Bio Ch. 6 and 7 Vocab
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
cellular respiration
the aerobic harvesting of energy from food molecules, the energy-releasing chemical breakdown of food molecules, such as glucose, and the storage of potential energy in a form that cells can use to perform work; involves glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation ( the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis/ ATP Synthase)
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
the series of electron carriers molecules that shuttle electrons during a series of redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP, located in the inner membrane of mitochondria, the Thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, and plasma membrane of prokaryotes
Glycolysis
A series of reactions that ultimately splits glucose into two molecules of pyruvate; the first stage of cellular respiration in all organisms; occurs in cytosol
Pyruvate oxidation
the oxidation of pyruvate to Acetyl CoA, with the release of CO2 and production of NADH. Preparatory reaction to the citric acid cycle
Citric Acid Cycle/ Krebs Cycle
The chemical cycle that completes the metabolic breakdown of glucose molecule begun in glycolysis by oxidizing acetyl CoA (derived from pyruvate) to carbon dioxide. The cycle occurs in the matrix of mitochondria and supplies most of the NADH molecules that carry electrons to the ETC, together with pyruvate oxidation, the second major storage of cellular respiration
Acetyl CoA
The entry compound for the citric acid cycle in cellular respiration'; formed from a two-carbon fragment of pyruvate attached to a coenzyme
ATP Synthase
The cluster of several membrane proteins that function in chemiosmosis with adjacent electron transport chains, using the energy of a hydrogen ion concentration gradient to make ATP
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Glycolysis followed by the redox/reduction of pyruvate to lactate, regenerating NAD+
Alcohol fermentation
Glycolysis followed by the reduction of pyruvate to ethyl alcohol, regenerating NAD+ and releasing carbon dioxide
Photosynthesis
the process by which plants, algae, and some protists and prokaryotes convert light energy to chemical energy that is stored in sugars made from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)
Autotrophs
An organism that makes it own food (often by photosynthesis) thereby sustaining itself without eating other organisms or its molecules. Plants, alagae, and numerous bacteria are autotrophs
heterotrophs
an organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms or substances derived from them in a consumer or decomposer ina food chain
Chlorophyll
A green pigment located within the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and in the membrane of certain prokaryotes. Chlorophyll participates directly in the light reactions, which convert solar energy into chemical energy
Stomata
A microscope pore surrounded by guard cells in the epidermis of a leaf. when stomata are open, CO2 enters the leaf and H2O and O2 exit. A plant conserves water when its stomata are closed
Stroma
The dense fluid within the chloroplasts that surrounds the thylakoid membrane; sugars are made in the stroma by the enzymes of the calvin cycle
Thylakoids
A flattened membranous sac inside a chloroplast. Thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll and the molecular complexes of the light reactions of photosynthesis; a stack of thylakoid is called a granum
Light reactions
The first of two stages in photosynthesis; the steps in which solar energy is absorbed and converted to the chemical energy ATP and NADPH, releasing oxygen in the process
Calvin Cycle
The second of 2 stages in photosynthesis; a cycled series of chemical reactions that occur in the stroma of a chloroplast, using the carbon in CO2 and the ATP and NADPH produced by the light reactions to make energy- rich sugar molecule G3P
Carbon Fixation
The incorporation of carbon from atmospheric CO2 into organic compound. During photosynthesis in a C3 plant, Carbon is fixed into a 3-carbon sugar as it enters the Calvin cycle. In C4 and CAM plants, carbon is first fixed to a 4- carbon sugar
Photosystem
A light- capturing unit of a chloroplast’s thylakoid membrane, consisting of a reaction-center complex surrounded by numerous light-harvesting complexes
Photorespiration
In a plant cell, a metabolic pathway that consumers oxygen, releases CO2, and decreases photosynthetic output, photo respiration generally occurs on hot, dry days when stomata close. O2 accumulates in the leaf and Rubisco fixes O2 rather than CO2. Photorespiration- no sugar molecules or ATP made
C4 Plants
A plant in which the calvin cycle is preceded by reactions that incorporate CO2 into a 4-carbon compound,which then supplies CO2 for the calvin cycle
CAM Plants
A plant that uses the Calvin Cycle for the initial steps that incorporate CO2 into organic material, forming a 4-carbon compound as the first stable intermediate
Greenhouse Effect
the warming of the earth due to the atmospheric accumulation of CO2 and certain other gases, which absorbs infrared radiation and radiate some of it back toward earth
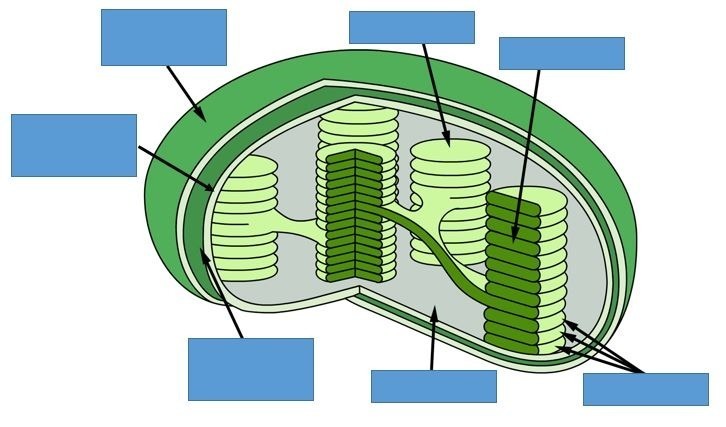
Draw and label (answer clockwise)
outer membrane, granum, thylakoid space, thylakoid, stroma, inner