Images and charts for E&E
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all chapters
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms

Name the three things in this picture from left to right.
Mangroves, seagrass, and coral reefs.
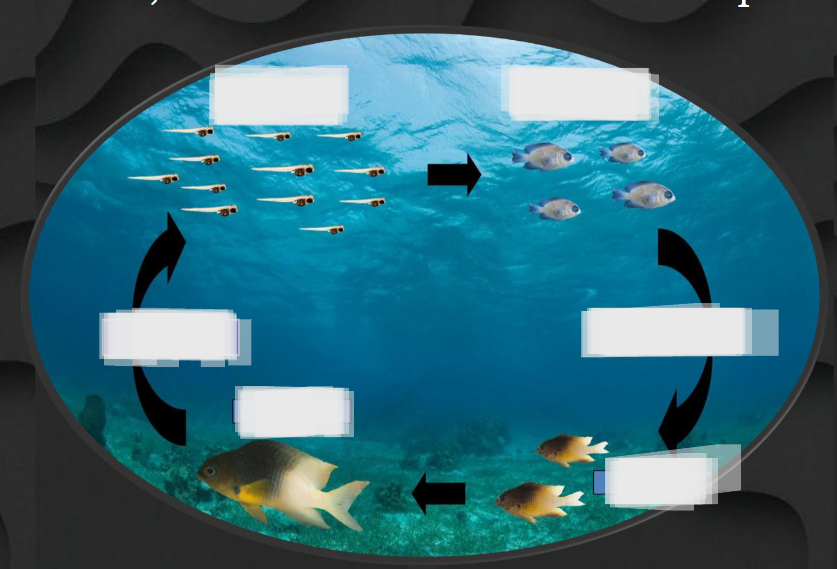
Starting from top left, name everything.
Early larvae, late larvae, settlement, juveniles, adults, spawning.
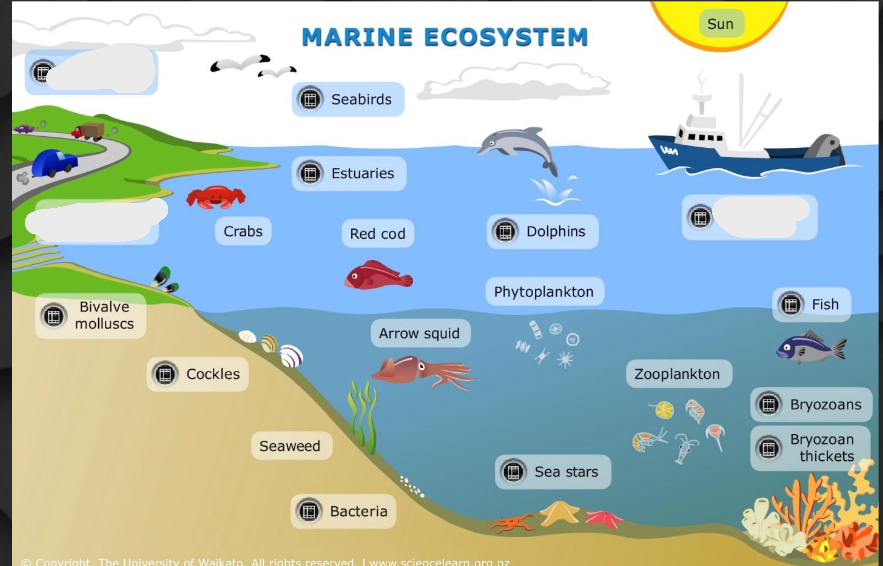
Name the three thigs that are not there. (start from top left and go down then to the right)
Ocean acidification, run off, commercial fishing.
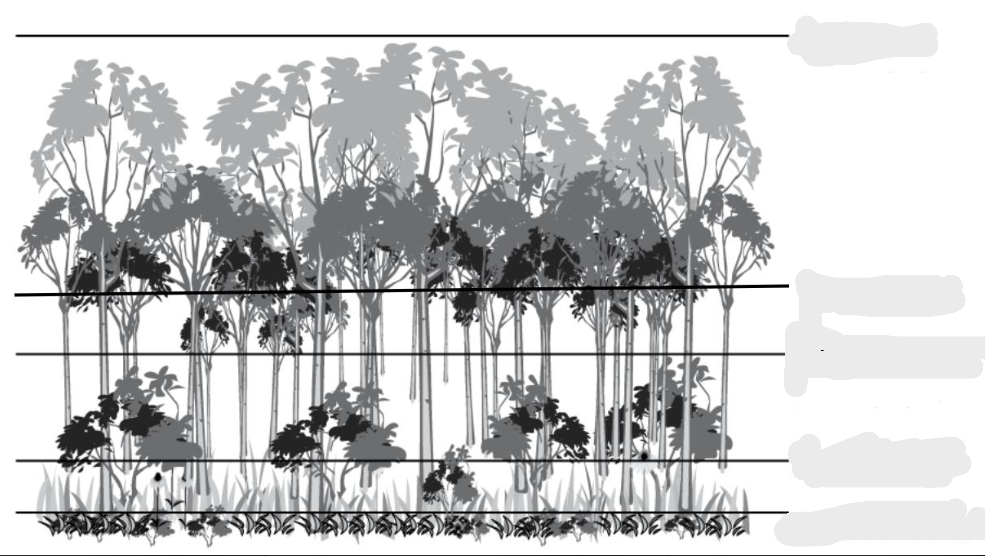
Name the things from top down.
Canopy, tree layer, shrub layer, herb layer, forest floor, root layer.
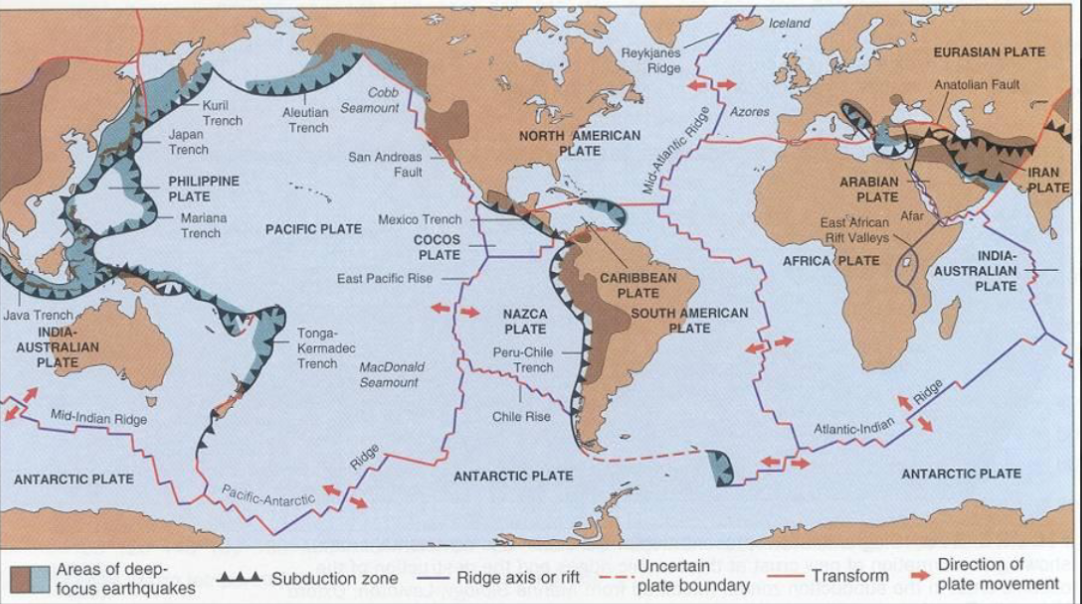
What is going on in this image?
This map shows earths tectonic plates and their boundaries where they meet, such as subduction zones, ridges, and faults. Shows how plates move, the arrows showing their direction, and marks areas of earthquakes and volcanic activity. Examples include the mid-atlantic ridge, where the plates pull apart to from new crust, and the mariana trench where one plate sinks beneath another.
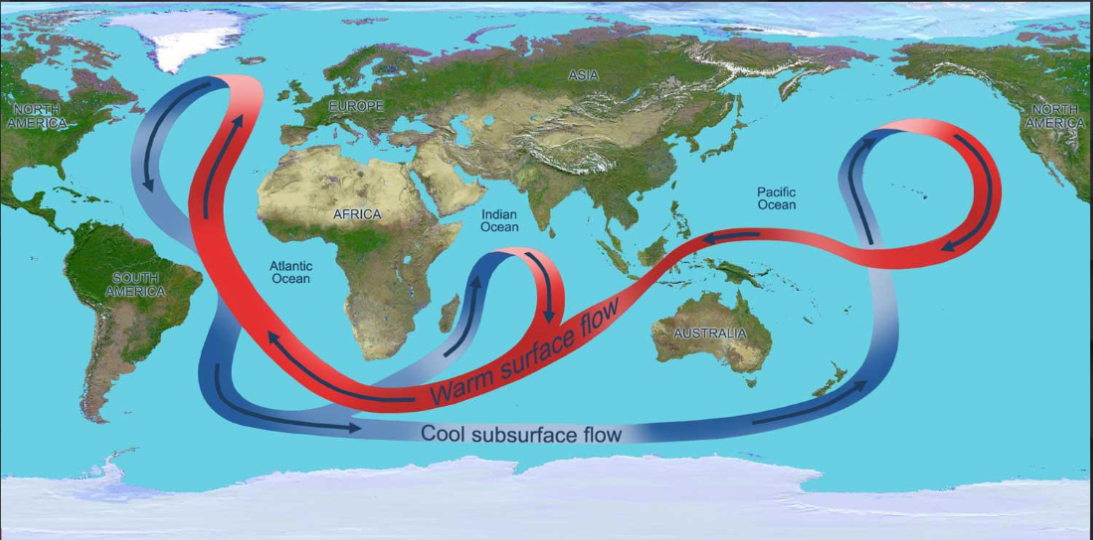
What do you see in this image
Shows the global ocean conveyor belt, also called thermohaline circulation. Maps how warm surface currents (red) move from the equator towards the poles, while the cool deep currents (blue) flow back toward the equator. Regulates earth’s climate by distributing heat and influencing weather patterns.
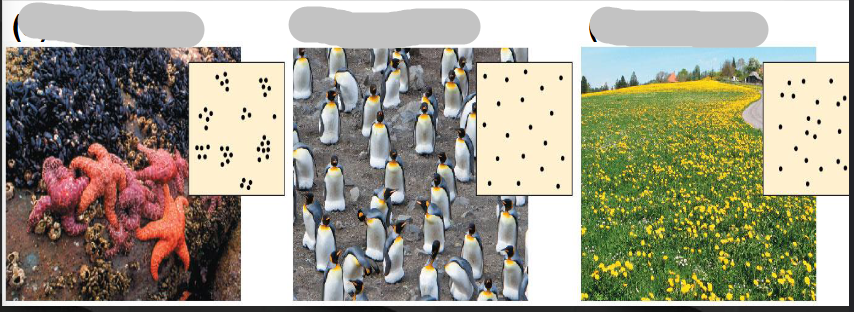
Fill in the blank (left to right)
Clustered, uniform, random
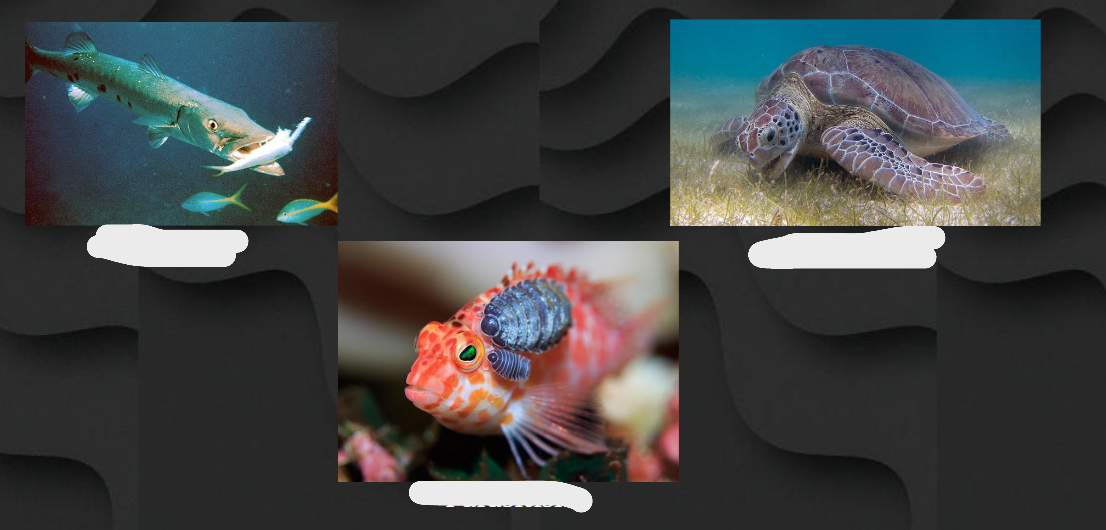

what is the images showing (l to r)
predation, herbivory, parasitism

name all
wildfires, loss of habitat, increased flooding, increased drought, increased greenhous gases, disruption to water cycle, destuction of fewnewable resources, destruction of homelands
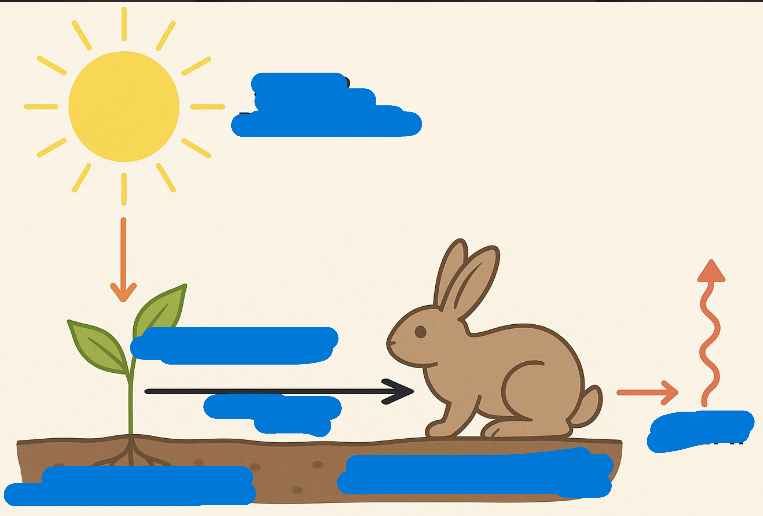
name from top down to right
solar radiation, chemical energy, food, autotrophs, hererotrophs, heat
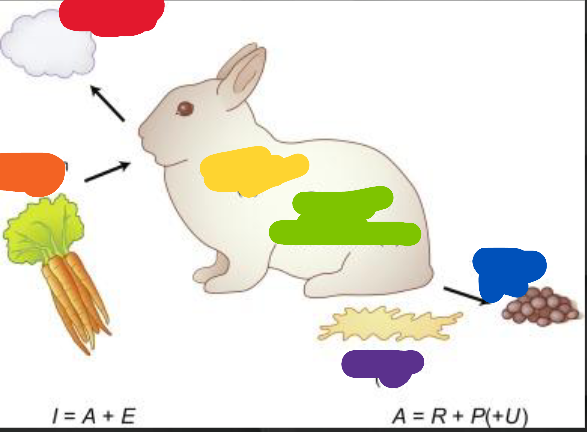
name the things in photo (rainbow
respiration, ingestion, assimilation, growth or production, egestion, excretion

name
habitat loss, introduced species, overharvesting, global change

name
grandchildren, like, grandfathers. TWO tendency to small change, espcially with physical change, THREE great fertility in proportion to support of parents
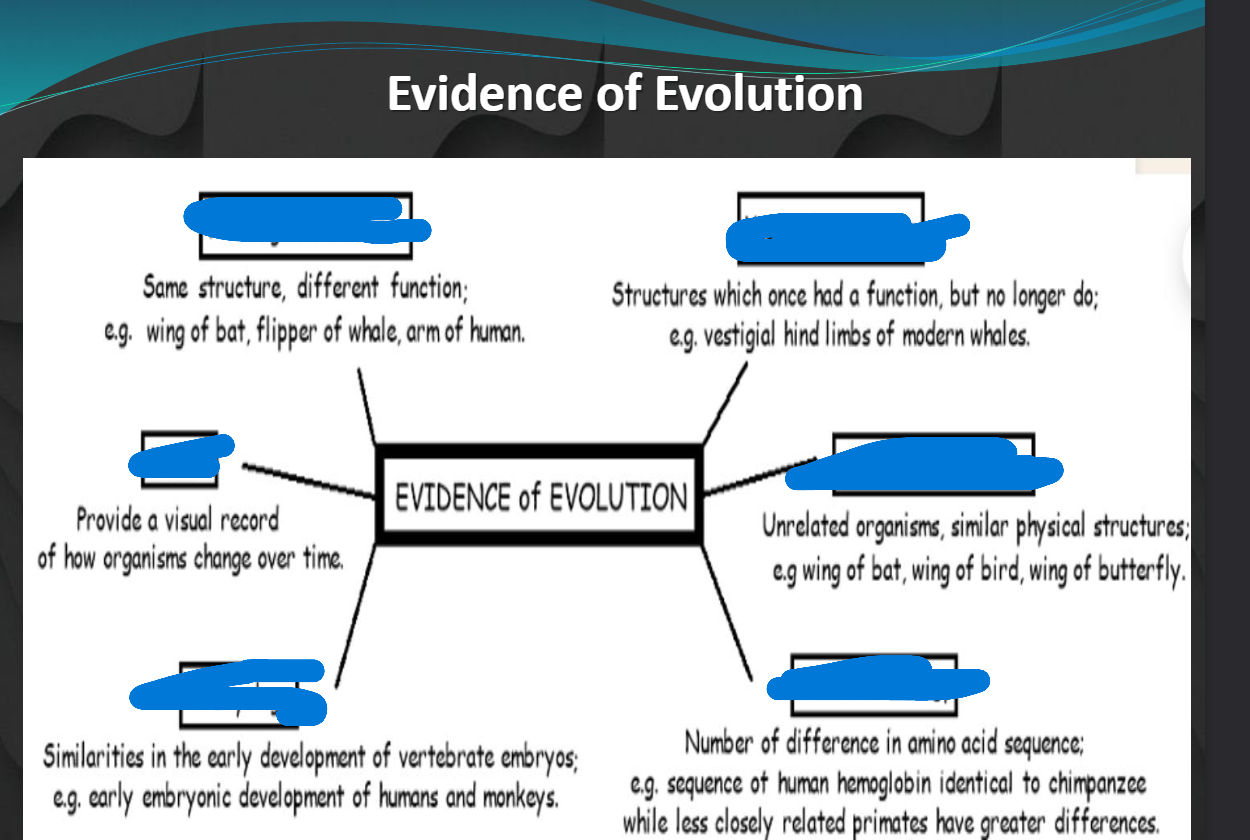
name (l, r, l, r, l, r)
homologous structures, vestigial strucures, fossils, analogous structures, embryology, molecular biology