Acctg Ch. 11 - Proprietorships, Partnership, and Corporations
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is a sole proprietorship?
They are owned by a single individual who is responsible for making business and profit distribution decisions
What are partnerships?
Allow persons to share their talents, capital, and the risk and rewards of business ownership
What are partnership agreements?
Prudent partners minimize misunderstandings by hiring attorneys to define the responsibilities of each partner and describe how income or losses will be divided.
What is a corporation?
A separate legal entity created by the authority of state government
What are stock certificates?
Document showing ownership interest issued to an investor in exchange for contributing assets to a corporation (ownership rights and privileges)
What is a closely held corporation?
Ownership of corporation can be transferred from one individual to another through exchanging stock certificates
What is the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002?
Created a 5-member Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) with authority to set and enforce auditing, attestation, quality control, and ethics standards for auditors of public companies
What is double taxation?
When a corporation pays income taxes on earnings and owners pay income taxes on distributions (dividends) received from corporations (taxed twice - first when income is reported on the corporation’s income tax return, second when distributions are reported on individual owner’s tax returns
What is a good illustrations of double taxation?
Glide corporation earns pretax income of $100,000 (in a 21% tax bracket), meaning the Glide will pay $21,000 in income taxes. The after-tax income of $79,000 (100,000-21,000) is distributed to stockholders (in the 22% tax bracket). Their individual income tax return will report $17,380. Ultimately, $38,380 is paid on the $100,000 of income earned by the corporation
How can companies deal with double taxation?
-Tax laws permit small businesses to elect “S Corporation” status = not taxed at corporate level, but when the owners who pay individual income taxes.
-Limited liability companies (LLCs) = taxed as sole proprietorships or partnerships
Why might anyone choose a corporate form?
-Limits an investor’s potential liability as an owner of a business
-Corporation is legally separated from its owners = creditors cannot claim owner personal assets as payment for the company’s debts
-Plaintiffs must sue the corporation, not its owners
Why are proprietorships and partnerships so popular?
B/c of limit liability: investors in a corporation may not be held personally liable for the actions or debts of a corporation
What is continuity?
Presumption that a corporation’s existence may extend well beyond the time at which any particular shareholder retires or sell their stock
What is transferability of ownership?
An investor buys or sells stock to acquire or give up an ownership interest in a corporation
Why is transferring ownership of proprietorships more difficult?
B/c they must find someone to willing to buy the entire business
Why is transferring ownership in partnership difficult?
B/c transfer may require a new partner to make significant investment and accept management responsibilities in the business.
What is the management structure of partnerships and proprietorships?
3 tiers:
1) Owners (stockholders)
2) Stockholders elect a board of directors
3) Board of directors hire professional executives
How can proprietorships and partnerships gain capital needed for investments?
Through a small number of private owners or borrowing rather than having millions of shareholders like corporations
How can the ownership interest (equity) in a business be composed of?
1) Owner/investor contributions
2) Retained earnings
*The way they are reported in financial statements differ for each type of business (prior, part, corp)
What are withdrawls?
Distribution of assets to the owners of proprietorships and partnerships
What is an example of equity in proprietorships?
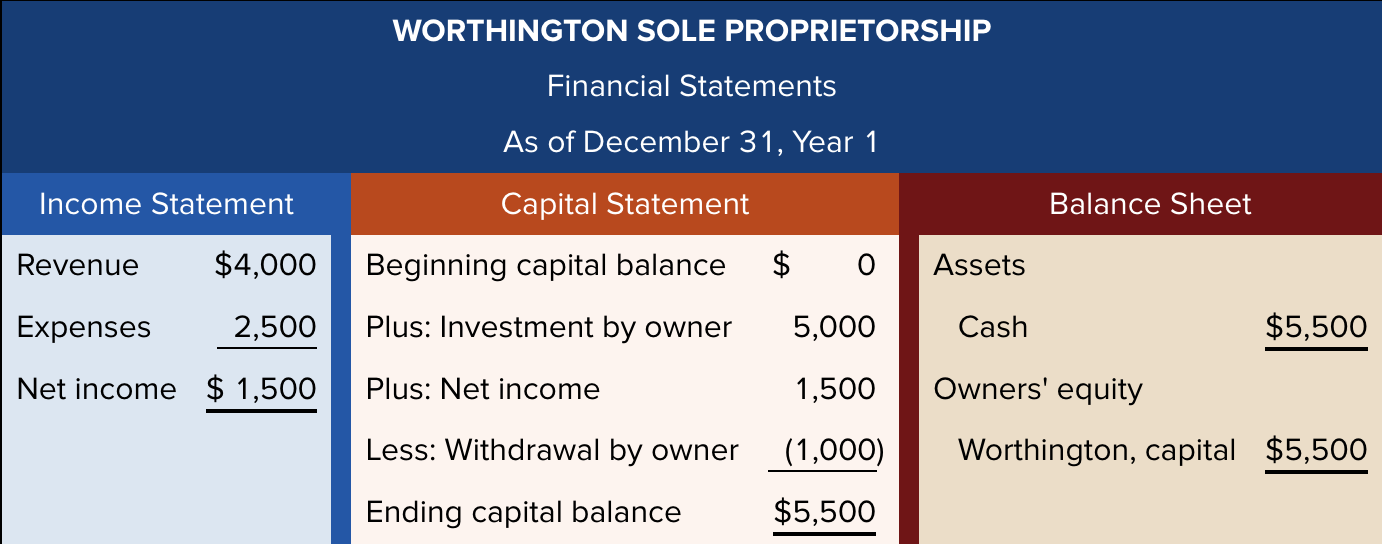
What is an example of equity in a partnership?

What is a par value to stock?
represents the maximum liability of the investors
What is legal capital?
Par value x the number of stock issued representing the minimum amount of assets that must be retained in the company as protection for creditors
What is stated value?
An arbitrary amount assigned by the board of directors to the stock
What is authorized stock?
States approve the maximum number of shares of stock that corporations are legally permitted to issue
What are issued stocks?
The authorized stock that has been sold to the public
What are treasury stocks?
When a corporation buys back some of its issued stock
What are outstanding stocks?
total issued tock - treasury stock = stock owned by investors outside the corporation
What is market value?
The price an investor must pay to purchase a share of stock
What is book value per share?
total stockholder’s equity which is (assets-liabilities) then divided by the number of shares of stock owned by investors
What are common stocks?
They bear the highest risk of losing their investment if a company is forced to liquidate and reap the greatest rewards
What are some rights that common stockholders get to enjoy?
1) the right to buy and sell stock
2) the right to share in the distribution of profits
3) the right to share in the distribution of corporate assets in the case of liquidation
4) the right to vote on significant matters that affect the corporate charter
5) the right to participate in the election of directors
What do preferred stockholders get?
-No voting rights
-amount of dividends are usually limited
What are preferences granted to preferred stockholders?
1) Preference as to assets: in case of bankruptcy - they must be paid the liquidation value before any assets are distributed to common stockholders
2) Preference as to dividends: Receive dividends before common stockholders (And a fixed payout)
What does it mean if preferred stock has cumulative dividends?
if a corporation is unable to pay the preferred dividend in any year, it is not lost but begins to accumulate
What are dividends in arrears?
When cumulative dividends have not been paid (cumulative are paid before common)