USMLE PREP #1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Replication
DNA to DNA (DNA Synthesis)
Transcription
DNA to RNA (RNA Synthesis), occurs in interphase
Translation
RNA to Protein (cytoplasm)
Reverse Transcription
RNA to DNA (Retroviruses)
Gene Expression
Turns on gene (activates transcription and translation)
DNA
What is bigger DNA or RNA?
Fragmenting
Breaks DNA into smaller pieces so its easier to analyze
Interphase
G0, G1, S, G2 (everything but M)
G0
This cell cycle phase does NOT divide (most cells are in this- neurons, muscle cells, non-nucleated RBCs)
G1 Cells
Cells that get ready to divide (nucleated red cells, epithelial cells, hair cells) 46 chromosomes and 46 chromatids (have not divided yet)
G1 Checkpoint
Uses signal transduction, triggered by hormones, to decide when a cell should enter S phase (DNA replication) Tyrosine Kinase Receptor (TKR) plays a key role
Adenine

Thymine
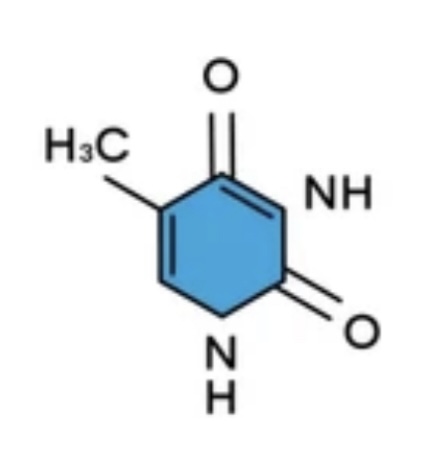
Uracil

Guanine
Cytosine
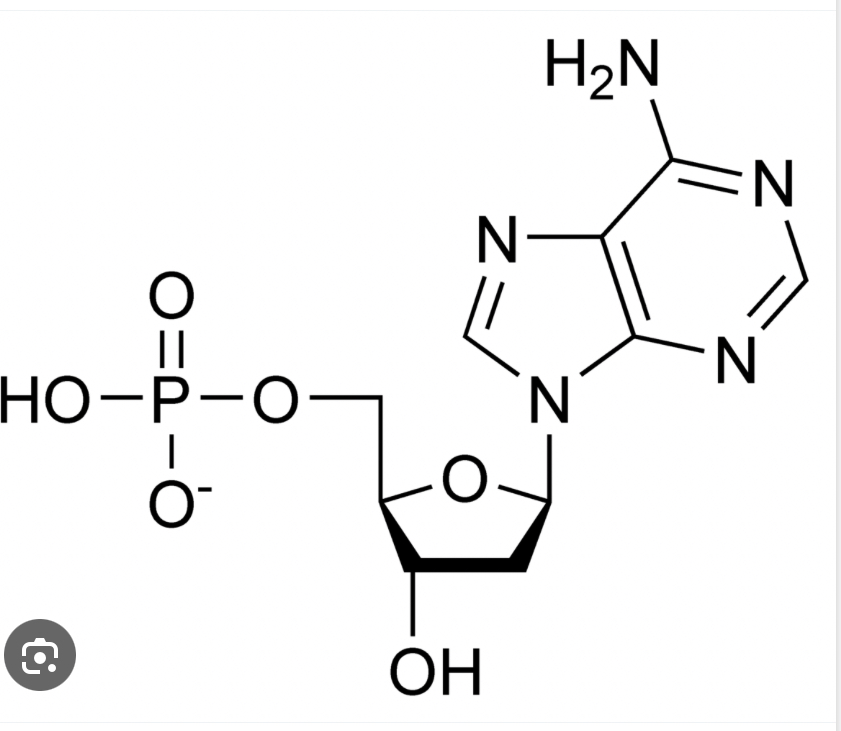
Nucleoside
Base and a sugar
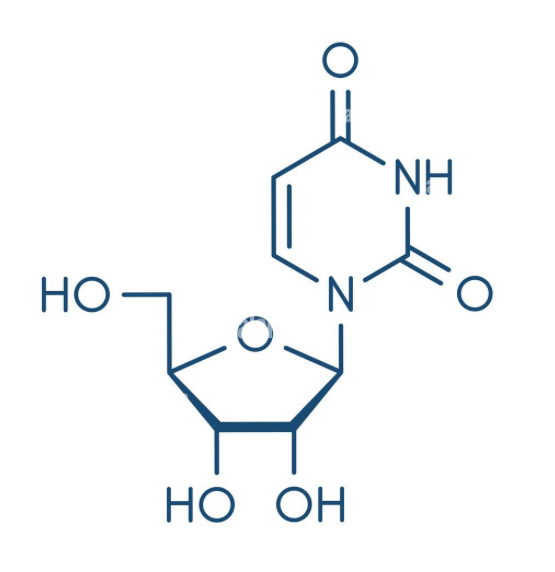
Nucleotide
Base, Sugar, and Phosphate (AMP, ADP, ATP)
Synthesis (S)
Phase in cell cycle that replicates DNA (DNA synthesis) 92 chromatids (46 Chromosomes)
Nucleic Acids
These are made up of nucleotides joined together by phosphodiester bonds.
There is usually a 5’ phosphate and a 3’ hydroxyl group
Nucleosomes
DNA wraps around histones to form
Positively
Histones are () charged
10 nm fiber
DNA + histone octamer (nucleosomes)
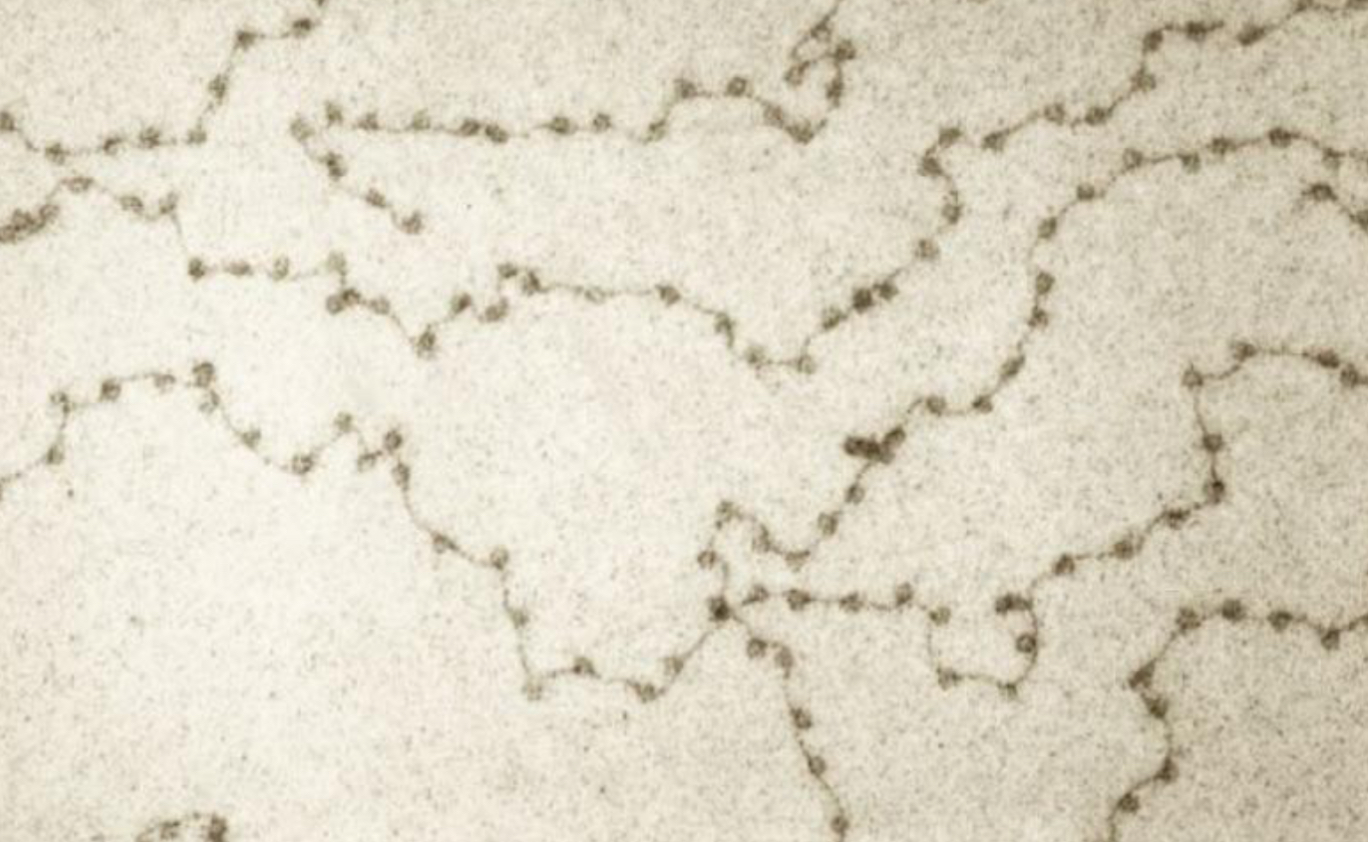

30 nm fiber
Nucleosomes added H1 histones (tighter package)
Higher-order chromatin
Nucleosomes with H1 histones and scaffolding proteins (even more condensed)
Heterochromatin
Very tightly packed, inactive (dark staining, inactive)
Euchromatin
Loosely packed, active (light staining, open and used for transcription)
Barr Bodies
One female X chromosome is inactive
Denaaturation
DNA strands are separated (around 92-95 degrees Celsius) PCR
Annealing
Primers bind (or renature) to the single stranded DNA (50 to 65 degrees Celsius)
Extension
DNA Polymerase extends the primers to form a new strand (72 degrees Celsius)
HIV
() has reverse transcriptase and requires a primer but lacks proof reading activity (does not have 3’ exonuclease activity)
Telomerase
Prevents chromosomes from shortening with # of replications (reverse transcriptase activity)
hMLH2, hMLH1
are the genes that finds the error and excises it, respectively
Lynch Syndrome
(DNA Instability) that exhibits incomplete pentrance (one good gene, one bad gene, NO CANCER, but you will still have Lynch, you need two for to develop pathology (cancer))
Uracil
Cytosine Deamination creates
3’ exonuclease
() is the proofreading enzyme
5’ exonuclease
() removes RNA primer
p53
() prevents damaged cells from going into S phase, induces apoptosis (suppresses tumor formation)
kDa, Daltons
Cells can be damaged in G1 like p53 (protein 53, 53 means 53(), 53,000 ())
Li-Fraumani Syndrome
If P53 turns mutated damaged DNA cells go into S phase causing ()
Loss of Function Mutations
Tumor Suppressive Genes (mutated p53, p53 does not work, creating cancer)
Gain of Function Mutations
Where a gene is mutated to make the gene “turn on” when it is not supposed to be “on”, creating cancer
primer
DNA Polymerase has to see a () on a chromosome to start replication
Promoter
RNA Polymerase binds to the () in order to start transcription, double stranded DNA
Gene
double stranded DNA, but only one stand is used as a template
Template Strand
Strand used in transcription, complementary to mRNA
Coding Strand
Strand NOT used in transcription, but is IDENTICAL to mRNA (U/T)
read
DNA is () in 3’ to 5’ direction
RNA
() is synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction
upstream
Promoter is always () to the gene
mRNA
made in euchromatin portion of the nucleus (light stained)
tRNA
made in euchromatin portion of the nucleus (light stained)
rRNA
made in nucleolus
Coding Strand
Complementary and anti-parallel to the template strand
Operon
Polycistronic gene region is also known as the
protein information
UTR (Untranslated Region) is a region with no ()
exons or introns, translational processing
Prokaryotic gene expression does not have () or ()
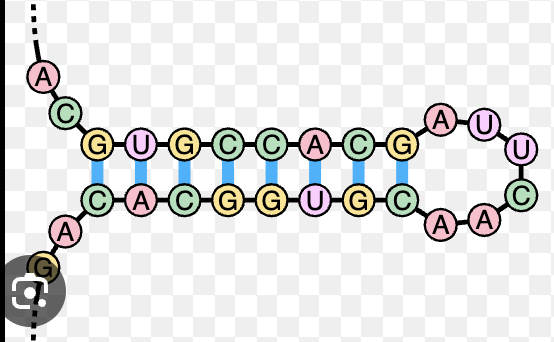
Stem-loop sequence
terminates RNA transcription (stretch G and C)
promoter
The () is replicated since it is DNA
operon
makes multiple genes in one RNA
shine dalgarno sequence
RNA binds to the () in the operon
rifampin
inhibits transcription (RNA polymerase) in bacteria (used to treat TB and meningitis)