Final Exam - Motion Perception
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Motion perception
transformation of two dimension patterns of light intensity by the visual system to create perception of object moving in a three dimensional world. Occurs due to changes in the spatial distribution of light over time across the retina. Based on visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive inputs.
spatial (location), temporal (time)
Perception of motion requires both _____ and ______ information.
Motion
continuous change in an object's location as a function of time. Perception of this characteristic is possible even with a lack of high spatial resolution, color vision, or binocular vision.
object movement
one's own movement
depth
advantages of motion perception include the pereception of these three things
Temporal frequency
the product of the velocity of the moving stimulus and the spatial frequency (cpd). Multiple of these values produced by a real objects composed of multiple spatial frequencies.
300 cps
For a sine wave grating with a spatial frequency of 30 cpd moving over a retinal point at a constant velocity of 10 degrees per sec, what is the temporal frequency?
shifts towards lower spatial frequencies
what is the effect of increasing velocity on the contrast sensitivity function?
independent
how does temporal frequency relate to target velocity?
Direction selective cells
cells that respond maximally to stimuli moving in a single direction, but weakly or not at all to stimuli moving in the opposite direction. These cells are responsible for direction specific adaption and motion aftereffects.
Direction specific adaptation
visual system adapts to constant motion in a particular direction. During prolonged viewing a moving stimulus can appear to slow down because sensitivity is impaired for a period of time after adaptation. Ie) grandfather clock swinging
Motion aftereffect
after prolonged viewing of a moving stimulus, a stationary stimulus appears to drift in the opposite direction. Ie) waterfall illusion
dorsal/magnocellular pathway
motion perception is useful in the assessment of this pathway?
Glaucoma
ocular disease whose neural damage is thought to be selective for the magnocellular pathway during early disease. Early diagnosis of this disease could be achieved through motion perception testing.
motion coherance
______ thresholds are elevated in patients having glaucoma
Moorfield's motion displacement test (MDT)
a diagnostic visual field test based on the detection of motion.
Color vision and stereo
these two entrance testings could be tested as normal, if only the magnocellular pathway is affected, but the patient could still have decreased motion perception.
faster
Closer objects appear to be moving (slower or faster) because the object is closer and covers a larger retinal area
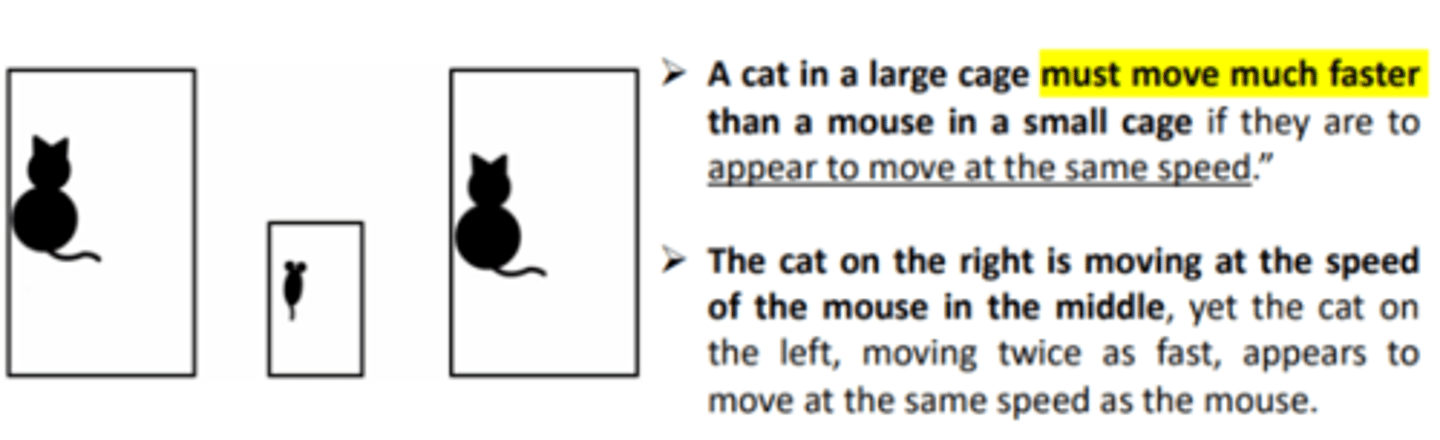
Velocity Transposition
size of an object and size of a reference from through which they move (context) influences the perception of velocity. This effect is known as...
increases
does threshold of motion (increase or decrease) with retinal eccentricity? Change is smaller when optical correction is used.
reduced
Perceived velocity is diminished when contrast is (increased or reduced)?
chromatic
Perceived velocity is diminished when moving stimuli is defined by only _____ content.
Real Motion
perception of motion where there is actual physical movement of an object. Adding context to a moving object makes it appear slower.
1
sensitivity to motion can be as high has how many seconds of arc?
fovea
Best motion threshold is at the...
Apparent Motion (stroboscopic, sampled motion)
the perception of real motion that is produced when a stimulus is present discontinuously. Ie) lights that are slightly displaced and are turned on and off alternately
Phi phenomenon
phenomenon occurring when lights are separated optimally and flashed at an optimal rate producing apparent motion. Ie) construction road signs
50-60
Time required to perceive apparent motion is around a _____ ms pause between stimuli
Korte's law
law that gives the space time relation for visual apparent motion. The farther apart two lights are the more time needs to pass between the activation of the first and the activation of the second in order to preserve the illusion of motion.
Induced motion
perception of motion in which a stationary object or a moving object appears to move or to move differently.
faster, slower
Moving target appears to move (faster or slower) when it is moving in the opposite direction of the background, and appears to move (faster or slower) when it is moving in the same direction of the background.
Autokinetic motion
type of apparent motion where a small spot of light appears to wander when it is actually stationary. Occurs due to very small eye movements in a dark environment due to the absence of a reference point.
Motion after effect
visual illusion experienced after viewing a moving visual stimulus for a period of time with stationary eyes. When switching fixation to a stationary stimulus it then appears to move in the opposite direction. Occurs as a result of motion adaptation. Ie) waterfall effect
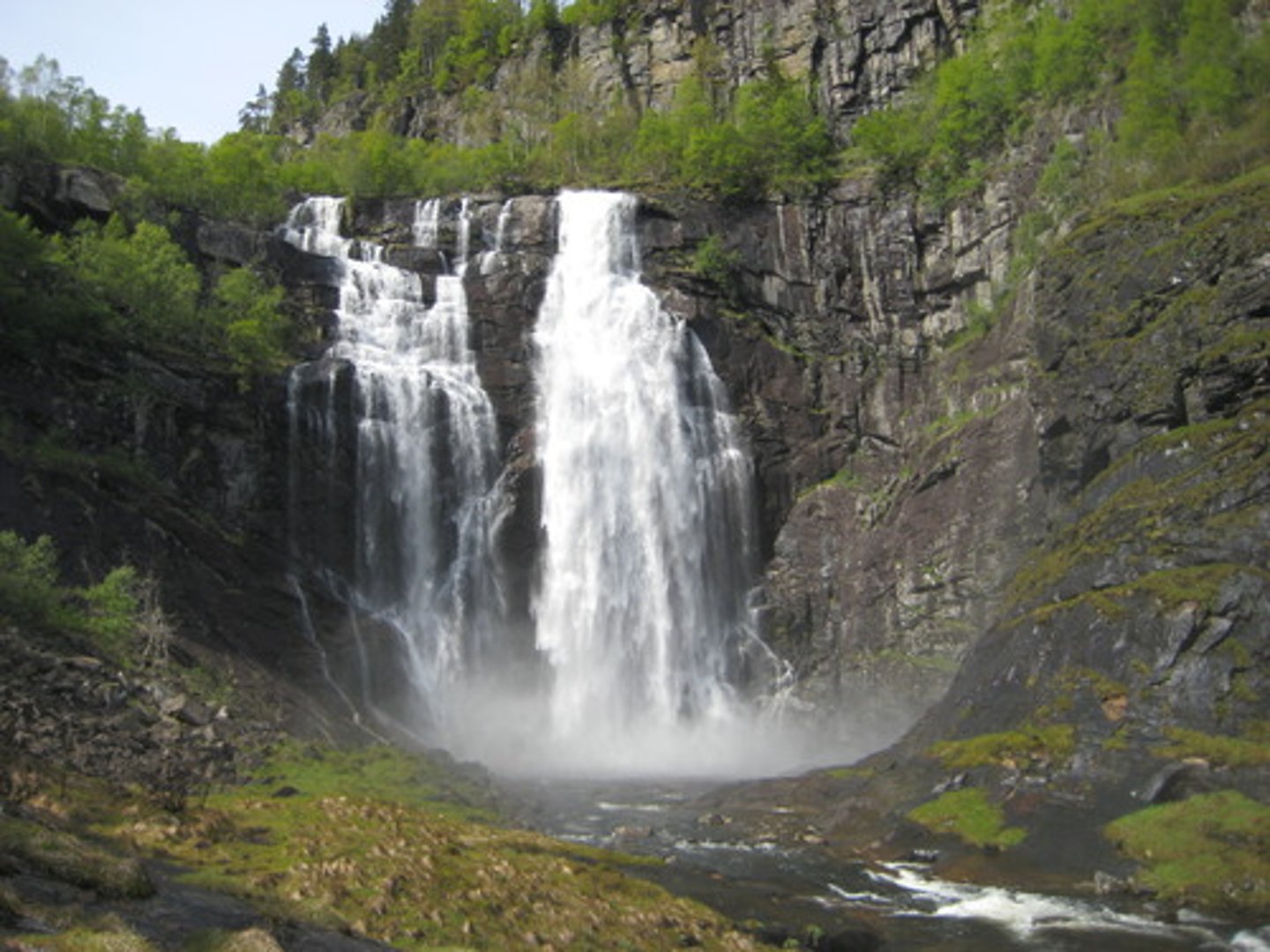

Motion parallax
the monocular cue for depth perception where objects closer than fixation appear to move in the direction opposite to your direction of movement. Objects further appear to move in the same direction.
Pulfrich effect
percept within lateral motion of an object in the field of view is interpreted by the visual cortex as having a depth component. This is due to relative difference in signal timings between the two eyes. Low contrast object is perceived to move slower than a higher contrast object because there is a delay in signal transmission. Ie) cataract, optic neuritis, MS
First order motion perception
motion perception characterized by changes in local luminance changes in the retina over time. Ie) flashing lights, drifting gratings
Local motion
perception of motion over a small part of the retina. Can be ambiguous and perceived very differently from global motion.
Global motion
perception of motion over a large part of the retina. The sum of local and global motion. Can be studies using RDT stimuli.
Random dot kinematograms
complex first order stimuli that require the integration of motion cues across visual space. Used to study global motion. Detection of this target is decreased by patients having glaucoma due to damage to the dorsal/magnocellular pathway.
Minimum displacement threshold
the minimum distance the dots of a RDK stimulus must move in order to elicit the perception of motion. Increased glaucoma patients
Second order motion perception
motion perception characterized by changes in contrast, texture, and flicker. Processed in higher order processing areas than first order motion perception. Have poorer temporal resolution and weaker motion aftereffect.
V5/MT (parietal area)
area of the brain along the dorsal stream that integrates first and second order motion signals. Sensitive to both the rate and direction of motion. Damage to this area results in impairment of motion perception
Akinetopsia
inability to perceive motion
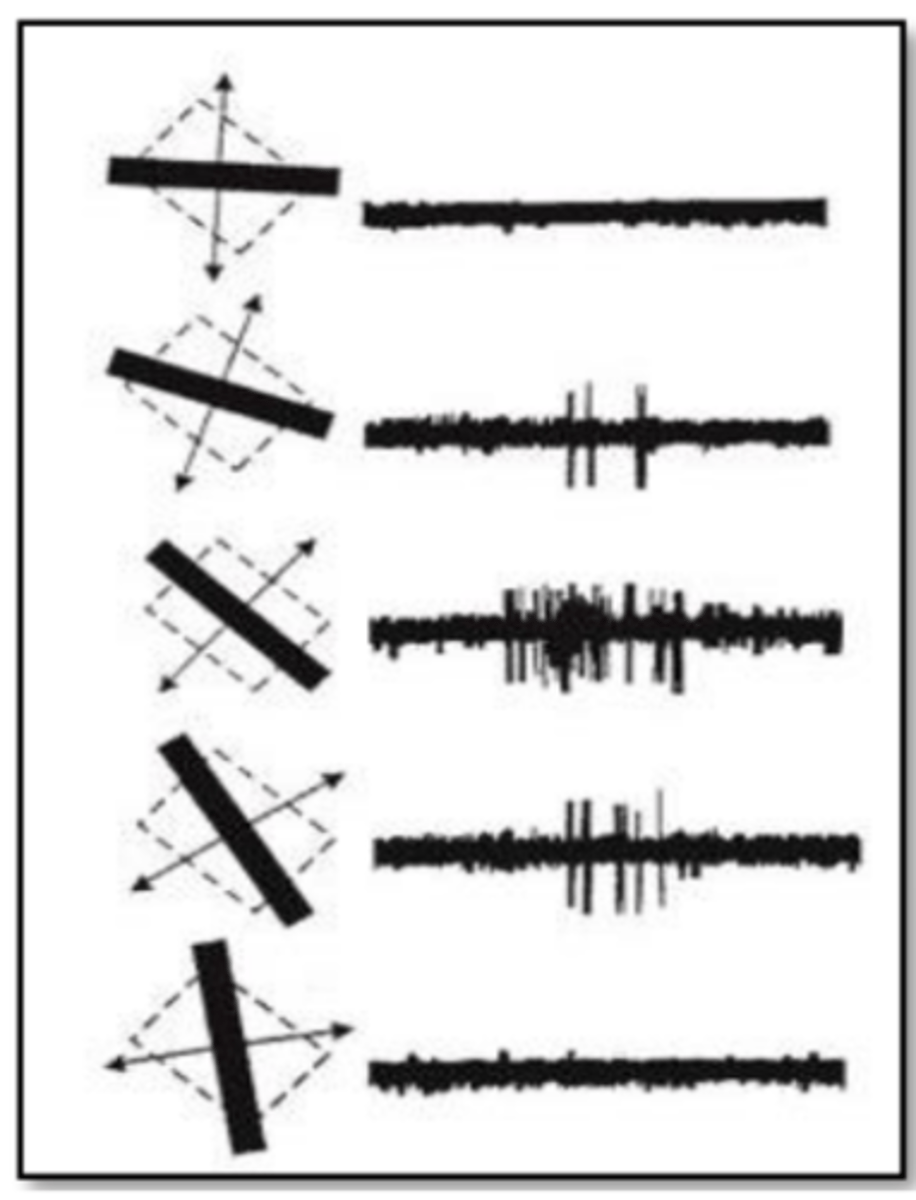
visual cortex V1
______ is very sensitive to elongated stimuli and their orientation
MT area
Newsome monkey study found that there are neurons of the ____ of the visual cortex that are tuned to respond to specific visual directions
Magno
_____ pathway processes high velocity motion
parvo
_____ pathway processes low velocity motion. Ie) amblyopes show reduced sensitivity to low velocities due to impairment of this pathway
Biological motion
ability to perceive the movement of natural things such as people, animals, etc. Processed differently than other forms of motion.
posterior superior temporal
Biological motion is perceived by the ______ sulcus of the cortex
Medial superior temporal (MST) area
area of the brain where vision is combined with vestibular and eye movement signals to help the visual system keep track of what is moving.
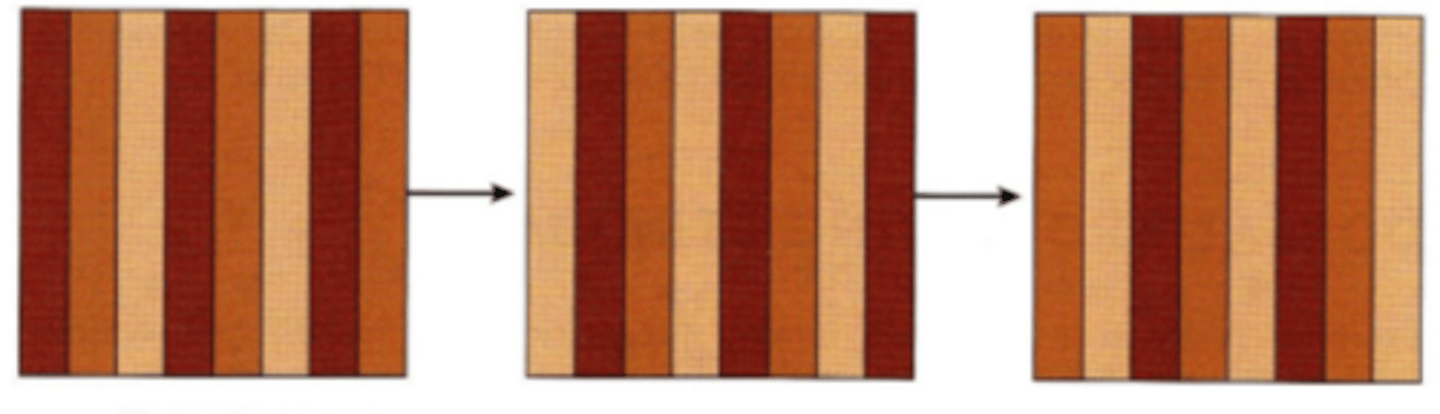
Isoluminant stimulus
stimulus containing bars of color of all the same luminance levels. Motion perception of these types of stimulus suggest the role of the parvocellular pathway in coding motion.
slower
Objects appear to move (slower or faster) under scotopic conditions versus photopic
mesopic
Motion perception is impaired in ______ conditions due to simultaneous activity of rods and cones
Dynamic VA
the ability to resolve a moving stimulus. Assesses the vestibulo-ocular reflex function
2
about how many lines difference is abnormal when measuring dynamic VA?
60-80
dynamic VA remains constant until ______ degree/second and decreases there after
Saccadic suppression
vision is suppressed shortly before, during, and after saccadic eye movements. Enables us to look from one object to another without smearing our vision. Caused by selective inhibition of the magnocellular pathway at high temporal frequencies initiated by a cortical signal.