PSYC 308: Abnormal Behavior - Test 1 Flashcards
The Four D's
Framework for defining abnormal behavior: Deviance, Distress, Dysfunction, Danger.
Deviance
Behavior deviating from societal norms or expectations.
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
The Four D's
Framework for defining abnormal behavior: Deviance, Distress, Dysfunction, Danger.
Deviance
Behavior deviating from societal norms or expectations.
Distress
Personal suffering or discomfort indicating abnormality.
Dysfunction
Interference with daily functioning and activities.
Danger
Behavior posing risk to self or others.
DSM-5
Diagnostic manual for mental health disorders.
Incidence
Number of new cases in a population over time.
Epidemiology
Study of disease distribution in populations.
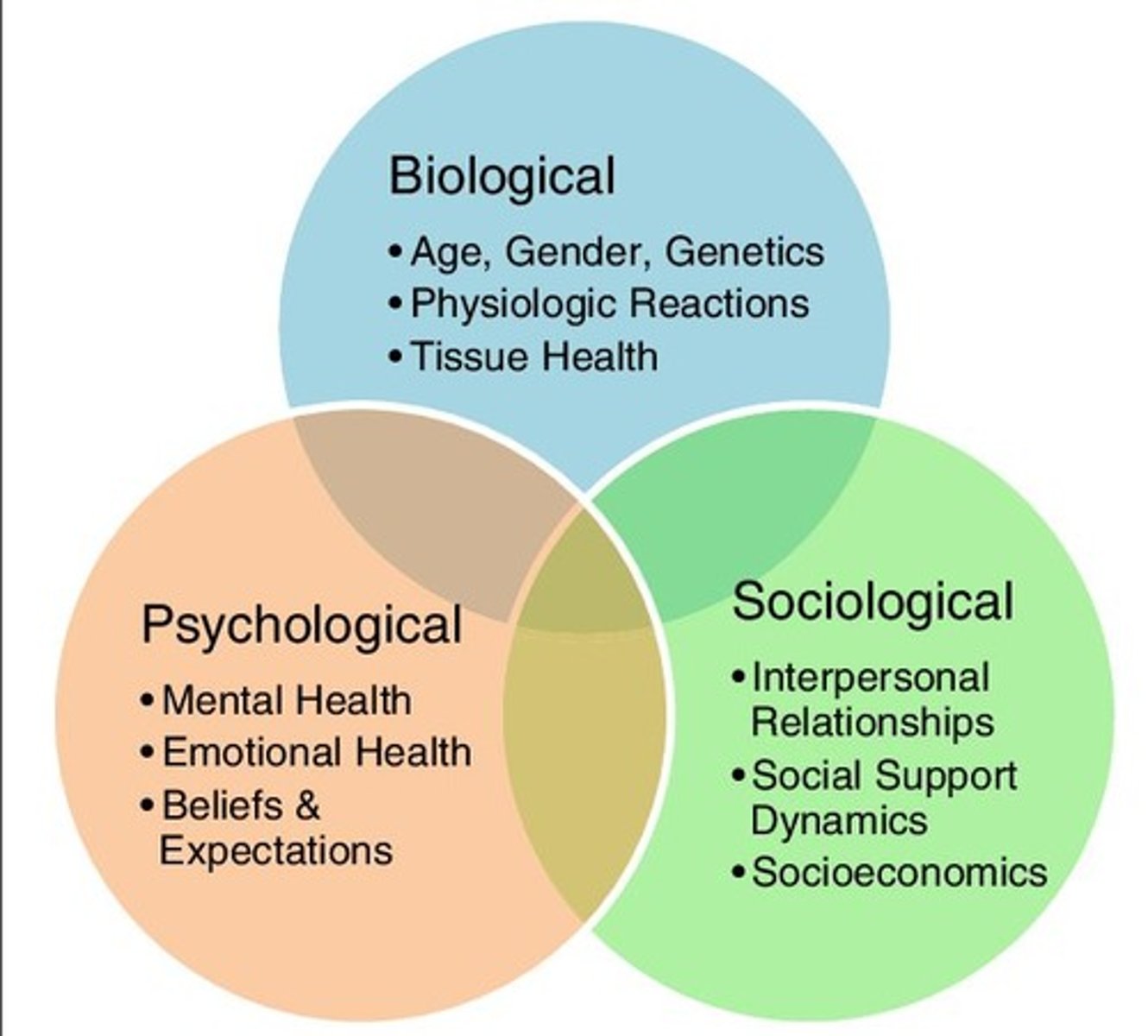
Biopsychosocial model
Framework considering biological, psychological, and social factors.
Life-course perspective
Impact of early life events on later mental health.
Self-Report
Participants evaluate their own behaviors and feelings.
Observations
Directly observing behavior to assess psychological conditions.
Experimental Research
Research method manipulating variables to determine causation.
Control Groups
Groups used for comparison in experimental studies.
Risk Factors
Aspects increasing likelihood of developing mental health issues.

Protective Factors
Aspects promoting mental health and resilience.
Case Studies
In-depth analysis of individual psychological cases.
Dysfunctional
Interferes with daily functioning, indicating a breakdown of cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning.
Retrospective Strategies
Looking back in time to understand the development of a disorder.
Prospective Strategies
Looking forward in time, following participants who are at risk of becoming disordered.
Single-Case Groups
Using a specific structure to explore single-case designs to assess individual responses.
ABAB Design
A structure that alternates between control and treatment conditions.
Cultural Impacts
The influence of culture on the perceptions of abnormality and definitions of deviance and dysfunction.
Maladaptive Behavior
Behavior that disrupts daily functioning or adaptation.
Risk Factor
Characteristic associated with increased condition risk.
Variable Risk Factors
Risk factors that can be modified or changed.
Fixed Markers
Risk factors that cannot be altered or changed.
Causal Risk Factor
Changing this factor affects the outcome variable.
Variable Marker
Changing this factor does not affect the outcome.
Diathesis-Stress Model
A framework linking predisposition and the trigger of environmental stress.
Resilience
Ability to adapt successfully to challenges.
Correlate
Variable associated with an outcome of interest. Correlation does not mean causation.
Necessary Factor
Essential for the occurrence of a condition.
Sufficient Factor
Alone can cause the condition to occur.
Contributory Factor
Increases the likelihood of a condition developing.
Synaptic Transmission
Neurotransmitters released into synapse for neuron communication.
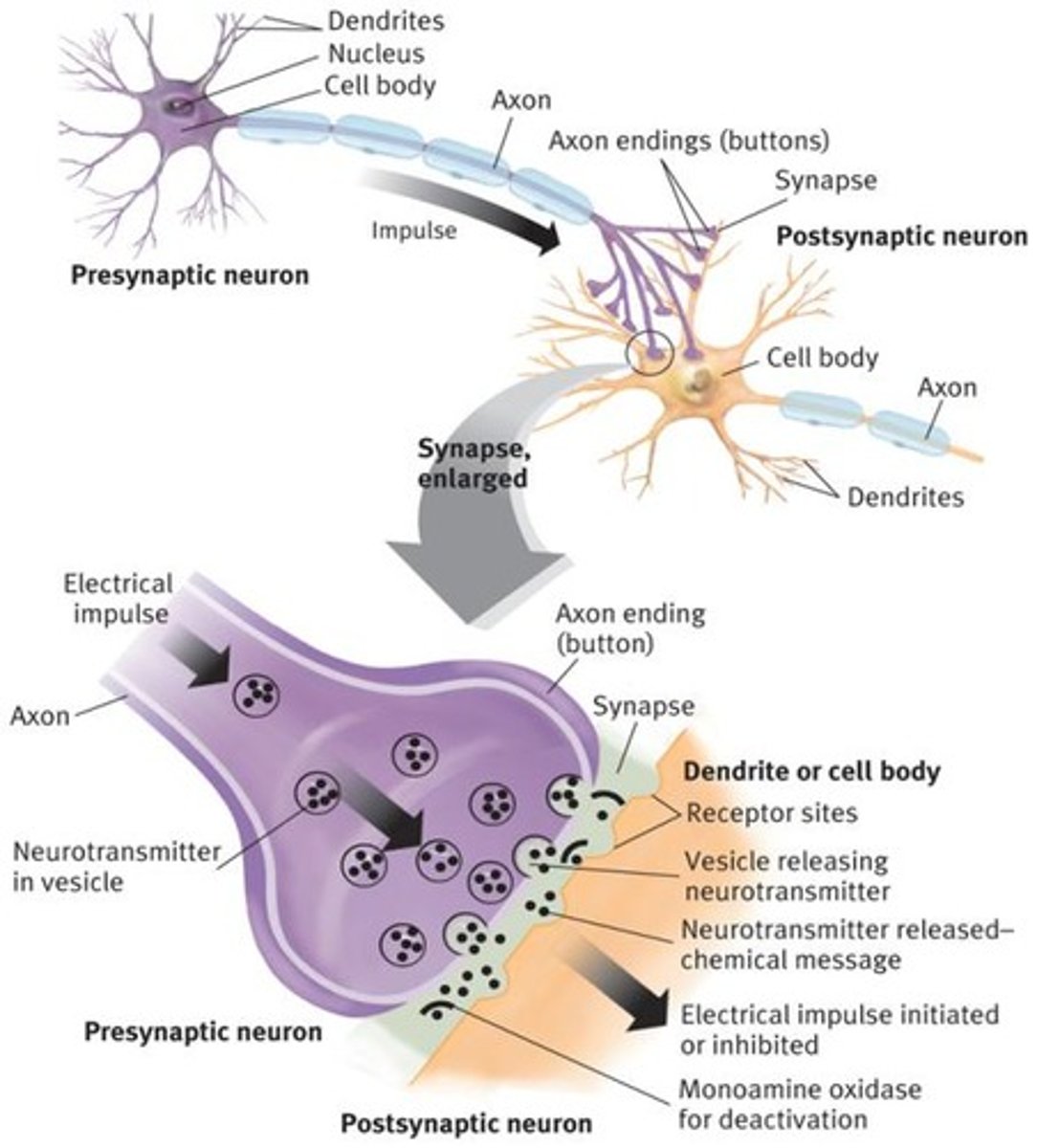
Neurotransmitter Imbalances
Implicated in many disorders and caused by excess release, deactivation issues, or receptor problems.
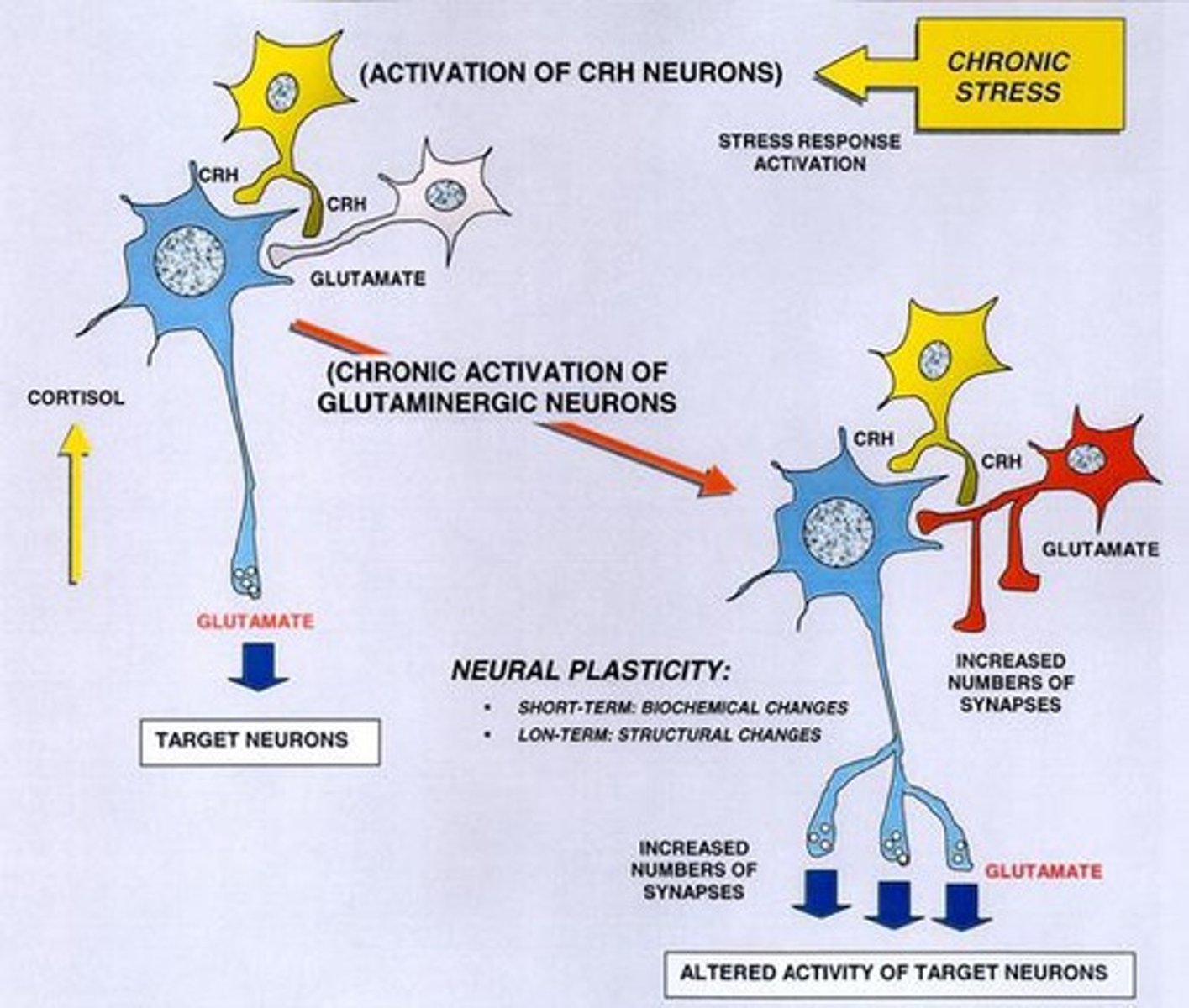
Neural Plasticity
Brain's ability to adapt and reorganize itself.
Temperament
Child's reactivity and self-regulation traits.
Biological Viewpoint
The viewpoint in which most emphasis is placed on biological factors such as brain abnormalities or hormonal or neurotransmitter imbalances.
Psychodynamic Perspective
Focus on unconscious processes and childhood experiences.
Ego-Defence Mechanisms
Strategies to protect ego from anxiety.
Psychosexual Stages
Freud's stages of childhood sexual development. Includes: Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latency, and Genital stages.
Freudian Criticism
Overemphasis on sex drive and unconscious motives.
Behavioural Perspectives
Focus on observable behaviors and environmental impact.
Observational Learning
Learning by observing others' behaviors.
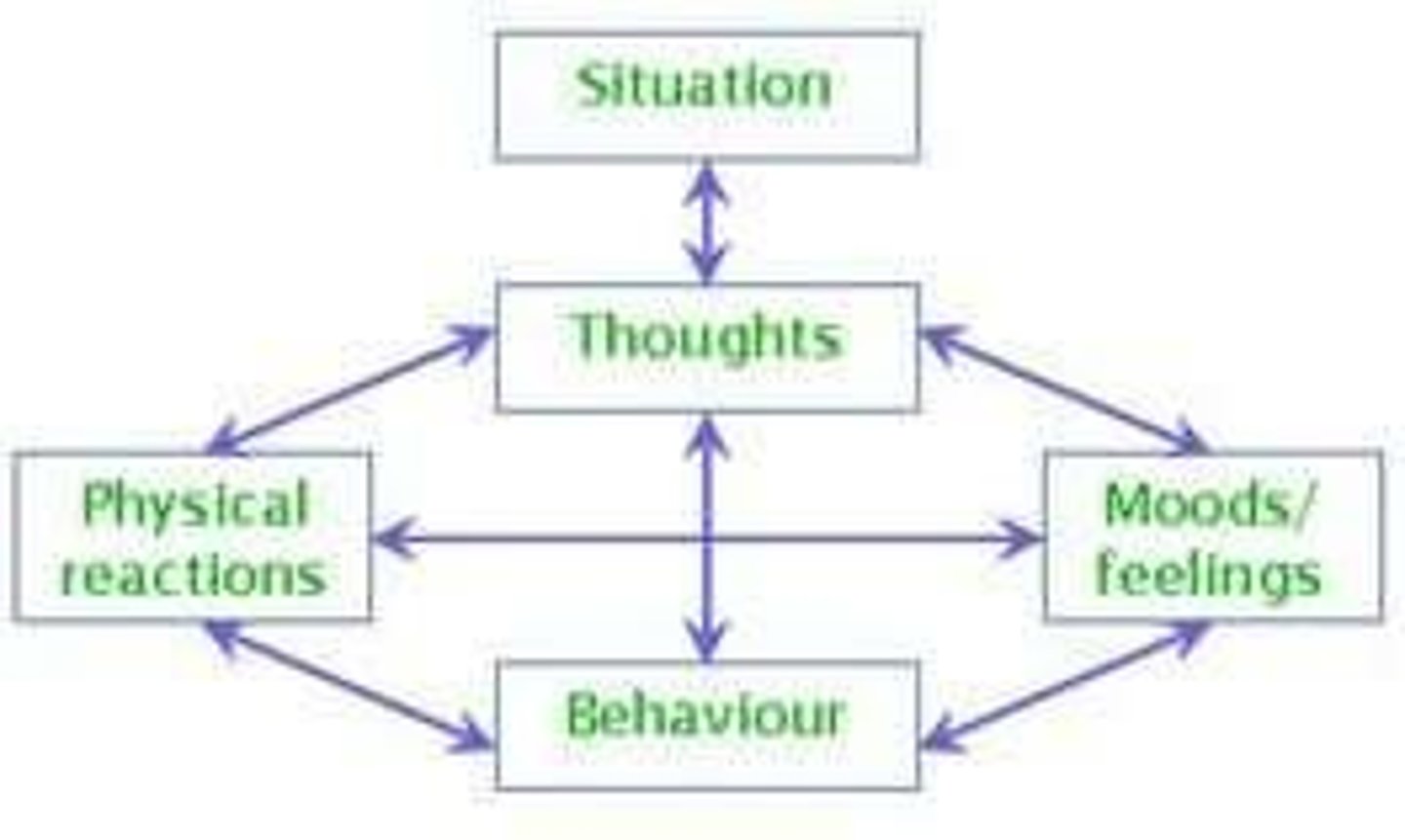
Cognitive-Behavioral Perspective
The combination of cognitive and behavioral components both contribute to mental health disorders. Distorted thoughts lead to maladaptive emotions and behaviors.
Schema
The mental frameworks we learn and continuously build to interpret the world. Representation of knowledge guiding information processing.
Self-schema
Personal views of identity and aspirations.
Assimilation
Integrating new experiences into existing frameworks.
Accommodation
Modifying frameworks to include new information.
Maladaptive schemas
Distorted cognitive frameworks from adverse experiences.
Attribution
Assigning causes to events or behaviors.
Attributional style
Characteristic way of assigning causes to events.
Self-serving bias
Tendency to attribute positive events internally.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Therapeutic approach combining cognitive and behavioral techniques.
Psychosocial perspectives
Focus on social influences on psychological health.
Social factors
Environmental influences affecting psychological well-being.
Trauma
Severe emotional response to distressing events.
Parental psychopathology
Parents' mental disorders impacting children's development.
Prejudice
Unjust discrimination impacting social relationships.
Socio-economic status
Lower SES correlates with higher mental disorders incidence.
Access discrimination
Hiring denial based on personal characteristics.
Treatment discrimination
Unequal pay and promotion opportunities for certain groups.
Health outcomes
Prejudice increases likelihood of negative health outcomes.
Cultural syndromes
Clusters of symptoms specific to certain cultures.
Cultural idioms
Culture-specific expressions of distress.
Cultural explanations
Diverse explanations for symptoms across cultures.
Cognitive Perspective
Focuses on mental processes affecting behavior.
Social-Cultural Perspective
Analyzes family dynamics and societal influences.
Psychoanalytic Perspective
Explores childhood conflicts and trauma effects.
Humanistic Perspective
Considers loss of faith in self-worth.
Causal Factors
Elements contributing to an individual's behavior.
Reliability
Consistency of a measure across evaluations.
Test-retest reliability
Same test yields same results over time.
Inter-rater reliability
Agreement among different clinicians' assessments.
Validity
Measure's accuracy in assessing what it claims.
Face validity
Tool appears to measure intended construct.
Predictive validity
Tool forecasts future behaviors or characteristics.
Concurrent validity
Agreement with independent measures of similar traits.
Standardisation
Consistency in test administration and presentation.
Initial Diagnosis
Identifying the problem and potential risks.
Baseline Assessment
Understanding initial condition before treatment begins.
Cultural competence
Understanding diverse backgrounds in mental health assessment.
Multicultural assessment
Evaluating individuals from various cultural contexts.
Prevalence
Frequency of a disorder within a population.
Ethnic minorities
Groups at higher risk for certain disorders.
Intelligence Quotient (IQ)
standardized measure of intelligence based on a scale in which 100 is average
WAIS
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, an IQ test.
Stanford Binet Test
Standardized test for measuring intelligence.
Matrix Reasoning
Nonverbal assessment of logical thinking skills.
Verbal Comprehension Task
Describing a word's meaning without using it.
Working Memory
Ability to hold and manipulate information.
Digit-Forward
Repeating numbers in the order presented.
Digit-Backward
Repeating numbers in reverse order.
Digit-Span Sequencing
Arranging numbers in ascending order.
Strengths of Intelligence Tests
High reliability, validity, and standardization within the population on which they are normed.
Weaknesses of Intelligence Tests
Cultural biases and performance influencing factors can influence test scores and skew results.
Clinical Interviews
Standardized psychiatric assessment of patient issues.
Self-Monitoring
Individual reflection on decisions and feelings.