production functions & cost curves
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what do firms have to decide?
whether and what quantity of a good to produce, whether to enter or exit the market (assume perfectly competitive market)
what determines the cost of production?
the cost of inputs
Q = f(K,L) where K and L are production inputs
L = labour
K = capital
what are fixed production inputs?
an input that cannot be varied in the short-term (eg. factories)
what are variable production inputs?
an input that can be varied by the firm at any time (eg. labour)
how do we calculate marginal product (MP) of an input?
marginal product of an input = change in total output by increasing that input by one unit
change in Q / change in input
MPinput depends on how much of each input you already have (100th labourer is less useful than 2nd labourer)
what is the law of diminishing marginal returns (DMR) for an input?
as more of a variable input is added, the MP of that input will decline
what are fixed costs of production?
the costs of fixed inputs paid in the short-term
what are variable costs of production?
the costs of variable inputs that the producer chooses to purchase in the short-term
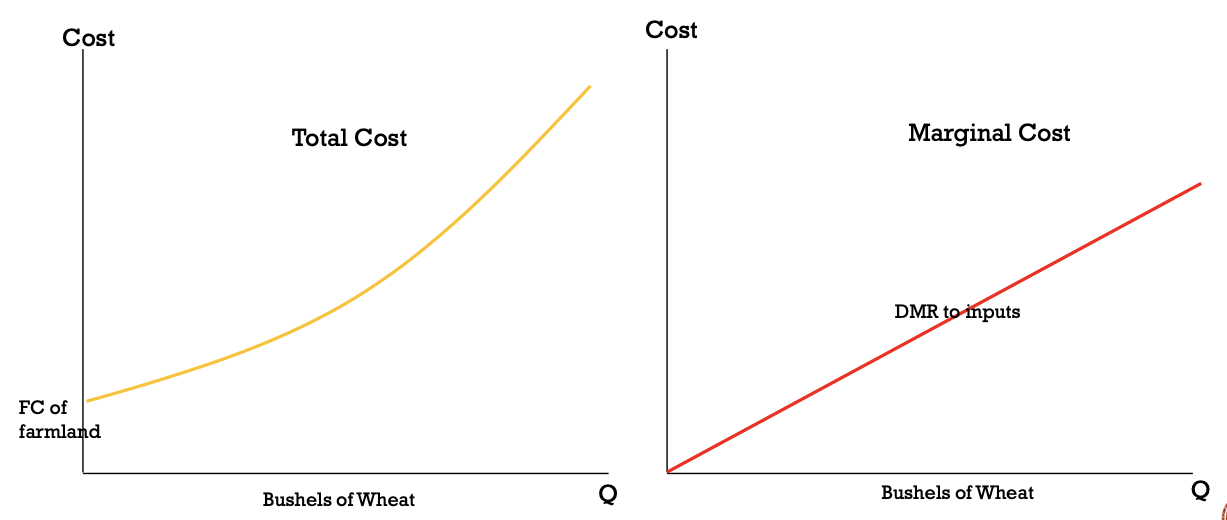
how do we calculate marginal cost of production?
marginal cost = total cost for producing the next unit of the good
change in TC / change in Q
MC depends on how much has already been produced
MC never contains fixed costs as they are the same no matter how many units are produced
what does diminishing marginal returns to inputs suggest?
that as Q increases, marginal costs will increase
(not worth employing the 100th labourer as they will yield a smaller increase in Q for the same price as the 99th labourer)
how do total cost & marginal cost curves differ?
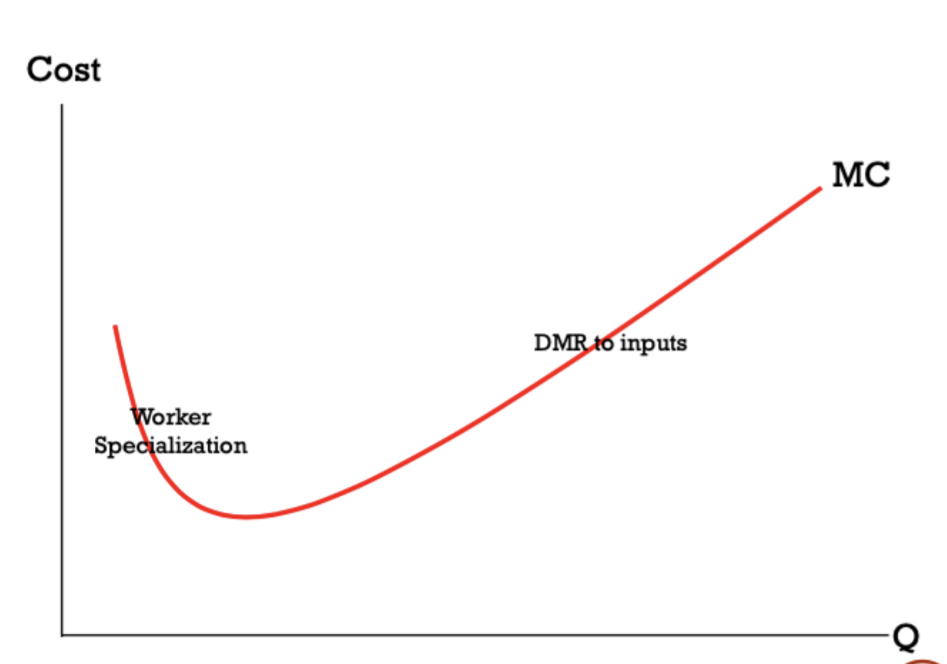
what is the exception to diminishing marginal returns?
worker specialisation
as soon as a 2nd person is employed, each can perform specialised tasks
at first, adding workers increases efficiency; when everyone is fully specialised, then DMR kicks in
how do we graph marginal costs taking into account worker specialisation?
MC is first downward sloping
eventually slopes upwards as everyone is specialised
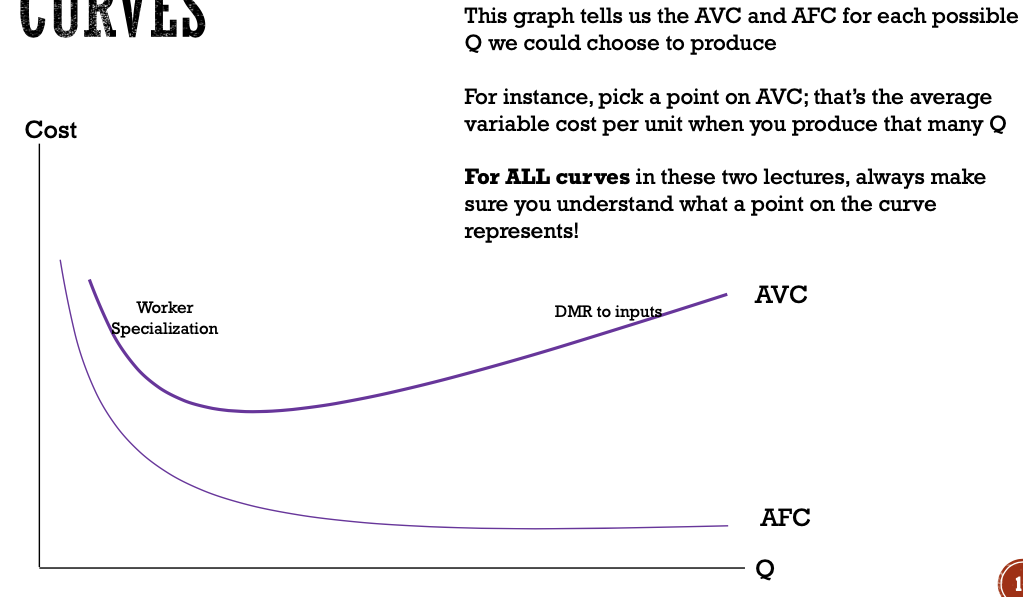
how do we calculate average total cost (ATC)?
total cost / quantity
ATC = average variable costs + average fixed costs
how do we graph average variable costs (AVC) & average fixed costs (AFC)?
AVC is initially downward sloping due to worker specialisation, then upward due to DMR to inputs
AFC is decreasing with respect to Q, since TFC is constant
how do we get the ATC curve from the AVC & AFC curves?
add them together
how does ATC look compared to Q?
at low Q, AFC dominates and ATC decreases when Q increases
at high Q, AVC dominates and ATC increases when Q increases
this leads to an ATC curve that is first decreasing at low Q and then increasing
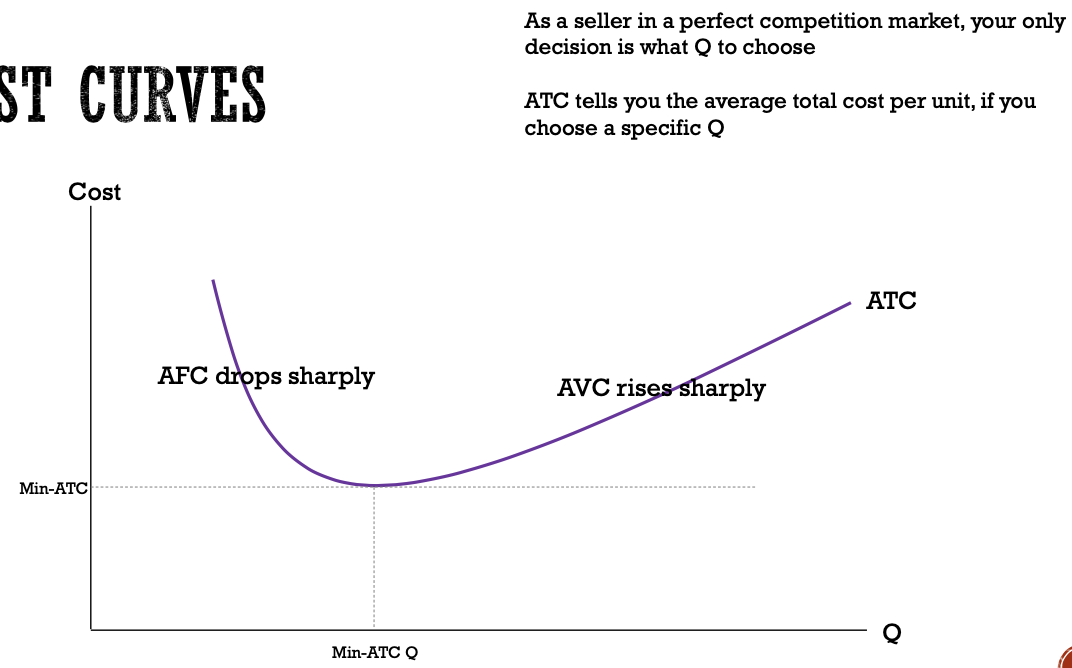
what does the minimum on the ATC curve represent?
this is the min-ATC quantity where the firm can produce each unit for the minimum possible ATC
this is the minimum-cost output where MC = ATC
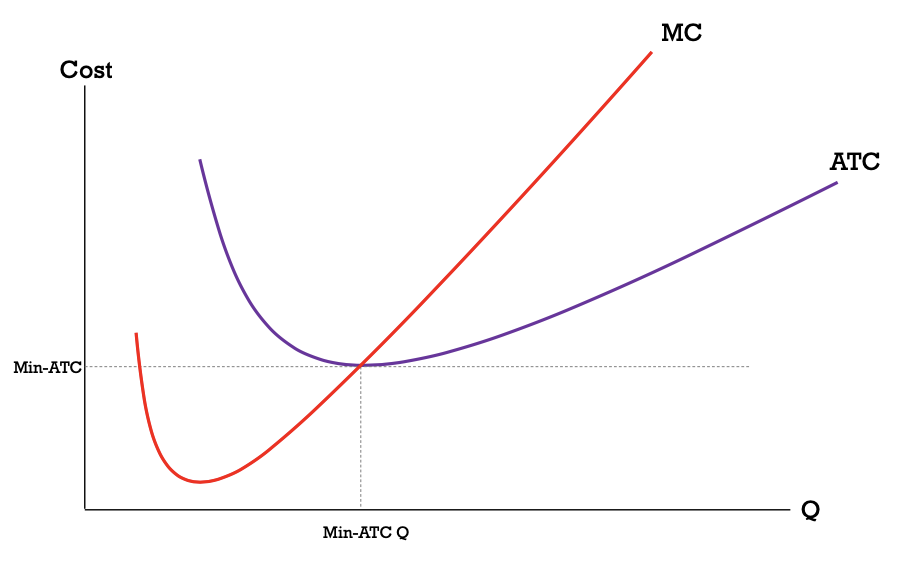
what does the minimum on the AVC curve represent?
the AVC curve intersects which MC at its local minimum
this is the min quantity at which the firm can produce for the least possible AVC
how do we calculate profits?
profits = revenue - costs
total revenue = P x Q
what are explicit costs?
accounting costs
eg. out of pocket payments such as wages
what are implicit costs?
opportunity costs
eg. what else could you have bought such as forgone wages when you are self-employed
cost curves include implicit costs to get overall economic profit
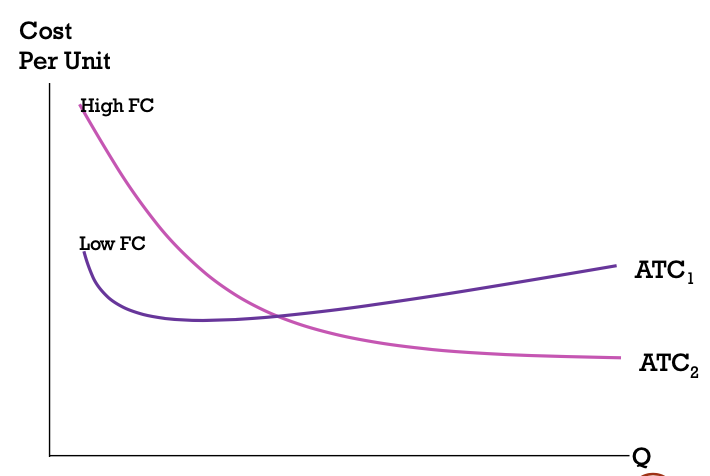
in the long run, what does a cost curve look like with a high FC compared to a low FC?
in the short run, FC cannot be changed
in the long run, choose the best FC investment for your expected Q
in this example, overall ATC is less if you invest in a high FC