Digestive system
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Structure of digestive system
Made of the gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs
Accessory organs
Salivary glands, Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas
Function of digestive system
Chemical and mechanical digestion/breakdown of food → turning food into small, usable molecules that can be absorbed and used in the body for different purposes
Mechanical procceses
Chewing, churning, peristalsis
Chemical processes
Acids
Enzymes:
- Pepsin (Proteins)
- Amylase (Carbs),
- Lipase (Lipids),
- Proteases (Proteins),
- Bile (Lipids)
Stages of food (order)
Bolus, chyme, feces
Salivary glands
Produces saliva, contains amylase (break down carbs), moistens food
Esophagus function
Transports bolus and liquid from pharynx to stomach
Performs peristalsis
Esophagus structure
Upper and lower sphincters
Peristalsis (esophagus)
Coordinated smooth muscle contractions that are wave-like. These contractions move bolus down the esophagus
Upper Sphincter
Protects bolus from entering the windpipe
Dysphagia
Can't swallow properly because upper sphincter isn't working properly
Lower sphincter
Protects upper digestive tract from blocking stomach acid from moving upwards
Acid reflux
Lower sphincter not working properly, acid goes back into esophagus
GERD
Lower sphincter not working properly, acid goes back into esophagus
Stomach functions
Mechanical digestion, chemical digestion
Pyloric sphincter
Smooth muscle in stomach that moves chyme into small intestine
Mechanical digestion
Smooth muscle of the stomach contracts to physically mix bolus with gastric juices (churning) → Chyme
Chemical digestion
Secretes hydrochloric acid and enzymes to break down food
Main enzymes: Pepsin (proteins) & Gastric Lipase (lipids)
Small intestine function
The body’s primary nutrient absorber, absorbing around 90% of the nutrients the body uses!
high surface area = more absorption Small intestine averages around 22ft long
Small intestine parts
Duodenum, jejunum, ileum
Duodenum
Receives chyme from stomach, neutralizes stomach acid, breaks
down chyme using enzymes such as bile
Jejunum
main site of absorption
a. Amino acids & sugars → bloodstream
b. Fatty acids → lymphatic system
ileum
absorbs vitamin B12 and bile, moves chyme to large intestine
Peristalsis (Small Intestine)
Moves chyme down the three segments of the small intestine
Rectum function
Stores feces, when full, it triggers your brain to tell you to use the bathroom
Last minute water absorption
Anus function
Internal (involuntary sphincter) opens when rectum is full
- external sphincter (voluntary) opens to release feces when you choose to
Salivary Glands
Produce saliva with enzymes, chemical breakdown
Liver
Production of bile, absorption of nutrients, detoxifies by filtering blood from small intestine
Gallbladder
Stores bile from liver, moves into small intestine (duodenum) during digestion of fatty foods
Pancreas
Produce amylase, lipase, proteases → moves through pancreatic duct and into small intestine (duodenum), neutralizes stomach acid, connects digestive system to endocrine system
Importance of Water
Prevent constipation (breaks down fibers)
Water is fuel for your body
Supports your digestive system to work
to its full potential
Celiac disease
An autoimmune condition triggered by gluten; small intestine; prevents nutrient absorption
Diverticulosis
Small pouches in the colon; often no symptoms
Crohn’s Disease
A type of inflammatory bowel disease
GERD
Chronic acid reflux
Gallbladder Disease
Often related to gallstones or inflammation
Glycolysis In/Out
Input:
Glucose
2 ATP
2 NAD+
2 ADP+Pi
Output:
2 Pyruvate
4 ATP
2 NADH
2 H2O
NAD+ Regeneration
In:
2 NADH
2 Pyruvate
Out:
2 NAD+
2 Lactate/Ethanol + CO2
Pyruvate Oxidation In/Out
In:
2 Pyruvate
Coenzyme A
NAD+
Out:
2 Acetyl-CoA
2 CO2
2 NADH
Krebs Cycle
In:
Acetyl-CoA
NAD+
FAD
ADP+Pi
Carbon MQs
Out:
4 CO2
6 NADH
2 FADH2
2 ATP
Oxidative Phosphorylation In/Out
Input:
NADH
FADH2
ADP + Pi
O2
Output:
34 ATP
H2O
Heat
NAD+
FAD
Cellular respiration stages + Location
Glycolysis - cytoplasm
Pyruvate Oxidation - mitochondrial matrix
Krebs Cycle - mitochondiral matrix
Oxidative Phosphorylation - inner mitochondrial membrane
Glycolysis purpose
Glucose is broken down into pyruvate so it can be used inside of the mitochondria
Pyruvate oxidation purpose
Pyruvate made by glycolysis is converted to Acetyl-CoA to it can be used during Krebs cycle
Krebs Cycle purpose
Finishes breaking down glucose/pyruvate to produce high amounts of electron carriers for OP
Oxidative Phosphorylation purpose
Electrons create a H+ gradient along the inner membrane. This powers secondary active molecular transport of H+ ions through a transport protein called ATP Synthase
H+ ions => ATP.
Aerobic vs Anaerobic
Aerobic = needs oxygen; cellular respiration
Anaerobic = no need oxygen; Fermentation
Oxygen as final electron acceptor
While H+ ions move through ATP synthase, an oxygen atoms bonds with a H+ ion to create water, allowing the process to continue.
Celluar repiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 = 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP
ATP-ADP Cycle
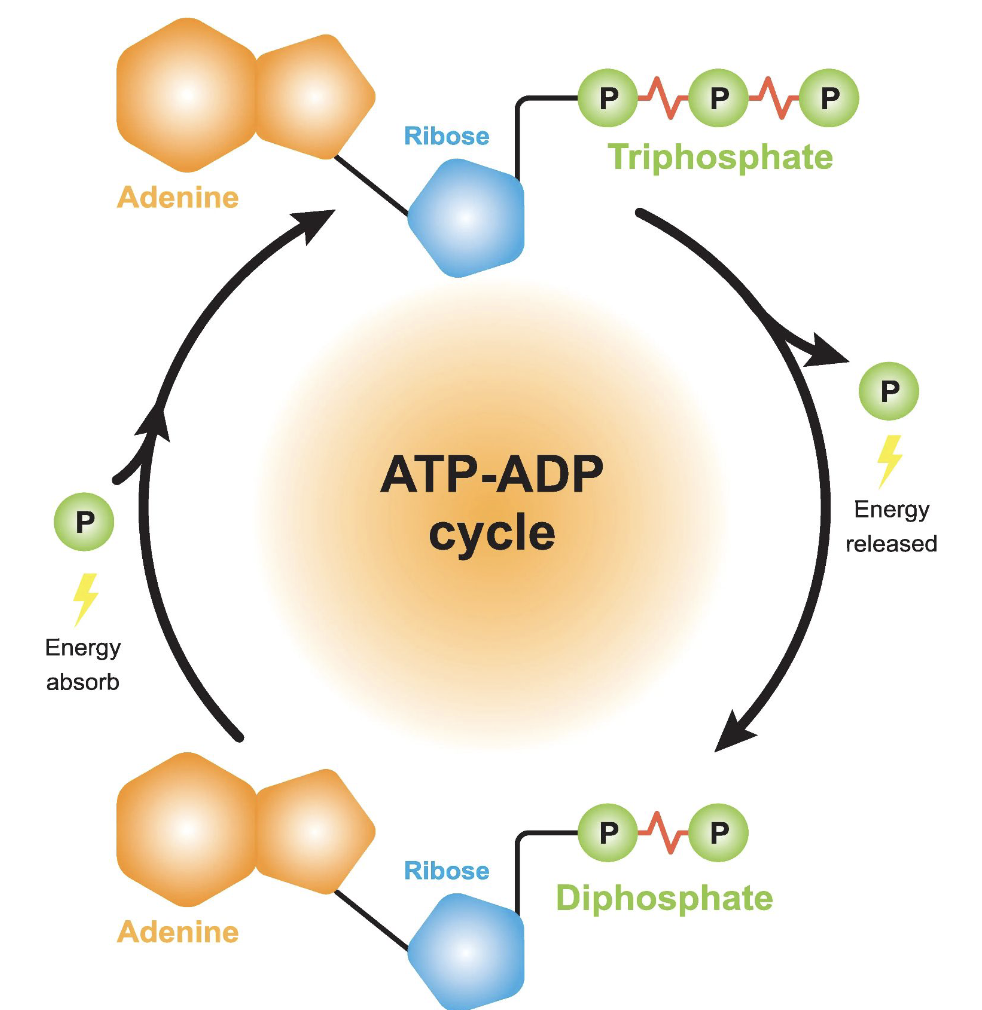
General function of the electron transfer chain
Generate an electrochemical proton gradient across the membrane
anaerobic respiration examples
- Bacteria
- Archaea
- Yeast (fungus)
- Muscle Tissue
Purpose of Fermentation
Fermentation is used to survive during times with little to no oxygen
Fermentation processes
Glycolysis, NAD+ Regeneration