chem paper 2
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
what are benefits of high atom economy
reduces production of unwanted products
makes process more sustainable
maximises profit
what are permanent dipole dipole forces
weak electrostatic forces of attraction between delta pos and delta neg charges on neighbouring moleucles
activation energy
minimum amount of kinetic energy particles need to react
effect of increased temperature on reaction rate
molecules will have more kinetic energy and will move faster - greater proportion will have energy greater than or equal to the activation energy
rate of reaction
change in the amount of a reactant or product over time
effect of conc on reaction rate
particles will be closer together
collisions will be more frequent - more chances for particles to react
what is reaction order
power to which the concentration of that reactant is raised in the rate equation.
what is the rate constant
number that connects the concentration of reactants in a reaction to the rate of that reaction.
as activation energy increases, what happens to k
k gets smaller
arrhenius plots
lnk = yaxis
1/T = x axis
line of best fit = = -Ea/R
y intercept = lnA
increased no. particles means
higher rate of reaction
more particles within a given volume, so more successful collisions per unit time
having a higher surface area ..
more frequent sucessful collisions with surface of catlyst per unit time
Magnesium ribbon reacts with hot water. Heated magnesium ribbon reacts with steam. State two differences between these reactions
Slower with hot water or faster with steam The hot water produces Mg(OH)2
/ the hydroxide OR steam produces MgO / the oxide (Slow) bubbling with hot water OR bright white light / flame / white solid with steam
State le Chatelier’s principle.
(If any factor is changed which affects an equilibrium), the (position of) equilibrium will shift / move so as to oppose / counteract the change.
State how, if at all, the number of molecules with the most probable energy (Emp) changes as the temperature is decreased without changing the total number of molecules.
increases
why are initial concentrations used
(b) (At time zero/start) the concentrations are known
(a) Suggest why the order with respect to iodine is zero.
iodine is not in rate determining step
what is structural formula
shows the atoms carbon by carbon, with attached hydrogens and functional groups
general formula
algebraic formula that can describe any member of a family of compounds
what is a homologous series
family of compounds with same functional group and general formula
differ by CH2
chain isomers
same functional groups but different arrangements of the carbon skeleton
position isomers
same skeleton and same atoms or groups of atoms attached - but the atoms/groups of atoms are attached to diff carbon atoms
functional group isomers
same atoms arranged into diff functional groups
bond angles in alkenes
120
carbon neutral
no net emissions of carbon dioxide/CO2 to the atmosphere
cracking of alkanes involves
breaking C-C bonds
fractional distillation process
crude oil vaporised at 350C
goes thru bottom of column and rises (there is a temp gradient in the column)
largest hydrocarbons dont vaporise - as BPS too high
fractions drawn off at different levels
why crack hydrocarbons?
high demand for lighter fractions
overall reaction with ozone
2O3 → 3O2
nucleophile
electron pair donor
nucleophilic substitution conditions
OH- : use warm aqueous NaOH/KOH
CN: ethanolic + aqueous KCN (under reflux)
NH3: ethanolic NH3
elimination conditions
OH- ions dissolved in ethanol (warmed) under reflux
what is a base
proton acceptor
c=c bond has
high electron density
why are carbocations with more alkyl groups more stable?
alkyl group are electron releasing - so they stabilise the positive charge
what are plasticisers
plasticiser makes polymer bendier
get between polymer chains and push them apart- reducing strength of IM forces between chains
dehydration conditions and mechanism
heat
conc sulfuric acid
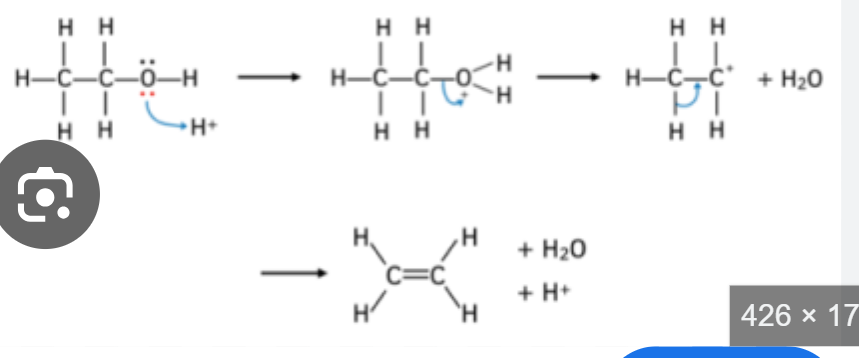
why are addition polymers unreactive
saturated
non polar carbon chain
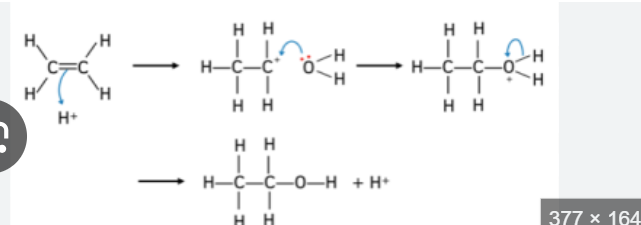
hydrating alkenes conditions
steam at 300C
high pressure
phosphoric acid catalyst
biofuel
fuel made from biological material that recently died
aldehyde to COOH eqaution
CHO + [O] → COOH
under reflux
primary alcohol to aldehyde
acidified potassium dichromate and distill
secondary alcohol to ketone
reflux
acidified potassium dichromate
testing for primary/secondary/tertiary alcohols
add 2cm3 acidified potassium dichromate
warm in hot water bath
orange to green
brick red precipitate
copper oxide
using mass spec, what can be determined
molecular formula
electrophilic additionn
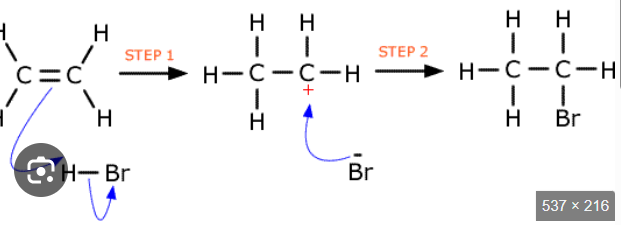
in electrophilic addition, Br-Br bond becomes
polarised
what is a racemate
contains equal quantities of each enantiomer
they have no optical activity
50/50 mix of each enantiomer
reducing an aldehyde/ketone
RCHO + 2[H] → RCH2(OH)
RCOR +2[H] → RCH(OH)R
reagent to reduce C=O
aqueous NaBH4
KCN
toxic gas
We could use HCN for this reaction but it is a toxic gas that is difficult to contain. KCN/NaCN are still, however, toxic, because of the cyanide ion.
HCN is also a weak acid - partially ionises
esterification conditions
conc sulfuric acid catalyst
reflux
what are animal fats and vegetable oils
esters of glycerol and fatty acids
hydrolysis of fats and oils
heat with NaOH (alkaline conditions)
glycerol + sodium salt (soap)
to convert back to fatty acid add HCl
making biodiesel
fat/oil + methanol → (KOH catalyst) glycerol + methyl ester (biodiesel)
methyl esters of long chain fatty acids = biodiesel
how to make aspirin
ethanoic anhydride and the benzene molecule with OH and COOH
why ethanoic anhydride over ethanoyl chloride
less corrosive
cheaper
doesnt produce toxic HCl fumes
benzene structure
planar
bonds lengths same in all bonds (lies inbetween single and double bond length)
p orbital electrons delocalise and increase stability
why substitution instead of addition reactions in benzene
benzene ring so stable
addition reactions would destroy delocalised ring of electrons
to only substitute with one NO, what do u need to do
temp below 55C
conditions for friedel crafts acylation
reflux
ether
acyl chloride
AlCl3
what are cationic surfectants
partially soluble
insoluble in water
quaternary ammonium salts
long hydrocarbon chain insoluble in water, will bind to non polar substances like grease; the positively charged ion is soluble in water
- used in conditioners
how do amines act as weak bases
accept protons
theres a lone pair of electrons on the N atom that forms a coordinate bond with H+ ion
aliphatic amines - stronger bases
forming amines from nitriles
LiAlH4 in dry ether + dilute aci
nitrobenzene → phenylamine
sn + hcl
add alkali (naoh)
nylon 6,6
1,6 diaminohexane and hexanedioic acid
clothing/rope
kevlar
benzen-1,4 dicarboxylic acid and 1,4-diaminobenzene
bulletproof vests/car tyres
terylene
benzene- 1,4 dicarboxylic acid and ethane-1,2-diol
clothes/bottles
polyamides and polyesters hydrolysed more quickly in
acidic and basic conditions respectively
zwitterions only exist near..
isoelectric point - pH where overall charge on the amino acid is zero
to break up proteins
reflux with HCL for 24 hours
describe disulphide bonding
amino acids part of protein - called residue
disulphide bonds occur between residues of the amino acid cysteine
how does cisplatin work
nitrogen atom on guanine base in DNA forms coordinate bond to platinum ion, replacing a chlorine ligand
prevents strands unwinding - so dna cant be replicated
TLC
plate coated with solid and solvent moves up plate
CC
solid packed in and solvent moves down column
used for purifying organic products
GC
for mix of volatile liquids
solid or solid coated by liquid and a gas
under pressure + at high temp
how does CO2 cause global warming
C=O Bonds in CO2 absorb infrared radiation (of 2350 cm–1 ) 1 IR radiation emitted by the earth does not escape (from the atmosphere)
conditions for basic ester hydrolysis
aqueous warm NaOH
bonding in benzene
1a) Each C has three (covalent) bonds 1b) Spare electrons (in a p orbital) overlap (to form a π cloud) 1c) delocalisation
why use two solvents in chromatography
Some of the amino acids did not separate/dissolve with the first/either solvent OR Some amino acids have the same Rf value or have the same affinity with the first/either solvent
disappearing cross graph
1/T = rate
plot rate (y axis) against T (x axis)
sketch plot
give practical reasons why the vol of gas is lower
hydrogen is lost before the syringe is connected
arrhenius graph axis
1/T on X axis
lnk on Y axis
benefits of using buchner flask to filter
filtration quicker, product drier
obtaining pure sample + crystalising method
why reflux?
explain process
allows reactant vapours to return to the organic mixture
heated to boiling point for a prolonged period of time
vapour is formed which escapes from the liquid mixture, is changed back to liquid and returned to liquid mixture
any mixture that initially evaporates can then be oxidised
why cool distillate
to reduce evaporation
when distilling a mixture - to obtain one of the liquids, how should the boiling temp be adjusted
boil ate boiling point of liquid u want
what does having different polarities of amino acids mean for amino acids having diff rfs
diff relative retention on stationary phase
why are acid strength of ethanedioic acid and ethanoic acid different
Stage 1: difference in structure of the two acids • The acids are of the form RCOOH • but in ethanoic acid R = CH3 • whilst in ethanedioic acid R = COOH
Stage 2: the inductive effect • The unionised COOH group contains two very electronegative oxygen atoms • therefore has a negative inductive (electron withdrawing) effect • The CH3 group has a positive inductive (electron pushing) effect
Stage 3: how the polarity of OH affects acid strength • The O–H bond in the ethanedioic acid is more polarised / H becomes more δ+ • More dissociation into H+ ions • Ethanedioic acid is stronger than ethanoic acid
ethanedioic acid + potassium manganate
5H2C2O4 + 16H+ + 2MnO4- → 2Mn2+ + 10CO2 + 8H2O
increasing the pressure of rate equation reaction by x3 - what happens to overall rate (two 1st order reactants)
increases by factor of 9
sodium carbonate + gallium II nitrate
gallium(III) hydroxide + CO2 forms
Explain qualitatively why doubling the temperature has a much greater effect on the rate of the reaction than doubling the concentration of E.
Reaction occurs when molecules have E>Ea
Doubling T by 10 °C causes many more molecules to have this E
Whereas doubling [E] only doubles the number with this E
how does the graph show that the order is zero
gradient constant
as conc decreases
A general equation for a reaction is shown.
A(aq) + B(aq) + C(aq) → D(aq) + E(aq)
In aqueous solution, A, B, C and D are all colourless but E is dark blue.
A reagent (X) is available that reacts rapidly with E. This means that, if a small amount of X is included in the initial reaction mixture, it will react with any E produced until all of the X has been used up.
Explain, giving brief experimental details, how you could use a series of experiments to determine the order of this reaction with respect to A. In each experiment you should obtain a measure of the initial rate of reaction

The following rate equation was deduced.
rate = k [CH3COCH3][H+]
(a) Suggest why the order with respect to iodine is zero.
iodine isnt in rate determining step
molecular formula of glycerol
HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH