work health and safety practices.
- Promote provision of advice, info, education and training in relation to work health and safety.
Owners have legal responsibilities to implement health and safety practices in workplace as soon as business is started:
- Provide safe work premises
- Assess risks and implement appropriate measures for controlling them
- Ensure safe use and handling of goods and substances
- Provide and maintain safe machinery and materials
- Assess workplace layout and provide safe systems of work
- Provide a suitable working environment and facilities
- Have insurance and workers compensation workers’ compensation insurance for employees.
Pros: prevent being fined/prosecuted, retain skilled staff
Cons: costly, time-consuming
WorkSafe Insurance
WorkSafe Victoria aims to reduce workplace injuries and supports injured worker by enforcing WH&S laws and providing insurance.
This insurance is compulsory for all Victorian employers. - Provides for the cost of benefits if workers are injured or ill as a result of work.
The insurance covers:
Replacement of lost income
Medical and rehab costs
Legal costs
Lump sum compensation in the event of a serious injury
Trade Practices Legislation
Australia has federal and state laws to ensure business and consumers are protected from unfair practices:
Federal
→ Competition & Consumer Act: specifies acceptable behaviour by businesses regarding product safety, pricing and competition.
- The ACCC (Australian Competition & Consumer Commission) administers this.
State
→ Fair Trading Act is administered by Consumer Affairs Victoria. -- Covers issues with: warranties, guarantees, refunds, vouchers, false advertising and product safety.
Failure to abide by these laws = heavy fines
External professionals
Freelancers: independent workers who charge businesses/individuals for work on a per job basis.
- EG freelancers may specialise in photography, design, copywriting, web design etc.
Bookkeepers: assists a business in keeping and processing business’s financial records.
Role: keep and record the financial records of a business.
Recruiters: enlists/enrols people as employees.
- Role: find & attract qualified applicants for open positions, review resumes, interview candidates
Sales professionals: trained and experienced in finding and persuading people to consume a product.
- Businesses will often engage them when difficult to find customers.
Marketing consultants: responsible for raising awareness of a business’s products and brand with their target markets
- Will often run campaigns involving advertising + other forms of communication with potential customers.
- Successful campaigns = increased brand awareness, increased sales.
Information technology (IT) technicians: provides computer/network support for a business.
- All business run some form of IT.
- IT service exist to support the needs of these businesses.
- Services EGs: setup of servers and software, troubleshooting problems that arise on a daily basis, maintain websites
Bank accounts
Separate bank account
→ Separate entity principle: states we should always record the transactions of the business and its owners separately. - Easier to do with separate bank accounts.
Pros:
- easier to monitor the financial performance + position of the business.
- easier to calculate business expenses
- simpler and less time consuming + costly to prepare tax returns
Factors to consider when choosing right bank account:
→ Bank fees: charges levied by banks for various services and transactions. (EG set-up, maintenance, minor transactional services).
- may be hidden/less obvious but banks are legally required to state this in the product disclosure statement.
→ Interest rates: the % of the amount a lender charges a borrower.
- determine how much money a business will make on amount in their accounts or how much they have to repay on any loans
→ Overdraft facility: when banks allow a business to withdraw more money than they have available in their account.
- usually used when business is temporarily low on cash flow.
→ Credit cards: cards that can be used to borrow money to make purchases, or transfer balances.
- different cards have different features (eg max. withdrawal amount)
→ Convenience and support:
- smaller banks and credit unions offer lower interest rates BUT less infrastructure are in place to support the owner.
Financial control systems
Financial control systems: systems used to help the business monitor, manage and report its financial performance.
- vary from business to business depending on size and nature.
Budgeting: predicting or estimating the business’ financial performance for a given period in the future.
→Used to control the business
→Business can ask questions about why certain goals were not reached by comparing actual with planned results.
→Completing budgets helps in establishing benchmarks to compare actual events.
Cash-flow management: cashflow is the total amount of money being transferred into and out of a business
→Crucial to survival of business - to have the cash needed to pay its day-to-day expenses. if poorly managed = failure
→Strategies:
-Keep track of money owed to business,
-Hire account staff to ensure customers pay in full/on time,
-Offer discounts to customers who pay early
-Withhold items to customers who owe money
-Arrange short term loans, or a bank overdraft.
Control of accounts receivable: accounts receivable is the money that a business is owed by its customers who have purchased on credit terms
→Vital - ensure cash flow, ability to pay bills, purchase more stock
→Strategies:
-Offering discounts, bonuses/rewards for prompt payment to receive money ASAP
Inventory control: system businesses use to ensure that costs associated with maintaining an inventory of materials are kept to a minimum.
→Why?
-Costs minimised as there are no idle assets.
-Inventory only arrives when needed/demanded
→How?
-Using barcodes and computerised stock records
-Physical stock-takes
-Security staff, cameras, security tags
Auditing: the process of testing and evaluating a business’ accounting processes and internal controls
→Internal audit is performed by employees of the business.
→External audit is performed by another business.
→Contracting experienced external auditors can provide the business with valuable feedback BUT costly
Record keeping strategies
Why?
-Required by law to keep records of financial transactions for at least 5 years for tax purposes.
-Accurate records are valuable tool for decision making.
-Investors and banks likely to invest/provide loans to a business that can demonstrate financial position.
-Can cut down and simplify the workload of managing accurate records
Process:
Source documents: written documents that provide evidence of a financial transaction
→Features:
-Date of transaction
-Names (and addresses if applicable) of parties involved
-Nature of transaction
-Amount of money involved.
Records: involves recording the source documents into a cashbook
→Cashbook provides all business’s cash receipts and cash payments - Compiled from the receipt and payment source documents
→Allows owner to:
-Keep control on cash
-Monitor the business’ cash flow position
-Determine balance of cash in business.
Reports: the process of using the information from the cashbook to create reports.
→2 main reports:
-Income statement – used to help business calculate how much profit has been made over a period of time.
-Balance sheet – shows business’ assets and liabilities (the financial position of a business) at a point in time.
Advice: when professionals (EG accountants) analyse the info and provide recommendations for owners to implement to improve the business.
Suppliers
Procurement: the process of researching and selecting suppliers, establishing payment terms, negotiating contracts and the purchasing of resources that are vital for maintaining the production of a business’ good/service.
-Choosing the right suppliers is crucial for successful business. If not, affects the ability of business to supply to their customers.
-If supplier doesn’t act in a socially responsible manner - Can damage the reputation of business by association.
Price:
→If business is to remain profitable, must keep costs low.
→Suppliers can be an area to reduce cost, but NOT ONLY area
Quality:
→The quality of goods supplied by suppliers heavily impact the quality of the final good/service.
→If business purchases from international suppliers, must ensure they meet with Australian quality and safety standards
Reliability:
→If business has a high turnover of stock, they often rely on quick and timely delivery from suppliers.
→If business doesn’t receive goods needed = lose sales, reputation may suffer
Proximity:
→Being in close proximity can save time and money (delivery costs)
→Sourcing locally is more environmentally friendly and help to support the local economy = more socially responsible.
Corporate social responsibility: the ability of a business to go above and beyond legal requirements to benefit the welfare of the community and environment.
→business reputation may be tainted by the association, good if suppliers are socially responsible, bad if not.
Pros and Cons of using suppliers who are socially responsible
Pros:
→Reduce business costs - savings achieved through greens initiatives (eg reducing use of energy)
→Improves reputation
→Customers likely to purchase
→Investors more likely to invest
Cons:
→Increased costs associated - suppliers likely to pass increased cost of production
→Maintaining supply chain with sourcing sustainable materials can be expensive and time consuming. (eg checking/maintaining suppliers are actually socially responsible)
→If changing to socially responsible suppliers, business will need to work with them to ensure quality is on par with competitors, if not more superior.
Policies and procedures
Policies and procedures must be developed and implemented to establish and communicate basic expectations about behaviour and decision making.
Policy: an established set of broad guidelines to be followed by all employees
→Promotes good practice.
→Help ensure employees are working within the requirements of the law.
→Help establish a positive culture within the business - can improve financial performance.
Types of policies e.g.
· Recruitment policy
· Privacy policies
· Customer service policies
· Anti-discrimination policies (Equal Opportunity Act 2010)
Procedures: a series of actions (or step-by step instructions) that enable a policy to be put into practice.
→Procedure can also be used to provide a means of resolving a dispute brought about by a breach of a policy.
→ Process for developing procedures:
1. Identify an issue/problem
2. Research and analyse business environments
3. Consult stakeholders
4. Develop a draft policy for review from stakeholders
5. Revise the policy
6. Approve and distribute the new policy
7. Monitor and evaluate the policy
Pros & Cons of Policies and Procedures
Pros:
→Help employees know what is expected of them with respect to standards of behaviour and performance
→Provides framework for consistent decision-making and clear routines in situations - employees don’t have to ask managers
→Allow owner/management to have accepted method of dealing with issues/misunderstandings
→Can prevent legal problems
→Provide owner/management mean of communicating info with new employees
Cons:
→Researching and writing policies and procedures may require legal expertise = costly and time-consuming
→Can be difficult to communicate policies throughout business as it needs to be properly implemented, enforced and monitored. - time consuming.
→Employees may view policies has substitute for effective management - policies are guidelines/standards for decision making and behaviour not instructions
→Development of policies can restrict innovation and flexibility - restrict owner’s ability to make quick decisions/change strategies
Technological and global issues
Technology
→Use of technology can be a blessing and a curse
-Pro: produce higher quality product more quickly - saving costs and increasing profit.
-Con: if unable to keep up with developments, unlikely to be successful long-term.
→ Technology in manufacturing e.g. 3D printing, robotics etc.
→ Technology in administration e.g. bookkeeping software, skype/zoom, gmail etc.
→ Remote work
-Flexible work option
-Reduces expenses associated with additional office space
-Time saved
-Worker productivity may increase
→ Technology in marketing e.g. social media advertising, establishing customer data bases.
-Pros: inexpensive, easy to use and monitor
-Cons: don’t always have control over what consumers’ reviews/criticisms
→ Customer database: a bank of info on existing and potential customers (ie buying habits, past interactions, personal details)
- Businesses need to ensure private details of customers are well protected from hackers who may profit from identity theft
Global
→__Globalisation:__ operating on an international scale to provide or produce goods and services.
→ Overseas suppliers and resources
-Access to global supply network
-Cheaper materials/products due to reduction in quotas and tariffs
→ Customers and overseas retailers
-Access to international customers
→Competitors
-Overseas competitors have more access to local customers
marketing
a total system of interacting activities designed to plan, price, promote and distribute products to customers.
customer base
the group of customers who repeatedly purchase the products of a business and are its main source of revenue
establishing customer base - pros and cons
PROS:
→ business can ensure that it is likely to be of value to customers - target customers return for repeated purchases
→sig. no. of customers develop loyalty to business
→higher sales and improved market share
CONS:
→ can be expensive - EG expenses related to necessary market research, marketing mix etc.
→ time consuming - logistics required EG determining internal + external factors, marketing strategies etc.
evaluating the effectiveness of marketing strategies
establish marketing plan - what is to be achieved?
monitor performance - what is happening?
evaluate performance - good/bad? why?
take corrective action - what can be done?
market research
the collection and study of statistics and other relevant data
WHY? helps reduce risk
market research process
determine info need - identify what exactly it wants to measure/find out about target market/customer base
collecting tools and techniques - primary or secondary data
analysis and interpretation - determine what the results mean
primary & secondary data
primary data: collected by the business to answer their specific questions. 3 methods -
→survey: gathering info by speaking to people through; interviews, focus groups, questionnaires, electronic methods etc
→experimentation: gathering data by altering factors under controlled conditions to evaluate cause & effects. (test marketing)
→observation: the recording of customer’s behaviour; can be mechanical (cameras, video, voice recorders etc or personal (eg researcher poses as customer)
secondary data: data that someone else has already collected. 2 methods -
→internal data: info that internal sources (inside business) have already collected. (EG customer feedback, financial statistics, research reports etc)
→external data: published data from sources outside of the business.(EG reports by the Aus Bureau Statistics (ABS))
brand identity
the message that customers receive about the business & its products (EG name, symbol, slogan, colour etc)
environments RECAP
internal: within the business, business has full control over.
→ owners/managers
→employees *need to understand marketing strategy
operating (external): outside of the business, affect an industry, some-little control over.
→customers *customer focused marketing strategy = success
→competitors *good marketing strategy will help distinguish
macro (external): outside of the business, affect all businesses, no control over.
→economic *strong economy = high consumer confidence, more likely to take on debt & weak economy = good marketing strategy should focus on quality+value over price
→technology *use of technology crucial nowadays, social media + methods of payment
target market
a specified group of people who a business decides are most likely to buy their product/service and focus their marketing efforts on.
side note - market segmentation: where you divide a total market into particular groups who share common characteristics
market dimensions
used to identify market segments
demographic - general characteristics (age, gender etc)
geographic - location or geographic units(rural, global etc)
psychographic - psychological characteristics and traits (personality, values, lifestyle etc)
behavioural - knowledge, attitude, response towards product
consumer behaviour
when businesses consider WHY do customers buy. 4 reasons:
psychological
→perception *positive perception of product is a must
→motive *why are they buying this?
→attitude *opinions
→personality
sociocultural
→family & roles
→peer groups
→social class
→culture and subculture
economic
→economic cycle *boom, recession etc
government
→regulations
marketing mix - 7PS (PRODUCT)
product: a good/service that can be offered in exchange for the purpose of satisfying a need/want (tangible or intangible)
→ total product concept: a collection of satisfactions (eg package, brand name etc) *separate or combined goods/services?
→ product positioning: the way a product image is developed (eg name, price, promotion, style etc)
→ branding and packaging
marketing mix - 7PS (PRICE)
price: the amount of money required for something. may be influenced by: quantity, quality, demand, cost of supplies
pricing strategies -
→ recommended retail price: price recommended by a wholesaler/manufacturer (only recommendation bc illegal to set a price if not directly selling to customer)
→ percentage mark up: the cost price is increased by a fix percentage at the final price.
→ price leadership & competition*:* to follow a price set by another seller (business as a price leader)
→ what the market will bear: setting a price dependent on what consumers will pay (eg auctions)
→ quotes: a price set specific to specialised products
→ price skimming: placing a high price on a new item
→ price penetration: placing a low price on a new product (to attract new customers)
→ premium pricing: setting an artificially high price to increase the prestige of product
→ price bundling: selling of a package of goods/services for lower price than individual product
→ psychological pricing: making the price look less than it is
marketing mix - 7PS (PLACE)
place: the physical or online location that enables a customer to purchase from.
customer access to product is through distribution channels;
→ producer to customer
→ producer to retailer to customer (retailer is intermediary, buys from producer and resells to customer)
→ producer to wholesaler to retailer to customer (wholesaler buys in bulk, then resells in smaller quantities to retailer)
→ producer to agent to wholesaler to retailer to customer (agent distributes to wholesaler but never owns product)
channel choice & market coverage;
intensive distribution: when business wishes to saturate market with its product (customers can shop at local outlets)
selective distribution: using a moderate proportion of possible outlets (clothing, furniture etc)
exclusive distribution: use of only one retail outlet for a product in a large geographic area
marketing mix - 7PS (PROMOTION)
aim: encourage, inform, attract, persuade, increase rep.
promotion mix: methods used in a business’ promotional campaign;
→ personal selling: involves the activities of a sale representative directed to a customer
→ opinion leader: person who influences others
→ publicity: any free news story about a business’ products (different from advertising, free and timing not controlled)
→advertising
marketing mix - 7PS (PEOPLE, PHYSICAL EVIDENCE,PROCESS)
people: everyone involved in the product of a business
physical evidence: everything that the customer sees when interacting with business
process: the flow of activities/mechanisms that take place when there is any interaction between the customer and business (eg delivery)
product life cycle
product life cycle: the length of time from a product’s introduction to its removal from the market. stages;
introduction
growth (brand acceptance, more known, increase)
maturity (fully accepted, sales peak)
decline (no longer appeals)
extension - revival of product. can be done through;
→export (sell overseas)
→diversification
-product diversification: increase range of products
-geographic diversification: increase locations
customer relations strategies
customer relations: involves an enhancement of the customer experience. through;
quality customer service
→ customer service: how well a business responds to needs/problems of customers (EG clear signage, staff etc)
seeking customer feedback
returns, refunds & complaints
→ability to deal with and resolve complaints (clear communication, policies etc)
customer loyalty programs
→ customer loyalty program: a reward-based program offered to frequent purchasers.
online presence
→ customer friendly, informative, easy to navigate etc
catering to a multicultural market
technological developments
technological developments: the overall process of invention and innovation of technology or processes.
types:
social media
→ con: lack of control over comments
email marketing
→con: potential scams/spam emails
search engine optimism
→ the process of improving a business’ website to increase visibility when people search for its products/services via various search engines
artificial intelligence
→ intelligence demonstrated by machines
data analytic
→ the science of analysing raw data & draw conclusions about that info/data - data focuses on sales, what customers want, where, when etc
management of data
→ data custodian: person responsible for management of data collected by business
→ data maintenance: process of keeping data current, complete and relevant
→ data access: involves determining who is allowed access and for what purpose
→ data security: involves ensuring data is safe.
→ data privacy: ensuring customers’ data is kept private and not shared with other businesses/orgs without their consent,
Business objective
A desired outcome or specific result that a business intends to achieve.
Making a profit
Expanding the business
Increasing market share.
Productivity
A measure of business efficiency comparing output produced with the quantity of inputs.
Human resource (HR) management
The effective management of the relationship between an employer and their employees.
Achieving objectives - staffing strategies
(Image)

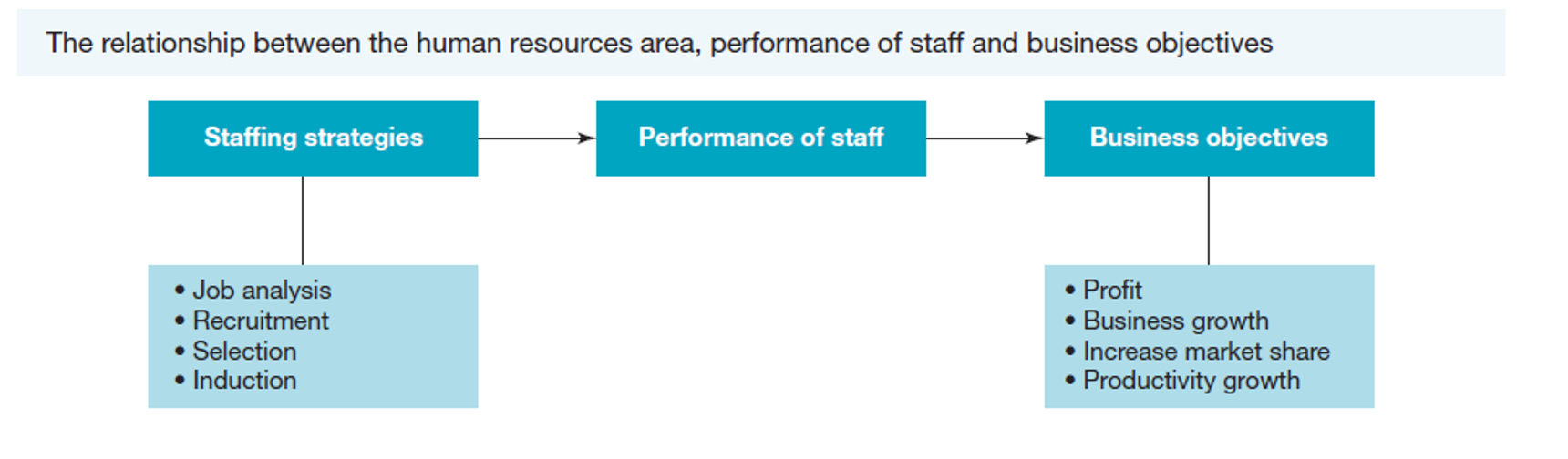
Relationship between HR, Staff Performance & Business Objectives
(Image)
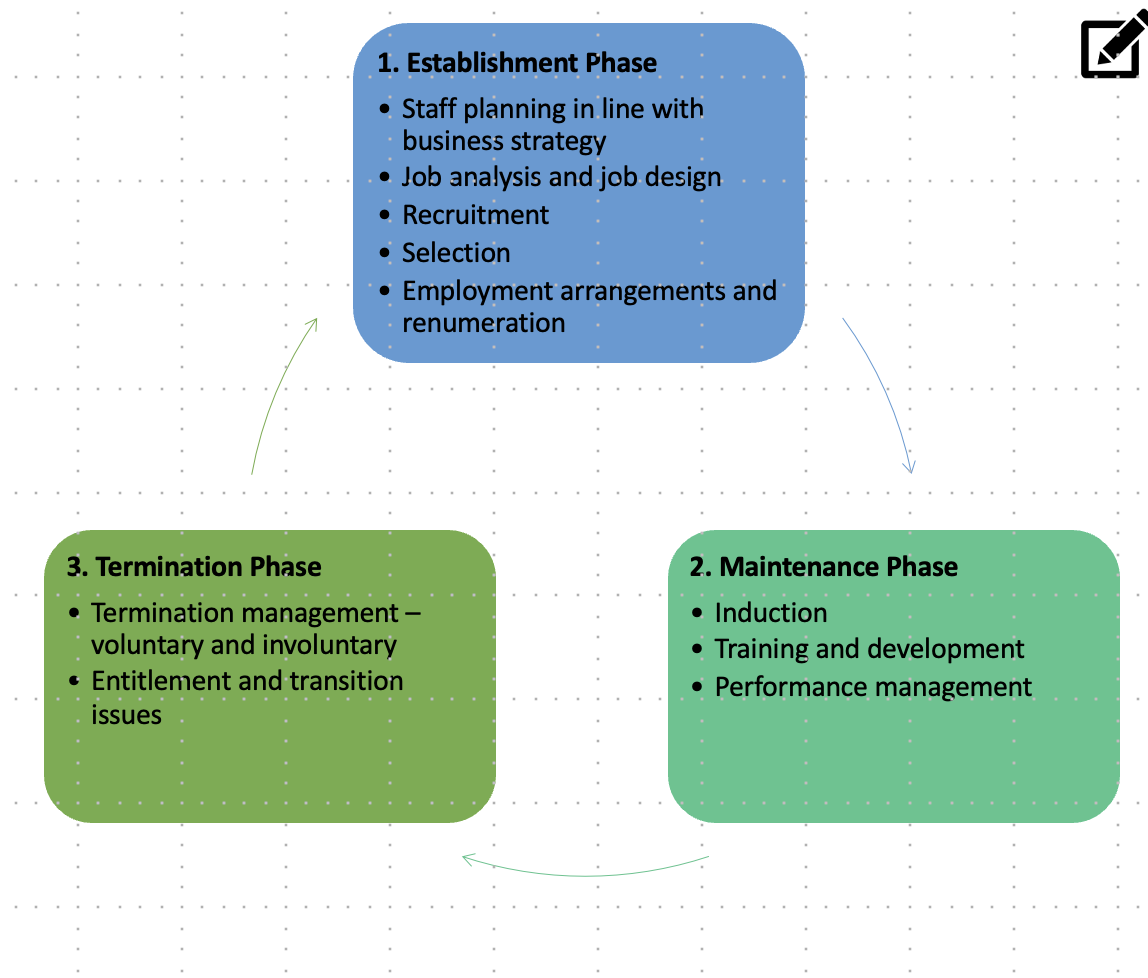
The Employment Cycle
a HR model that tracks the journey an employee takes at a business (Image)
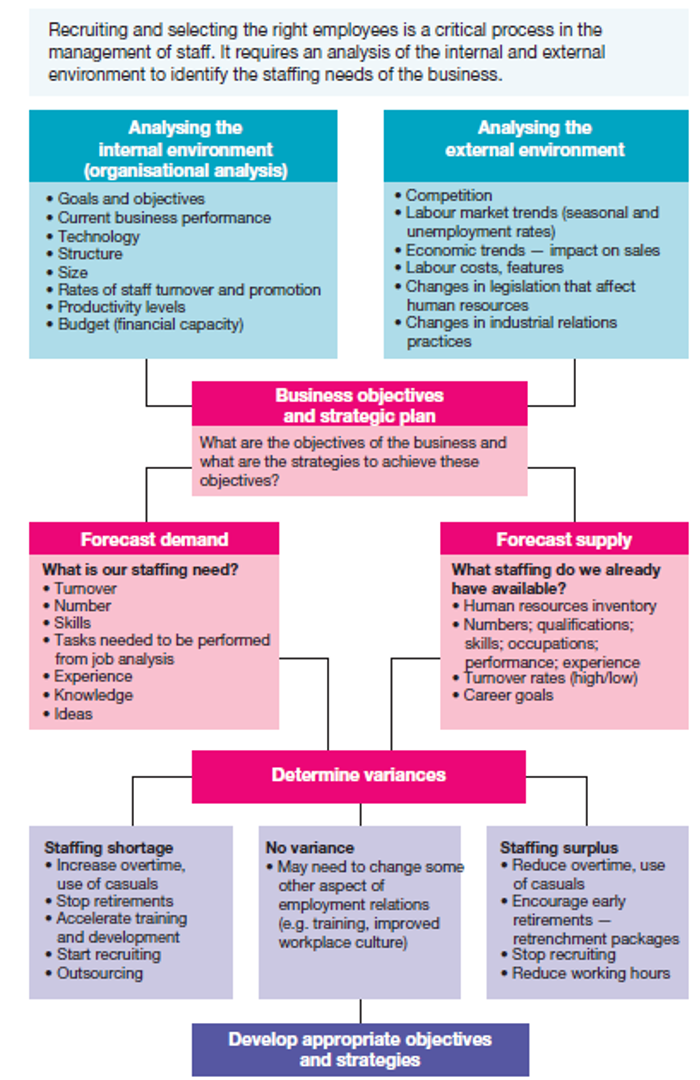
HR Planning
Involves forecasting the no. of employees available and the no. of qualified employees demanded in the future.
Business Objectives and Strategic Plan
(Image)
A business should combine all of this information when planning for its staffing needs, to help determine:
No. of employees required.
Qualifications of employees and their knowledge, skills, previous experience and ideas.
When and where employees will be needed.
Technological issues
The questions that arise from the growing use of tools, techniques or systems by businesses to solve problems or serve a purpose
Eg of development:
E-businesses - use the internet to conduct the full range of business activities.
Impact of Technology on staffing needs
Creation of new jobs or other jobs becoming redundant
Existing employees might need to be trained to use new technologies.
New technology might lead to a reduction in staffing requirements.
Rates of pay might need to be adjusted to take into account new required skills of employees.
Many employees could be expected to carry out workplace tasks outside of normal work hours (due to increased online access).
Employees can become more mobile and flexible due to connected tablet computers and smartphones.
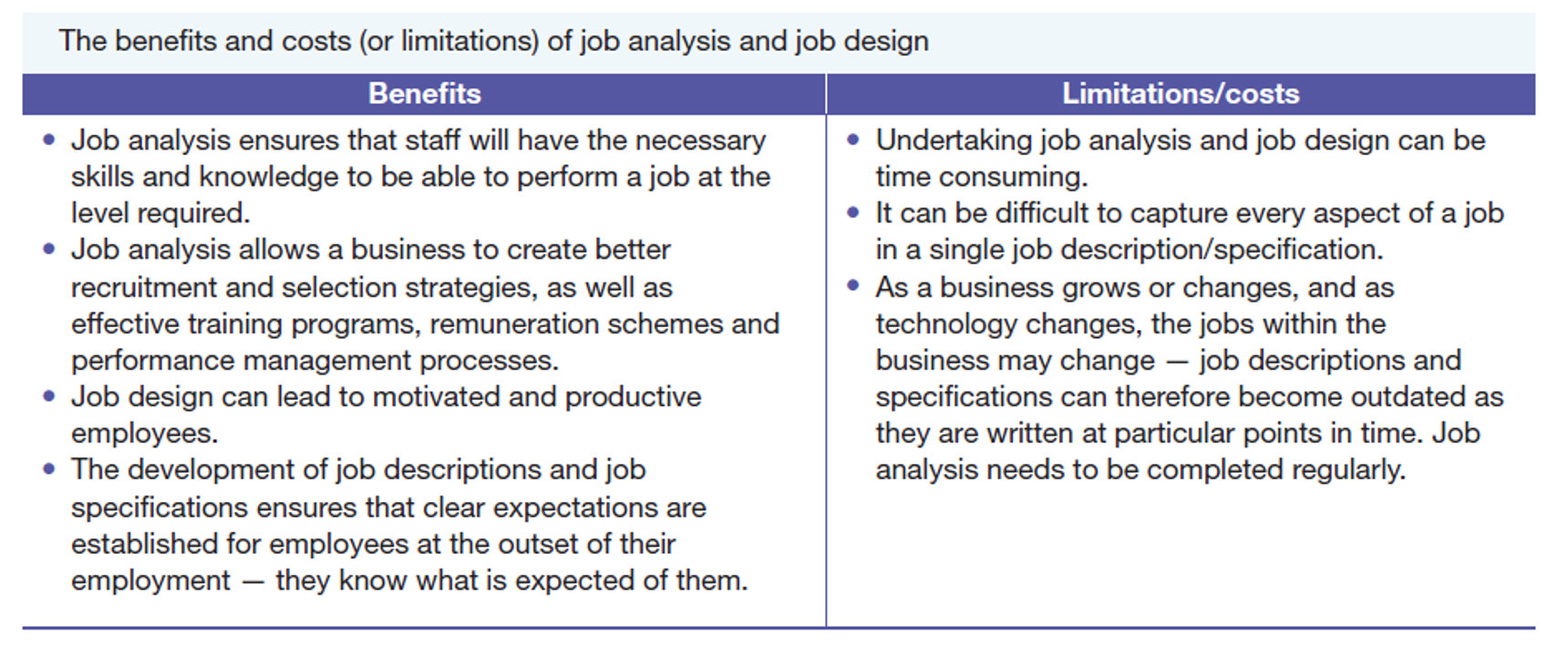
Job analysis
Study of an employee’s job - to determine the duties performed, time involved with each duties, the responsibilities involved and the equipment required.
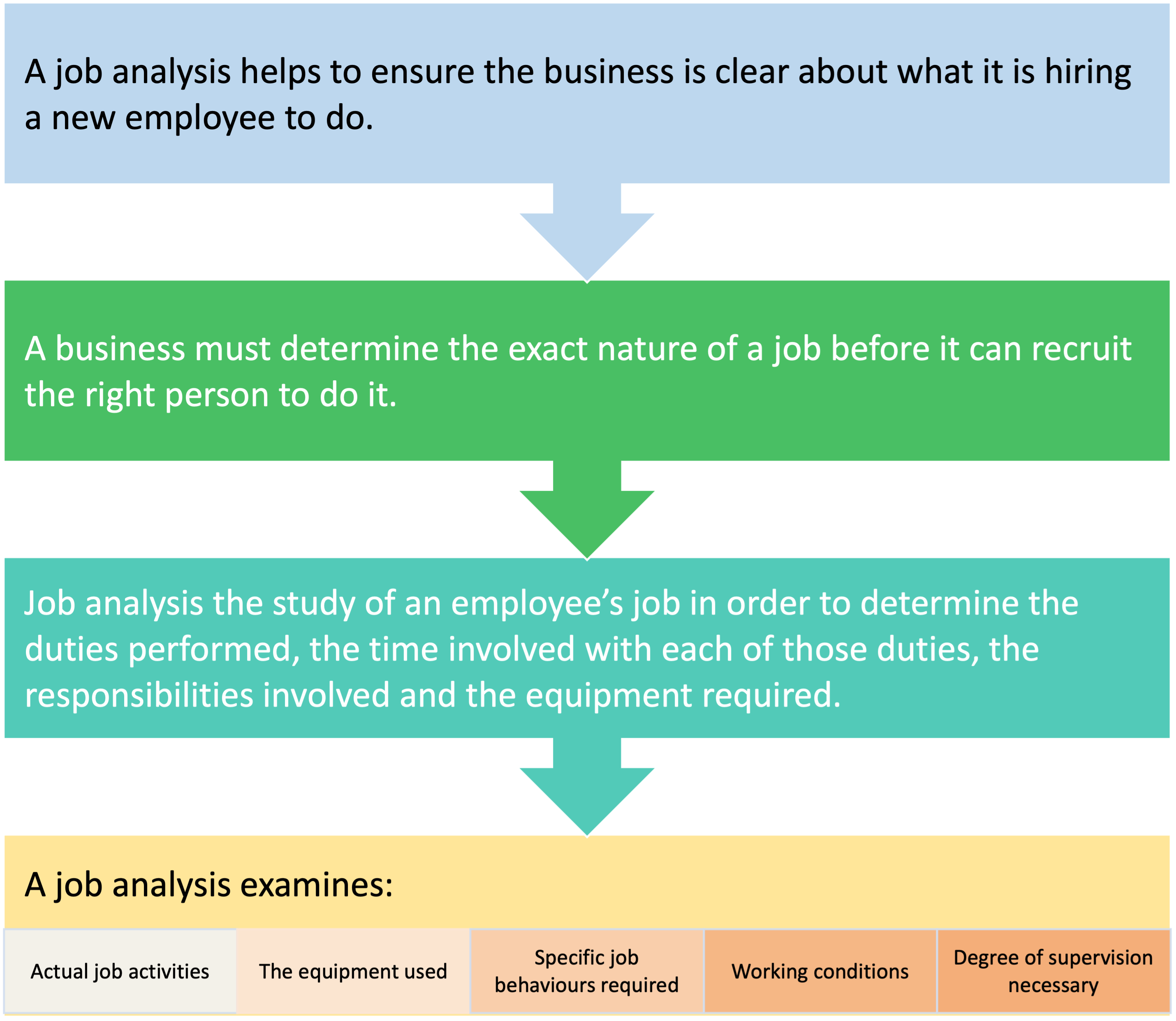
Job Analysis - Methods
Observation method - involves observing workers carrying out their tasks. It help determine:
Different types of activities carried out to achieve a result.
Sequence in which those tasks are carried out.
Skills needed to perform the relevant tasks.
2 other forms of observation used:
Work sampling – samples of different tasks are observed for short periods of time.
Work diary/log – the employee observes THEIRr own work activities and records it over a given period
Interview method
Often, standard set of interview questions is used to maintain consistency across a group of employees. - May be asked regular duties etc.
Questionnaires
Employees can be asked to provide written answers to questions about their duties, responsibilities and skills.
Critical Incident Technique
Staff responses to particular incidents are judged to be effective or ineffective based on the actions taken.
Involves examining events leading up to the incident, the actions taken by the staff member that were effective/ineffective, the consequences of those actions and the degree of control the employee had over those consequences
Job Description
Written statement describing the employee’s duties, tasks and responsibilities associated with the job. - Eg job title, purpose responsibilities, standards etc
Job Specification
List of key qualifications needed to perform a particular job in terms of education, skills and experience
Job Design
Details the number, kind and variety of tasks that individual employees perform in their jobs.
Job design approaches
Job Rotation: where employees switch from one job to the other for a period of time.
Job Enlargement: employees are given more things to do within the same job.
Job Enrichment: employees are given more control and independence over how they do their work.
Pros and Cons of Job Analysis & Job Design
(Image)
Recruitment
The process of attracting qualified job applicants
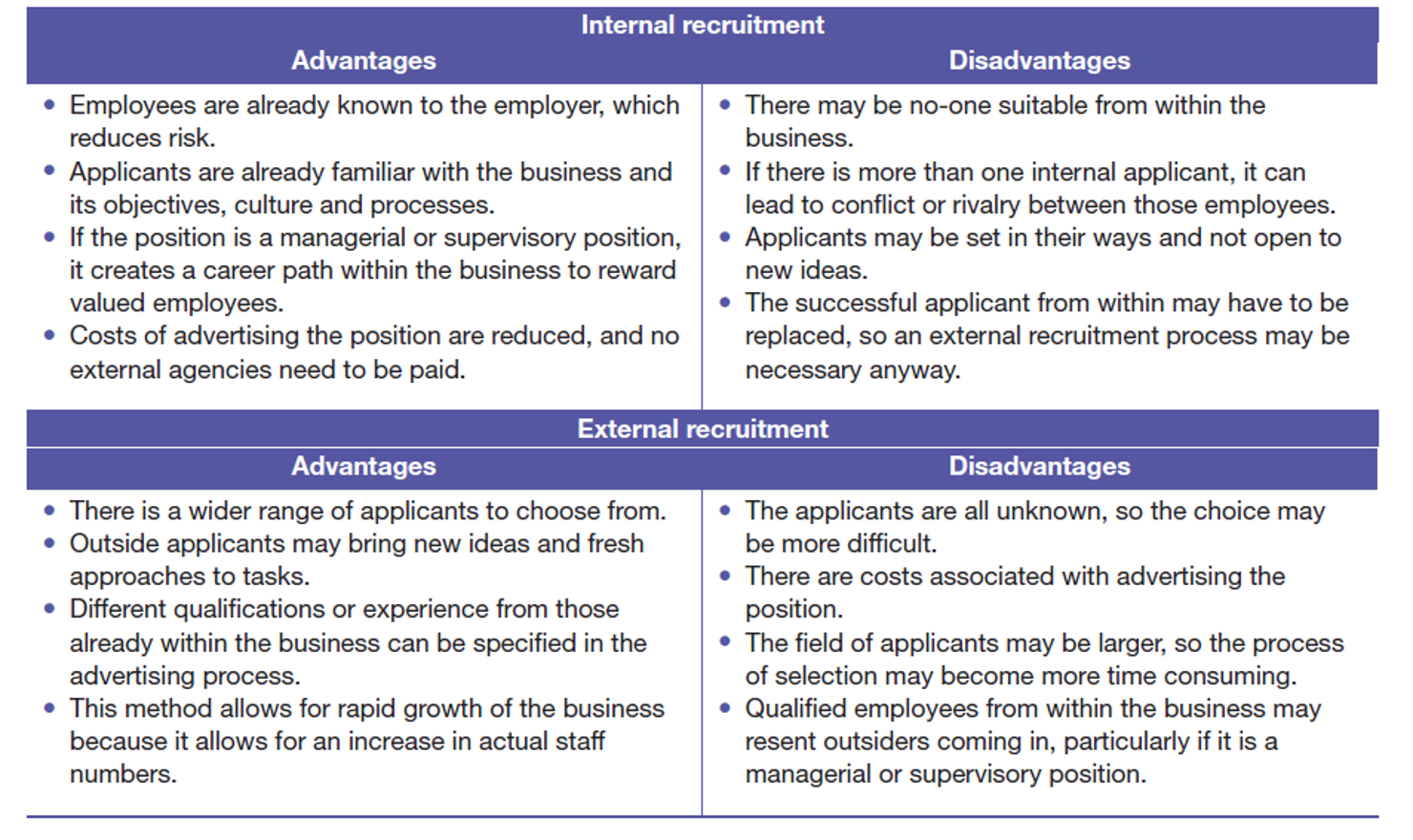
Internal recruitment
Filling job vacancies with employees, rather than looking outside the business
Eg:
Word of mouth amongst employees
Notice on a staff noticeboard
Email
Consider existing records and résumés
Promotions
External recruitment
Used to find suitable applicants from outside the business.
Eg:
Company website
Social media
Govt. employment/recruitment services
Online recruitment agencies - businesses that specialises in finding suitable candidates to fill vacancies for a variety of different employers.
Pros and Cons of Internal and External recruitment methods
(Image)
Selection
Choosing the candidate that best matches the business’s requirements.
Process:
Applications
Screen applicants
Shortlist candidates
Interviews
Referee checks
Offer job
Selection methods/options
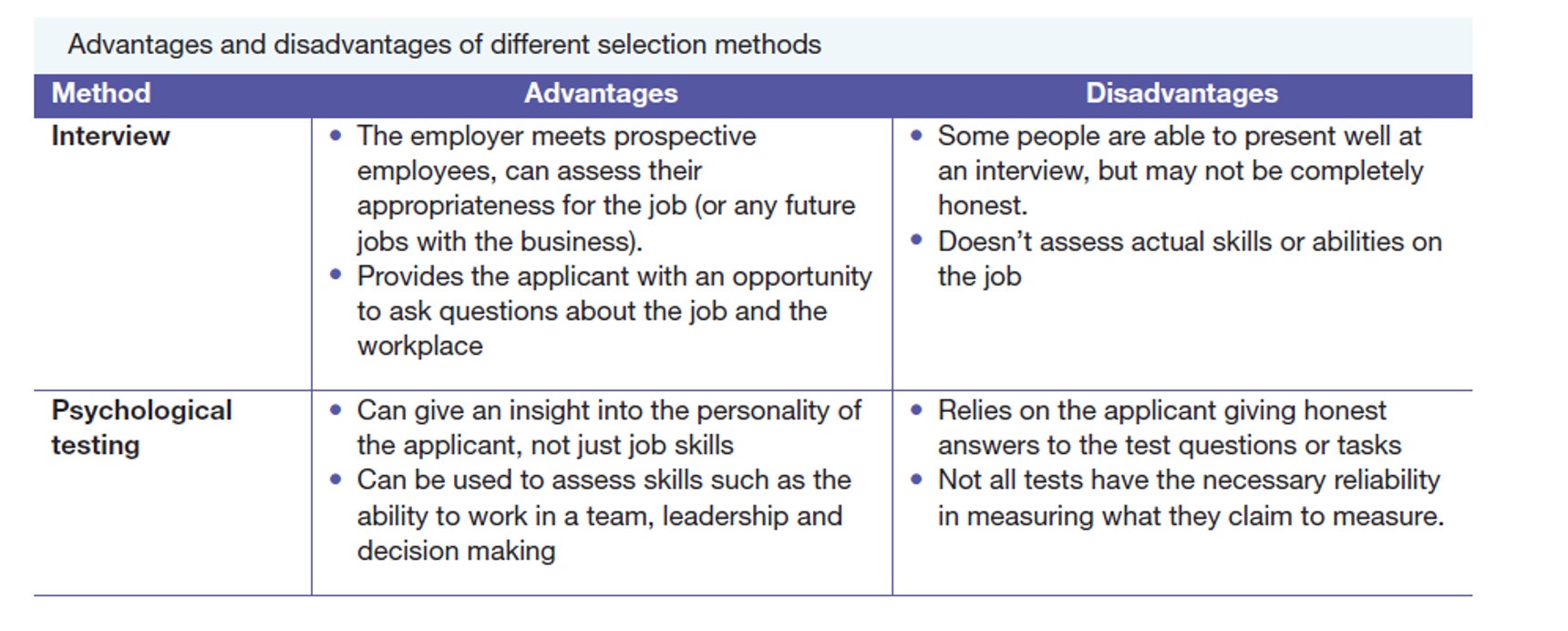
Application forms: basic info (name, contact number) or more detail eg skills and experience.
Tests: written or practical and are designed to test aptitude, intelligence or ability.
- Psychological and work testing are most common.
- Psychological testing: test a candidate’s personality to determine how they may respond in certain types of work situations
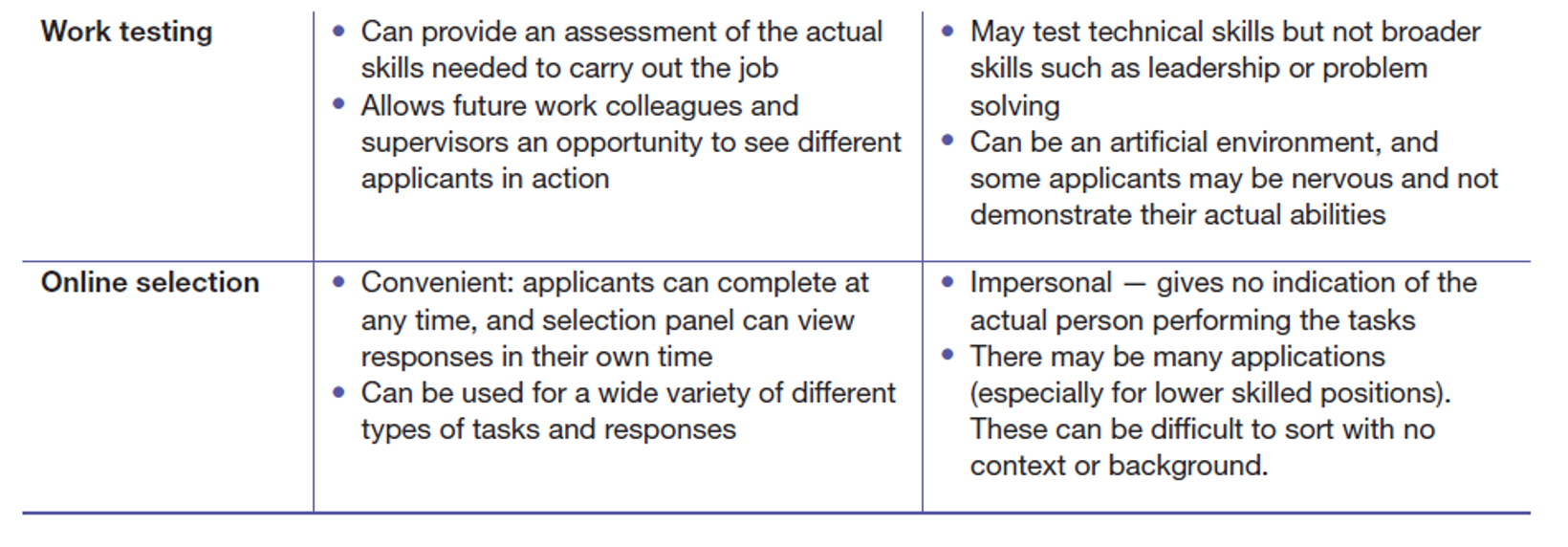
- Work testing: is tests specific technical knowledge and skills that are needed to carry out the relevant work.
Online selection: when some part of the screening process is conducted online. (Eg online multi-choice test)
Interviews (most common)
Background checks: the employer verifying information by contacting referees
Medical examinations (if physical attributes required for job)
Pros and Cons of selection methods/options - Interview & Psycho testing
(Image)
Pros and Cons of selection methods/options - Work testing & Online selection
(Image)
Employment arrangement
The conditions of work offered to an employee
Types of employment arrangements
Full-time: work between 35 – 38 hrs per week.
Part-time: work less than standard full-time hours.
Permanent: employed on an ongoing basis.
Fixed-term: employment has a pre-arranged finishing date.
Casual: employed on an hourly basis. No entitlements to long-service leave, sick leave etc. Hence may be paid “loading” on top of normal hourly rate.
National Employment Standards
A set of minimum standards for employment, employees are entitled to.
Legislated by the federal government (Fair Work Ombudsman),
Apply to all full-time and part-time employees, whether permanent or fixed term.
National Employment Standards - entitlements
Hours of work
Employer must not request/require more than 38 hours of work in a wk, unless the additional hours reasonable & special provision of penalty rates is applied. - Employees have right to decline
Parental leave
Entitled to 12mths unpaid parental leave in relation to birth or adoption of a child.
Offers and requests to convert from casual to permanent employment.
Casual conversion - casual employees who have worked for 12 mths need to be offered option to convert to full-time/part-time (permanent) employment by their employer.
Flexible working arrangements
Include reduced hours, different start and finish times or home-working arrangements.
Annual leave
4 weeks for most, with part-time employees entitled to a pro rata amount.
Personal/carer’s leave, compassionate leave and family and domestic violence leave
Full-time 10 days each year & part-time employees the equivalent pro rata amount.
Casual employees are entitled to take leave
Community service leave
Employees, including casual employees, can take community service leave
Long service leave
Granted after a long period of working for the same employer.
Public holidays
Employees are not required to work on public holidays but will be paid for the hours that they would have worked. - can refuse.
Notice and redundancy pay
Fair Work information statement / Casual employment information statement
National Employment Standards - entitlements
Hours of work
Employer must not request/require more than 38 hours of work in a wk, unless the additional hours reasonable & special provision of penalty rates is applied. - Employees have right to decline
Parental leave
Entitled to 12mths unpaid parental leave in relation to birth or adoption of a child.
Offers and requests to convert from casual to permanent employment.
Casual conversion - casual employees who have worked for 12 mths need to be offered option to convert to full-time/part-time (permanent) employment by their employer.
Flexible working arrangements
Reduced hours, different start and finish times or home-working arrangements.
Annual leave
4 weeks for most, with part-time employees entitled to a pro rata amount.
Personal/carer’s leave, compassionate leave and family and domestic violence leave.
Full-time: 10 days each year & part-time: the equivalent pro rata amount.
Community service leave
Granted after a long period of working for the same employer
Long service leave
Employees are not required to work on public holidays but will be paid for the hours that they would have worked. - can refuse.
Public holidays
Employees are not required to work on public holidays but will be paid for the hours that they would have worked. - can refuse.
Notice and redundancy pay
Employers and employees may need to give notice when they end the employment relationship.
Fair Work information statement / Casual employment information statement
Employers must give every new employee a copy of the Fair Work Information Statement (FWIS) before/ ASAP after, they start new job.
Have to give every new casual employee a copy of the Casual Employment Information Statement (CEIS) at the same time
NES - Superannuation
Employers are required to make super contributions for all employees 18-69 who are paid more than $450 before tax in a calendar month.
Employees under 18 years of age must work for 30 hours/more in a week to be entitled to have super payments made
Employment contracts
Contracts are governed by the Fair Work Act 2009
A typical contract includes:
- Expectation the employee will adhere to policies and procedures
- Title or classification of the role
- Start date (and end date if a fixed term contract)
- Who is the direct supervisor
- Specific duties
- Hours of work
- Rates of pay
- Leave arrangements
All employment contracts must conform to the provisions of the 10 National Employment Standards, and conditions relevant to Awards or Enterprise Agreements.
Employment contracts - Awards
Legally binding agreement that sets out the minimum wages and conditions for a group of employees across an industry
Eg:
Minimum wages
Overtime and penalty rates
Special allowances
Leave details
Employment contracts - Enterprise Bargaining Agreement (EBA)
An agreement that has been negotiated directly between an employer and the employees of an enterprise/business.
Unions can be involved in this negotiation on behalf of employees
EBAs usually provide better pay and conditions than an Award - Employer will expect more
EBAs usually provide better pay and conditions than an Award
Employment contracts - Individual Common Law Contracts
Employees can negotiate individual contracts that do not have to include Award conditions.
Usually only apply to relatively highly paid professionals and are subject to a minimum level of pay.
The minimum is set July 1st each year
Employee expectations - Conditions of Employment
Refer to what an employer has agreed to give the employee in return for the employee’s work
Eg:
Hours of work
Leave entitlements
Employee expectations - Remuneration
Refers to the financial payment an employee receives in return for working for an employer. - Can include:
Wages are an hourly or weekly rate of pay.
Salary is a fixed amount paid to an employee each year (usually paid fortnightly or monthly).
Businesses can also pay employees through additional incentives:
Eg
Financial incentives (bonuses)
Other rewards (use of a company car)
Remuneration package: a combination of a base wage and other benefits.
Employee expectations - Flexible Working Conditions
Patterns of work that allow businesses to work more efficiently or allow employees to balance work and family responsibilities.
Employee expectations - Job security
Refers to whether an employee believes they are likely to lose their job either through being made redundant or being dismissed.
Employee expectations - Work-life balance
About achieving the right amount of time for work and for personal or family life
Pros:
Reduced stress
Increased productivity
Enhanced image
Work (Occupational) Health and Safety Legislation - WHS
The WH&S Act 2011 (Cth): National set of WH&S safety laws that ensure consistently high level of protection for Australian workers and reduce compliance costs for businesses.
OH&S Act 2004 (Vic): Regulates workplace safety in VIC
Under the WH&S Act, employers must:
Establish health and safety committees.
Notify WorkSafe of deaths or serious injuries in the workplace, and any plans to carry out dangerous work.
Give employees the necessary information, training and supervision of their work.
Provide a safe system of work and maintain a safe work site.
WorkSafe Victoria
Administers WH&S legislation in VIC
Has authority to:
Inspect work sites;
Issue improvement;
Issue prohibition notices; and
Prosecute employers for any breaches of health and safety requirements.
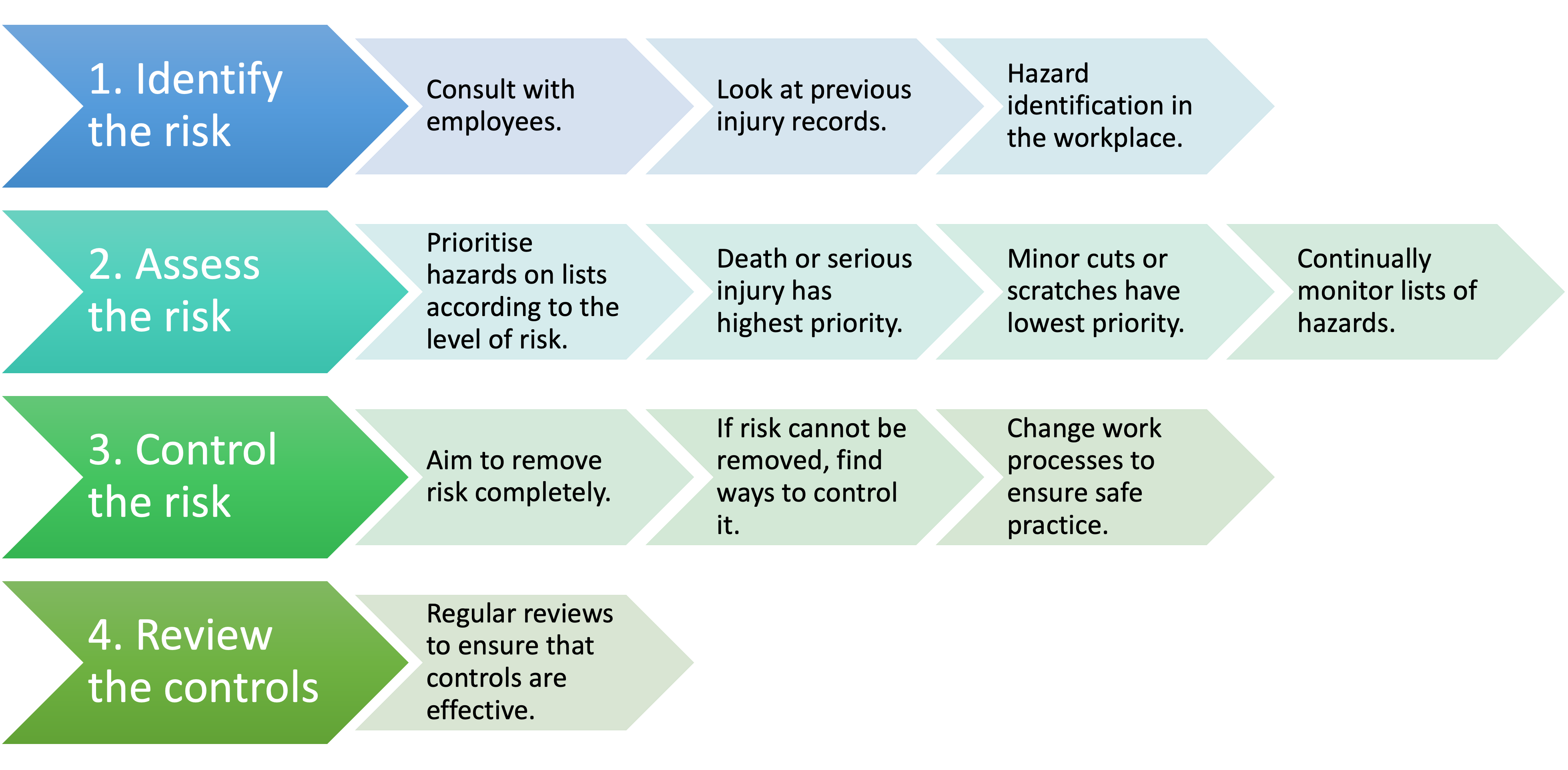
Safe workplace strategies
(Image)
Equal Employment Opportunity Act 2010
Victorian Equal Opportunity Act 2010
Racial Discrimination Act 1975
Sex Discrimination Act 1984
Human Rights and Equal Opportunity Commission Act 1986
Disability Discrimination Act 1992
Age Discrimination Act 2004
This legislation makes it illegal to discriminate against any employee or prospective employee on the basis of the above.
Employers’ obligations under the Equal Employment Opportunity Act 2010
Eliminate discrimination
Take reasonable and balanced measures to get rid of discrimination, sexual harassment and victimisation.
Ensure that employees do not discriminate against each other on the basis of their personal characteristics, status or beliefs.
Eg:
Job ads worded to not exclude anyone from applying.
Encourage diversity in the workplace and cooperation
Interview questions relate to a person’s skills & work experience only
Equal pay for equal work and equal access to promotion
Agencies to support the EEO Act - Victorian Equal Opportunity and Human Rights Commission (VEOHRC)
Role:
Inform + educate the public on equal opportunity and human rights issues.
Receive and resolve disputes.
Provide access to a dispute resolution process
Methods:
Mediation
Conciliation
VEOHRC was established under the Equal Opportunity Act 2010 (Vic).
Agencies to support the EEO Act - Workplace Gender Equality Agency (WGEA)
Set up to work with employers to improve gender equality in the workplace. It:
Issues guidelines to assist employers and provides advice on how they can improve gender equality in their businesses;
Collects info from employers on their progress in achieving gender equality; and
Provides educational and assistance programs.
Induction
Process of acquainting new employees with the business - Eg history, objectives, policies and practices
Methods:
Hands on training
Tours of the business premises
Quizzes and tests to check knowledge
Making sure those running induction programs are friendly and welcoming
Using a mentor or buddy system
Benefits of Induction
Reduce stress and anxiety around starting a new job.
Build confidence by:
- Assisting the employee to feel a part of the business.
- Establishing good working relationships with coworkers and supervisors.
Ensure awareness of safety policies and procedures.
Socially responsible recruitment and selection - CSR
HR management requiring employer to treat all employees fairly, honestly and respectfully.
Employers taking time to provide feedback to unsuccessful applicants.
Employers looking at the implications of hiring policies and practices on the community (Eg groups traditionally discriminated against in society.)
Employer Arrangements - CSR
Recognise and reward effort
Offer educational opportunities - provide employees with opportunities to improve themselves
Consult with employees on important workplace issues
Equal opportunities for promotion
Policies regarding bullying and sexual harassment
Work life balance
Flexible working arrangements
Workplace diversity - CSR
Refers to the differences between employees in a business.
Eg:
•Employing mature-age workers.
•Employing people with a disability.
•Allowing employees to celebrate religious holidays/fulfil their religious obligations.
CSR in Staffing
Remote-working opportunities
Paying above Award wages.
Provide personal as well as professional development opportunities.
On-site childcare facilities or gym
Paid jury service or community service leave
Overseas Recruitment
Businesses that require employees with special expertise may recruit applicants from overseas. BY:
Online advertising of positions;
Video conferencing - interviews to be conducted online
Psychological testing, background and reference checks can be conducted online.
Overseas Postings
When businesses that have branches/subsidiaries in other countries send their employees to work for a time in those overseas postings.
Transnational Companies
Companies that operate in more than one country. (Also known as multinational corporations)
Offshoring
The process of moving parts of their business operations to another country