integumentary system!
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
what is the largest organ in the human body?
skin
what percent of total body weight in the integumentary system?
15%
what is the function of the integumentary system?
-microbial function
-formation of vitamin D
-temperature
-sensory
-excretion
describe the epidermis?
outer, protective layer
describe the dermis?
thick layer of connective tissue. allows skin to stretch and contract
describe the hypodermic?
subcutaneous layer
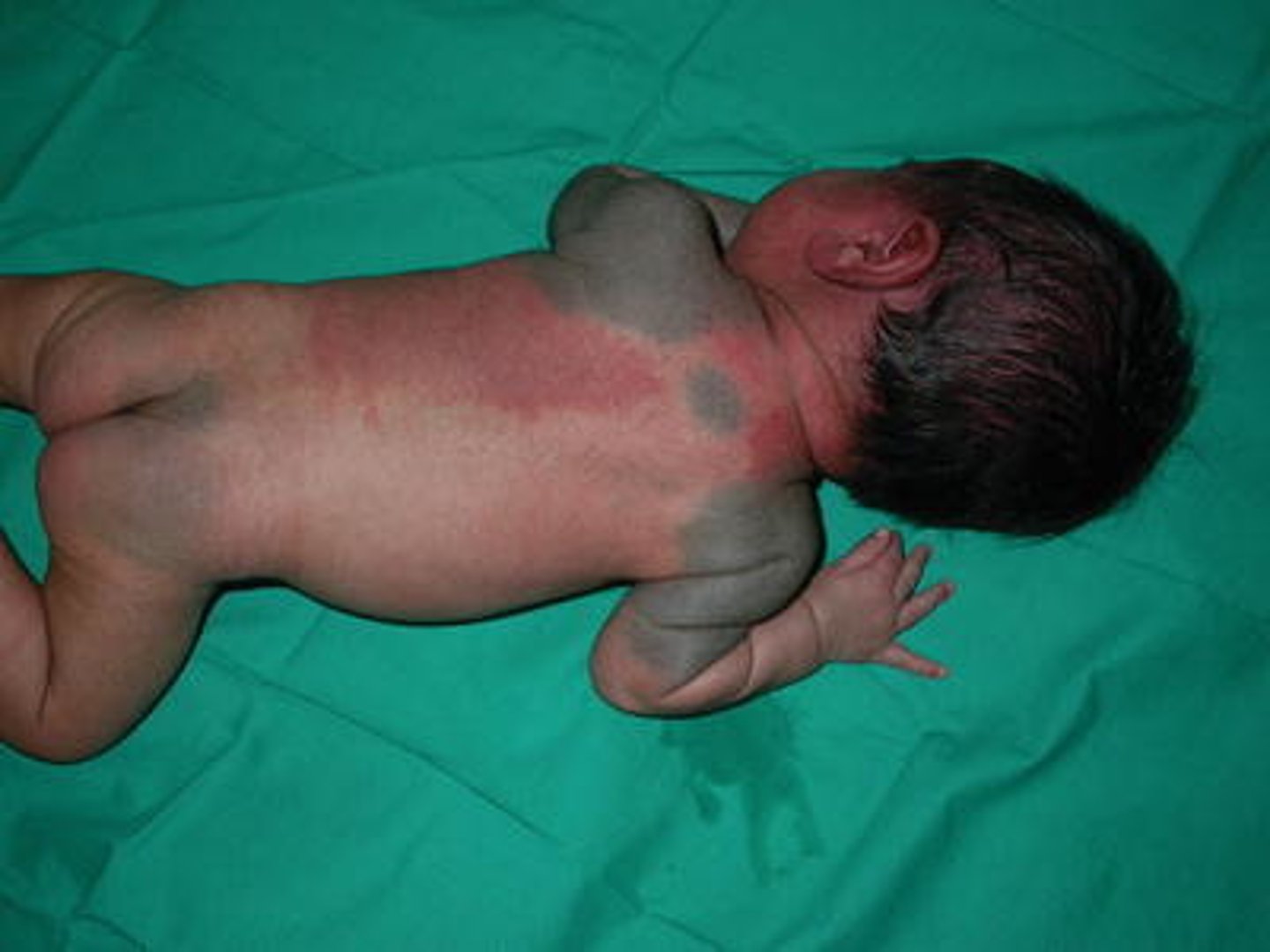
what are Mongolian spots?
dark purple spots. more common in asian and black neonates. are usually gone around ages 6-10
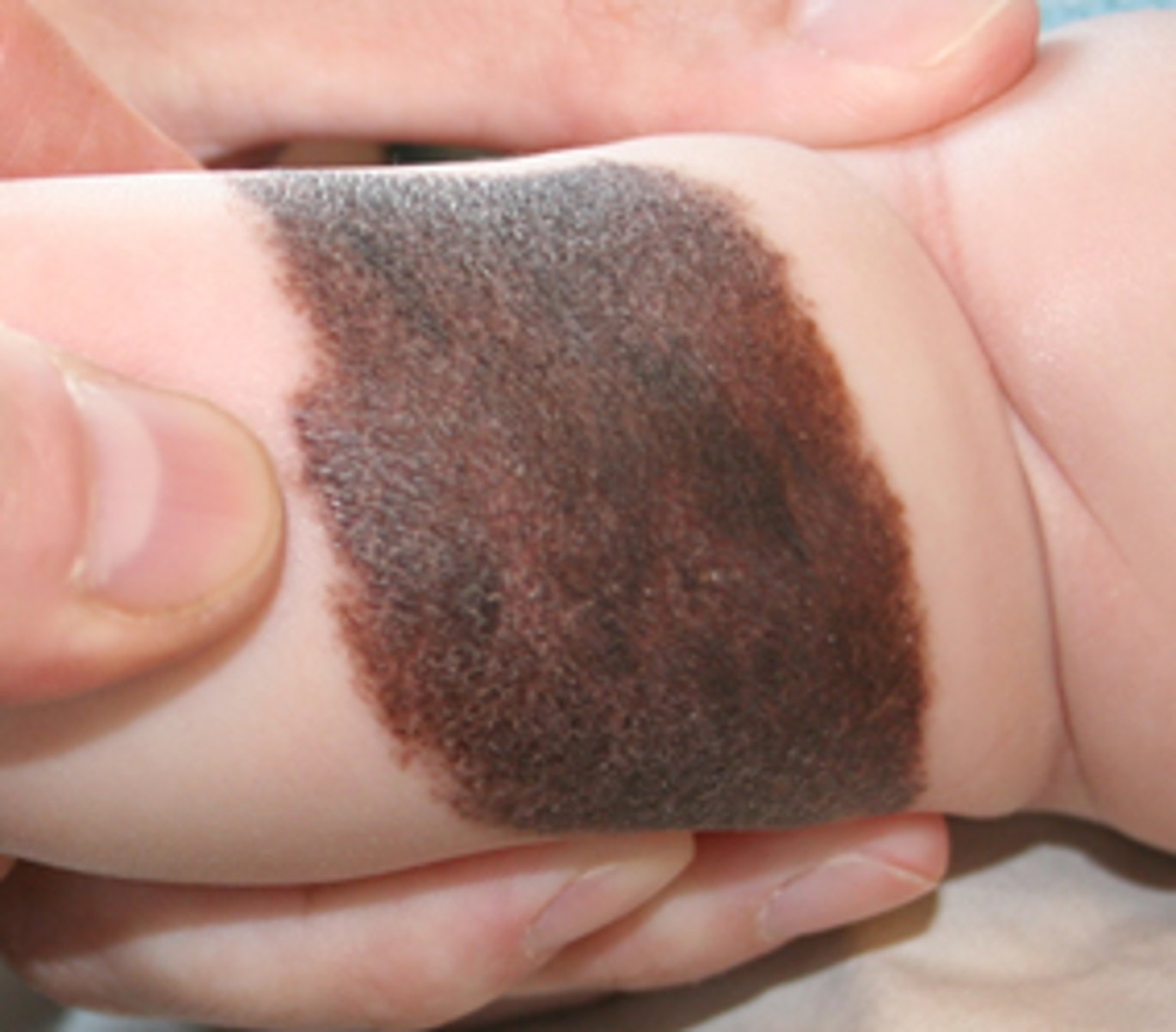
what does congenital nevus increased the risk of?
increase the risk of developing melanoma
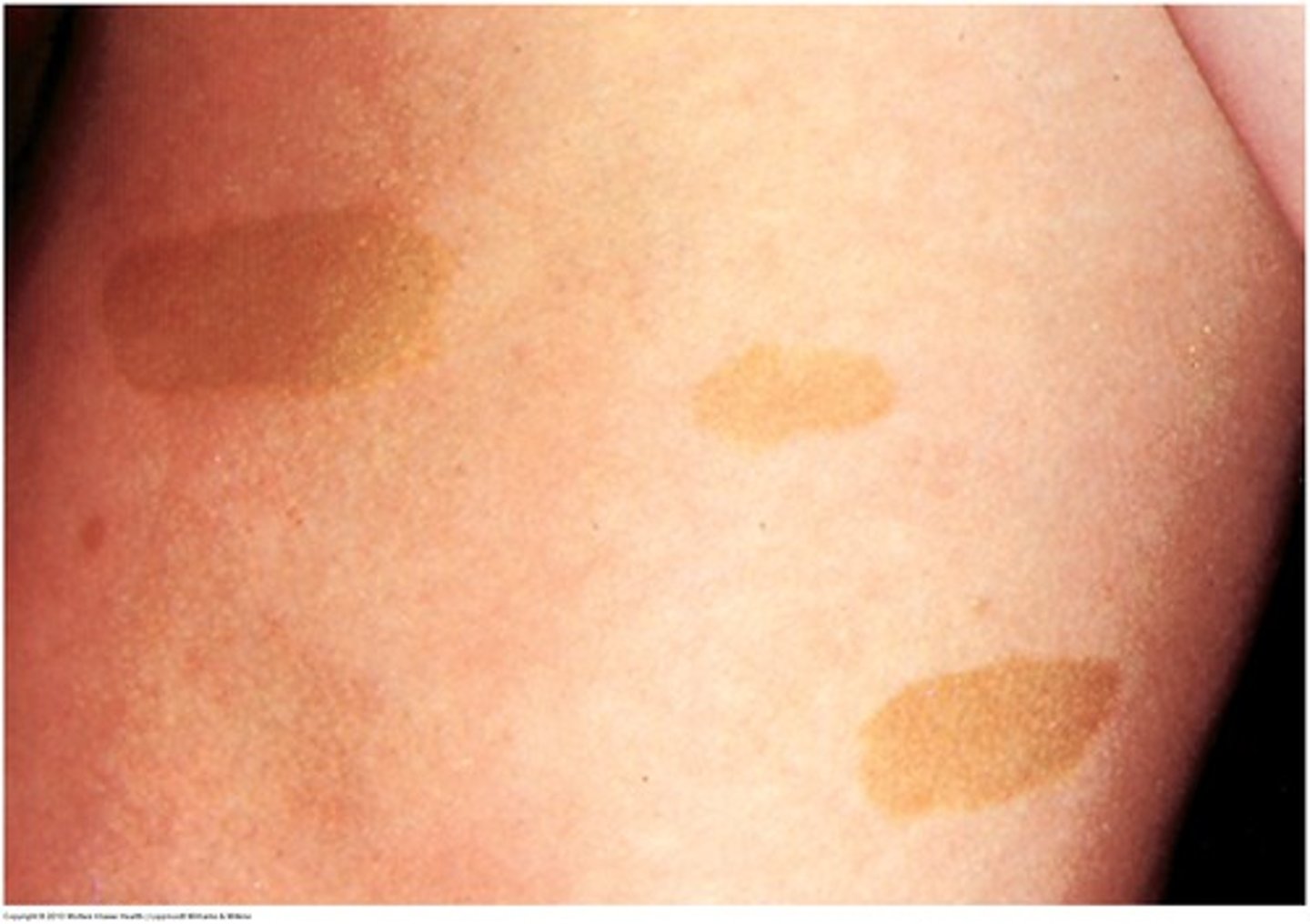
what may cafe au lait be associated with?
neurofibromatosis type 1
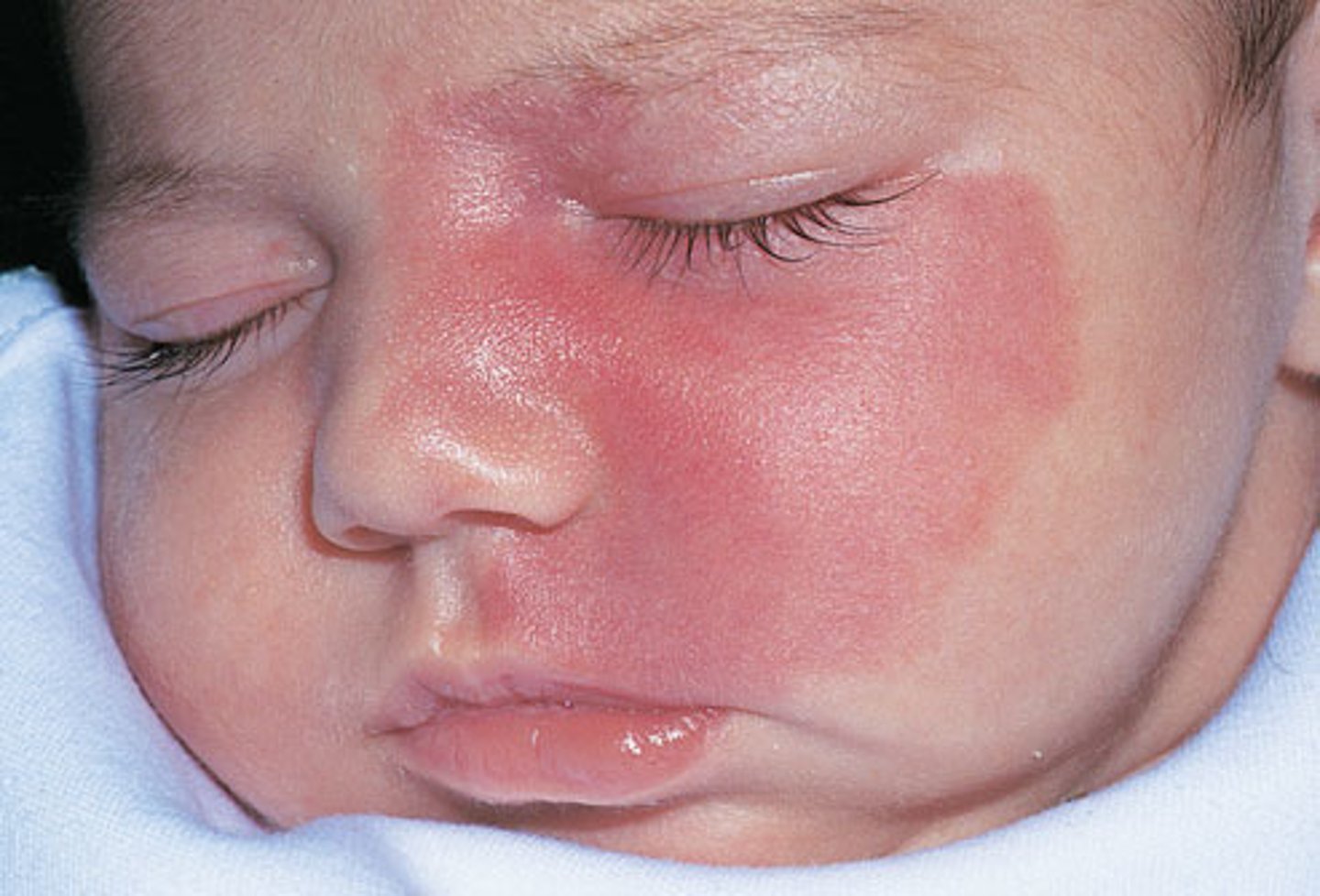
where is nevus simplex or macular stain common?
eye lids, nape of neck
describe port wine stains?
vascular mass formations. grow with time
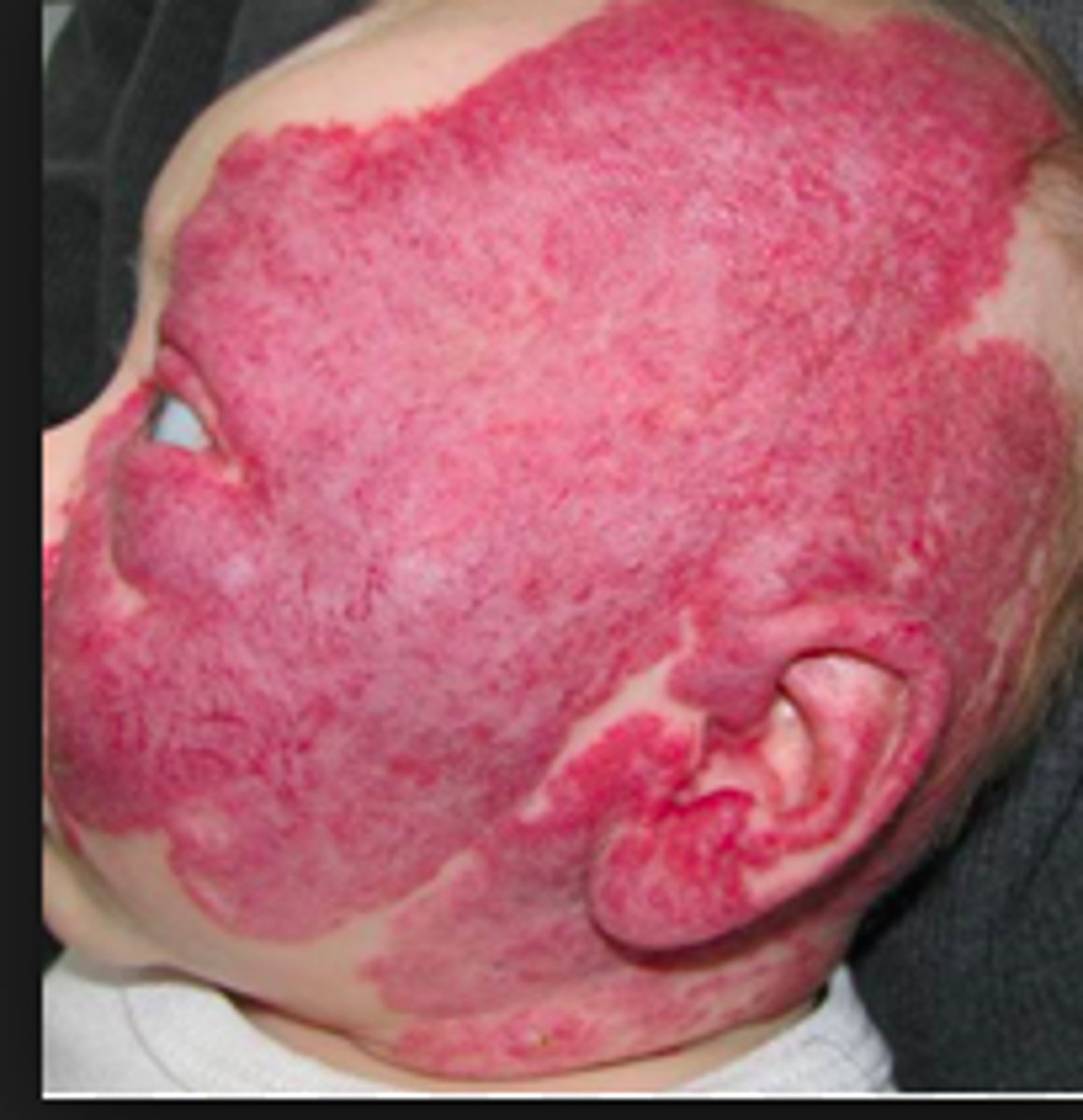
what are some inflammatory disorders of the skin?
-contact dermatitis
-atropic dermatitis
-eczema
-psoriasis
what is contact dermatitis?
localized inflammatory response to chemical or physical agents
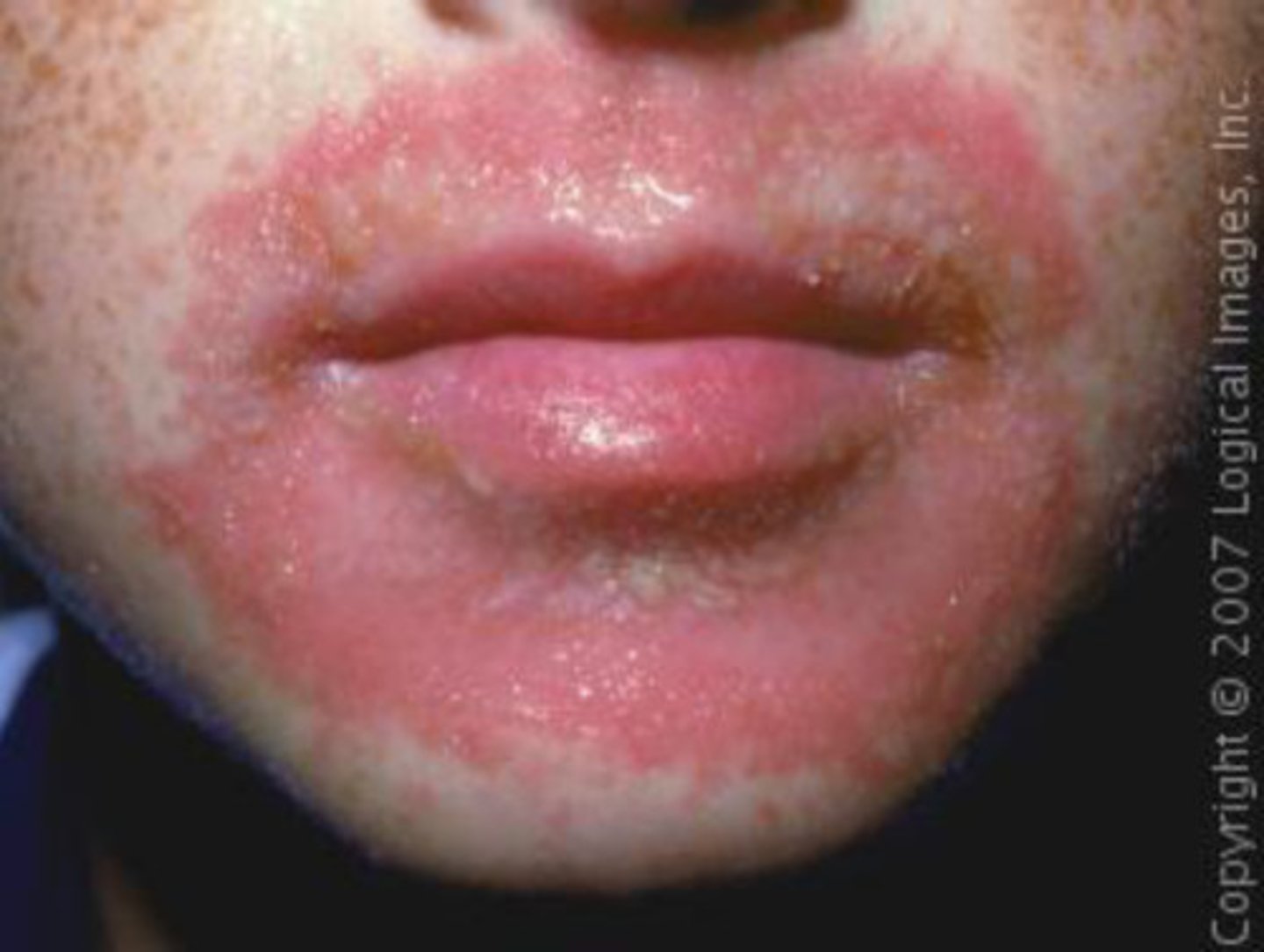
what are common irritants of contact dermatitis?
-soaps and detergents
-chemicals
-poison ivy
-metals -> nickle
what are clinical manifestations of contact dermatitis?
-erythema
- itching or burning
-vesicles/bullae (fluid filled pimples)
-patches
what is atropic dermatitis also known as?
eczema
what types of factors does atropic dermatitis have?
genetic and environmental factors
what is the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis?
-skin barrier dysfunction
-immune system dysregulation
causes of atopic dermatitis?
-family history
-stress
-impaired skin barrier
-nervous system imbalance
-immune dysfunction
-environmental pollution
-excessive hygiene
what are clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis?
-dry, itchy skin
-usually found in the folds of skin
-episodes of remission and exacerbations
how may atopic dermatitis appear in infants and toddlers?
appear as a rash on the scalp, face or arms and legs
how does atopic dermatitis appear in children?
may begin inside creases of the elbows or knees, the neck, wrists, ankles, and/or crease between the buttocks/legs
how does atopic dermatitis show in adults?
on the inner creases of the elbow or knees, hand, and/or nape of the neck
what is the treatment for atopic dermatitis?
-skin hydration (less frequent bathing)
-emollients and moisturizers (fragrant free soaps)
-eliminating irritants
-medication therapy
describe bleach baths for atopic dermatitis?
may help reduce inflammation and itching
topical corticosteriods potency and class?
1 super high potency and 7 least potent
what is psoriasis?
chronic inflammatory skin disease; hyper proliferation (extra build up of skin cells)
what is the most common type of psoriasis?
chronic plaque psoriasis. in the scalp, extensor elbows, knees, gluteal cleft
what are the clinical manifestations of psoriasis?
-thick, silver plaques
-well defined borders
-pruritic
-itchy
-red raised lesions that is itchy
what makes psoriasis worse?
stress
what is gute?
drop like. dudden eruption of really small psoriasis plaques
what is pustular psoriasis?
acute on the spread of widespread ephemeral, scaling, pustules
what areas does psoriasis effect?
areas like the axilla or underneath the armpit, perennial, or genital regions
psoriasis
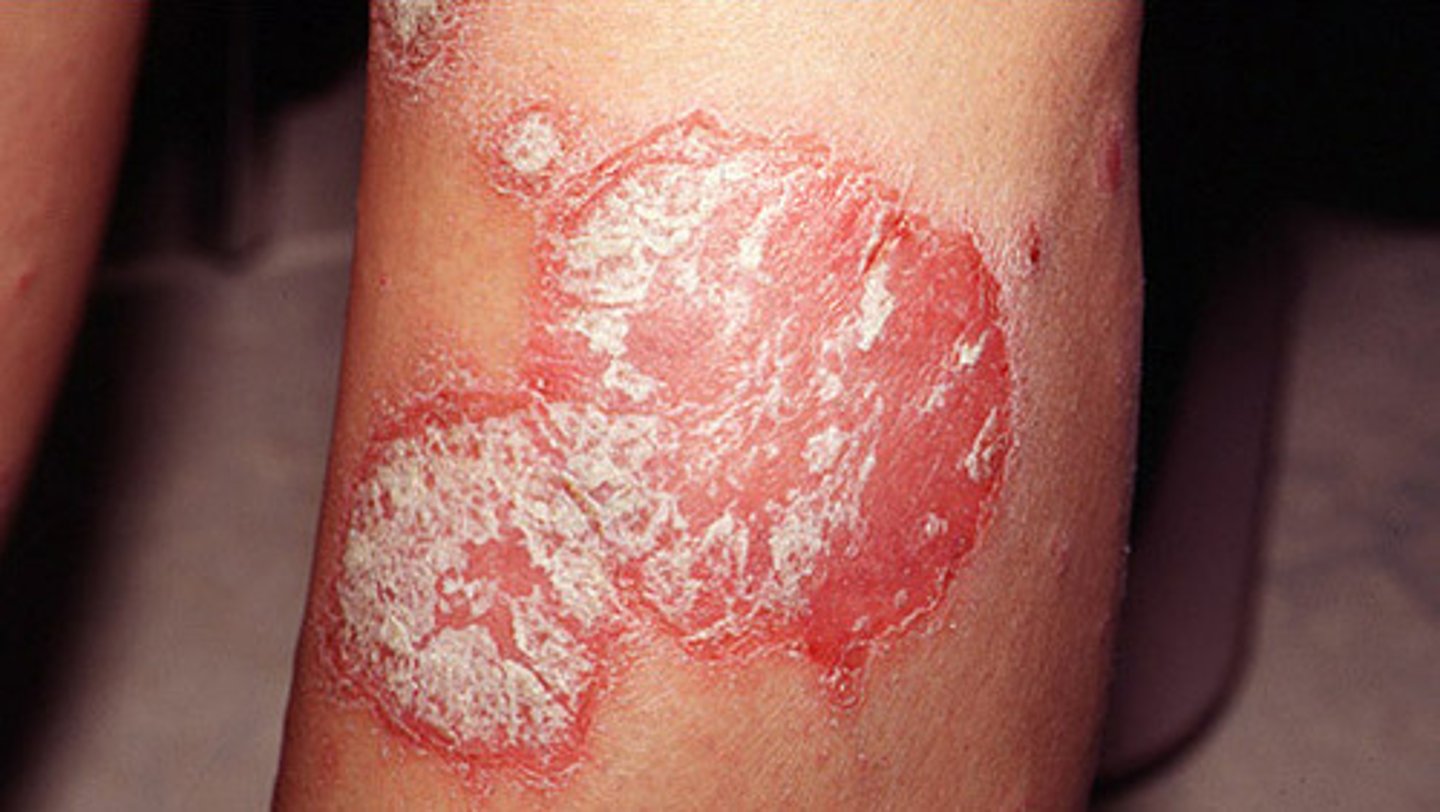
what is the curative treatment for psoriasis?
no curative treatment, goal is to manage symptoms
what are the topical ways to help manage psoriasis symptoms?
corticosteroids and calcitriol
what is calcitriol?
type of vitamin D that helps skin cell production
what is systemic psoriasis treatment?
methotrexate
what is methotrexate?
immunosupprescent for severe forms of psoriasis when other methods have failed. used with folic acid to prevent adverse effects. adverse effects are hepatoxicity and increased risk for infection
what is urticaria also known as?
hives
what can urticaria be triggered by?
medication, food, insect sting
what happens during urticaria?
mast cells are activated which release histamine which causes the swelling and itching
what can urticaria be accompanied by?
angioedema
what may urticaria appear with?
anaphylaxis
when is urticaria be considered with a medical emergency?
angioedema and SOB
what is a treatment for urticaria?
epinephrine
hives
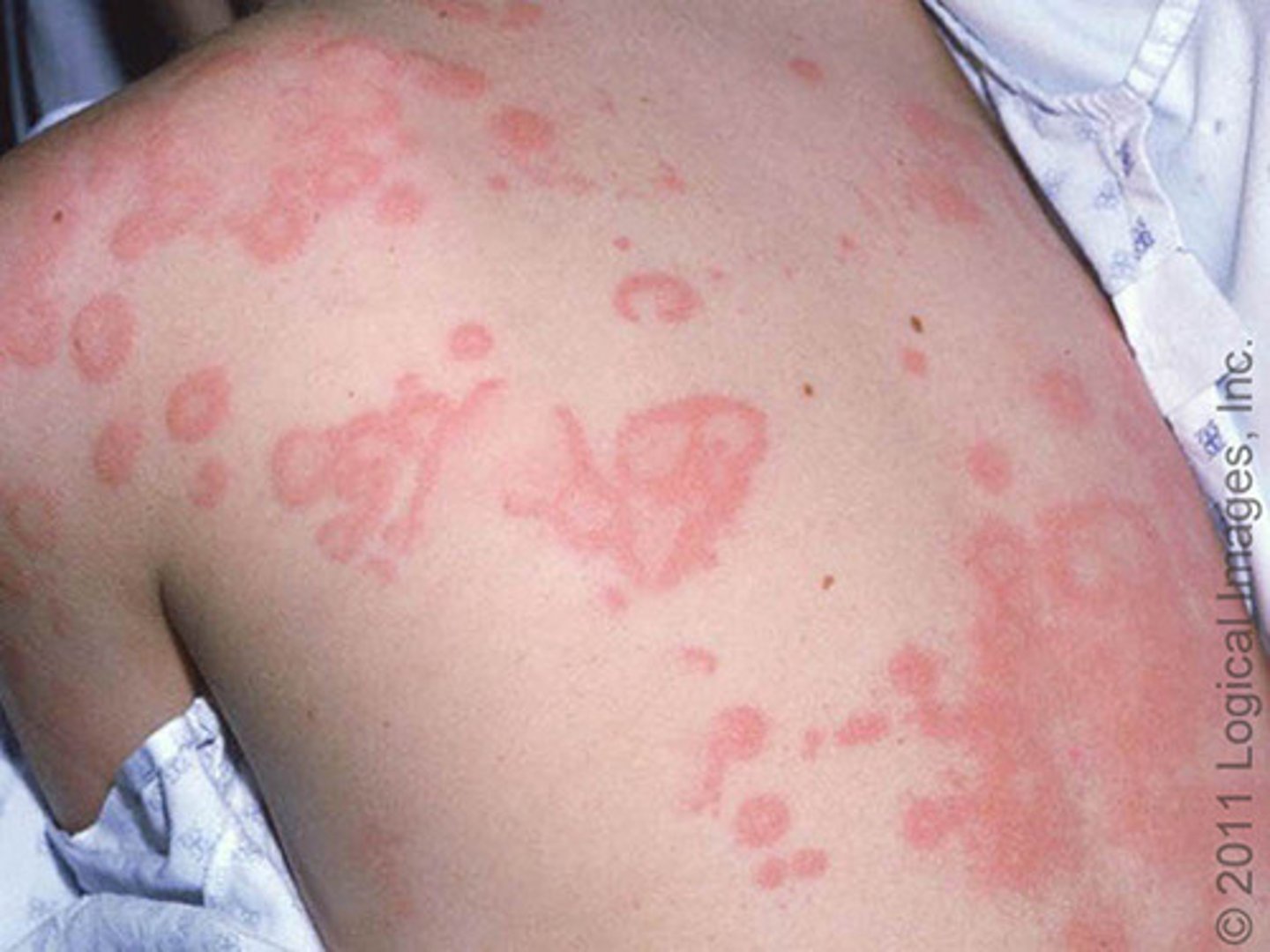
what are infectious disorders of the skin?
bacterial, viral, parasitic, and fungal
what is folliculitis?
infected hair follicle. painful and itchy
what can folliculitis be caused by?
tight fitting clothing, shaving or waxing, hot tubs
what to do for the treatment of folliculitis?
antimicrobial cleanser (benzoyl peroxide). for more severe use oral antibiotics
folliculitis
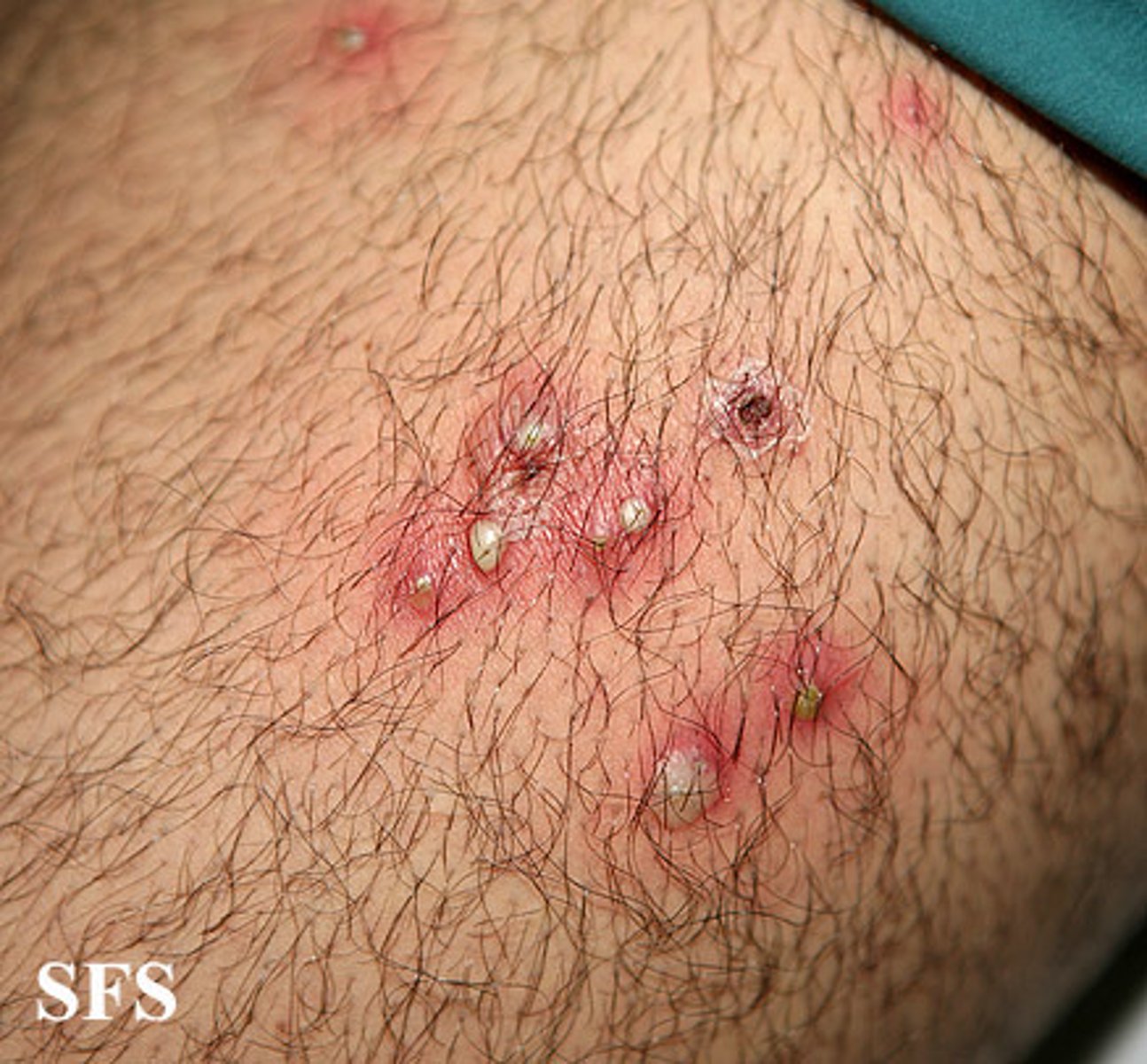
what is cellulitis?
infection of the skin. dermis and subcutaneous layers
what are the clinical manifestations of cellulitis?
swelling, erythema, tenderness, and warmth. can go all the way around the limb
what are risk factors of cellulitis?
decreased immune system, any cuts or abrasions
what to use for severe cases of cellulitis for treatment?
systemic antibiotics
what is an abscess caused by?
staphylococcus aureus or methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
what does an abscess look like?
painful, red nodule
what is the treatment for abscess?
antibiotics, may require surgical damage
what is impetigo?
superficial bacterial infection of the skin
is impetigo contagious?
YES
who is impetigo most common in?
children age 2 to 5
what are the clinical manifestations of impetigo?
-honey crusted lesions
-crusts
-painful
-usually involves face and extremities
what is the treatment for impetigo?
Mupirocin is first line of treatment. 3 times a day for 5 days. antimicrobial ointment
when can kids return back to school with impetigo?
after 24 hours after mupirocin treatment. if lesions haven't crusted over keep them covered
what is necrotizing soft tissue infections?
infection in the soft tissue that leads to the destruction of the muscle and fat
what are the clinical manifestations of necrotizing soft tissue infections?
-severe pain
-erythema without sharp margins
-crepitus
-fever
-tachycardia
what is crepitus?
gas build up and when you push on it it feels and sounds like Rice Krispies
what is the treatment for necrotizing soft tissue?
-aggressive surgical debridement
-systemic antibiotics
-can be fatal
-can lead to amputation
how is HSV transmitted?
via oral secretions
clinical manifestations of HSV?
painful, vesicular lesions
HSV1?
mouth and lips
HSV2?
genitals
when is HSV more likely to be spread?
when the lesions are active
when is antiviral therapy more effective?
when started within 72 hours of the lesion appearing
what are the two variations of varicella zoster virus?
chickenpox and shingles
when do symptoms develop in chickenpox?
15 days after exposure
how does chicken pox develop?
macules to papules to vesicles
clinical manifestation of chicken pox?
itchy
clinical manifestation of shingles?
painful, unilateral vesicular eruption
how does shingles happen?
activation of latent VZV. people who have had inactive chicken pox
what is the treatment for shingles?
antiviral treatment -acyclovir
what is scabies?
mite infestation of the skin
how is scabies transmitted?
via direct contact
what are the clinical manifestations of scabies?
severe pruritic (itching), worse at night. burrows in the skin
what is pediculosis?
lice infestation
pediculosis capitis?
head lice
pediculosis corporis?
body lice
pediculosis pubis?
pubic lice
pediculosis ciliaris?
eyelash lice
what are the clinical manifestation of pediculosis?
itchy scalp, nits.
what is the treatment for pediculosis?
permethrin., wash sheets and clothing on high heat
directions for permethrin for head lice?
-apply on clean, towel dried hair
-leave on for 10 minutes
-comb remaining nits out
-apply 9 days later is nits are still observed
directions for permethrin for scabies?
-apply to the entire body from the neck down
-leave on for 8 hours
what are fungal infections also known as?
tinea infections. can affect many parts of the body
what in tinea corporis?
ringworm
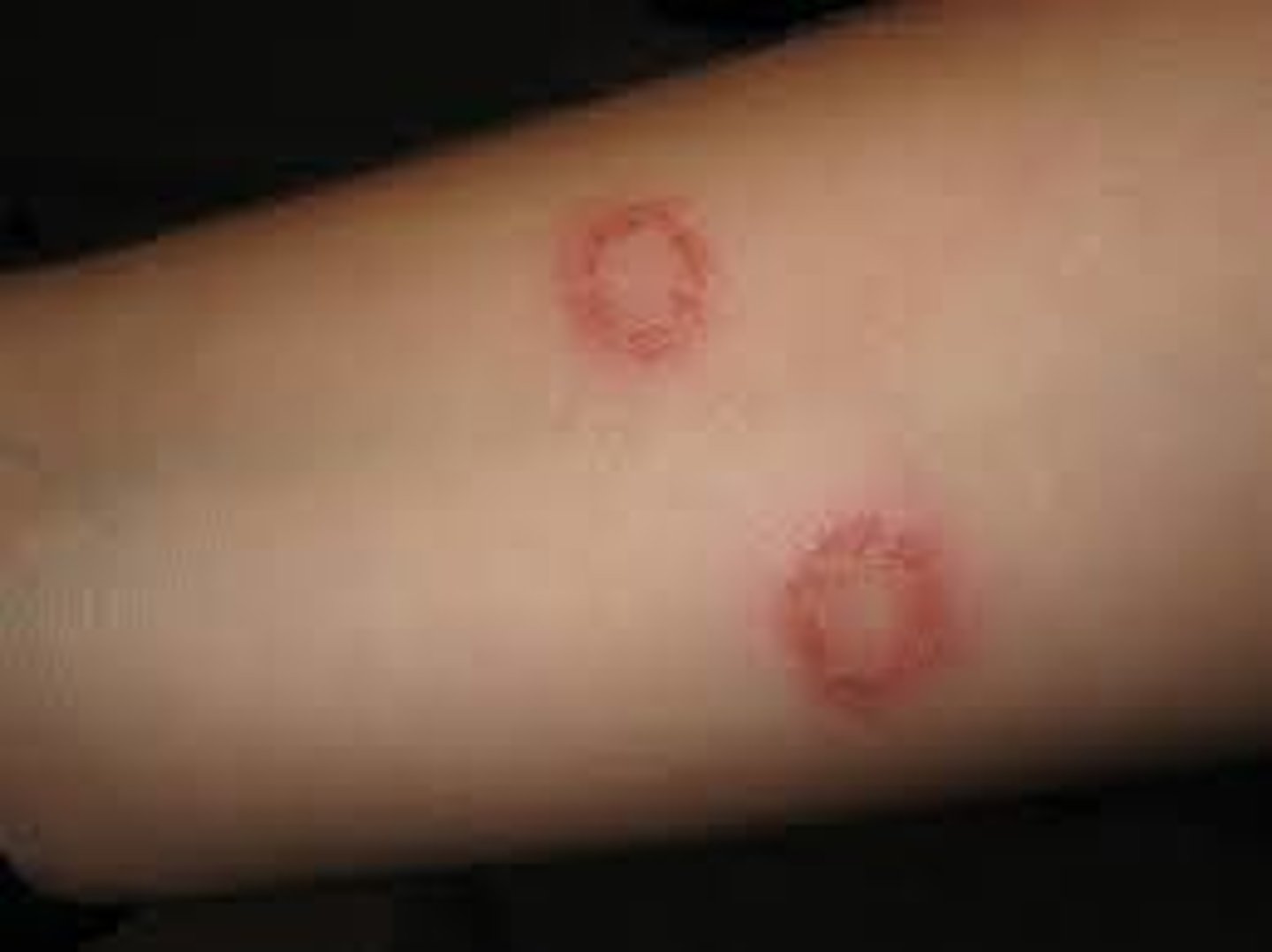
topical anti fungal agents?
clotrimazole and ketoconazole
systemic anti fungal agents?
fluconazole and terbinafine
what are nursing considerations for anti fungal agents for oral?
have a risk of hepatotoxicity. take for six to 12 weeks
what are examples of integumentary trauma?
burns and pressure injury