432 Exam 3
1/462
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
463 Terms
What is an anomeric carbon?
A carbon that has two forms (anomers). During cyclization, the carbon can change chirality into alpha and beta anomers. Cyclization occurs when the hetero oxygen is protonated and the ring is broken. The reformation of the ring is where the anomers appear.
What is a reducing sugar?
A linear sugar with an aldehyde (C(O)H) that can be oxidized to carboxylic acids (COOH). Aldehydes are good electrophiles and can be oxidized (gain/accept electrons). The sugar is not reduced, the sugar is the reducing agent.
What is a pyranose sugar?
A sugar with a 6-membered ring
What is a furanose sugar?
A sugar with a 5-membered ring
What is the number assigned to an anomeric carbon?
1
What monosaccharides is maltose composed of and what is its linkage?
2 Glucose; α-1,4
What monosaccharides is sucrose composed of and what is its linkage?
1 glucose and 1 fructose; α-1,β-2
What monosaccharides is lactose composed of and what is its linkage?
1 galactose and 1 glucose; β-1,4
How are anomeric bonds named (α/β)?
Named based on hydroxyl orientation. β=up; α=down
In SNFG, what does a blue circle represent?
Glucose
In SNFG, what does a yellow circle represent?
Galactose
In SNFG, what does a green pentagon represent?
Fructose
What kind of bonds does glycogen and starch have?
Linear alpha-1,4 bonds and branching alpha-1,6 bonds
How is glucose chemically stored?
Covalently bonds to protein glycogenin
What is cellulose?
Linear chains of glucose with beta-1,4 linkage
Why can’t humans digest cellulose?
Cellulose is made of beta-1,4 glucose linkages. Humans don’t have beta-1,4-glucanases, or cellulase
What are glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)?
Repeated linear disaccharide units with an amino sugar and uronic acid.
What is hyaluronic acid degraded by?
Hyaluronidase
What is the function of chondroitin sulfate?
Cartilage structure/function
Joint shock absorption
Connective tissue
What is the function of hylauronic acid?
Extracellular matrix
Vitreous humor of eye
Joint lubrication
Dermis
What is the function of heparin?
Help mast cells store histamine
Cell adhesion
Bind to positively charged molecules
Help growth factors bind or inactivates them until heparin is degraded
What charge does heparin have and why?
Strongly negatively charged due to sulfation
What is antithrombin-binding pentasaccharide?
A deviation of herapin’s regular sugar sequence. 30% of heparin molecules contain one of these. It activates antithrombin III which inhibits clotting Factor Xa.
What is the function of antithrombin-binding pentasaccharide?
Activates antithrombin III to inhibit clotting factor IIa. This is due to clotting factor IIa needing heparin to bind to ATIII and thrombin, resulting in an anticoagulant effect
How do ketone bodies lead to coma and death?
Increase blood pH which inhibits the binding of O2 to hemoglobin
What is a lipid?
A hydrophobic molecule with a high ratio of C/H to heteroatoms
What is the main function of lipids?
Energy storage
Reduced compounds undergo oxidation
Hydrophobic = condensed packing
Insulation
Low thermal conductivity and high heat capacity
Shock absorption
Membranes, Enzyme cofactors, Hormones, Pigmentation
What does it mean when a molecule is highly reduced?
Each atom in its structure can undergo more individual oxidation steps
Other than hydrophobicity, why is it more efficient to store energy as lipids/fatty acids as opposed to glucose?
For every carbon atom in a fatty acid, we get out more ATP molecules than the carbon atoms in glucose. This is because fatty acids are more reduced (have less C-O bonds)
Why are organs covered in a layer of fat?
To protect them from trauma by absorbing kinetic energy
What is a complex lipid?
A lipid containing a fatty acid; a long chain of C/H
What are the 2 classes of lipids?
Those not based on fatty acids
Those containing fatty acids (complex lipids)
What are the 2 classes of complex lipids?
Storage lipids (neutral)
Membrane lipids (polar)
Why are membrane lipids polar?
Part of them need to be in contact with water
What are the classes of membrane lipids?
Phospholipids
Glycolipid
Archaeal ether lipids
What are the classes of phospholipids?
Glycerophospholipids
Sphingolipids
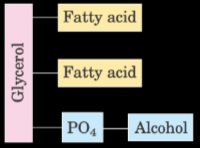
What is the structure of glycerophospholid?
2 fatty acids and PO4-alcohol bound by glycerol
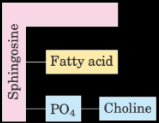
What is the structure of a phospholipid sphingolipid?
1 fatty acid and PO4-alcohol bound by sphingosine
What are the classes of glycolipids?
Sphingolipids
Galactolipids
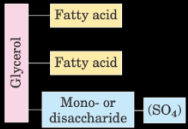
What is the structure of galactolipids or sulfolipids?
2 fatty acids and a mono/disaccharide or SO4 bound by glycerol
What does saturated mean?
No double bonds; max amount of hydrogen bonded to each carbon
What is a monounsaturated fatty acid?
A fatty acid that has 1 double bond
What conformation of double bonds do most natural unsaturated fatty acids have?
Cis
What are polyunsaturated fatty acids?
Fatty acids with 2 or more double bonds
How are fatty acids named?
X:Y(Δq,r,s) n-Zanoic acid
n = normal form (no branching)
Z = nomenclature for number of carbons
X:Y = X carbons and Y double bonds
q,r,s = the numbers of the lowest carbon of the double bond
Deprotonated ends in -ate
Omega is numbered in reverse direction
What is the trend between melting point and carbon chain length?
Melting point increases with carbon chain length
What is the trend between solubility and length of the carbon chain?
Solubility increases with carbon chain length
Between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, which has a higher melting point and why?
Saturated fatty acids have higher melting points because they can be packed tighter which increases the energy needed to melt; unsaturated fatty acids are bent due to the double bond and are less efficiently packed
What type of lipid determines your blood type?
Glycosphingolipids
What are glycosyltransferaes
Transfer glycogroups to sphingolipids
If you have no glycosyltransferases what is your blo0d type
Type O
If you have glycosyltransferases for N-acetyl-galactosamine what is your blood type and what antibodies do you have?
Type A; Type B antibodies
What are the classes of eicosanoids
Prostaglandins
Thromboxanes
Leukotrienes
What is the function of prostaglandins?
Induction of Inflammation and fever
What is the function of leukotrienes?
Smooth muscle contraction in lungs
Why do eicosanoids have similar structures?
They all have arachidonate as a precursor
Cyclooxygenases 1 and 2 make which eicosanoids?
Prostaglandins and thromboxanes
How do NSAIDs affect the production of prostaglandins and thromboxanes?
NSAIDs inhibit COX 1 and 2 which are the enzymes used to produce prostaglandins and thromboxanes
How is asthma treated in relation to leukotrienes?
Inhibition of leukotriene receptors induces smooth muscle relaxation in the lungs
Is glycolysis catabolism or anabolism?
Catabolism
Is gluconeogenesis catabolism or anabolism?
Anabolism
What is anabolism?
The use of energy to build complex molecules
What is catabolism?
The break down molecules for energy
What are the reactants and products used in gluconeogenesis?
2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 GTP + 2 NADH —> glucose
When do we perform gluconeogenesis?
When we have excess energy; uses more energy than is put out
Why is ATP used for energy
Thermodynamically stable
phosphates can activate other molecules
Provides right amount of energy to drive reactions
Is Pi and ADP or ATP more stable
Pi and ADP
What are the products of the Krebs cycle?
3 NADH
FADH2
GTP
2 CO2
What is the input for the Krebs/Citric acid cycle?
Acetyl-CoA
How does glucose become acetyl-CoA?
Glucose undergoes glycolysis to become pyruvate which is oxidized into Acetyl-CoA
What compartment does glycolysis take place in?
Cytoplasm
In what tissues does glycolysis take place in?
All tissues
Why does the brain, heart, and muscle tissues have an ATP buffer?
Constantly need ATP in case it gets too low because it cannot be created instantaneously
Glycogen is broken down into what molecule?
Glucose
Glycogen is synthesized from what molecule?
Glucose
What is the function of F26BP?
Stimulates PFK-1 and inhibits FBPase-1
What are the reactants of fatty acid biosynthesis?
1 acetyl-CoA + 7 malonyl-CoA
What tags proteins to be degraded by a proteasome?
The ubiquitin chain
Where does step 1 of the urea cycle occur?
The mitochondria
Where does steps 2-5 of the urea cycle occur?
The cytoplasm
11/14 after this card clinical nutrition
What are the primary goals of nutritional care in the inpatient setting
Reaction to the event and stabilization of the patient
What area the primary nutritional needs for patients
Energy: 25-35kcal/kg
Protein: 1/2-2 g/kg
Describe a cardiac diet
Low sodium (<2000 mg/day)
Low saturated fat
What is a renal diet?
Restricted in sodium, potassium, and phosphorus. Protein
may be restricted pre-dialysis or increased during dialysis
What is a consistent carbohydrate diet?
Provides a consistent amount of carbohydrates at each meal to manage blood glucose in patients with diabetes.
What conditions is a cardiac diet for
CHF and MI
Describe a dysphagia diet
Texture modified diet consisting of pureed or mechanically soft foods with thickened liquid
Who is a dysphagia diet for?
Patients with difficulty swallowing as determined by a speech-language pathologist (SLP)
What is enteral nutrition (EN)?
Tube feeding. Nutrients deliverd bia tube into stomach/small intestine
What is parenteral nutrition (PN)?
Nutrients are delivered directly into the blood via IV
Compare/contrast enteral and parenteral nutrition
Enteral
Maintains gut integrity
Safer
Less expensive
Parenteral
Last resort when GI non-functional
How is
How is type 2 diabetes in ambulatory care managed with medical nutrition therapy?
How is cardiovascular disease in ambulatory care amanged with medical nutrition therapy
How is obesity and weight in ambulatory care managed with medical nutrition therapy?
How are GI disorders in ambulatory care managed with medical nutrition therapy?
What are the key ambulatory interventions in nutritional care?
Education
Counseling and behavior change
Motivational interviewing
Goal setting
Addressing social determinants of health
What are the 3 pillars of nutritional needs
Energy
Protein
Fluid
What is the Mifflin-St Jeor Equation for men and women and what does it calculate?
Men: 10×weight (kg)+6.25×height (cm)−5×age (y)+5
Women: 10×weight (kg)+6.25×height (cm)−5×age (y)−161
Resting energy expenditure (REE)