cardiac action potential phases
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
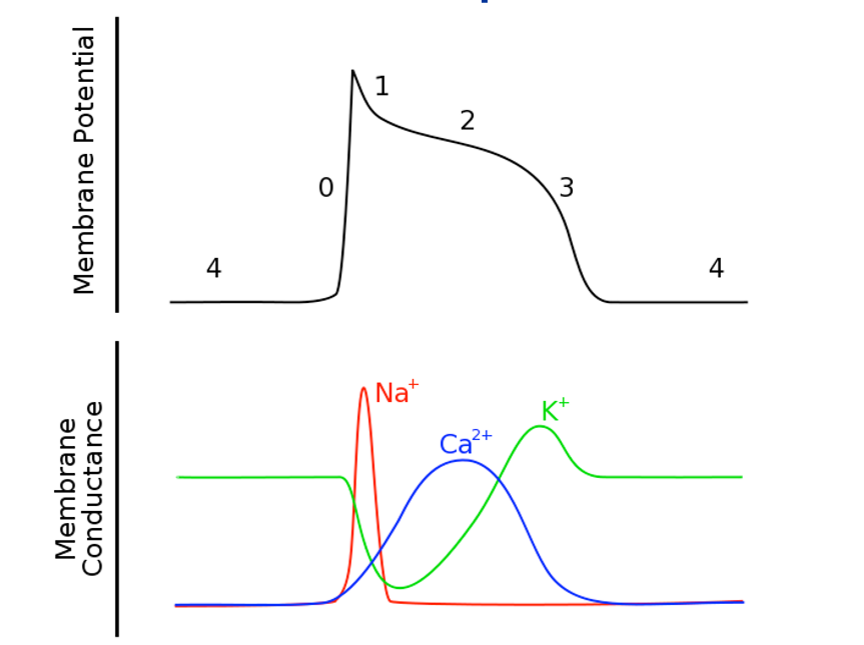
what are the phases (0-4) of ventricular muscle action potential
Phase 0: Rapid depolarization (Na⁺ influx)
Phase 1: Partial repolarization (Na⁺ inactivation)
Phase 2: Plateau (Ca²⁺ influx balanced by K⁺ efflux)
Phase 3: Repolarization (Ca²⁺ inactivation, K⁺ permeability ↑)
Phase 4: Resting potential (no pacemaker potential)
why do atrial action potentials have shorter duration than ventricular ones
because of stronger repolarizing K⁺ currents
what is “funny” current (If)
mixed Na⁺/K⁺ inward current responsible for spontaneous depolarization in pacemaker cells
how does parasympathetic input affect SA/AV node
ACh activates M₂ receptors → opens K+channel GIRK (G-protein–coupled inward rectifier K⁺) channels → hyperpolarisation → slows conduction → slows pacemaker rate
how does sympathetic input affect cardiac rhythm
noradrenaline activates β₁-adrenoceptors (via GPCR) → ↑ cAMP → enhances pacemaker and Ca²⁺ currents → faster HR and stronger contraction
which parts of the heart do parasympathetic system innervate
mainly innervates SA and AV nodes
which parts of the heart do sympathetic system innervate
all parts, particularly ventricular muscle