sfl 160 byu final exam
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Overt messages
explicit messages, words we use
covert messages
unspoken messages (ex. implicit communication, body language)
decoding
the process of interpreting covert messages
seeking meaning
listening is key, focusing on understanding the other person not thinking about a response or rebuttal
seeking clarification
asking for help; active listening; asking about unclear messages
seeking congruence
focusing on what we can do: lining up the covert and overt messages
Communication as Control
Using communication to attempt to change someone
Competitive communication
using comm. to win an argument or appear dominant
forms of unhealthy communication
criticism, contempt, defensiveness, stonewalling
criticism
blaming your partner
contempt
verbal or nonverbal communication that attempts to put your partner below
defensiveness
defending yourself in the face of a perceived attack
stonewalling
withdrawing from interaction
Healthy types of communication
seeking meaning (understanding), seeking clarification (asking for help), seeking congruence (combining overt with covert)
Conflict
a disagreement that is usually extended over a period of time
conflict resolution
how families resolve disagreements
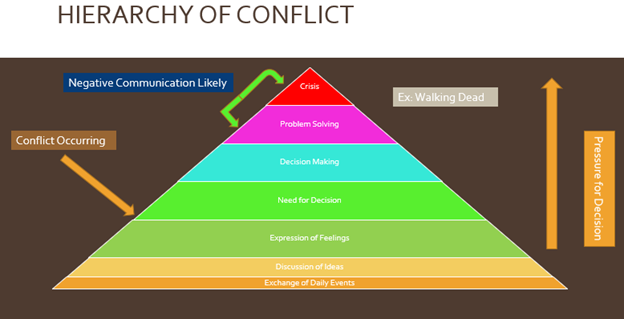
Hierarchy of conflict
levels from bottom to top
exchange of daily events, discussion of ideas, expression of feelings, need for decision, decision making, problem solving, crisis
in the hierarchy of conflict, after which step is considered a conflict occurring?
between the expression of feelings and the need for decision
Development of Conflict Key
Key: unhealthy conflict resolution always involves unhealthy communication styles
What are the two common aspects of negative conflict resolution in relationships
linear causality model (initiation): my response is just a direct reaction to your negative communication.
Circular causality model (escalation): I respond negatively to my partner who then in turn responds even more negatively to me.
Sentiment Override
When our feelings or perceptions regarding the relationship influence our perception of communication messages.
unhealthy communication and conflict resolution in families often occur when emotions begin to interfere with healthy communication patterns.
Negative override: when our feelings or perceptions regarding the relationship influence our perception of communication messages
positive override: when positive perceptions of a person or relationship push us to assume the best about our partner.
Balance between intimacy and distance in families
task in being connected vs. being differentiated from one another
Intimacy
being close, familiar, or affectionate with another person.
Individuality & Intimacy
Individuality: being your own person,
intimacy: being affectionate and close with family members
this is a different way to view intimacy and distance in families
enmeshment
definition: a lack of tolerance for individuality, in the presence of high intimacy.
Enmeshed families
Key: in enmeshed families, personal boundaries become highly permeable and family boundaries become rigid
Breaking out of the enmeshment
two things need repairing:
personal enmeshment: blurring of me/ you boundary, needs to do personal exercises that promote healthy boundaries, and getting distance from the system
family enmeshment: breaking the family cycles → open communication + family goal = breaking enmeshment
avoiding the lack of cohesion
Circumplex Model
Cohesion (does the family system have buy in)
flexibility (how adaptable is the family when equilibrium is lost?)
communication (how to move from different areas of cohesion and flexibility)
Four levels of cohesion
disengaged: struggle with commitment and attachment
connected: time apart is more important but still family time, some family decisions.
cohesive: time together is valued as more important
enmeshed*: total loyalty demanded little private space
four levels of flexibility
rigid: one person in charge | very controlling environment
structured: few rule changes, rules enforced, less discussion (democratic)
flexible: shared roles, rules change to be more appropriate age
chaotic: limited or no leadership, decisions are impulsive, and roles shift from one to another
Gender Terms
Sex: refers only to male and female anatomy
gender: refers more broadly to the attitudes and behaviors expected of and associated with the two sexes.
gender identity: the way you view yourself as either male or female
gender roles: the things you do as you act out the role of being male or female.
Gender Stereotyping: broad cultural expectations held by individuals that a person behaves in ways because she or he is female or male.
Three Aspects on Our View on Gender:
Innate: premortal/pre-existing
biological: genetic and biological differences
experienced: interactions with others (parents/media)
Power
one who gets to make final decisions on family process. (one who has a large influence over others.
Four different types of Family Patterns in leadership
Husband dominant
Wife dominant
Syncretic - most of the family decisions are made by a joint decision between and the husband.
Autonomic - Fewer family decisions are made by a joint decision
ABC-X Model of Family stress
A= the stressor (can be small vs. large)
B= the family’s resources meeting the stressor (anything to help)
C=the perceptions of the family to the stressor (very predictive)
X=the crisis/ the reaction/degree of stress
Adaptation and resiliency
Resiliency: refers to people who benefit from stressful events (the crucible metaphor)
adaptation: process which people change their actions, thoughts, values, and tendencies in reaction to stress
Romantic Relationships
Contain a special type of intimacy = love
not fixed
strongly culturally driven
has unique anxieties and stresses
Modern changes to romantic relationships
marital relationship is becoming more important with a deemphasis on socialization and education
relationships have become less tied to religious authority
communication and dating have been radically altered by technology with more emphasis has been placed on getting expert advice.
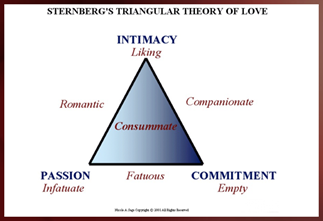
Sternberg love triangles
Comprised of three things: commitment, intimacy, passion
Only Intimacy
liking
only passion
infatuate
commitment only
empty love
passion & commitment
Fatuous
Pasion and intimacy
Romantic
Intimacy and commitment
companionate
Intimacy, Commitment, and Passionate.
consummate
Lee’s love styles
agape, eros, mania, ludus, storge, agape, pragma
eros
passionate, erotic love
mania
obsessive, jealous love
ludus
just for fun love
storge
committed love
agape
selfless love
pragma
rational love
Role of Attraction
Often conceptualized as the catalyst for contact
men: more universal definition of attraction
women: more presonalized definition of attractoin
over time sex frequency diminishes but marriage satisfaction goes up