Chapter 1: Meaning, Nature, and Types of Communication
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Nature of Communication
It is inevitable.
It is used for self-expression
It express thoughts and feelings
It gives context for different purposes, behavior, and situation.
Communication
It comes from the Latin word “communicare” meaning “to share” or “to make ideas”, derived from the word “communis” meaning “common or shared.”
Communicare
Communication comes from the LATIN word?
“to share” or “to make ideas”
Communicare means
Communis
Communicare is derived from the word?
Communication
It is the process of meaning through a channel or a medium (media).
Communication
It is the process of using messages to generate meaning.
Communication
It refers to the sending and receiving messages.
Communication
It is about sharing opinions, information, ideas, and feelings.
Communication
It is the systemic process of interaction through symbols.
Communication
It is the transmission of message from source to receiver.
Communication
It is the action of sending information to oneself via LANGUAGE.
Types of Communication
Verbal
Non-verbal
Written
Visual
Listening
Verbal Communication
It states that words are assurance, meaning that it should be exact and should not have other meanings.
Verbal Communication
All types of communication that uses spoken or unspoken (sign language.
Verbal Communication
It can be formal or informal.
Verbal Communication
A good speaker of this communication always adjusts to its environment.
Nonverbal Communication
It states the “words are assurance but actions speak louder than words.”
Nonverbal Communication
It states that “what is being said is only half the battle, the rest lies in what is not being said.”
Nonverbal Communication
It refers to the movements of the face, posture, eye contact, and hands.
Written Communication
It is a form of verbal communication.
Written Communication
It is a type of communication that uses verbal words but is still different than spoken verbal communication.
Written Communication
Its message lives on, perhaps even in perpetuity.
Visual Communication
It states that “we live in a visual world, but it does not mean that we shouldn’t look at what does not meet the eye.
Visual Communication
It aids the verbal and written communication.
Listening
It states that the “best speakers are good listeners”
Listening
It refers to the comprehension in the process of communication.
Listening
It does not only equate to hearing, but comprehending.
Elements of Communication
Sender
Channel
Code
Noise or Barrier
Message
Feedback
Encoding and Decoding
Pearson et al
He provided a comprehensive set of communication elements.
Sender
The process of communication is started by the _______.
Sender
When the ________, has chose a meaning, they encrypt the message and choose a chnnael to send it through the recipient.
Receiver
They decode, interpret, and respond to the message of the sender.
Receiver
They give the original sender a response or feedback.
Message
It is the verbal and non-verbal form of idea, thought, or feeling that one intends to communicate to another person or group of people.
Channel
It refers to the means with which the message is delivered.
Medium, Channel
As the message moves from the sender to the receiver, it passes through a _______ or ________.
Feedback
The reaction or response of the receiver is called _______.
Feedback
It provides insight into how the receiver interprets and understands the message of the sender.
Code
It pertains to language.
Code
It is a systematic arrangment of symbols used to create meanings in the mind of another person.
Encoding
It is defined as the process of translating an idea or a thought into a code.
Decoding
It is the process of assigning meaning to an idea or a thought.
Noise Barrier
It is anything that stops a receiver from full comprehending a message.
Noise
It can be both External (Physical), Internal (Psychological), Biological (Physiological), Meaning (Semantic)
External (Physical), Internal (Psychological), Biological (Physiological), Meaning (Semantic)
Noise has four types:
External (Physical)
Any external, tangible, or auditory interference in the environment that distracts from the message. Examples include loud machinery, a passing airplane, a baby crying, or a flickering light.
Physiological Noise (Biological)
Biological factors within the sender or receiver that interfere with communication. Examples include hunger, fatigue, illness, or hearing impairments.
Psychological Noise (Internal)
Cognitive or emotional interference that prevents effective listening or understanding. Examples include stress, anxiety, bias, prejudice, or wandering thoughts.
Semantic Noise (Meaning)
Occurs when the sender and receiver apply different meanings to words or symbols, causing misunderstanding. Examples include the use of technical jargon, slang, or language barriers
Technical/Mechanical Noise
Interference caused by the medium or technology used to transmit the message. Examples include poor internet connection, static on a phone call, or a blurry video screen.
Cultural Noise
Occurs when differences in cultural backgrounds, norms, or beliefs lead to misinterpretation of messages.
Noise
It can disrupt communication any time.
Models of Communcation
Linear Model
Interactive Model
Transactional Model
Linear Model
It is the transmission model that is based on the assumption that communication is trasmitted in a straightforward manner-from a sender to a receiver.
Linear Model
It contains: Sender, Message, Receiver

Linear Model
It clearly reflects that communication is a one-way process.
Linear Model
There are two prominent models under this: Laswell’s and Shannon & Weaver’s Models
Laswell’s Verbal Model
It is the simplest model of communication.
Laswell’s Verbal Model
In this model, communication flows from in one direction from the sender with a message which is sent via a certain medium towards the receiver to bring about a certain result.
Medium
In Laswell’s Verbal Model, communication flows from in one direction from the sender with a message, which is sent via a certain _______ towards the receiver to bring about a certain result.
Laswell’s Verbal Model
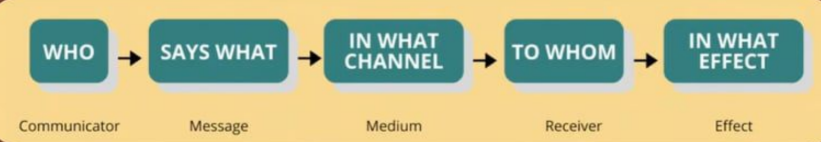
Communicator, Message, Medium, Receiver, Effect
These are the 5 components of Laswell’s Verbal Model. (CMMRE)
Communicator
It is the “Who?”
Message
It is the “Say What”
Medium
It is the “In what channel?”
Receiver
It is the “To Whom”
Effect
It is the “In What Effect”
Shannon & Weaver’s Model
It is a modification of Laswell’s model by adding the concept of noise.
Shannon Weaver’s Model
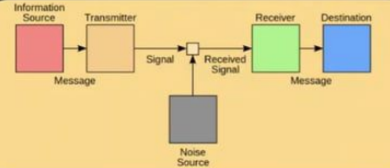
Information Source, Transmitter, Noise Source, Receiver, Destination
These are the 5 COMPONENTS of the Shannon Weaver’s Model. (IS-TRA-NOS-RE-DES)
Message, Signal, Received Signal, Message
These are the 4 SENT COMPONENTS between the 5 COMPONENTS of the Shannon Weaver’s Model.
Message
It is sent by the Information Source to the Transmitter.
Signal
It is transmitted between the Transmitter and the Receiver. Possibly, the Noise Source may affect it.
Noise
What is the concept added by the Shannon & Weaver’s Model?
Shannon & Weaver’s Model
In this model, the information source is the sender who sends the message to the transmitter (channel).
Shannon & Weaver’s Model
In this model, the signals sent and received are affected by the noise.
Noise
It is the interference that disrupts and distorts the understanding of message.
Shannon & Weaver’s Model
In this model, the receiver is another receiving instrument such as telephone, ears, eyes.
Receiver
In the Shannon & Weaver’s model, the _________ is another receiving instrument such as telephone, ears, eyes, etc.
Destination
It is the person who receives the message.
Interactive Model
It is a model made by Wilbur Schramm’s.
Wilbur Schramm
Who is the proponent of the Interactive Model?
Interactive Model by Wilbur Schramm
In this model, communication is a two-way process which involves an exchange or an interaction between the sender and the receiver.
Interactive Model by Wilbur Schramm
The receiver gets the message, he processes it, provides own interpretation, and delivers back to the sender.
Interactive Model by Wilbur Schramm
The message in this model is sent back to the sender, called feedback.
Feedback
It is the message sent back to the sender.
Interactive Model by Wilbur Schramm
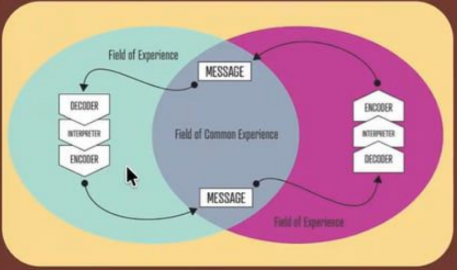
Personal Fields of Experience
It plays an important role, whether shared or not, in the Interactive Model.
Personal Fields of Experience
According to Schramm, it explains why misunderstanding occurs.
Personal Fields of Experience
These either enhances or weakens the communication process.
Personal Fields of Experience
When communicators share this, the BETTER they understand each other.
Transactional Model
This model was adapted from Wood 1997 in response to the failure of the interactive model to portray the dynamism of human communication.
Wood 1997
The Transactional Model was adapted from?
Failure of Interactive Model
The Transactional Model was adapted as a response to the __________ to portray the dynamism of human communication.
Transactional Model
It has a time element which influences how people communicate.
Time Element
The Transactional Model has a _________ which influences how people communicate.
Transactional Model
It depicts communication as varying (not constant) and dynamic (not static)
varying, dynamic
The Transactional Model depicts communication as ______ and ______.
Transactional Model
In this model, the outer lines indicate that communication occurs within systems that influence people such as culture, context, family background.