A &P Chapter 4
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
primary tissue types
epithelial tissues
connective tissues
muscle tissues
nervous tissues
Defined by kind and number of cells, amount and composition of ECM and specific functions
epithelial tissues
tightly packed sheets of cells with no visible ECM
cover and line all body surfaces and cavities
specialized tissues form glands that manufacture secretions (sweat, saliva, or chemical messengers, like hormones)
connective tissues
connect all other tissues to one another like Velcro
ECM is a prominent feature for most connective tissue types
cells scattered throughout
bind, support, protect, and allow for transportation of substances
muscle tissues
capable of generating force by contracting
little ECM between cells
nervous tissues
capable of generating, sending, and receiving messages
cells that support this activity within unique ECM
Extracellular matrix
substances in liquid, thick gel, or solid form that surround cells of tissue
ground substance and protein fibers
ECM functions
provides tissue with strength to resist tensile and compressive forces
direct cells to proper positions within tissue and holds those cells in place
regulates development, mitotic activity, and survival of cells in a tissue
holds cells in their proper positions
ground substance
most of ECM
extracellular fluid/interstitial fluid with water, nutrients, ions, and macromolecules
ground substance macromolecules
GAGs, proteoglycans, CAMs
Glycosaminoglycans
GAGs
polysaccharide chains
chondroitin (small) and hyaluronic acid (enormous)
negative charges of sugars attract positively charged ions in ECF
these ions create a concentration gradient within ECF and draw water out of cells and blood vessels via osmosis, which trap water in ECM and help it resist compression → Gradients Core Principle
Proteoglycans
GAGs bound to protein core
thousands of these bind to a very long GAG (ex hyaluronic acid) and forms huge ______ aggregates which make ECM firmer, more solid, and resistant to compression
aggregates form barrier to diffusion of substances through ECM and protect underlying tissue from invading microorganisms
Cell-adhesion molecules
different types of glycoproteins
adhere cells to cells
adhere cells to surroundings
hold everything in place within ECM like glue
bind to cell surface proteins, protein fibers, and proteoglycans
maintain normal tissue architecture
protein fibers
embedded within ground substance
long molecules composed of multiple fibrous subunits with ropelike structure
enormous tensile strength
three types: collagen, elastic, and reticular
collagen fibers
make up 20-25% of all proteins in body
composed of multiple repeating subunits
form white fibrous protein
restraint to tension and pressure
elastic fibers
surrounded by glycoproteins
extensibility allows fibers to stretch without breaking and return to their resting length
reticular fibers
thin, short collagen fibers
form meshwork or scaffold that supports cells and ground substance of many tissues
form weblike structure in organs such as the spleen that helps trap foreign cells
cell junctions
another way cells bind to one another
neighboring cell’s plasma membranes are linked by integral proteins
3 major types: tight, desmosomes, and gap
tight/occluding junctions
hold cells closely together
space between is impermeable to movement of macromolecules
integral proteins of adjacent cell’s plasma membranes are locked together and form a seal around apical perimeter of cell like a zipper
seal may not be complete, allowing leakage for some tissues
Ex: between cells in blood vessels (prevent blood cells from exiting vessels)
desmosomes
linking integral proteins
allows for materials in ECF to pass through space between cells (more like a button)
increase strength of tissue by holding cells together → mechanical stress is more evenly distributed
integral “linker” proteins are attached to intermediate filaments of cytoskeleton for structural reinforcement
located in tissues that are subjected to a great deal of mechanical stress (ex: epithelia of skin)
gap junctions
small pores formed by protein channels between adjacent cells
allow small substances to flow freely between each cell’s cytoplasm
located in between cells that communicate with electrical signals
illustrate cell to cell communication core principle
epithelia tissues
on every external and internal body surface
barrier between body and external environment
line organs and fluid filled cavities
epithelial tissue functions
protection - shield underlying tissues from mechanical and thermal injury
immune defense - form physical barrier to prevent invasion by microorganisms; specialized immunity cells are scattered throughout tissue
secretion - form glands that produce hormones and oils
transport into other tissues - selectively permeable membranes
sensation - rich nerve supply; detect changes in internal and external environments
basement membrane components
basal lamina and reticular lamina
two layers glue epithelia tissue to underlying connective tissue, anchor underlying blood vessels in place, and provide barrier between epithelia and underlying tissues
basement membrane
beneath cells; where ECM is found
basal lamina
ECM is synthesized by epithelial cells
consist of collagen fibers and ground substances
reticular lamina
synthesized by underlying connective tissue
consists of ____ fibers and ground substance
simple epithelia
single cell layer
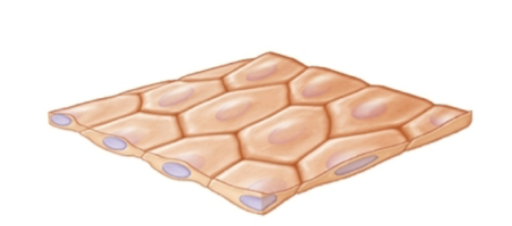
stratified epithelia
more than one cell layer
best as productive barriers where subjected to high degrees of mechanical stress
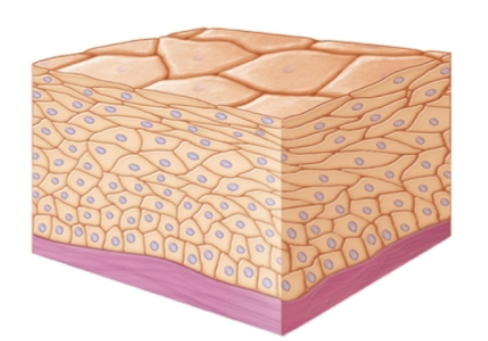
epithelia classification
classified by number of cell layers and shape of cells in those layers
cuboidal cells
short

squamous cells
flattened
columnar cells
tall and elongated

simple epithelia function
adapted for transportation of substances between different tissues
some have microvilli for increased surface area
some have cilia (move through hollow organs)
structure-function core principle
types of simple epithelia
simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified columnar epithelium
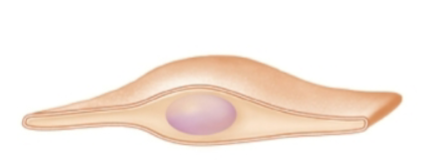
simple squamous epithelium
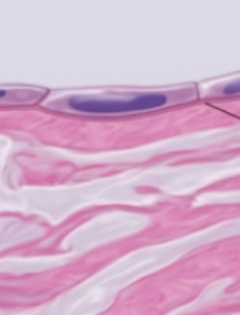
simple squamous epithelium function
adapted for rapid diffusion of substances (oxygen, carbon dioxide, fluids, and ions)
located in air sacs of the lung (parietal pleura), specific segments of kidney tubules, and lining of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and alveoli
simple cuboidal epithelium
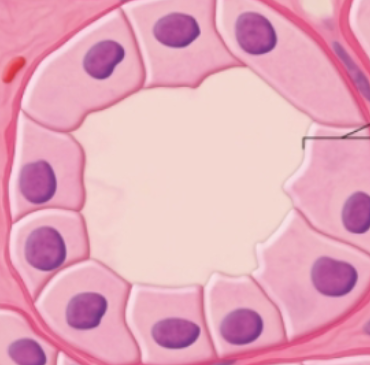
simple cuboidal epithelium function
large central nucleus
thin enough for rapid substance diffusion
located in segments of renal tubules, respiratory passages, the ducts of many glands (ex: salivary; mammary), and thyroid gland
simple columnar epithelium
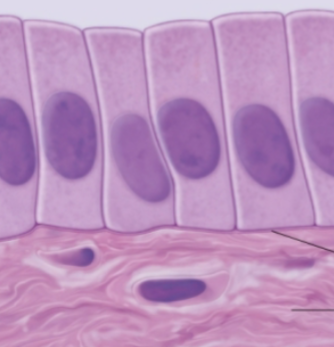
simple columnar epithelium function
nuclei in basal portion of cell
The apical plasma membranes of these cells are often folded into microvilli, which increases their surface area for absorption → mostly in small intestine
may also contain cilia on apical plasma membrane → mostly for uterine tubes and segments of respiratory tract
lines digestive tract, uterine tubes, gall bladder, certain kidney tubules
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
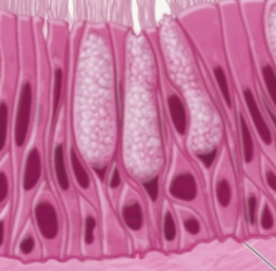
pseudostratified columnar epithelium function
nuclei are at varied heights which gives a layer look
only one cell layer thick with basal plasma membranes firmly in contact with basement membrane
ciliated
line upper respiratory tract, a part of the male urethra, and nasal cavity
types of transport across simple epithelia
paracellular transportation and transcellular transportation
paracellular transportation
substances “leak” between cells in epithelial membrane
limited due to tight junctions that makes spaces between cells nearly impermeable
passes through narrow space between cells
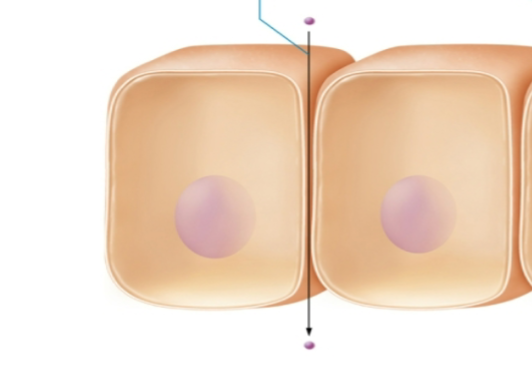
transcellular transportation
think through
substance enters cell by crossing plasma membrane, diffuses across cytosol, and exits through plasma membrane at opposite side
stratified epithelium types
keratinized stratified squamous; nonkeratinized stratified squamous; stratified cuboidal; stratified columnar; transitional epithelium
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
apical cellular layers are dead + lack nuclei
filled with keratin (a protein) which make tissues tough and resistant to friction
well adapted for outer layers of skin
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
apical cellular layers retain nuclei and are still alive
located in regions subjected to mechanical stress where surface must remain moist
located in mouth, throat esophagus, and vagina
stratified cuboidal epithelium
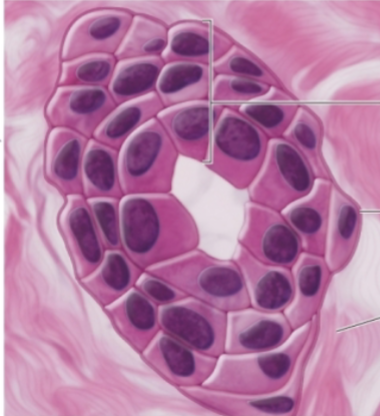
stratified cuboidal epithelium function
rare in humans
two cell layers
lines ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and the pancreas
lines developing ovarian follicles and seminiferous tubules
stratified columnar epithelium
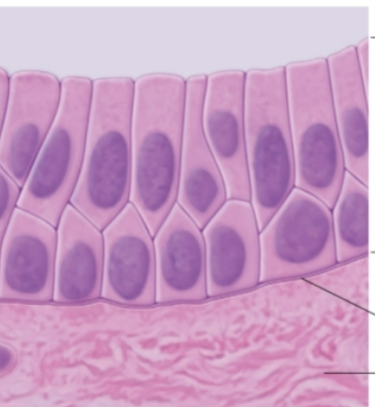
stratified columnar epithelium function
rare in humans
few layers - apical layer is columnar and basal layer is cuboidal
located in male urethra, cornea of eye, ductus deferens and ducts of certain glands (ex: salivary glands)
transitional epithelium
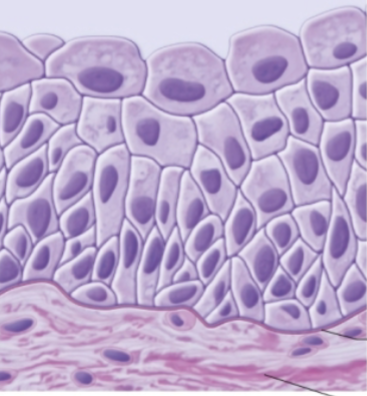
transitional epithelium function
only in urinary system
lines interior of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra
cuboidal basal layers and apical cell layers are dome-shaped when the tissue is relaxed
apical cells can flatten which allows tissues to stretch → think about bladder expanding to hold pee
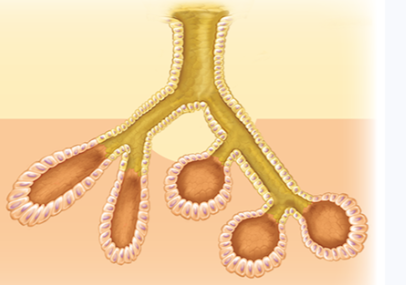
gland
arises from epithelial tissue that migrated into deeper connective tissue instead of remaining at surface
synthesizes and secretes product from designated secretory cells
classified by shape or how products are released
mechanisms: endocrine/exocrine
endocrine glands
secretes products, usually hormones, directly into blood stream without use of ducts which allows product to have large effects on distant cells
the communication between cells in distant areas of body → cell-cell communication core principle
exocrine glands
release products onto apical surfaces of epithelium (external surface of body) or lining hollow organs that open to outside of body
products that are secreted from gland through epithelial-lined duct only have local effects in gland-vicinity
glands vary in complexity
3 possible configurations: acinar, tubuloacinar, and tubular
goblet cells
most common unicellular exocrine gland
in digestive and respiratory tracts
secrete mucus that protects underlying epithelium
exocrine gland classification
multicellular
classified according to structure of ducts and shape of clusters of secretory cells
simple glands - don’t branch
compound - do branch
simple tubular
long and straight
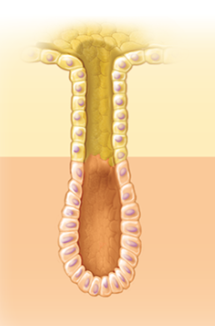
simple acinar
spherical
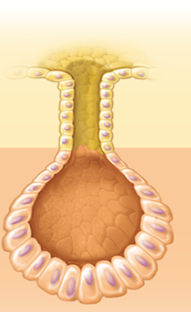
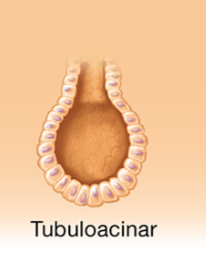
tubuloacinar
both tubular and acinar portions
compound acinar
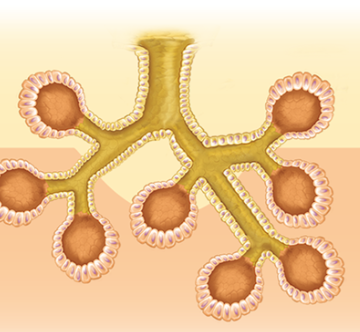
compound tubuloacinar
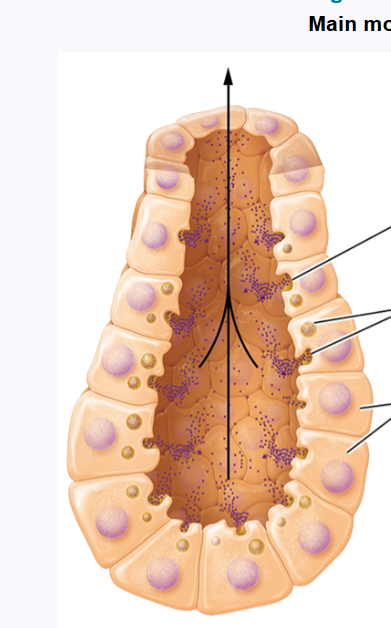
merocrine
used by majority of exocrine glands (including salivary and sweat glands0
products packages in secretory vesicles for release by exocytosis into ducts
holocrine
used by sebaceous glands in skin to secrete sebum
secretory cells accumulate product in cytosol and only release product when cell ruptures and dies
cells replaced by mitosis at gland base
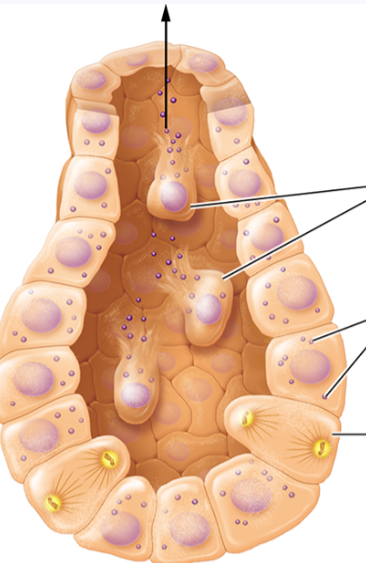
apocrine
rare type of secretion
portions of cytoplasm are pinched off when product is being secreted
observed during liquid lipid droplet secretion in lactating mammary glands of many mammal species
connective tissue functions
connecting and binding - anchor tissues layers in organs and link organs together
support - bone and cartilage support weight of body
protection - bone tissue protects internal organs; cartilage and fat provide shock absorption; components of immune system are throughout tissues
transport - blood is fluid ____ tissue; main transport medium in body
connective tissue components
cells (surrounded by protein fibers and embedded in ground tissue) and ECM
connective tissue proper
widely distributed in body
connect tissues and organs to one another
components of internal architecture of some organs
cells of connective tissue proper
fibroblasts; adipocytes; mast cells; phagocytes; other immune system cells
fibroblasts function
most common resident cell
mature cells with properties of immature blast cells
make protein fibers and ground substance (components of ECM)
continually produce collagen proteins
fibroblasts
adipocytes
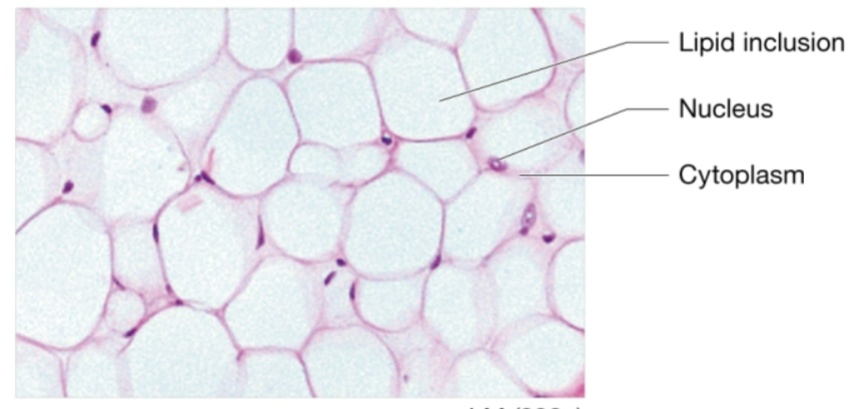
adipocytes function
fat cells
in many different connective tissues
cytoplasm filled with single large lipid inclusion (triglycerides) - takes up most of cell so nucleus is pushed to the side