Neurobiology of decision making 1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
How are decisions linked to memory?
Decisions we make are typically chosen from retrieving past experience from similar situation you have encountered before to inform current situation with what you've experienced in the past.
- informs future actions.
What is the prediction-Choice-Outcome loop? fellows (2018)
make predictions about different options of choices - informs decision which then leads to an action > outcome
- subconsciously monitor outcome from action compared to prediction - did it match your intent?
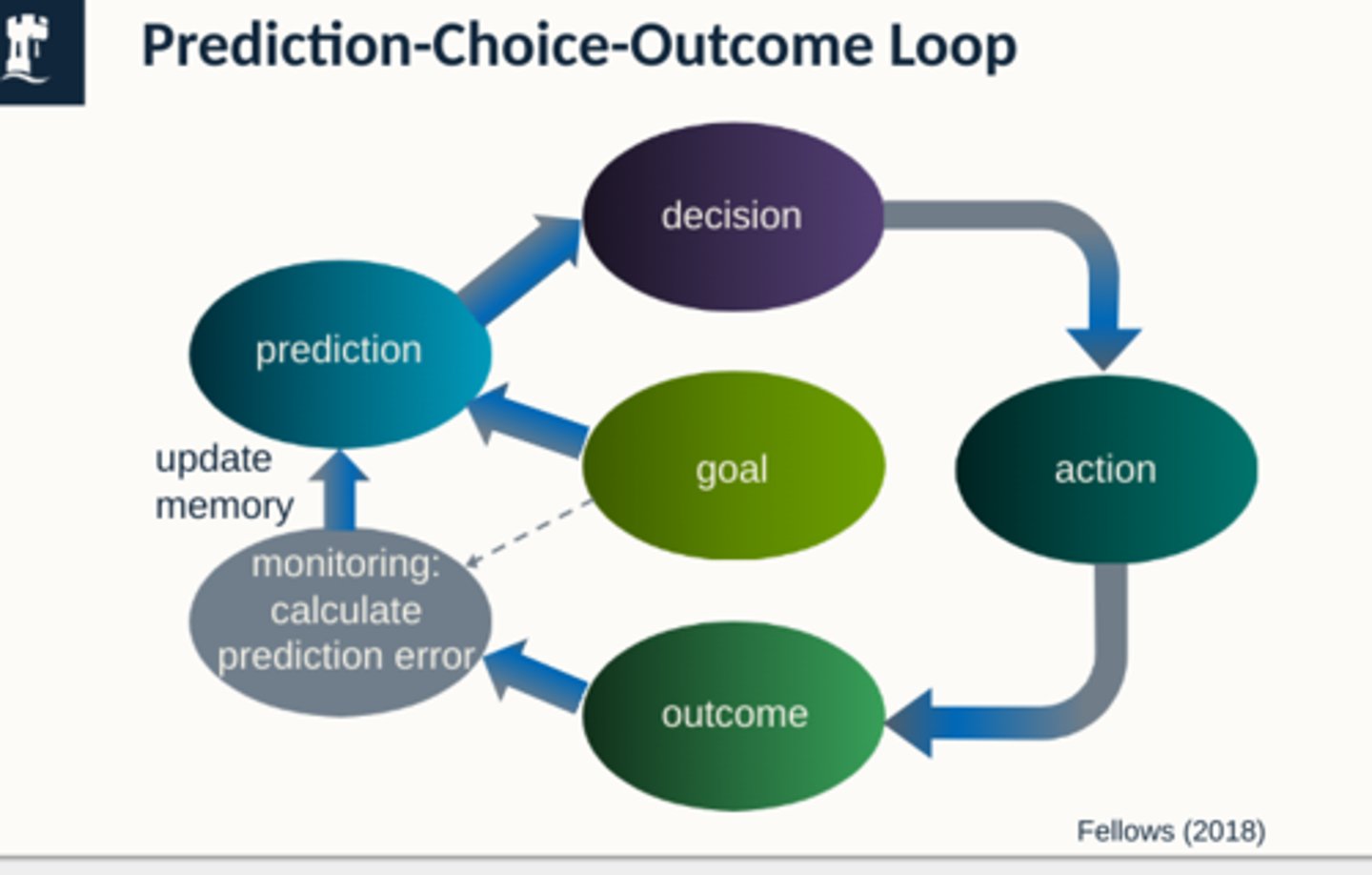
What is a prediction error?
A subconscious calculation of how much the outcome matched the intention
- if outcome is better/worse than expected you get a + or neg prediction error
- brain used this calculation to update memory to make more precise decisions in future
what are the general features that influence our decision making to optimize our decision making processes?
- tend to try to avoid harm
- minimise costs of time required
- effort and avoid missed opportunities
- MAXIMISE REWARD
How does effort required influence decision making?
people want minimal amount of effort required for maximum outcome (can be mental or physical)
How does probability of success/failure influence decision making?
likelihood reward intended is actually received
- what is the probability of failure?
What is how valuable a reward is perceived as be influenced by?
value of reward is modified by context in that particular moment
- e.g really want a pizza when hungry but may not want so much when on a diet (context!)
How does missed opportunities influence decision making?
if you decide to do something - automatically exclude alternative options
- makes decisions difficult depending on what the alternatives are
What are inherent biases in decision making that acts as a shortcut in decision making by default?
- people tend to stick with an option they have chosen before particularly when there is a large range of choices.
- temporal discounting
what is temporal discounting?
when people choose immediate small rewards over bigger future rewards e.g £20 now or £60 later.
- unless benefits are made explicit.
When do people take gambles?
when there are certain losses
when do people choose certain gains?
when the other option is a gamble
What two types of decision making processes are there?
1. Simple perceptual decisions
2. more complex decisions.
What is an example of a simple perceptual decision?
Perceptual decision task in rhesus monkeys (Hanks & Summerfield 2017)
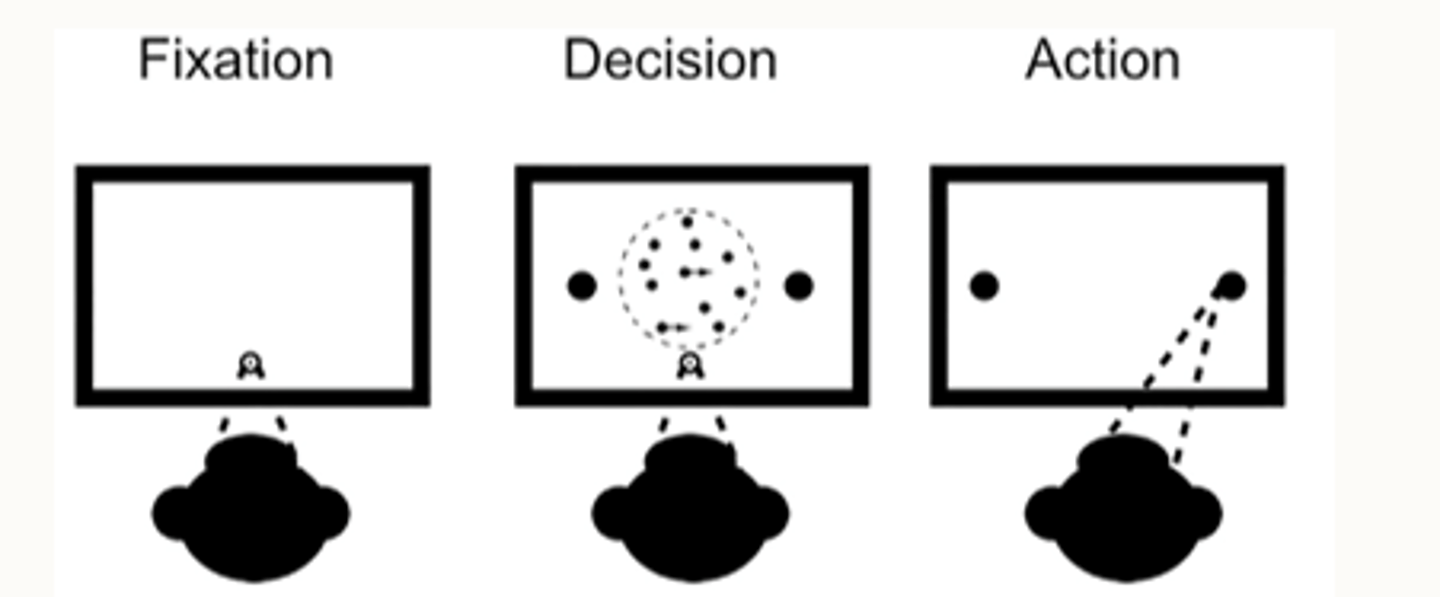
What did Hanks & Summerfield 2017 do in their study?
- monkey trained to focus on fixation cross
- % of dots moved coherently or randomly across screen
- had to decide whether dots were moving to left or right.
- noisy sensory signal accumulated is concerted into discrete motor act .
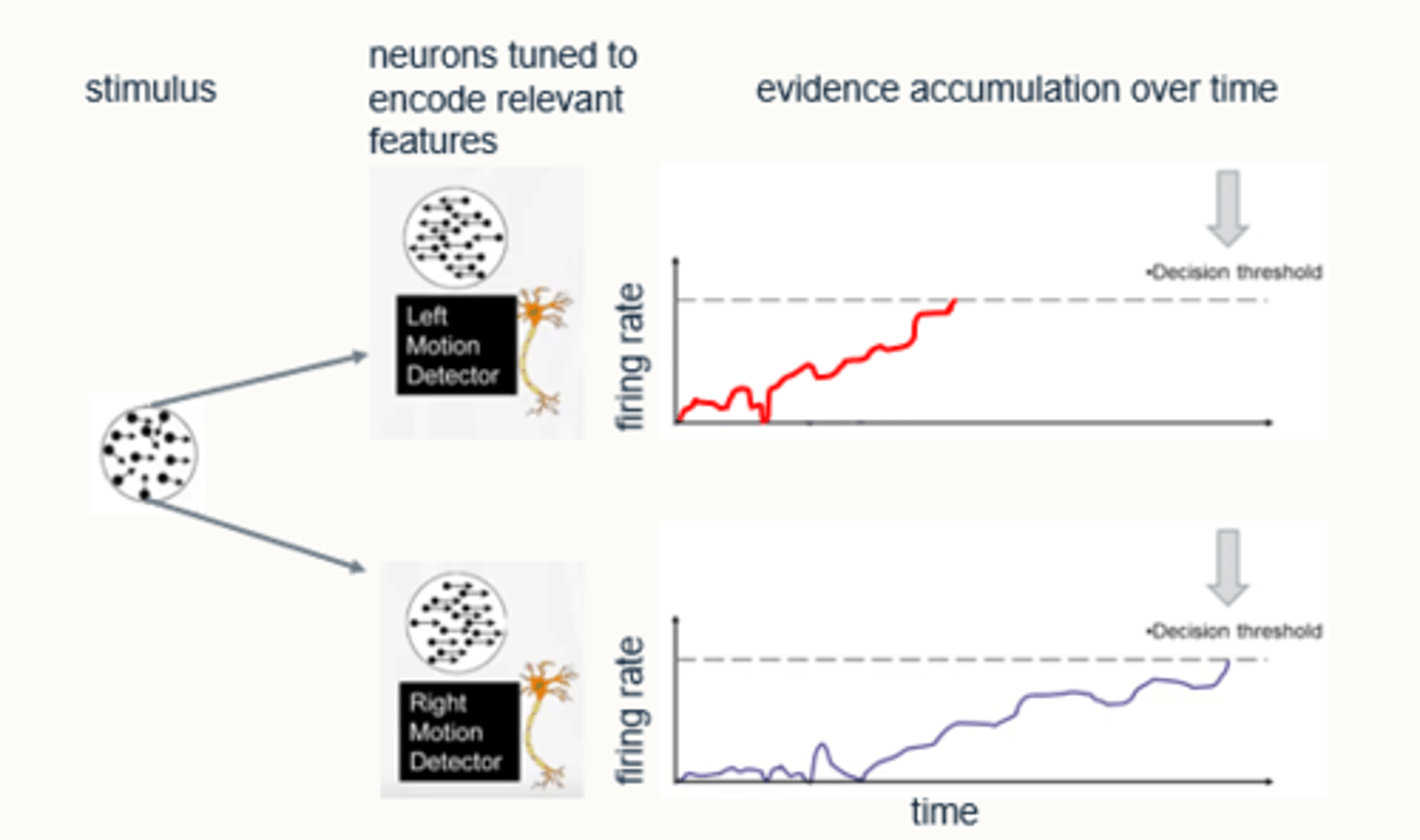
Neuronal evidence for simple decision making (Shadlen et al 1996)
Motion processes are activated and respond to left or right sided motion.
- evidence is being accumulated which increases firing rate the more input there is over time.
- threshold reached = decision made which results in an action.
- eye movement given as a response
What is the first stage of perceptual decision making?
1. detection of sensory evidence - what motion stimuli are there/alternatives
What is the second stage of perceptual decision making?
2. integration of evidence over time to inform decision - because evidence is noisy.
What is the third stage of perceptual decision making?
3. checking if the threshold has been reached
- appropriate action taken.
Where in the brain does evidence accumulation take place?
MT/V5 - responsible for encoding the relevant feature (motion detection)
Parietal and dorsal PFC - function not so clear
Sensorimotor areas - particular response actions (e.g hand) and evidence accumulation.
which model best describes evidence accumulation over time?
The Heterogenous model of memory - evidence is collectively encoded by groups of neurons that respond in diverse ways to new information.
What are mental maps in decision-making?
Complex decision making processes rely on internal models of the current task
- experiences are organised in internal models/mental maps
- maps adapt depending on context and experience
What are the historical roots of mental maps?
Edward Tolman's rat spatial maze.
- Rat had created a mentalrepresentation of the spatial dimensions of the maze (A and B are close together)
- encoding of transitive relations to build mental map.
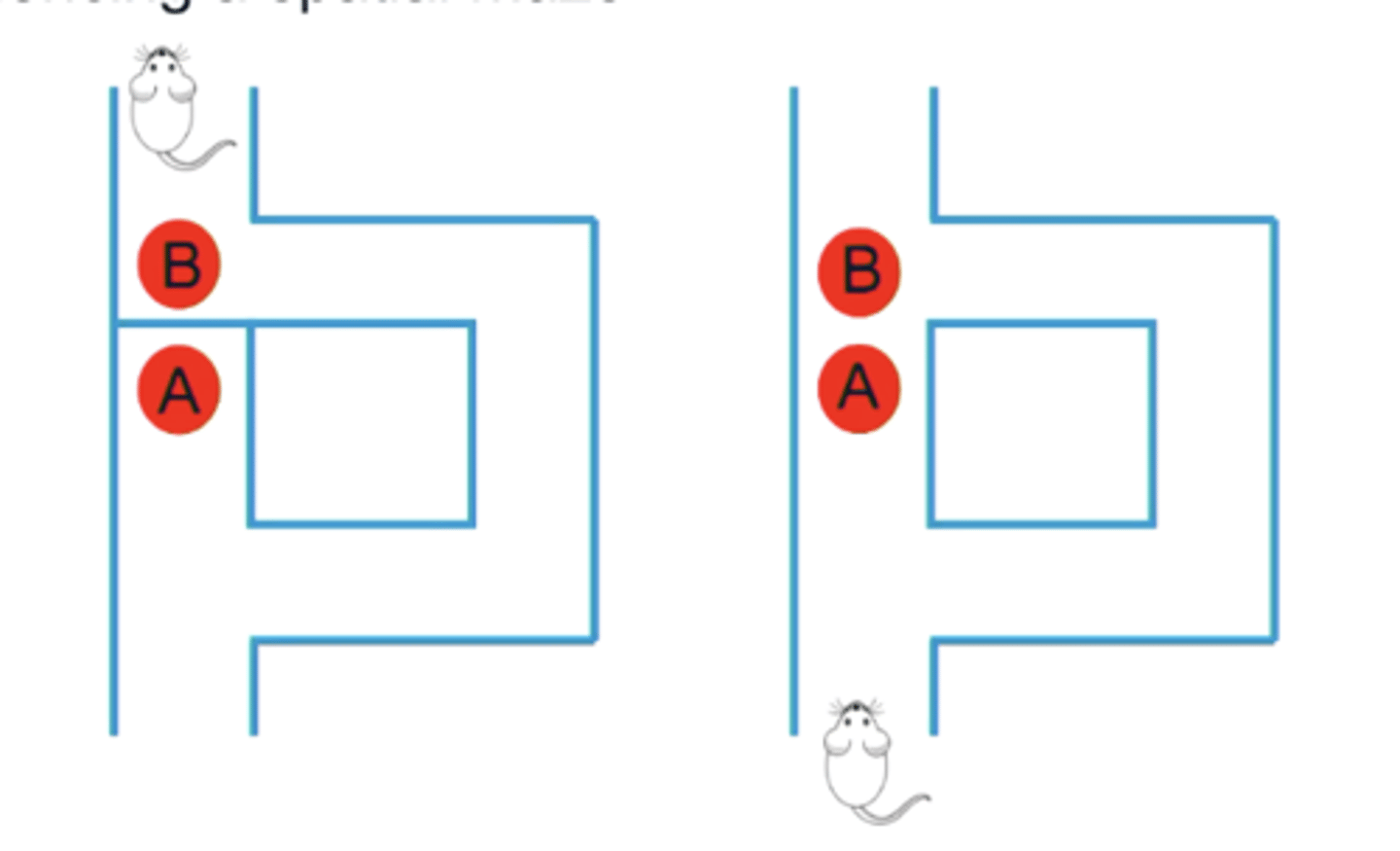
Can mental maps in decision-making be applied to non-spatial tasks?
Yes - e.g learning a new coding task overtime will become easier to learn through short-cuts acquired to make task easier
problems can be described as a series of decisions to guide you through different steps
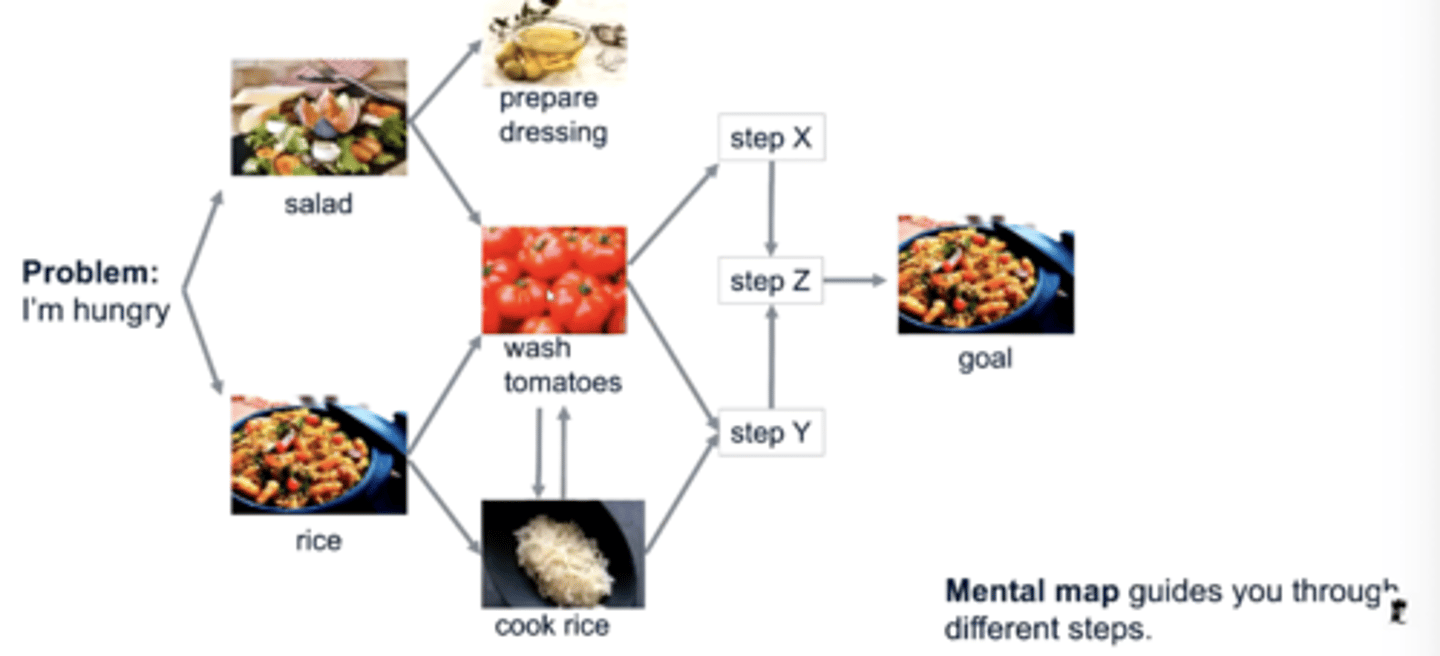
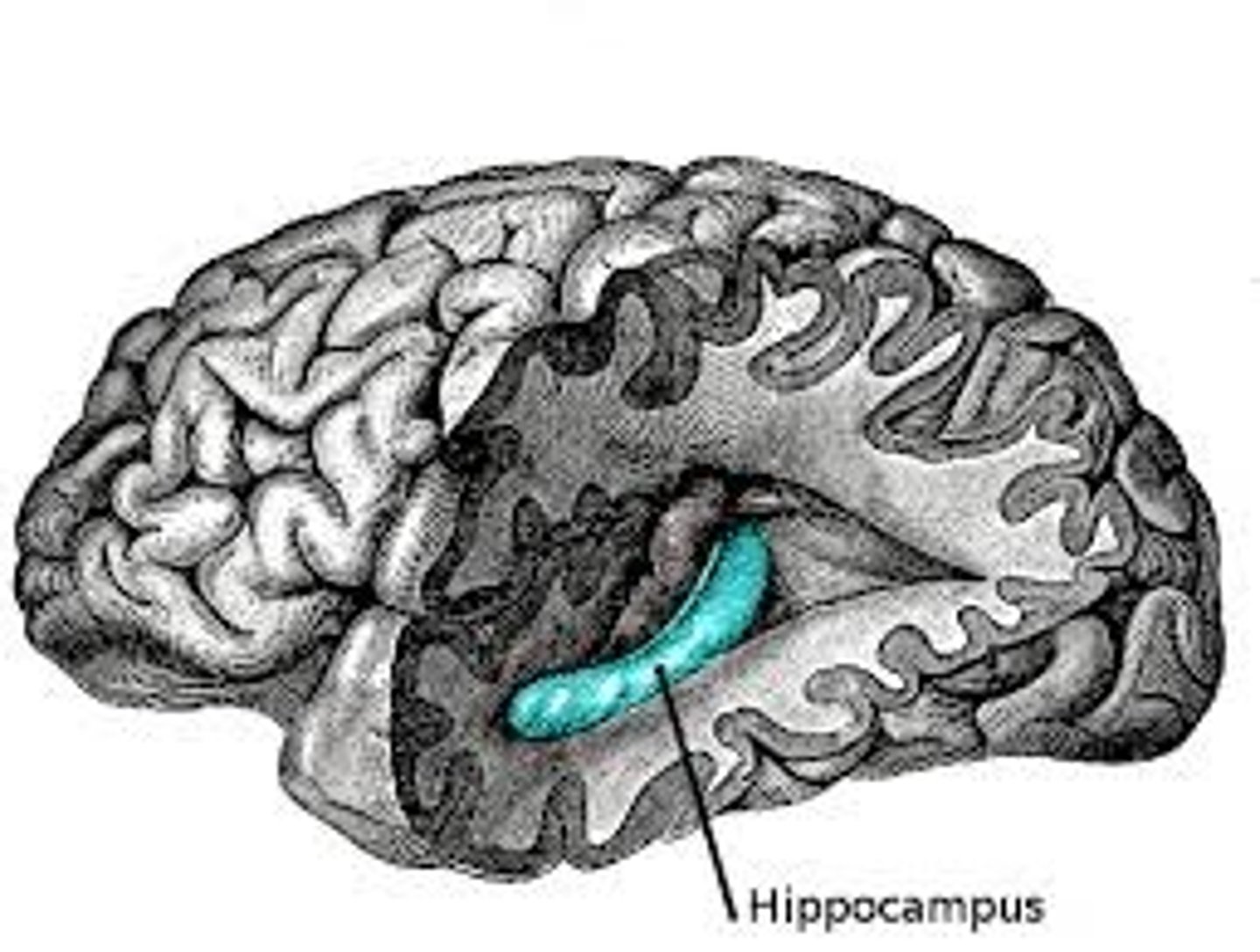
Which part of the brain is associated with long-term memory/mental maps/decision making
the hippocampus - to form our decisions and make predictions.
- update experiences in memory.