Final Exam: Cardiology full
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
what is the #1 cause of death in the US?
CAD
what is chest pain at rest also known as?
unstable angina
which demographic is variant (prinzmetal) angina most common in?
young females
what are the types of acute coronary syndrome?
unstable angina, NSTEMI, STEMI
what clinical manifestations are required for dx of MI?
2/3 of the following:
1. ACS chest pain
2. EKG injury/infarct
3. increased heart enzymes
STEMI vs. NSTEMI: full-thickness necrosis?
STEMI → transmural
STEMI vs. NSTEMI: partial thickness necrosis?
NSTEMI → non-transmural
What is the first line of treatment for STEMI?
PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention)
Must happen within 90 minutes of onset
if PCI is unavailable, what is the next line of treatment for STEMI?
fibrinolytics
door to needle within 30 mins
are fibrinolytics used in NSTEMI?
NO!
which anticoag is preferred for NSTEMI?
lovenox (enoxaparin)
which anticoag is preferred for STEMI?
heparin
What is the TIMI score?
used to determine the likelihood of ischemic events in UA/NSTEMI
Score > or = 3 is high risk and should be treated aggressively
what is the treatment for NSTEMI/UA with TIMI >5-7?
PCI
if PCI is contraindicated in STEMI pts, what should be done?
CABG
what is the diagnosis if EKG shows T wave inversion and reciprocal ST depression?
NSTEMI
what should not be used in drug-induced MI?
B-blockers → could cause coronary vasospams
when should drug-induced MIs be treated like a STEMI?
if there is change on EKG
what drug should always be given to pts presenting with chest pain?
aspirin or clopidogrel
Which Killip Classification:
No evidence of heart failure
class 1
Which Killip Classification:
rales, crackles, S3, JVD?
class 2
Which Killip Classification:
Cardiogenic shock, SBP <90, low CO
Class 4
Which Killip Classification:
acute pulm edema
class 3
a patient who recently had an MI presents with complains of chest pain that is worse when laying flat, better sitting upright. EKG shows diffuse ST changes in all leads. what is the treatment?
dresslers syndrome (Post MI pericarditis) → colchicine and NSAIDs
what should a stress test never be used for?
unstable angina
acute MI
severe AS
what are absolute contraindications for thrombolytics?
1. any prior brain bleed
2. known cerebral vascular lesion
3. known brain tumor
4. ischemic stroke within last 3 months
5. suspected aortic dissection
6. active bleed
7. significant closed head/facial injury within 3 months
which drugs are always given following acute MI?
1. aspirin for life
2. DAPT/ASA+P2y12 (aspirin or clopidogrel) if stent
3. BB (at least 6 months)
4. ACEI (at least 3 months)
5. statins
which type of HF is characterized by inability to pump?
systolic → HFrEF
which type of HF is characterized by inability to fill?
diastolic → HFpEF
what is the treatment regimen for acute HFrEF?
LMNOP:
Lasix
Morphine
Nitrate
Oxygen
Position (upright)
what is the treatment regimen for chronic HFrEF?
fantastic 4:
1. MRA (spironolactone)
2. BB (only in stable HF) metoprolol
3. ARNI/ACEI/ARB
4. SGLT2 inhibitors
Ascites is a symptom of left or right heart failure?
right
heart failure classifications and HF symptoms are on cardio E1 pt. 1 quizlet
:)
what is the MC type of cardiomyopathy? what are the risk factors/causes?
dilated → CAD/HTN, alcoholism, peripartum, idiopathic
is the EF high or low in dilated CM?
low
which CM shows 4 chamber enlargement with diffusely decreased contraction on echo?
dilated CM
which type of CM has systolic dysfunction d/t weak ventricular contraction and thin ventricles?
dilated CM
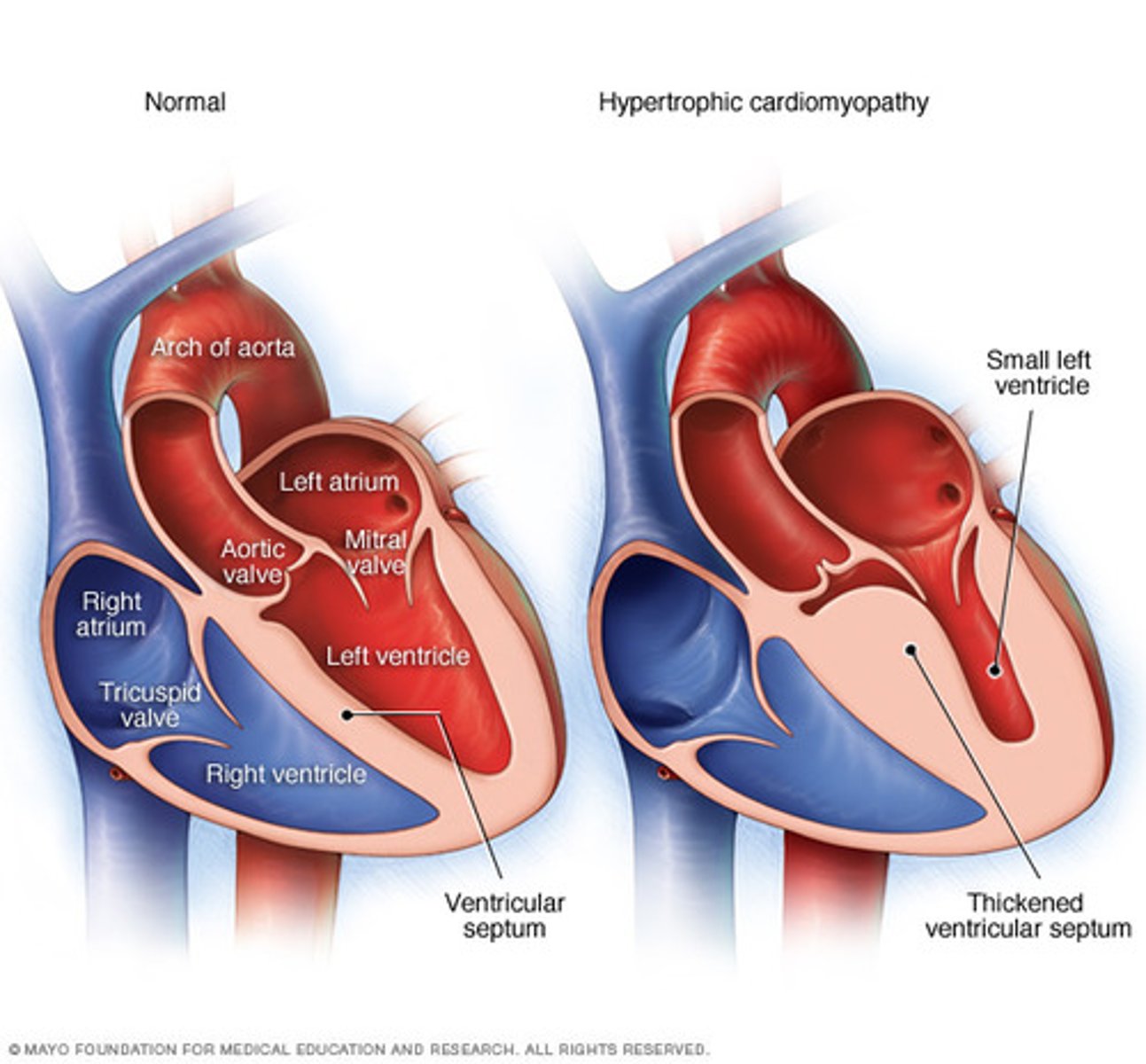
which type of CM has diasoltic dysfunction d/t LVH?
HOCM
is EF low in HOCM?
no its high or normal
what is the treatment for HOCM?
Beta blockers and CCBs
what does an echo in HOCM show?
small LV chamber
which CM shows dagger-like Q waves and LVH on EKG?
HOCM
which type of CM has diastolic dysfunction caused by decreased compliance d/t infiltrative processes in ventricles?
restrictive
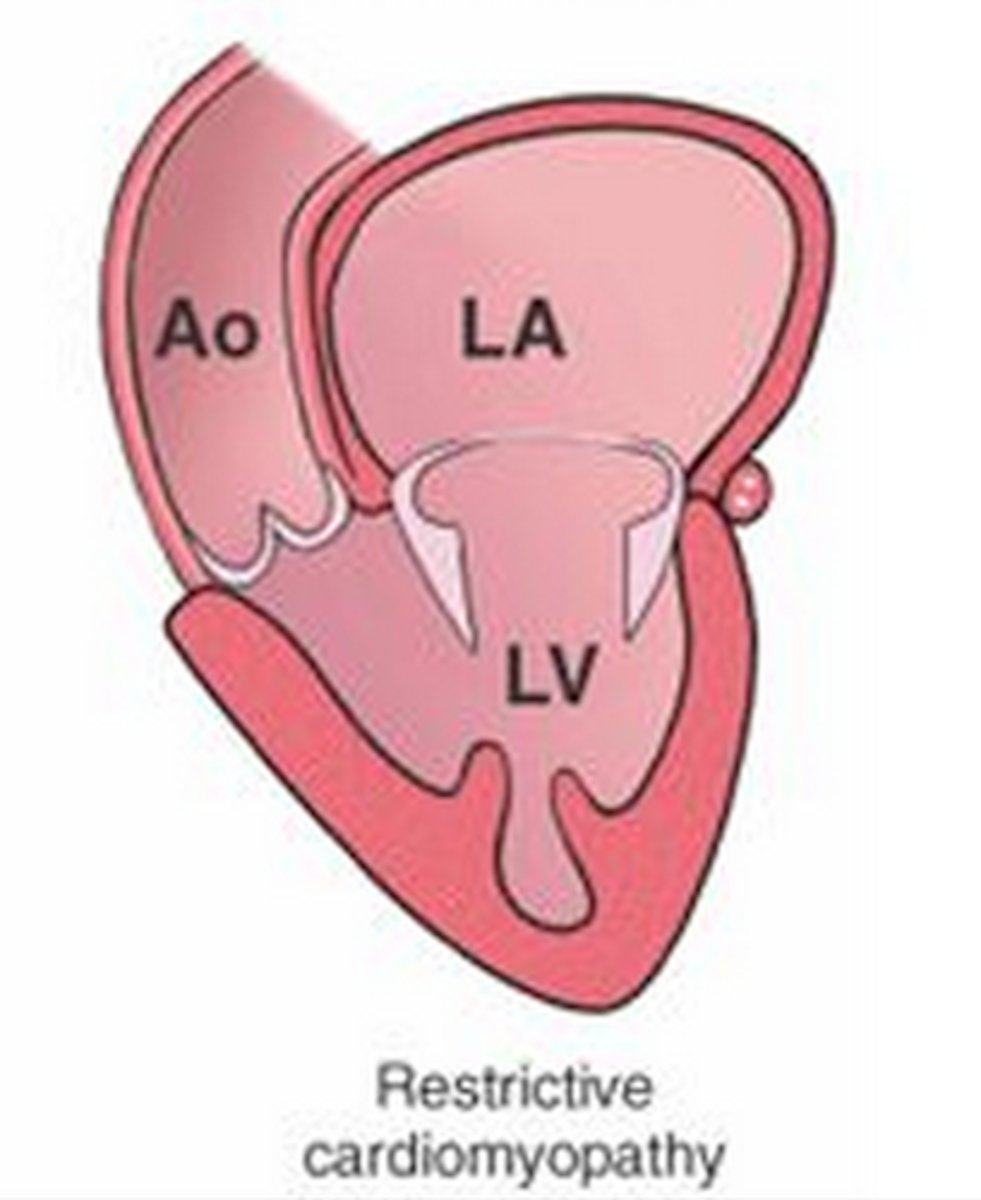
which type of CM shows atrial enlargement?
restrictive
which cause of restrictive CM shows glistening pattern on echo?
amyloidosis
which type of CM shows apical ballooning?
Takotsubo → broken heart syndrome
a patient presents with pleuritic chest pain that improves when leaning forward. on PE, you auscultate a continuous friction rub. what is the etiology?
pericarditis → coxsackie
what is the gold standard for diagnosis of pericarditis?
2D TTE
what is the first line of treatment for pericarditis?
NSAIDs and colchicine
what would you expect to seen on CXR in pericarditis?
water bottle silhouette
what is beck's triad and what is it associated with?
beck's triad:
1. JVD
2. hypotension
3. muffled heart sounds
associated with cardiac tamponade
if a patient with muffled heart sounds and hypotension is found to have pulsus paradoxus or kussmaul's sign, what is the treatment?
cardiac tamponade → medical emergency → pericardiocentesis
Which diagnosis is suggested by electrical alternans on EKG?
pericardial effusion
a patient with history of breast cancer treated with RT presents with fatigue, DOE and JVD. what do you expect to find on CXR?
large calcified fibrotic ring → constrictive pericarditis
what are the risk factors for constrictive pericarditis?
radiation
infection
cancer
cardiac sx
what is the first line of treatment for acute constrictive pericarditis?
NSAIDs and colchicine if hemodynamically stable
if unstable → immediate pericardiectomy
what is the treatment for late (chronic) constrictive pericarditis?
pericardiectomy
what is the viral etiology of myocarditis?
coxsackie virus
what is the gold standard for dx of myocarditis?
endomyocardial biopsy
what test should be done if myocarditis is suspected?
echo
what is the first line of treatment for myocarditis?
NSAIDs or ASA + colchicine
what is the treatment for peripartum myocarditis?
IVIG
what is the gold standard for dx of pulmonary HTN?
right heart cath
what should be given first to all pulm HTN patients?
CCBs
what size of abdominal aortic aneurysm has an increased risk of rupture and should be surgically treated?
5.5 cm or greater
who needs to get annual US to rule out AAA?
males aged 65-75 with hx of smoking
what is cardarelli's sign?
abnormal pulsations of trachea associated with AAA
which type of Aortic aneurysm is more likely to rupture?
saccular
a 70 year old male presents with complaints of severe abdominal pain that radiates to his back. he has a 20 pack year history. what diagnostic study should be performed?
CTA!
gold standard for AAA
what are the risk factors for aortic aneurysms?
CAD and HTN
old male smokers
hypercholesterolemia
PVD/elevated CRP
68 year old male smoker presents with tearing back back and cough. you auscultate a loud systolic murmur at the mid thoracic region. what would you expect to seen on CXR?
thoracic AA → widened mediastinal silhouette, enlarged aortic knob, displaced trachea
what is the cause of tearing chest pain in aortic dissection?
intimal tear of aorta causes blood flow to rip layers of the aorta apart → false lumen
where is the dissection located if the patient has anterior chest pain?
ascending aorta
where is the dissection located if the patient has interscapular pain?
descending aorta
what are the classifications for aortic dissection?
deBakey and Stanford **
what is the gold standard for dx of aortic dissection?
CTA
notice the trend of CTA being used for aortic stuff!!
what is the first line of therapy for aortic dissection?
B-blockers
what are risk factors for PAD?
smoking, diabetes, age
venous or arterial disease: absent pulses?
arterial
venous or arterial disease: claudication?
arterial
ABI: Classification of PAD Severity
- 1-1.4 = normal
-0.8-1 = mild PAD
- 0.5-0.8 = Moderate PAD
- < 0.5 = Severe PAD
arterial or venous disease: alopecia?
arterial
what is important management of PAD?
supervised exercise to increase circulation
+ aspirin/clopidogrel
what are the 6 Ps of acute ischemia?
Pain
Pallor
Pulselessness
Paresthesias
Poikilothermia
Paralysis
what is non-atheromatous intense inflammation followed by arterial/venous occlusive disease?
Thromboangitis obliterans (Buerger's disease)
who is at risk for Buerger's disease?
Smokers!!! Stop smoking to treat. esp. male smokers
what is the first line therapy for Raynaud's?
CCB
what diagnosis has a fishnet pattern on extremities and trunk?
livedo reticularis
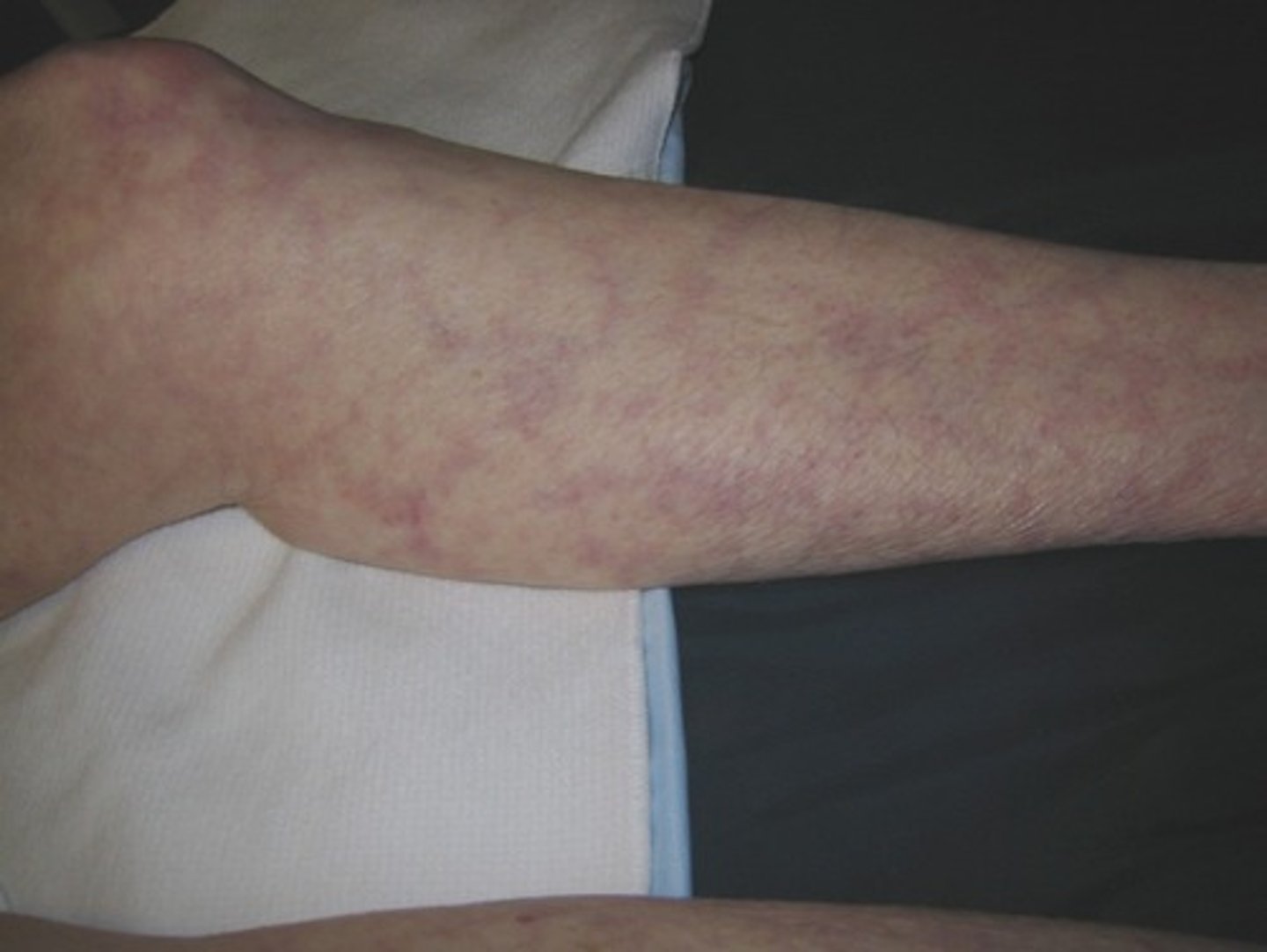
arterial or venous disease: medial ulcers?
venous
arterial or venous disease: varicose veins?
venous
what is the first line treatment for varicose veins?
NSAIDs
arterial or venous disease: lateral ankle/dorsal foot ulcers?
arterial
if a patient with PAD has pain at the buttock/hip, which artery is affected?
aortoiliac
if a patient with PAD has pain at the thigh, which artery is affected?
common femoral or aortoiliac
arterial or venous disease: cold extremities?
arterial → "punched out" ulcers
if a patient with PAD has pain at the upper calf or lower calf, which arteries are affected?
upper = superficial femoral
lower = popliteal
if a patient with PAD has pain in their foot, which arteries are affected?
tibial or peroneal
what is atropine used to treat?
sinus bradycardia
which drugs are contraindicated for WPW?
BB, CCB, adenosine, digoxin → slows down AV/SA and makes WPW worse
what is the treatment for acute unstable WPW?
synchronized cardioversion