Artur's "Celebration of Knowledge"
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
In Vealey's 2024 Mental training in Sports model, what are the four main categories in Mental Skills?
Personal Foundation Skills
Performance Skills
Personal Development Skills
Team Skills
In Vealey's 2024 Mental training in Sports model, what are the three main categories in Mental Health?
Emotional wellbeing
Psychological wellbeing
Social wellbeing
What are the four phases of Vealey's 2024 Mental training?
Education
Acquisition
Practice (use and refine)
Integration/Implementation
When should you implement a psychological skills training program?
in the off-season
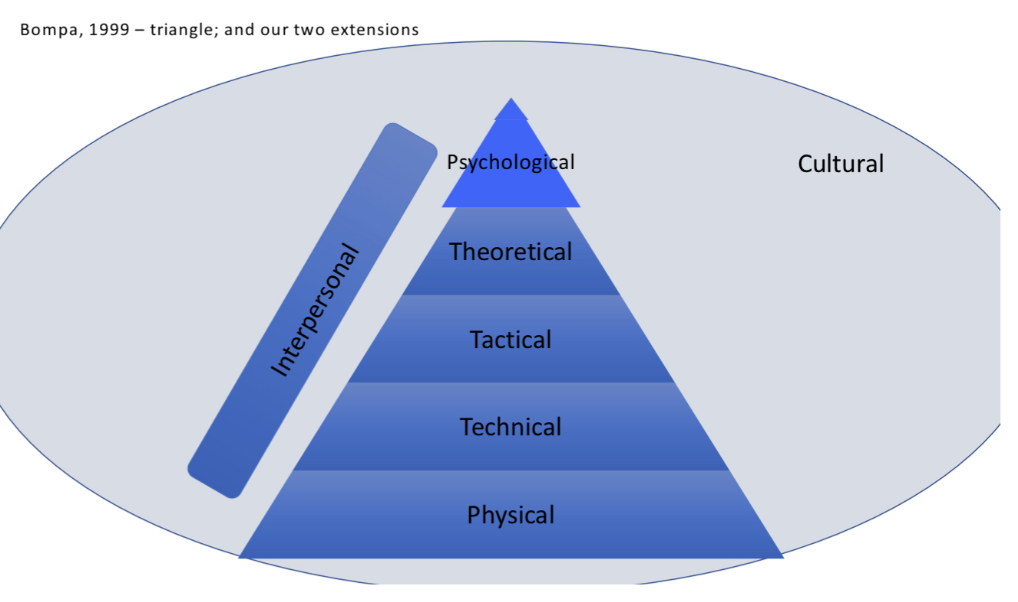
In Boompa's (1999) model of sport preparation, what are the seven categories from top to bottom? (NOTE: one category goes along the other 5, and one surrounds the entire model)
What does it mean to be an authentic sport psychologist?
When creating a theory, understand first, then attempt a change
At the same time, be true to your own personality and character
What are the five main points of authenticity in a sports psychologist?
Knowledge of psychology/sport sciences
Sport psychology knowledge and experience
Knowledge/experience of a specific sport
Adapt to context and individuals w/ whom they are working
Pursue own excellence in consulting
What are KSA’s?
Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities that a person uses in performance
What is performance psychology?
study/application of human performance psychological principles
aims to help people consistently perform in upper range of capabilities while also enjoying the performance process
What is cultural sport psychology?
focuses on understanding experiences of marginalized groups and offers theory-driven interventions with diverse athletes
What is cultural competence?
being aware, understanding, and able to interact with/respect people of differing cultural backgrounds
What is intersectionality?
idea that everyone is made up of a unique system of social identities, therefore we experience different forms of oppression, discrimination, and privilege
What is social justice?
everyone deserves equal rights and opportunities in all aspects
What is self confidence?
Feeling of self-assurance & belief in one's power
How can you enhance self confidence?
Know your strengths
Focus on what’s in your control
Look for reasons why you should succeed
Engage in factual disputing/countering arguments when confidence waivers
Maintain “right now” focus
Use positive self-talk and images
Identify situations where confidence may be challenged and create effective responses to maintain confidence
Be clear on process/outcome balance for enhancing, regaining, maintaining performance
Project confidence in body language/other non-verbal behavior
What can stand in the way of self-confidence?
Perfection is essential
Catastrophizing (awfulizing)
Worth depends on achievement
Personalization (self or other depreciation)
Fallacy of fairness (low frustration tolerance)
Blaming (self or others)
All-or-none thinking (labeling)
One-trial generalizations
Shoulds (demandingness)
Emotional reasoning
What is an explanatory style?
the way an athlete internally responds to and explains both the good and bad events that occur in life
What is permanence explanatory style?
the degree to which one feels events will repeat and continue to affect one’s life either negatively or positively
What is pervasive explanatory style?
the degree to which one feels that a particular experience will generalize to other contexts
What is personalization explanatory style?
the degree to which one sees himself or herself as the primary causal agent in events
What are the three types of explanatory styles?
permanence
pervasive
personalization
What are the misconceptions of confidence?
Either you have it or you don’t
Only positive feedback can build confidence
Success always builds confidence
Confidence = outspoken arrogance
Mistakes inevitably destroy confidence
What is self efficacy?
person’s belief in their ability to perform tasks and achieve goals
What are five sources of self-confidence?
enactive mastery experiences
vicarious experience
verbal persuasion
physiological states & emotional states
imaginal experiences (imagery)
What are Vealey’s (1998) sources of self-confidence in sport?
physical/mental preparation
physical self-presentation
social support
vicarious experience
coach’s leadership
environmental comfort
situational favorableness
What are labels/constructs for perfectionism?
perfectionists receive judgment based on their skills and performance
ex. “perfectionists” are always the best out of everyone (gets good grades, dances the best, never misses a target, etc.)
What is perfectionism?
need to achieve high, personal standards and a desire to excel in performance
What are desirable aspects of perfectionism?
Mental preparedness
Confidence
Motivation
Ability to peak under pressure
Goal setting/concentration
What is positive perfectionism described as?
considered normal, adaptive, healthy
What is negative perfectionism described as?
maladaptive/pathological; associated with dissatisfaction, social dictated standards, fear of failure, unhelpful fear of being judged
What is an adaptive perfectionist?
positive; generalized w/ high levels of organization, self-orientated focus, high personal standards, satisfaction towards goal achievements
higher self esteem
What is a neurotic perfectionist?
negative; someone who emphasizes on experiences of anxiety and fear of failure
What is a maladaptive perfectionist?
negative; more focused on the negative qualities in personal efforts (ex. stress); have a black-and-white view on people, their issues, and themselves (“it’s either good or bad and not in between”)
lower self esteem
What is necessary perfectionism?
high need for mastery/achievement
Improving a skill because you want to master it, not because you want to be perfect
What are social context demands for dance?
expectations from instructors, family, peers
What are physical context demands for dance?
ideal body type for different genres of dance (ex. Ballerinas are socially stigmatized to have tall, slim bodies)
What are technical context demands for dance?
Different genres of dance require emphasis on usage of different body parts/techniques
What are cultural/emotional context demands for dance?
people find different values in dance; also able to express different feelings depending on how the dance is portrayed by the person
What are historical context demands for dance?
dance genres have different origins/historical context
What are collaborative context demands for dance?
relationships between other dancers, choreographers, instructors, the audience
What is achievement goal theory?
An individual’s goal perspective state- task or ego involvement- results from individual differences and situational factors.
What is motivational climate?
environmental factors (task- and ego-involving cues) that lead individuals to construe competence in different ways and pursue different goals
What is the difference in people who strive for mastery and those who strive to beat competition?
Mastery compares to themselves, competitive compare to other competition
How do you describe and adaptive pattern?
high task orientation and ego climate
How do you describe a maladaptive pattern?
ego climate and low perceived ability
What is perceived task involving climate?
coach reinforces effort, cooperation of teammates, learning, and improvement
everyone on team contributes to team success
What is ego-involved climate?
coach punishes mistakes, fosters rivalry among teammates, gives more attention to most talented players
self-handicapping
What is ego involving motivational climate?
anxiety and performance-related worry, handicapping, dropping out of sport
What does TARGET mean?
Task — what is asked to learn/complete)
Authority — kind/frequency of participation in decision making process
Recognition – procedures & practices used to motivate & recognize athletes for progress & achievement
Grouping – how brought together or kept apart in training & competition
Evaluation – standards set for athletes’ learning & performance & procedures for monitoring & judging attainment of standards
Timing – appropriateness of time demands placed on learning & performance
What are three psychological mediators?
Competence, autonomy, and relatedness
What is competence?
When one feels sufficiently efficacious to interact effectively w/ environment
What is autonomy?
percieve that we are acting according to our own volition and have options and choices (we are our own person)
What is relatedness?
viewing relationships w/ important individuals as being supportive and respectful
What is amotivation?
when a person has no sense of personal control w/ respect to sport engagement
no extrinsic/intrinsic reasons for doing activity and no longer sure why they are continuing the sport
What are four ways for extrinsic motivation to be regulated?
External, introjected, identified, integrated
What is external regulation of extrinsic motivation?
(least autonomous) behavior for reward
What is introjected regulation of extrinsic motivation?
participate because you feel like you have to
What is identified regulation of extrinsic motivation?
engage as a means to an end
What is integrated regulation of extrinsic motivation?
doing it because someone thinks it aligns w/ their values/needs
What is self determination theory?
theory that says satisfying autonomy, competence, and relatedness can lead to optimal motivation and psychological health
What is autonomy supportive coaching?
coaching style that encourages athletes to be independent and self-determined
What is Deci’s Theory of Cognitive Evaluation?
theory that says external rewards affect intrinsic motivation, which are dependent on controlling or informational aspects of an event
According to Deci’s Theory of Cognitive Evaluation, what happens if an event is meant to control behavior?
autonomy/intrinsic motivation decrease
extrinsic motivation increases
According to Deci’s Theory of Cognitive Evaluation, what happens if an event is not meant to control behavior?
autonomy/intrinsic motivation remain high
extrinsic motivation is unaffected
According to Deci’s Theory of Cognitive Evaluation, what happens if an event is meant to inform competence?
competence and intrinsic motivation increase
According to Deci’s Theory of Cognitive Evaluation, what happens if an event is not meant to inform competence?
competence and intrinsic motivation decrease
What does Harter’s (1978) Competence Motivation theory entail?
innate motivation leads to task mastery
According to Harter’s (1978) Competence Motivation theory, what does a successful attempt look like?
Self-efficacy → high competence motivation → persistence
According to Harter’s (1978) Competence Motivation theory, what does a unsuccessful attempt look like?
negative affect/feeling incompetent → low competence motivation → fewer mastery attempts → losing motivation/drop out
What is trait vs. state?
Trait = typical style of behavior (part of personality)
state = situation effects on behavior (“right now” feeling)
What is emotional intelligence?
personality trait or learned ability to regulate emotions/interpersonal behavior (trait vs. skill; social intelligence)
What do the ACSI-28 subscales measure in cognitive strategies and success?
coping w/ adversity
peaking under pressure
goal setting/mental prep
concentration
freedom from worry
confidence/achievement motivation
coachability
What is a personality paradox?
range of personality styles that are available to be used in different contexts
static traits lose prominence and behaviors fluctuate around multiple polarized attributes
What does CAPS entail?
cognitive strategies reflect behavior aspect of personality and interact with personality traits
What are the cognitive strategies in CAPS?
Encoding
Expectations/beliefs
Emotions
Goals/values
Self-regulation/competence
What is OCEAN?
the broad dimensions of personality
Openness
Conscientiousness
Extraversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
What is flow?
the state in which people are so involved in an activity that nothing else around them matters, even during extreme challenges
What do flow and peak performance share?
both involve concentration on task
be in control without trying
time = weird
doing activity because enjoyable
performing w/o concern of self evaluations
challenge = skill (equal match)
activity immersion
relax/focus on present
What are limitations of peak performance research?
correlation studies have no evidence of casuality
psychological skills vs. sport skill/ability level hypothesis
response bias due to previous knowledge of peak performance
retrospective/recall bias (how reliable is data?)
How is flow experienced by elite athletes? (Jackson, 1996)
challenge/skill balance
absorption in activity
clear goals
unambiguous feedback
concentration
paradox of control
loss of self consciousness (in tune)
enjoyable experience
Transformation of time
What is selective attention?
capacity to focus on one element and ignore others
What is vigilance?
maintaining constant level of attention
What are allocating attention also called?
shifts
What is goal-focused attention?
keeping specific goal/task in mind despite distractions
What is meta awareness?
ability to track the quality of one’s own awareness
What is mindfulness training?
general attention training
What is “don’t think of a pink elephant” an example of?
ironic effect
What is choking?
mix of poor focus/heightened anxiety from overthinking, self consciousness, and trying to hard to control skill execution
What is a clutch performance?
psychological state associated w/ peak performance
involves deliberate focus, heightened awareness of situational demands, and intense effort
In what situations are the amount of attention dependent?
dual tasks (primary vs secondary)
number of stimuli
level of anticipation
sport/concentration training and experience
neurotransmitters (dopamine, norepinephrine)
arousal level (cue utilization)
stage of learning
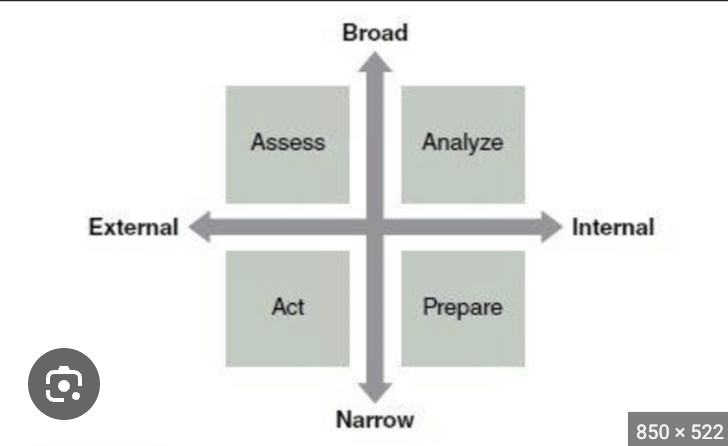
What is Nideffer’s (1976) theory of attention?
width = broad vs. narrow attentional focus
direction = internal vs. external attentional focus
B/E = assess
B/I = analyze
N/E = perform
N/I = rehearse
What is arousal?
general state of physiological and psychological alertness/readiness
What is activation?
readiness of particular systems in body/mind for a task
What is task specific activation?
focusing attention/readiness for particular action
What is cognitive activation?
focusing attention/cognitive resources on challenge
How do arousal and activation go hand in hand?
increased arousal/activation stem from high levels of stress (physical tension)
excessive muscular tension interferes execution of skill (prevents coordinating movement appropriately)
What are competitive stressors?
demands associated with competitive performance
What are organization stressors?
demands associated with sports organization
What are personal stressors?
demands associated with personal life
What is state anxiety?
immediate emotional state characterized by apprehension, fear, tension, increase in physiological arousal