CS21003 - Multi-Paradigm Programming
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
NEED TO ADD: stack, deq, file handling, all C++, hash tables
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What is the file extension for files in C?
.c
C - get input function
scanf()
Format specifier for int
%d
Format specifier for float
%f
C - display output function
printf()
Format specifier for double
%lf
Format specifier for char
%c
Format specifier for string
%s
#include <> vs ““
<> is used for libraries and “" is used for header files
Is C an OOP?
No
int numbers[?][?] = {
{1,2.3},
{4,5,6}
};Fill in the question marks
2 3
What is the keyword for setting a constant (at the top of file)
#define
Flag to rename .exe file when using gcc compilation
-o (gcc hello.c -o my-prog)
What do structs contain?
attributes
What is the include we need for printf?
<stdio.h>
How to guard header files?
#ifndef __FILE_H__
#define __FILE_H__
#endif
Write a hello world program in C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}Fill in the blanks (put commas between answers)
#....... (1) <stdio.h>
.......... (2)
{
printf("Welcome!\n").. (3)
}
include, int main(), ;
n++ vs ++n
The expression ++n increments n before its value is used, while n++ increments n after its value has been used.
(ex: int n =5;
x = n++; sets x to 5
x = ++n; sets x to 6)
What is a pointer?
A variable that contains the address of a variable
Declare a pointer with variable name: age and type: int
int *age;
Fill in the blank line
int myAge = 20;
//pointer age stored address of myAge
..................
printf("%d", *age);int *age = &myAge;
Declare a pointer with variable name: name and type: char
char *name;
Find the error
char myName[] = "Maddie";
char *name = &myName;
printf("%s", name);There should not be an & before myName
int a[10];
1. Defines an array 'a' of size 10
2. A block of 10 consecutive objects named a[0], a[1], ... , a[9]
Name an alternative to scanf()
gets(), fgets(), getline(), getchar(), getc(), fgetc()
What is the difference between strlen() and sizeof()?
sizeof includes the \0 char when counting
strncpy(char `destination, char `source, size_t n);
(` = *)
Copy up to ‘n’ chars from one string to another
strncmp(str1, str2, n)
Compare up to ‘n’ chars between 2 strings
What does strcmp return if both strings are the same?
0
strlen()
Get length of string
strdup()
Duplicate a string by making another copy of it in memory
What library do we need to include to use atoi/atof?
<stdlib.h>
What does atoi() do?
Converts string to int
What does atof() do?
Converts string to float
Is there an error if functions are declared before main() but defined after main()?
No
Create a struct ‘person’ with attributes ‘name’ (50 chars) and ‘age’
struct person{
char name[50];
int age;
);Set int pointer ‘pInt’ to null then set it to the memory address of ‘num’
int *pInt = NULL;
pInt = #What will this output?
int number = 10;
int *numPtr = &number;
*numPtr = 22;
printf("%d\n", number);22
Find the error (what does it output?)
int a[5] = {0,1,2,3,4};
for (int *p = a; p < a + 5; p++){
printf("%d\n", p);
}p in the print statement should be *p (currently outputs memory addresses)
Fill in the blanks
.......... student {
char name[20];
int marks;
} Student;typedef struct
How do you limit the number of characters a user can input?
Put a number between % and s (e.g. %99s)
Write ONE line of code in C to get an ‘ID’ of 10 characters or less
scanf("%10s", ID);Fill in the blanks (comma between)
printf("The length of (1) is (2)", col, strlen(col));%s, %zu
int cmp = strcmp(myStr1, myStr2)
if (.......){
printf("SNAP!");
}Fill in the blank
cmp == 0
What is the difference between static and dynamic memory allocation?
Static memory is allocated at compile time, has a fixed size, and is automatically freed whereas dynamic memory is allocated at runtime, can change size, and must be manually freed
Which header file needs to be included for dynamic memory allocation?
<stdlib.h>
Name memory allocation functions in C
malloc(), calloc(), free() realloc()
malloc()
Allocates a specified number of bytes of memory and returns a pointer to the first allocated byte
calloc()
Similar to malloc but initialises all of the bytes allocated to zero – useful when allocating arrays of numbers or other values
free()
Frees the memory allocated. You must free any memory that you allocate with malloc() or calloc()
realloc()
Can be used to resize a previously allocated space
Fill in the blank
int (1)ptr1 = malloc(size);
*
Fill in the blanks
newNode->(1) = pStack->top;
pStack->top = (2);next, newNode
What is a graph?
A data structure that consists of a finite collection of vertices/nodes and edges
How are graphs represented in a computer?
As an adjacency matrix/adjacency list
What is an unweighted edge recorded as?
1
What is Breadth-First Traversal?
A graph traversal algorithm that explores all nodes at the current "level" before going through all deeper levels
Name 3 applications of BFS
Indexing web pages, GPS, social media friend recommendations
What is Depth-First Traversal?
A graph traversal algorithm that explores one node at the current "level" before going through all deeper levels of that node
Name 3 applications for DFS
Path finding, exploring dependencies, solving puzzles
What are the two main steps of implementing push operation in a stack?
top++ //increment top
stack[top] = push_value //put value in next available location
Steps for DFT
Choose start node (current_node)
Mark current_node as visited (node location)
Find first non-zero value in row current_node. If not visited, visit
Stack will keep record of nodes traversed
Make next node current_node (e.g. if node 0 then node 1 becomes current_node)
Repeat from 2
How to backtrack during DFT?
Pop current_node to backtrack to previous node
Go through new current_node to find path
If no new path backtrack further (new current_node)
What does this code do?
int visited[VERTEX_NUM];
for (inti i=0; i<VERTEX_NUM; i++)
visited[i] = 0;//An array to store the nodes we have visited already
What does this code do?
What does this code do?
top++;
stack[top] = node;Adds a node to the stack
What does this code do?
node = stack[top];
top--;Removes a node from the stack
What notation is file complexity expressed in?
Big O
What is the best, worst and average case for finding a number in an unsorted array?
Best: O(1)
Worst: O(n)
Average: O(n/2)
What is the best and worst case for conducting binary search?
Best: O(1) (first mid-point)
Worst: O(log n)
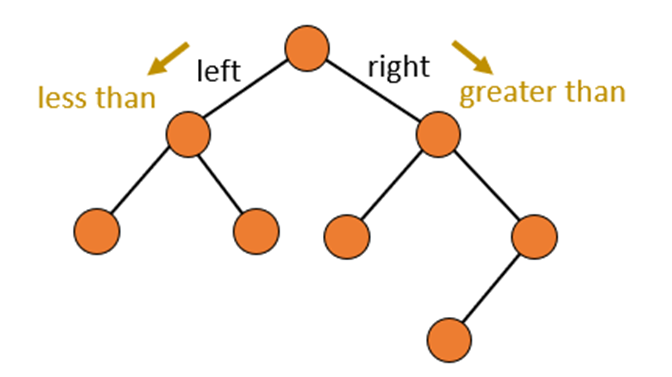
What is the best worst and average time complexity for a binary tree?
Best: O(1) (empty tree)
Worst: O(n) (unbalanced tree linked list basically)
Average: O(log n) (reasonably balanced)
What is the best and worst time complexity for a bubblesort?
Best: O(n) (list is already sorted)
Worst: O(n2)
What is an exponential complexity?
The complexity increases exponentially as ‘n’ increases - O(2n)
What is an example of a situation with exponential complexity?
Password cracking
Write code to open (and close) a file in write mode (no input val)
pointer var: fptr, filename: filename.txt
FILE *fptr;
fptr = fopen("filename.txt", "w");
fclose(fptr);What line of code can be used to check a file (pointer var: fp) is created successfully?
if (fp != NULL)
Name the file access modes
“r”, “w”, “a”, “r+”, “w+”, “a+”
“r”
Open a file for reading. The file must exist.
“w”
Open a file for writing. The file is created if it doesn’t exist. If a file of the same name already exists, it is truncated (made empty)
“a”
Append data at the end of an existing file. The file is created if it doesn’t exist
“r+”
Open an existing file for reading and writing
“w+”
Open a file for reading and writing. The file is created if it doesn’t exist. If a file of the name name already exists, it is truncated (made empty)
“a+”
Open a file for reading and appending
C++ - display output function
cout
C++ - get input fuction
cin
What is the include we need for cout?
<iostream>
What is the file extension for files in C++?
.cpp
What is the namespace we need for cout?
std
Is C++ an OOP?
Yes
Write a hello world program in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}What does this code do?
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < l; j++){
cout << "*";
}
cout << "\n";
}Displays a rectangle of stars (w x l)
Fill in the blanks (comma between answers)
#include <iostream>
#include (1)
using namespace std;
int main()
{
(2) file("file.txt");
if (3()) {
cerr << "Error opening file!" << endl;
return 1;
}
if (file.4()) {
cerr << "Serious error" << endl;
return 1;
}
else if (file.5()) {
cerr << "Non-fatal error" << endl;
return 1;
}
else if (file.6()) {
cout << "\nEnd of file reached." << endl;
}
if (file.7()) {
cout << "File is good for I/O operations." << endl;
}
file.8();
return 0;<fstream>, ifstream, !file.is_open, bad, fail, eof, good, close
When is ‘cerr’ used?
To display an error message
The ___ function is the entry and exit point in a C/C++ program